PDA III - Exam 3: Antidepressants and Depression - RW
1/361
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
362 Terms
What type of antidepressant is Fluoxetine?
SSRI
What makes Fluoxetine unique in terms of selectivity?
It's an SSRI, without high SERT selectivity
It's active metabolite, Norfluoxetine, is a potent SERT inhibitor
Why dose Fluoxetine, an SSRI, not have high SERT selectivity?
Due to stereochemistry and active metabolites
How does stereochemistry affect Fluoxetines SERT selectivity?
Fluoxetine is a racemic mixture of R- and S-enantiomers
Only the S-enantiomer is highly selective for SERT
What is the active metabolite of fluoxetine?
Norfluoxetine
Which TCAs are more selective for SERT?
Tertiary amine TCAs
Imipramine, Amitriptyline, Doxepin, Clomipramine
How do active metabolites affect Fluoxetines SERT selectivity?
S-norfluoxetine is a potent and highly selective SERT inhibitor
S-enantiomer is stereo-selectively created by metabolism at a higher rate than the R-enantiomer
So, once Fluoxetine is metabolized it becomes SERT selective
Which TCAs are more selective for NET?
Secondary amine TCAs
Desipramine, Nortriptyline, Protriptyline
What is the common ring structure TCAs share?
6-7-6 tricyclic ring structure
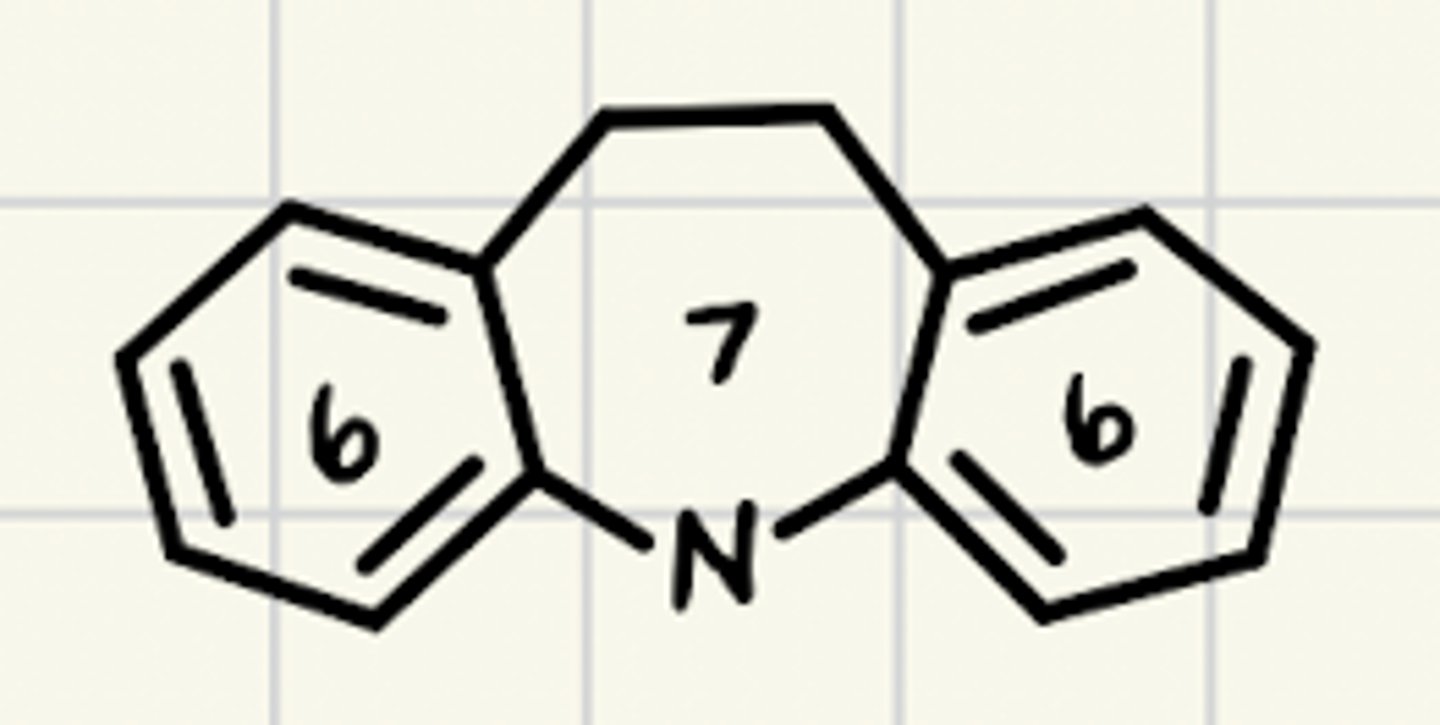
What are characteristics of the TCA ring structure?
