COMM-201 Final Review
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Review of entire course for the final, contra accounts are highlighted
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
the basic accounting equation
Assets
=
Liabilities
+
Shareholder's Equity
Resources controlled by the company that have measurable value and are expected to provide benefits to the company
Amounts owed by the business to creditors
Owners' claims on the business resources
Contributed capital
Retained earnings
Balance Sheet
company title
statement title
at date
includes assets, liabilities, shareholder’s equity
double underline grand totals
underline totals
covenant
something the bank puts into the loan to make them more comfortable with handing the loan out
Income Statement
company title
statement title
for the period ended
revenues, expenses, net income
use parentheses to indicate negative values
net income is the only double underlined
Cash Flow Statement
company title
statement title
for the period ended
cash flows from OIF activities
direct method
gross receipts and payments
indirect method
adjusts net income to compute cash flows from operating activities
Statement of Retained Earnings
Shows the amt of this year's earnings (net income) that have either been paid out to stockholders (dividends) or retained in the business
Current Assets/Liabilities
will be used up in the next 12 months/will be paid back within the next 12 months
Tangible Assets
physical assets owned for producing goods/services
ex. equipment, building, land
Intangible Assets
long-lived assets with special rights, but no physical existence
ex. trademarks, patenets, copyrights
Goodwill
the premium a company will pay to purchase another company
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts (+xA, -A)
the estimated amount of uncollectible accounts receivable balances
Accumulated Depreciation (+xA, -A)
accumulation of depreciation to reflect the use of long-lived assets over their useful lives
Wages Payable (+L)
an amount owing to employees for work they’ve already performed
Deferred Revenue (+L)
cash has been received though revenue (goods sold/services provided) has not yet been provided
Current Portion of Long-Term Debt
the amount of principal payments from the long-term debt balance that will be paid in the next twelve months
Revenue: Sales Revenue (+R, +SE)
the gross amount of revenue the company has earned once the risks and rewards pass to the customer
Revenue: Sales Returns (+xR, -SE)
amount of returns that customers have made
Revenue: Sales Allowances (+xR, -SE)
amount of discounts the company gives customers on invoice payments and allowances (refunds without returning products)
Bad Debt Expense (+E, -SE)
the expense of selling on account to customers who do not pay in full; the amount of potentially uncollectible customer accounts the company expects they will not collect
General Operating Expenses (+E, -SE)
expenses incurred as part of the operations of the company
ex. rent, utilities, supplies, general administrative
Dividends (+L)
distribution of a company’s earnings to its shareholders as a return on their investment
NOT AN EXPENSE
Retained Earnings (+SE)
amount the company has earned through profitable business operations
Contributed Capital (+SE)
amount owners directly invest in the company in exchange for shares
What are the three categories of cash flow?
Operating: day-to-day business (buying goods, paying wages, etc.), Current assets/liabilities
Investing: acquire/sell long-term assets (equipment, buildings, etc.), non-current assets
Financing: obtain/repay lenders and shareholders, non-current liabilities/shareholder’s equity
Temporary Accounts
track financial results for a limited period of time, these balances are zeroed out at the end of each accounting year.
includes: revenues, expenses, dividends declared
Permanent Accounts
track financial results from year to year, their ending balances carry forward to the next year
balance sheet accounts are permanent accounts
Revenue Earned Table
Cash is received before the revenue is earned | Cash is received in the same period as the revenue is earned | Cash is received after the revenue is earned |
