Diagnostic Ultrasound
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Farm Animal
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
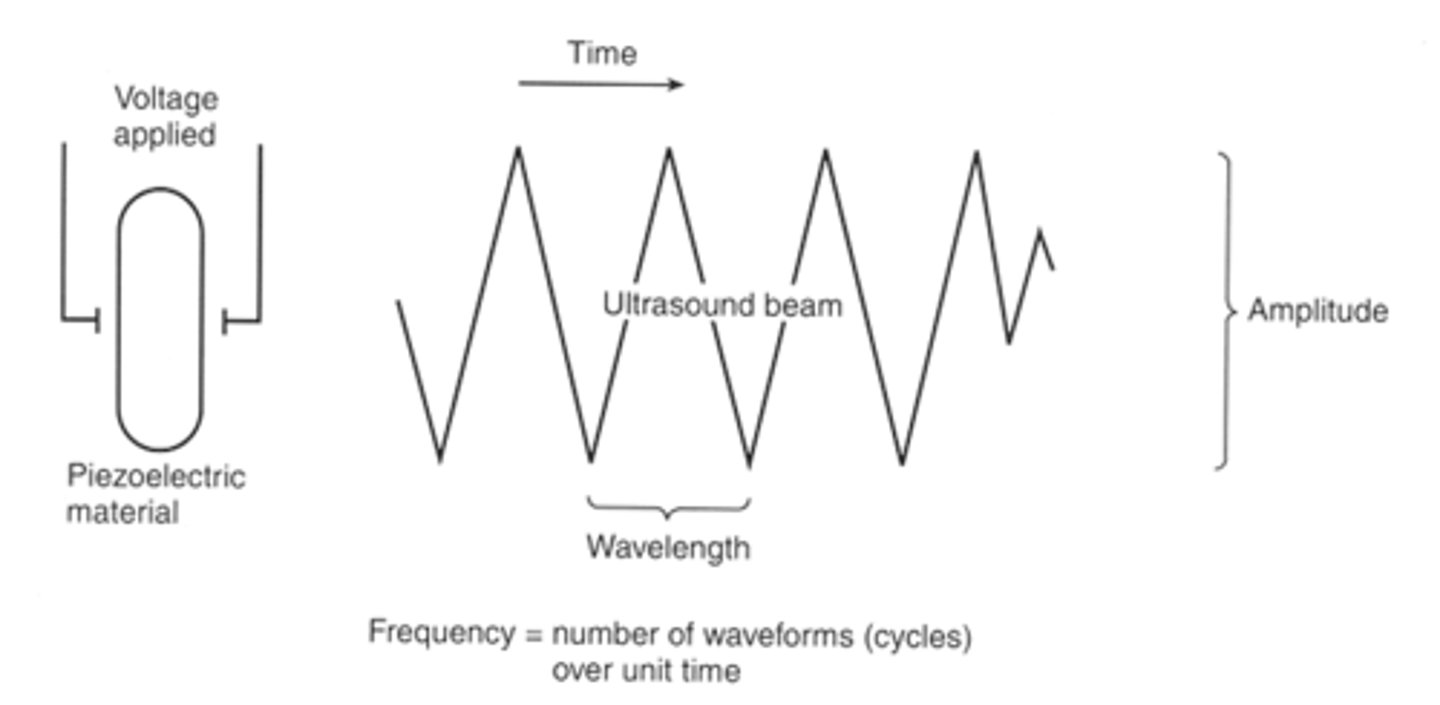
How are ultrasound waves produced?
Running alternating current through special crystals causing the piezoelectric effect. This releases ultrasound waves in pulses.
How does depth of penetration of an ultrasound beam relate to frequency?
Penetration directly proportional to 1/frequency.
How does resolution (detail) relate to frequency?
Resolution directly proportional to frequency.
What are the types of probes in ultrasonography?
-Sector (crystals moving)
-Linear (crystals in line)
-Convex (linear bent into curve)
What is the benefit of sector ultrasound probes?
They have a smaller outlet and detector for ultrasound waves meaning they are useful for looking at small/hard to view structures (e.g. looking between ribs).
What is the limitation of sector ultrasound probes?
They contain moving parts within the probe that move the crystals, leaving them prone to damage.
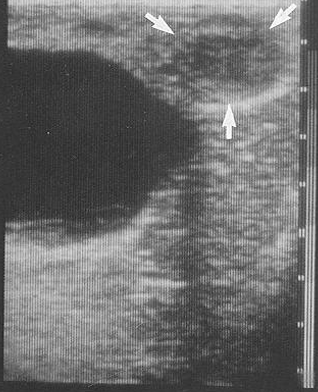
Describe how the reverberation artefact occurs in ultrasonography and how it appears
Ultrasound waves hit objects and reflect back to the scanner head, these waves can then reflect off of the scanner head and then reflect off the tissue again, back to the scanner head. This leads to artefactual whitening in a linear pattern.