Not required for binding with SERT or NET
Adds lipophilicity
Needed for CNS active drugs to reach the CNS
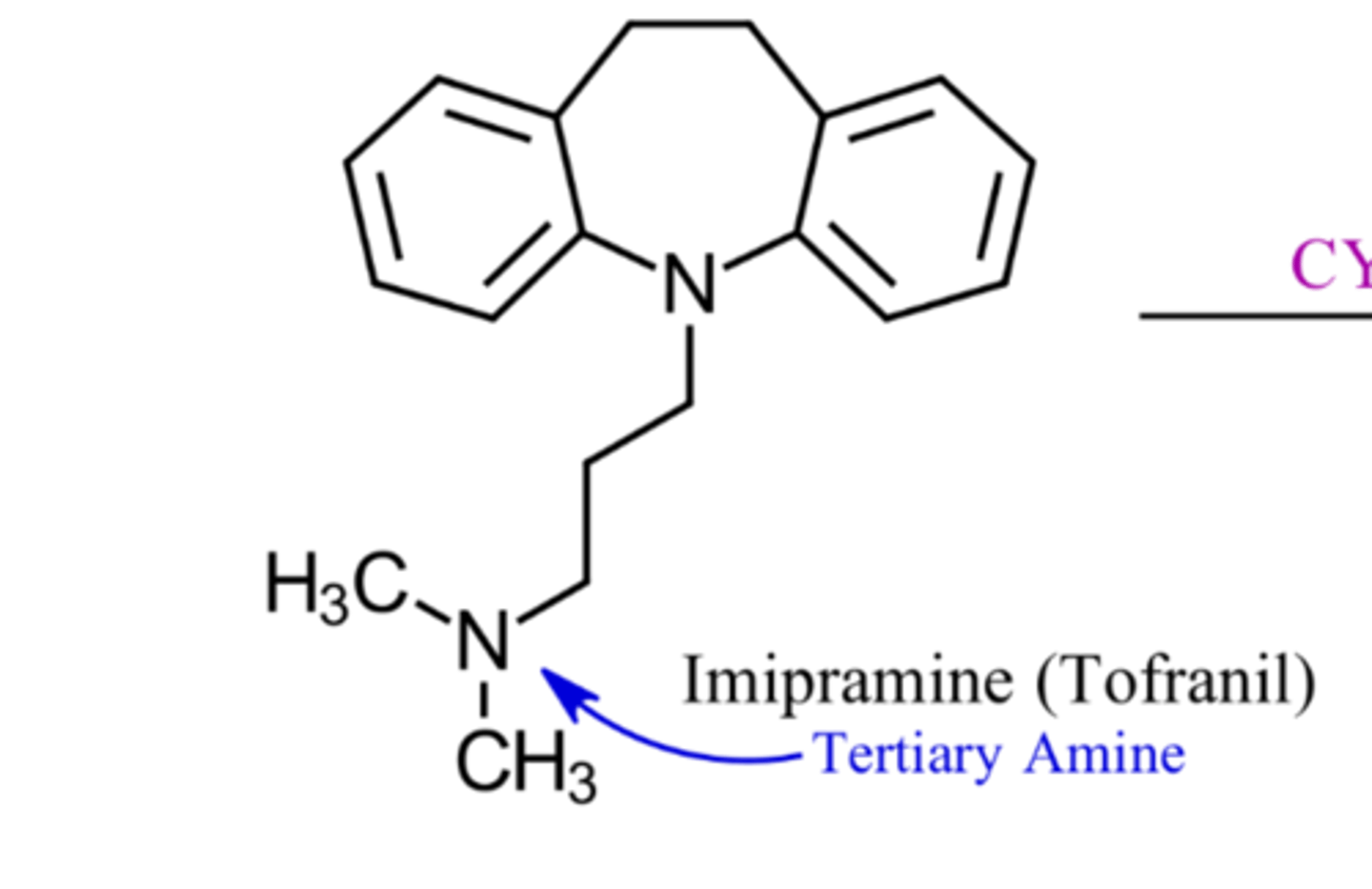
What structural characteristic of TCAs are essential for activity?