Dr cash Cr deferred revenue Dr deferred revenue Cr revenue | Dr cash Cr revenue | Dr accounts receivable Cr revenue Dr Cash Cr accounts receivable |
Expenses Incurred Table
Cash is paid before the expense is incurred | Cash is paid in the same period as the expense is incurred | Cash is paid after the expense is incurred |
Dr prepaid expenses Cr cash Dr expense Cr prepaid expense | Dr expense Cr cash | Dr expense Cr accounts payable Dr accounts payable Cr cash |
FOB Shipping Point
(Free on Board) goods are owned by the customer the moment they leave the seller’s premises
FOB Destination Point
(Free on Board) goods are owned by the seller until they are delivered to the customer
Cost of Goods Sold Equation
*(Beginning Inventory + Cost of New Purchases) - Ending Inventory
*otherwise known as cost of goods available for sale
LC&NRV
lower of cost and net realizable value
requires inventory to be written down when the nrv or replacement cost falls below original cost
NRV: value likely to be realized when sold
FIFO
First in, first out
costs are assigned assuming the first item purchased is the first item sold
WAC
Weighted average cost
total inventory costs are averaged over total inventory units
(price 1 + price 2 + price 3)/3 = price
Specific Identification
the cost of each inventory item is individually identified and (when sold) recorded as COGS
Journalizing Bad Debt
Dr Accounts receivable
Cr sales revenue
Dr bad debt expense (+E, -SE)
Cr allowance for doubtful accounts (+xA, -A)
Dr allowance for doubtful accounts (-xA)
Cr accounts receivable (-A)
Straight-Line Depreciation
Assumes equal use over life
Equation: (cost - residual value) / useful life (in years)
Units of Production
based on actual production
equation: (cost - residual value) / useful life (in units)
Double Declining Balance (Accelerated)
greater benefit in earlier years
equation: (cost - accumulated depreciation) * rate
rate = 2 / useful life
Depreciation v Amortization
Depreciation: cost of a tangible asset’s use in a period
Amortization: cost of an intangible asset’s use in a period
Disposal of Tangible Assets
Gain if > book value, loss if < book value
Journal Entry
Dr Cash
Dr Accumulated Depreciation
- Cr Equipment
- Cr Gain on Disposal (+R, +SE)
Payroll Liabilities
Gross Pay - Payroll Deductions = Net Pay
Gross Pay: salaries and wages expense
Payroll Deductions: liabilities owed to government and other organizations
Net Pay: liabilities owed to employees
CPP and EI contributions
CPP: match the employee’s contribution
EI: 1.4x employee’s contribution
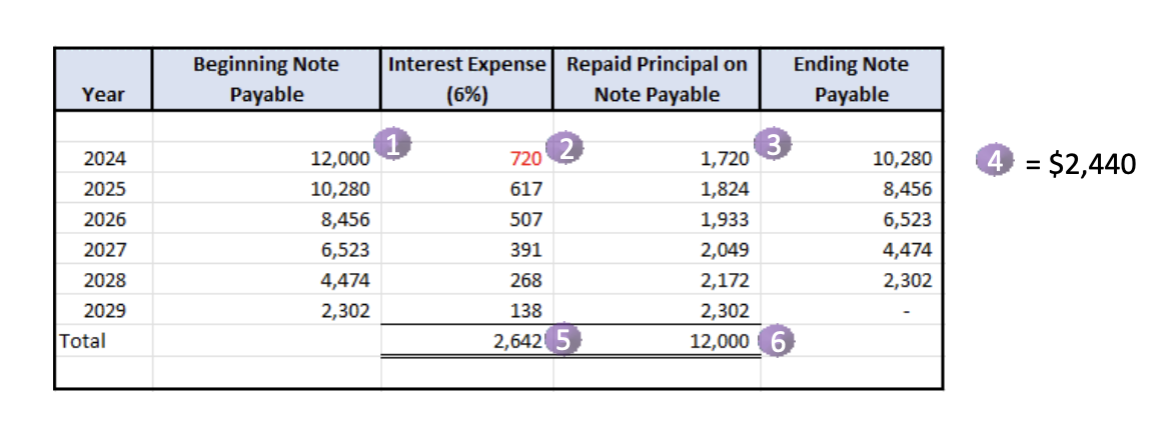
Instalment Notes
Beginning note payable balance
interest paid in the period
actual amount deducted from the note payable balance
value of 2 + 3 in any given period is cash paid
total amount of interest paid over life of the note payable
total amount of principal paid over life of the note payable should = the beginning balance
Inventory Purchase Entries
Purchase of inventory | Transportation costs | Purchase return | Purchase allowance | Purchase discount |
Dr inventory Cr accounts payable | Dr inventory Cr accounts payable | Dr accounts payable Cr inventory | Dr accounts payable Cr inventory | Dr accounts payable Cr Cash Cr inventory |
Always affects accounts payable and inventory in some way
Prepaid Expense (+E, -SE)
Purpose: cash paid for the future benefit of an expense
Prepaid rent expense, prepaid insurance expense, etc
Common entry:
Dr prepaid expense
Cr cash
Dr expense
Cr prepaid expense
IFRS
international financial reporting standards
ASPE
accounting standards for private enterprises
Financial Statements Effects on Creditors
creditors: people/business to whom money is owed
does the company own enough assets to pay liabilities? — B/S
will the company generate enough cash in future periods to repay loans? — SCF
Financial Statements Effects on Investors
investors: people/businesses who own some of the company
has the company earned profits? — I/S
does the company have history of paying dividends? — R/E
Prepaid Insurance
paid cash in exchange for service in the future
asset, therefore debit it
What is paying with visa considered to be?