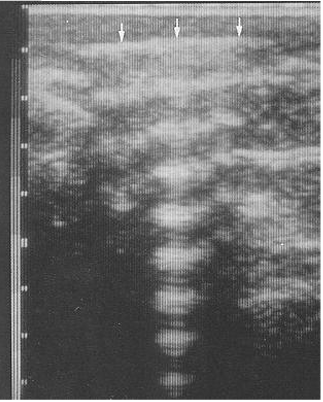
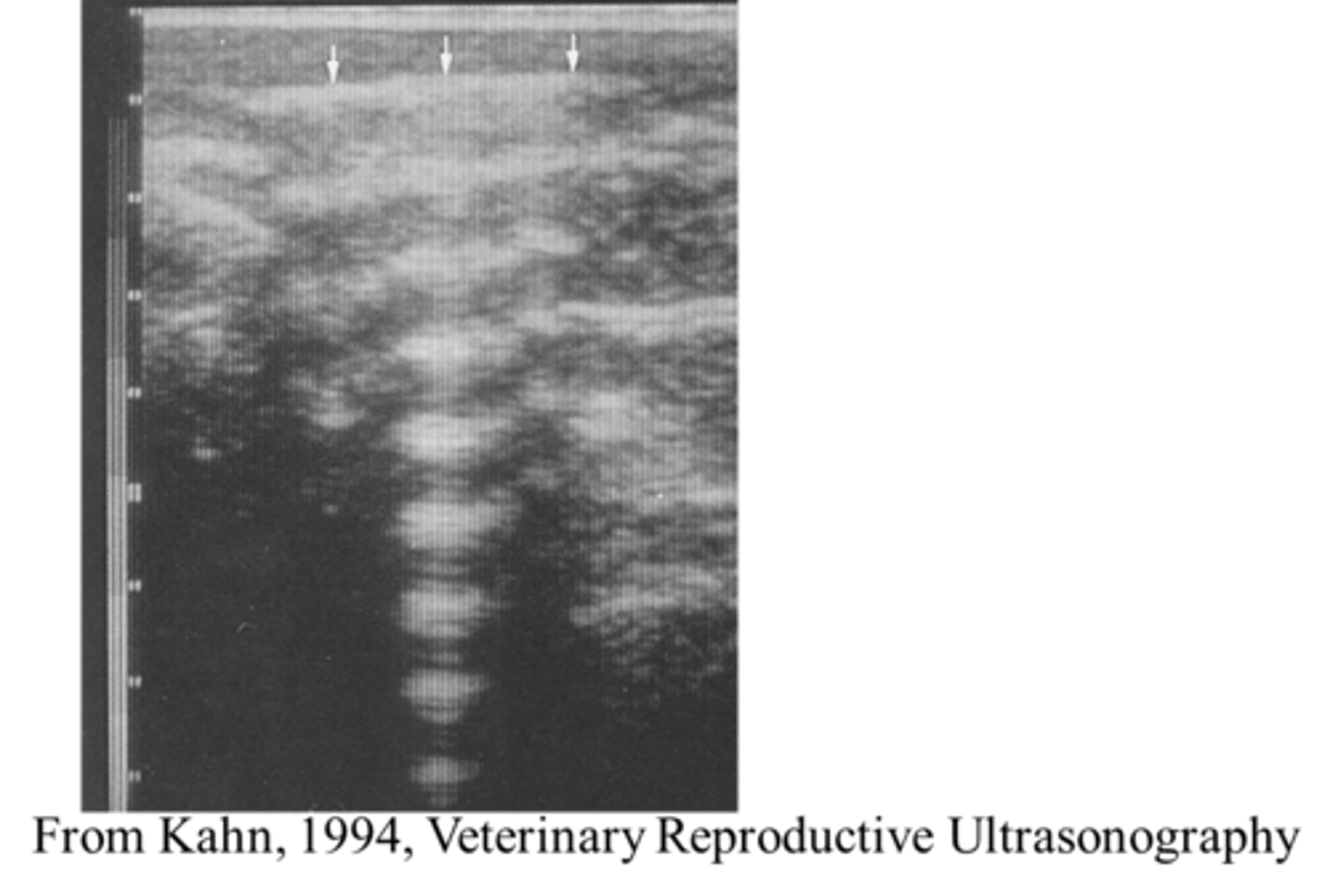
What ultrasound artefact is seen here?
Reverberation.
How is the reverberation artefact useful for follicles/vessels?
When the beam is perpendicular to a follicle or vessel, the reverberation artefact will consequentially cause the wall to become whiter.
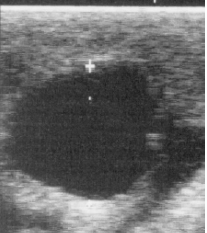
Why does acoustic enhancement cause artefacts?