3-carbon spacer between the N on the ring and the N on the side chain
What effect does side chain chemistry have on TCAs selectivity?
Tertiary amine TCAs are more selective for SERT
Secondary TCAs are more selective for NET
What tertiary amine is the exception to the rule, and is more selective for NET?
Doxepin
What are characteristics of tertiary amine TCAs structures?
N bonded to 3 carbons
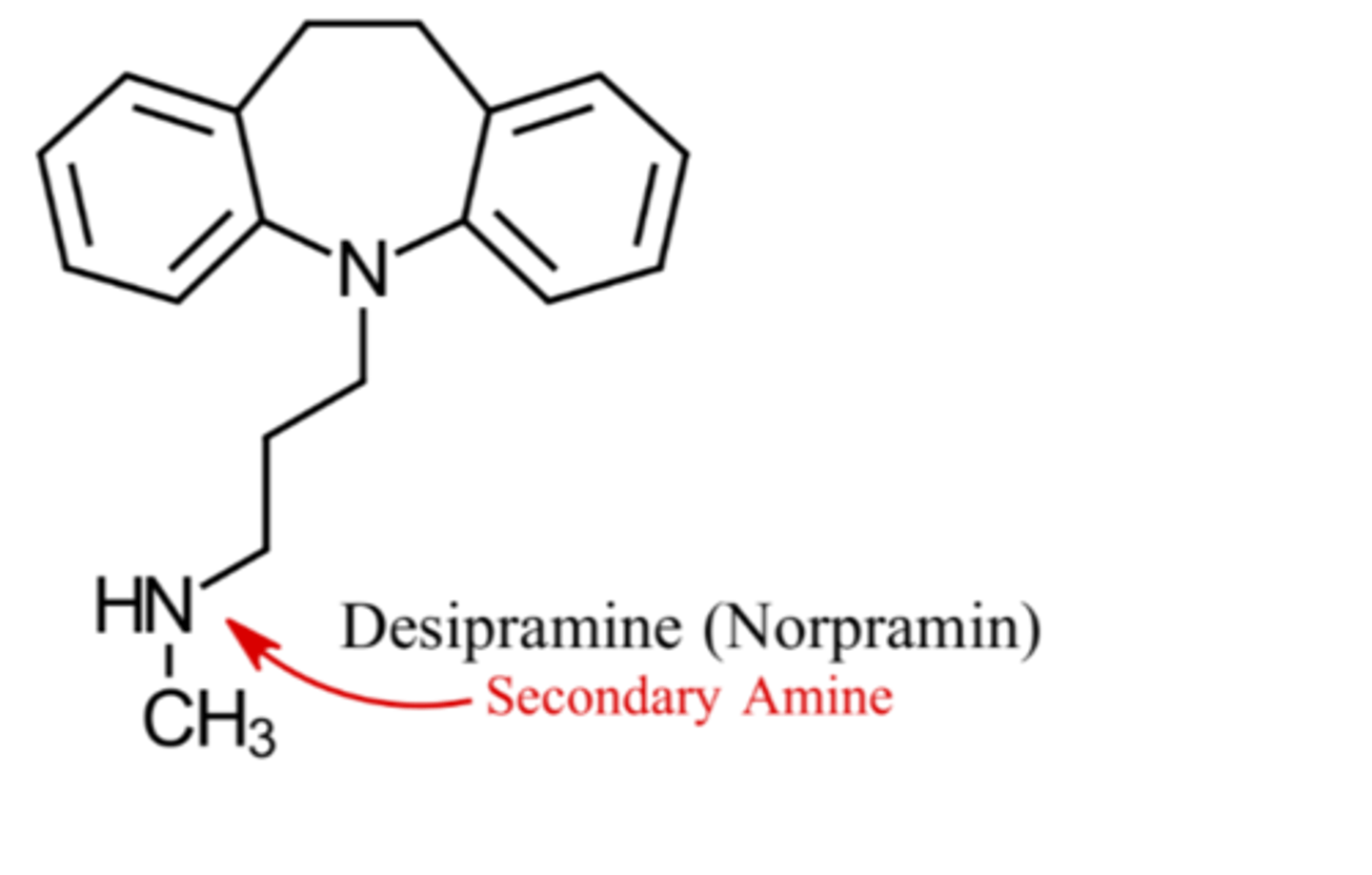
What are characteristics of secondary amine TCAs structures?