Cash
Deferral Adjustments
update what’s there
some/all of asset’s future benefits have expired or been used up in current period creating an expense or
the company provides provides goods or services to earn revenue and satisfy existing liability
Accrual Adjustments
include what’s not yet there
assets and revenues are generated in the current period but haven’t been recorded
The Closing Process
take temporary accounts and close them to equity accounts
transfer net income/loss and dividends to retained earnings
The amount credited or debited to retained earnings in the first journal entry must equal net income or net loss on the income statement
Entries:
1 | 2 |
dr revenues……xx Cr expenses…….xx Cr retained earnings…….xx | Dr retained earnings…….xx Cr dividends declared…….xx |
Each revenue account needs to be debited separately and each expense account needs to be credited separately The effect is that retained earnings goes up by an amount equal to net income If a loss, we debit retained earnings for a net loss | Retained earnings goes down by amount equal to dividends |
Post-Closing Trial Balance
An internal report prepared as the last step in the accounting cycle to check that debits equal credits and all temporary accounts have been closed
The Three Types of Employee Fraud
Corruption: using tax payer money for personal power, people in position of power and trust usually
Asset Misappropriation: (embezzlement) stealing actual assets from a company
Financial Statement Fraud: lowest frequency but causes the greatest losses, presenting financial statements that doesn't reflect the company in actuality
The 5 Principles for Reducing Fraud
Principle | Explanation | Example |
Establish responsibility | Assign each task to only one employee | Give a separate cash register drawer to each cashier at the beginning of a shift |
Segregate duties | Do not make one employee responsible for all parts of a process | Inventory buyers do not also approve payments to suppliers |
Restrict access | Do not provide access to assets of information unless it is needed to fulfill assigned responsibilities | Secure valuable assets such as cash and restrict access to computer systems (passwords, firewalls, etc.) |
Document procedures | Prepare documents to show activities that have occurred | Pay suppliers using prenumbered cheques and digitally documented electronic fund transfers |
Independently verify | Check others' work | Compare the cash balance in the company's accounting records to the cash balance reported by the bank and account for any differences |
Perpetual v Periodic Inventory Systems
perpetual: updating as inventory changes occur
periodic: do not update inventory until the end of the period
2*/10*, n/30*
a discount of 2% if paid within 10 days, otherwise the full balance is due within 30 days
*these numbers are subject to variations
Consignment Inventory
inventory held by a company on behalf of someone else
Land Improvements
since land has an indefinite lifespan, this refers to the fences/sidewalks/pavements/etc. that improve the land
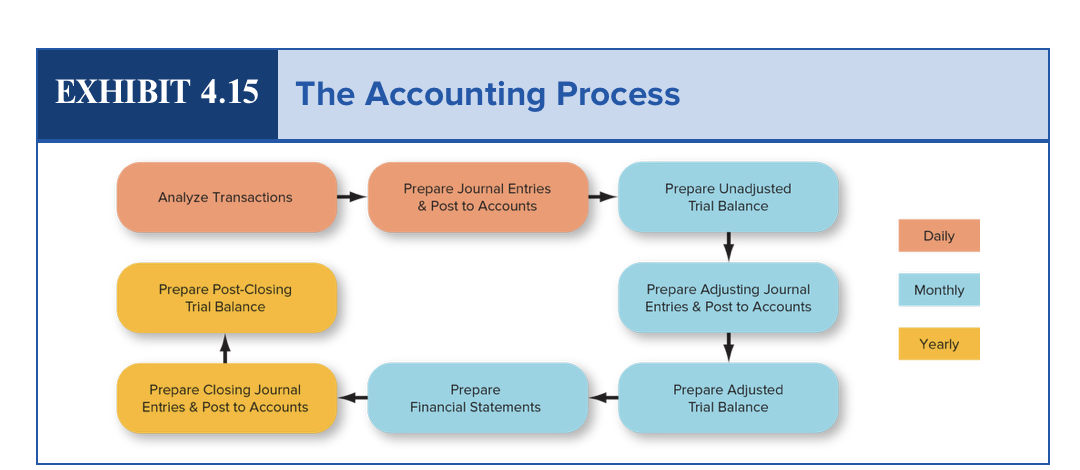
The Accounting Process
Construction in Progress
cost of constructing new buildings and equipment
once finished, they move to their respective accounts
Book/Carrying Value
the amount an asset/liability is reported (or carried) at in the financial statements
property and equipment at cost - accumulated depreciation = net property and equipment = book value
Capitalizing v Expensing
Capitalizing: adding to the asset
needed to obtain the inventory
future benefit is the sale
Expensing
may not sell the inventory
What are accrued liabilities?
liabilities for expenses that have been incurred but not yet billed/paid at the end of the period
also called accrued expenses
Contingent Liabilities
potential liabilities resulting from a past transaction, the ultimate outcome will not be known until a future event occurs or fails to occur
What’s the date of our final?
June 25, 2025 @ 2:00 PM
What enhances the usefulness of financial statements?
Timeliness
Understandability
Comparability
Verifiability
What principle do private companies use?
ASPE or IFRS (their choice)
ESG
Environmental, Social, and Governance
Accounting for Business Activities
Picture → Name → Analyze
paying with a cheque is ?
(accounts payable, cash, notes payable)
cash