N bonded to 2 carbons
Which TCAs are tertiary amines?
Imipramine
Amitriptyline
Doxepin
Clomipramine
Which TCAs are secondary amines?
Desipramine
Nortriptyline
Protriptyline
How are TCAs metabolized?
Extensively metabolized by CYP450
Via demethylation and hydroxylation
How do TCAs block SERT/NET activity?
TCA's bind to a distinct site on the transporter
(diff than NT and other ADs)
Binding causes conformational change
Reduces NT binding affinity for the transporter
What structural characteristic of TCAs causes them to bind extensively to receptors?
Planar structure
Able to fit into sterically tight binding sites
Which TCA side chain chemistry is associated with more side effects?
Tertiary amines
Do tertiary or secondary amine TCAs cause more side effects?
Tertiary amines
Are more SERT selective or more NET selective TCAs associated with more side effects?
More side effects with SERT selective drugs (tertiary amines)
What receptor is associated with sedation side effects?
H1
What receptor is associated with orthostatic hypotension side effects?
a1
What receptor is associated with dry mouth side effects?
M1
What receptor is associated with urinary retention side effects?
M1
What receptor is associated with constipation side effects?
M1
What side effects are associated with TCAs?
Sedation
Orthostatic hypotension
Dry mouth
Urinary retention
Constipation
More SEs w/tertiary amines
What factors limit the use of TCAs?
Lots of ADRs
Overdose may be lethal (CV SEs)
Since tertiary amine TCAs cause more SEs, why would they ever be used?
Sedation beneficial in insomnia
Some pt.'s may respond better to tertiary amines
Are SSRIs more selective for SERT or NET?
SERT
What is the common structural characteristic of SSRIs?
All have ionizable amine
Why do all SSRIs have an ionizable amine?
Contributes to binding with target site
Via ionic binding with basic amino acid residues
Which SSRIs are single isomers?
Escitalopram
Paroxetine
Sertraline
What is the definition of enantiopure?
Only contains one enantiomer
What is the definition of diasteriopure?
Drug with 2 chiral centers, that are diaseromers
Are SNRIs more selective for SERT or NET?
Close to equal selectivity for SERT and NET
What are structural characteristics of Arylpiperazine antidepressants?
All contain piperazine ring
Attached to an aryl (aromatic ring) group
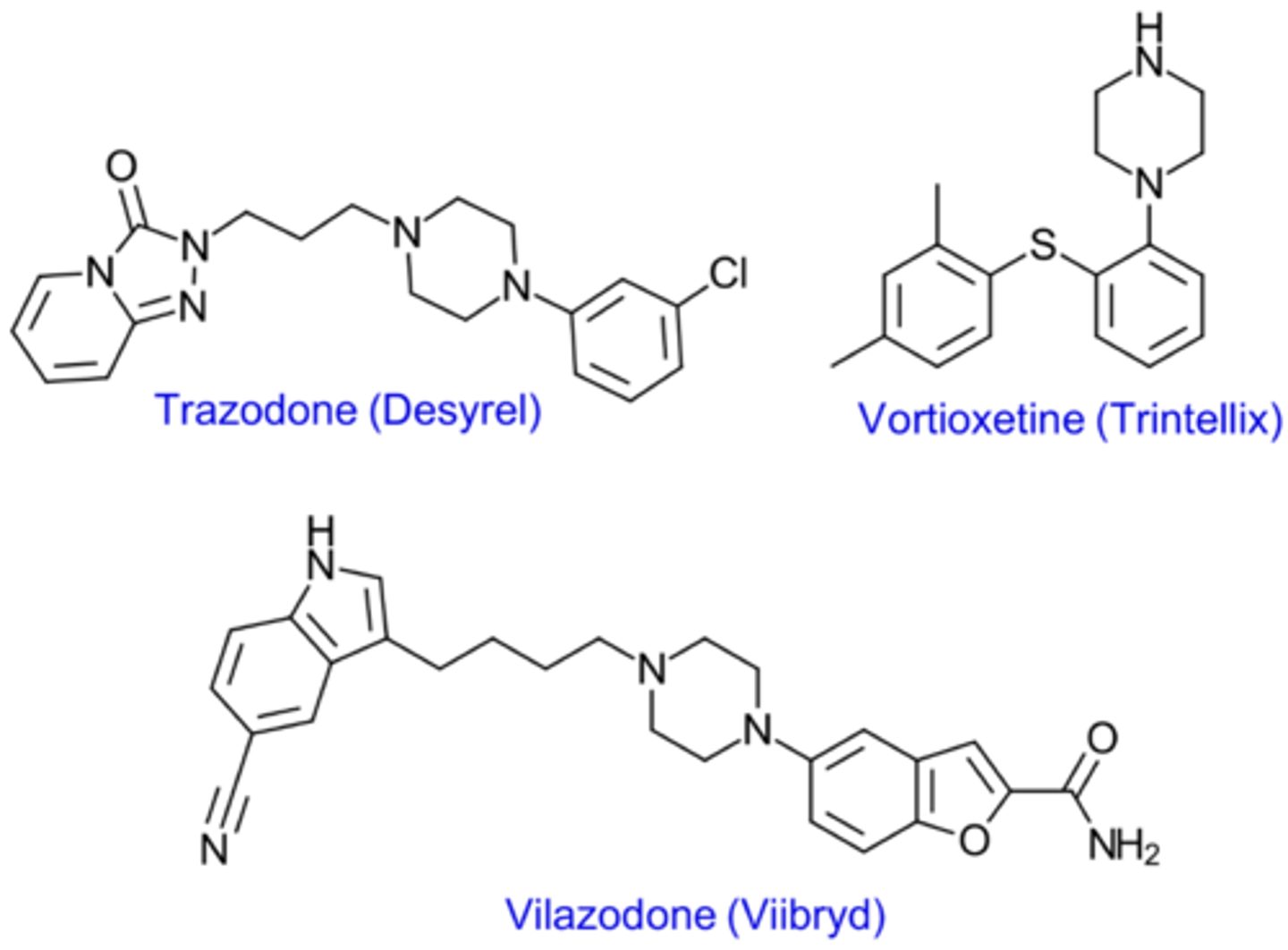
Which drugs are examples of Arylpiperazine antidepressants?
Trazodone
Vilazodone
Vortioxetine
"Atypical ADs"
What is meant by the term "atypical" antidepressaants?
Mechanism involves something other than just inhibiting NT reuptake
What are characteristics of Trazodones binding profile?
Weak SERT Inhibitor
Antagonist at 5-HT1A receptors
What are characteristics of Vilazodone binding profile?
Inhibits SERT
Partial agonist at 5-HT1A receptors
What are characteristics of Vortioxetine binding profile?
Inhibits SERT
Antagonist at multiple 5-HT receptors
What are common characteristics of antidepressant metabolism?
ADs are extensively metabolism
Many have active metabolites that extend their DOA
CYP inhibition is common
What is the primary CYP isoform metabolizing TCAs and a majority of other ADs?
CYP2D6
Which CYP isoforms are major contributors to AD metabolism?
**2D6
3A4
1A2
C19
2B6
Metabolism of which 2 ADs is distinct?
Bupropion and desvenlafaxine
What is different about the metabolism of Bupropion?
Metabolized to hydroxy-bupropion and tow diastereoisomers
What is different about the metabolism of Desvenleflaxine?
Metabolized by UGT
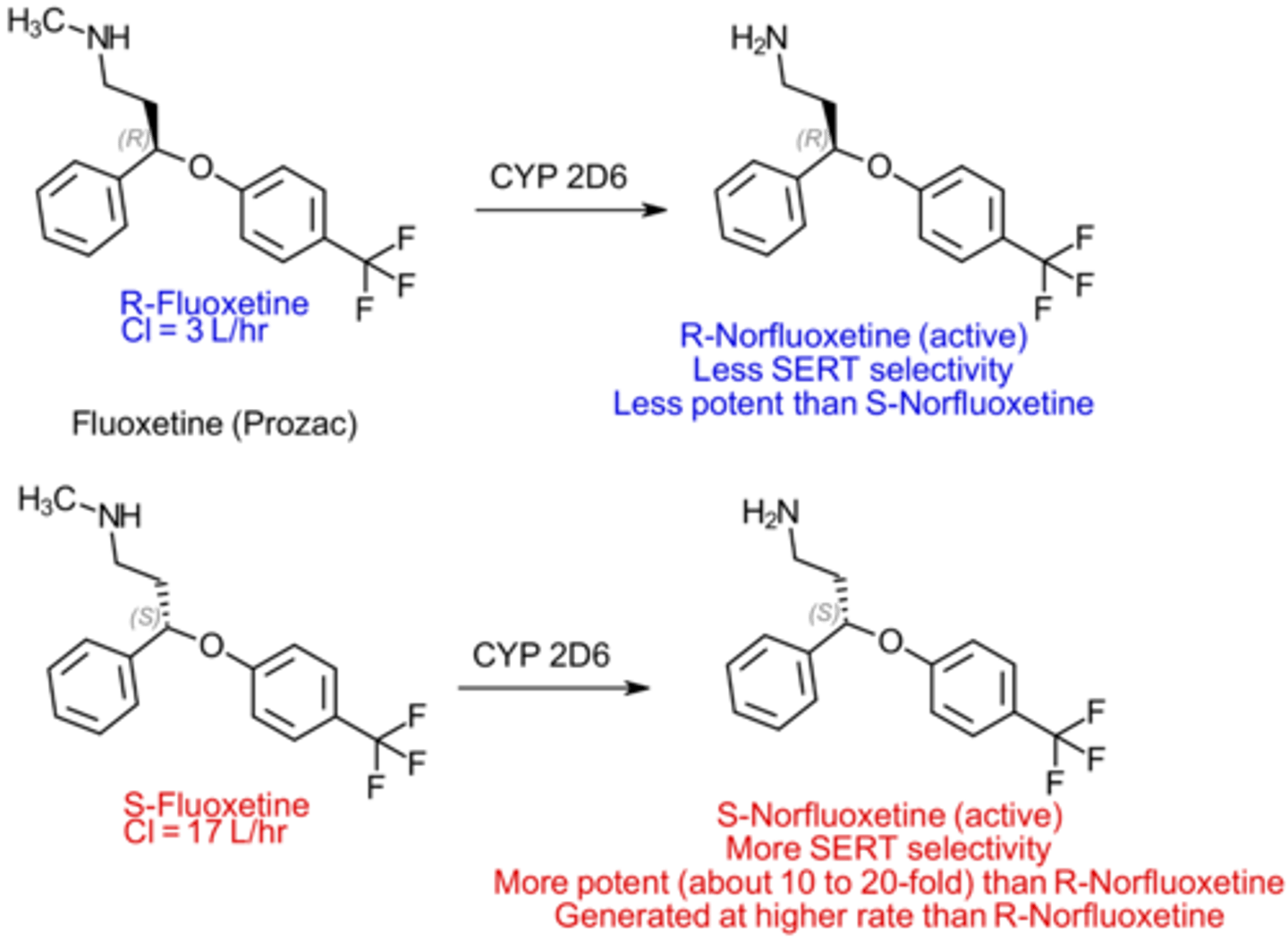
How is fluoxetine metabolized?
Metabolized by CYP2D6
Norfluoxetine is the most common metabolite
Active as an SSRI
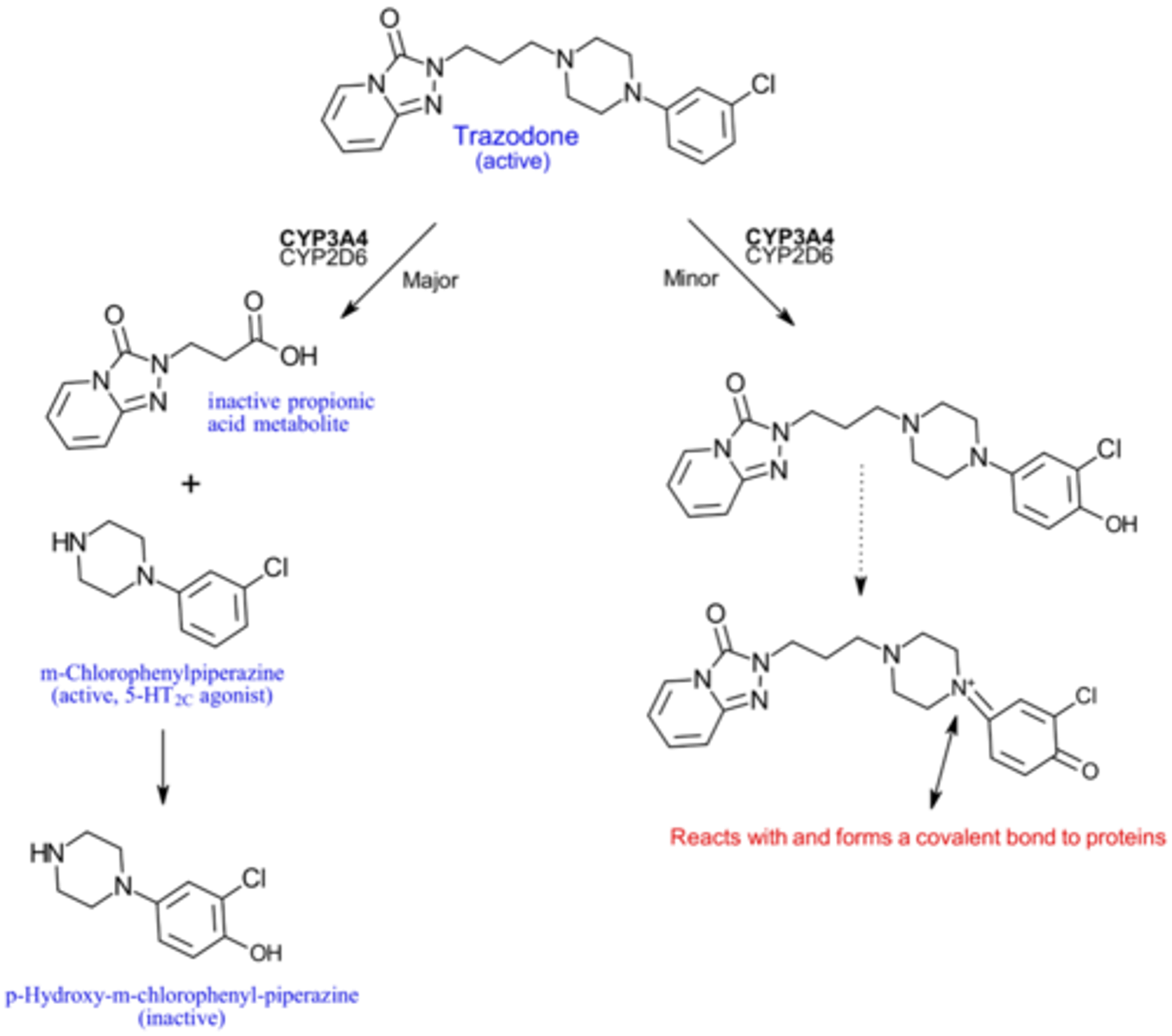
How is trazodone metabolized?
Metabolized by CYP3A4
To an active (MCPP) and inactive metabolite
Minor pathway involves metabolism to a reactive metabolite that causes hepatotoxicity
What is depression defined as?
A disorder of mood ann emotion
What are the types of depression?
Major (unipolar) depression
Bipolar depression
Reactive (exogenous/secondary) depression
What is major depression defined as?
Recurring episodes of dysphoria (sadness) and negative thinking
Due to biochemical deficits in the brain
What is bipolar depression defined as?
Episodes that cycle between depression and mania
What is reactive depression defined as?
Normal state of sadness, felt in response to loss or disappointment
Not a mental illness, unless it is disproportionate or prolonged
How many symptoms are required for major depression diagnosis?
At least 5 symptoms for at least 2 weeks
1 of the 5 has to be depressed mood or anhedonia
What are criteria for major depression diagnosis?
≥5 symp for ≥2 weeks
Symp. severe enough to disrupt life
Not caused by drug abuse, medication, or illness
Can be w/ or w/o psychosis
What is described by Atypical depression?
Increased appetite
Hypersomnia
What are symptoms of major depression?
*Depressed mood
*Anhedonia (inability to experience pleasure)
Inc. or dec. in appetite
Insomnia or hypersomnia
Inc. or dec. in psychomotor (physical) activity
Fatigue
Loss of self-esteem
Diminished ability to think, concentrate, and make decisions
Suicidal thinking
Will untreated depression resolve on it's own?
Untreated depression resolves in 6-9 months
But episodes will continue to occur with increasing frequency and intensity
What usually precedes the first episode of depression?
Stress
Later episodes can occur w/o stress
What is described by the Monoamine Hypothesis of major depression?
Depression is a result of low monoamine levels
Which NTs are monoamines?
NE
5-HT
DA
Which monoamines are the main ones thought to be involved in depression?
NE and 5-HT
Where did the Monoamine Hypothesis of major depression originate from?
Reserpine
An irreversible VMAT inhibitor that prevents monoamine storage in vesicles, leading to dec. levels
SE of this drug was depression
Thought to be due to monoamine depletion
What evidence supports the Monoamine Hypothesis of major depression?
ADs work by increasing monoamine signaling
Depressed patients have low levels of NE and 5-HT metabolites
(suggesting low utilization)
What is a shortcoming of the Monoamine Hypothesis of major depression?
ADs that target monoamine systems have clinical lag
Despite causing an immediate inc. in NT signaling
What activates the HPA axis?
Stress
What normally occurs in the HPA axis once it is activated by stress?
Hypothalamus releases CRF/CRH
CRH acts at the pituitary and causes ACTH release
ACTH acts at adrenal gland and causes cortisol release
What is the effect of cortisol release in the HPA axis?
Exerts negative feedback on the hypothalamus and hippocampus
Preventing further cortisol release
(and toxic cortisol buildup)
What happens to the HPA axis in depressed patients?
All stress hormones are higher in the HPA
What happens to stress hormone levels in the HPA axis in patients with depression?
High CRF levels
Which causes high ACTH levels
Which causes high cortisol levels
What happens to the pituitary and adrenals in depression patients?
Pituitary and adrenals are enlarged
Due to hypersecretion of stress hormones
What is the cause of the dysfunction in the HPA axis in patients with depression?
Abnormalities in the hypothalamus
What hypothalamus abnormalities cause HPA axis dysfunction?
Too many CRF producing cells, producing too much CRF
Not responding to negative feedback
What is a possible cause of hypothalamus abnormalities in depression?
Genetic variation
Causing an increased number of CRF producing cells in the hypothalamus
Pt. more prone to developing major depression
What are characteristics of the normal circadian rhythm of cortisol?
Cortisol begins to increase at 6 am and peaks in the early morning
Then decreases until the next morning, when the cycle restarts
What is the effect of depression on the circadian rhythm of cortisol?
Circadian rhythm of cortisol is flatter and higher in depression
High cortisol all day every day in depression patients
What is described by the Glucocorticoid Hypothesis of major depression?
Depression due to atrophy of dendrites and spines in the PFC/hippocampus and decrease neurogenesis in the hippocampus
Why is stress thought to cause depression, based on the Glucocorticoid Hypothesis of major depression?
Prolonged high glucocorticoid levels cause hippocampal neurons to become damaged and unresponsive
What is the effect of the hippocampus on CRF release?
Hippocampus inhibits CRF release by the hypothalamus
Via glucocorticoid receptors
(which respond to cortisol)
What is the effect of cortisol induced damage to hippocampal neurons?
Damaged hippocampal neurons become unresponsive to cortisol
Can't perform negative feedback on hypothalamus
Hypothalamus continues to release ACTH
More and more cortisol is released
Causing more damage
What is the effect of cortisol (stress) on hippocampal neurons?
Cortisol causes atrophy of hippocampal neurons
Loss of dendrites and spines
What is the effect of loss of dendrites, due to atrophy, in the hippocampus?
Neuron's function is impaired
Hippocampus can't inhibit hypothalamus
In what areas of the brain does cortisol (stress) cause loss of dendrites and spines?
Hippocampus and pre-frontal cortex
What are the two effects of cortisol (stress) in the hippocampus)
Loss of dendrites and spines
Dec. neurogenesis
Where does neurogenesis occur?
Hippocampus
Does neurogenesis occur in the PFC?
NO
Why are neurons not able to replace the neurons lost to cortisol atrophy?
Neurons are post-mitotic
Can't undergo mitosis to replace lost neurons
What cells are able to perform neurogenesis?
Neural progenitors (aka neuronal precursors)
What happens during neurogenesis?
Neural progenitors undergo mitosis
Differentiate into a new neuron
Why are neuronal progenitors able to perform neurogenesis?
Not yet differentiated into neurons
Still mitotic
What is the effect of stress (cortisol) on neurogenesis?
Cortisol inhibits neurogenesis
How does cortisol inhibit neurogenesis?
Either kills neuronal progenitors, or prevents them from becoming neurons
How does Glucocorticoid Hypothesis of major depression explain the clinical lag of antidpressants?
Takes time to develop dendrites
(spines develop quickly)
Takes time for neural progenitor cells to undergo neurogenesis, and then exert an effect
What evidence supports the Glucocorticoid Hypothesis of major depression?
Depressed patients have decreased hippocampal vol.
Due to loss of neurons
Both ADs and ECT decrease CRF levels
(hippocampus inhibiting the hypothalamus after therapy)
What are neurotrophins?
Short peptides
Stimulate migration, development, and survival of neurons
What is BDNF?
brain derived neurotrophic factor