If ultrasound waves travel through a structure which is less attenuating (absorbing) or a more transparent structure, the tissue of interest behind it may be shrouded due to more waves being transmitted through and hence reflecting back and reaching the scanner head. This causes false hyperechoic (white) regions to form.
What structures can potentially cause acoustic enhancement artefacts?
-Cysts
-Urinary bladder
-Large blood vessels
(anything filled with fluid)
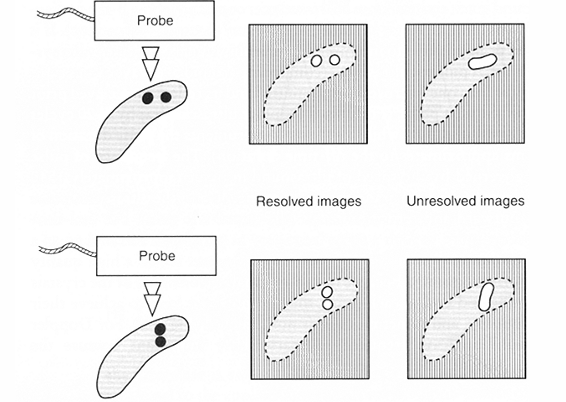
How can artefacts occur due to poor resolution?
If the resolution is poor, it will be difficult to differentiate between two separate structures which are small.
How can ultrasound be used to determine bloodflow?
doppler —> frequency of reflected wave changed by movement of structure as reflects the wave
will show higer frequency if blood moving towards scanner
How is ultrasound useful for large animals which are used for breeding?
Determining the stage of pregnancy or oestrus.
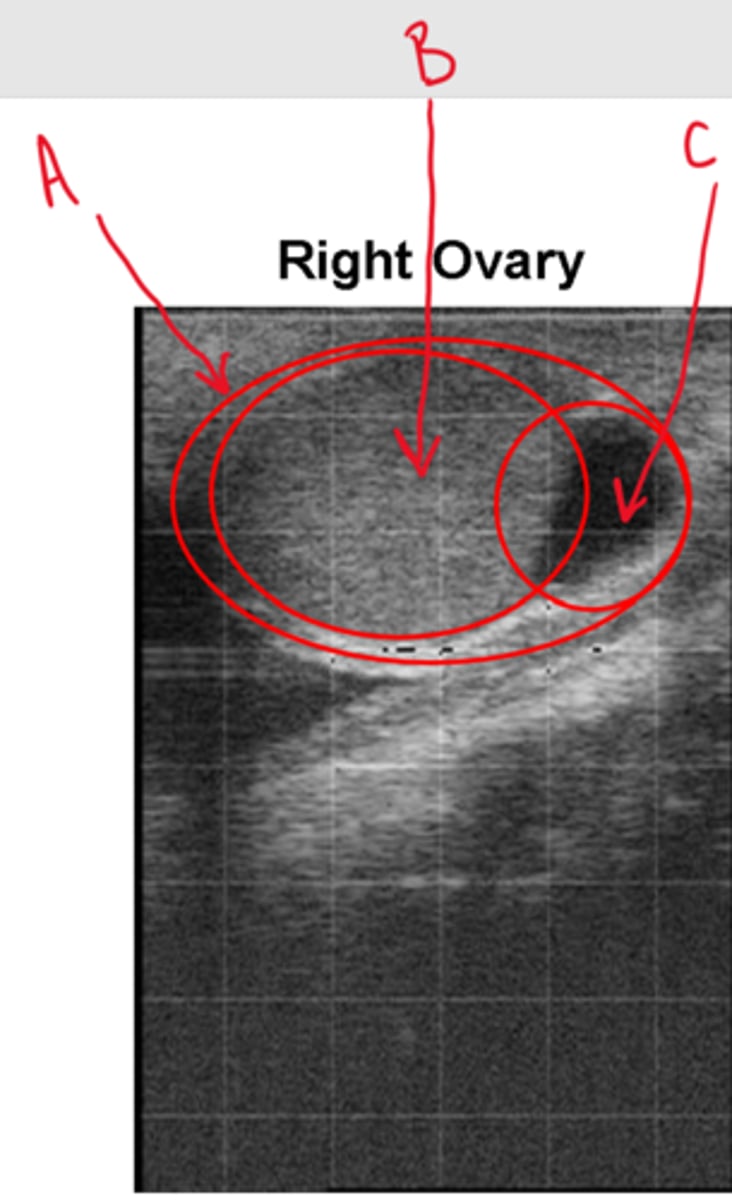
Label this ultrasound of the right ovary
A = Ovary
B = CL
C = Follicle
What are the uses of bovine reproductive ultrasonography?
Allows:
-Pregnancy determination
-Age determination
-Sex determination
How can you distinguish between a uterus in oestrus and a uterus in pregnancy?
Pregnancy:
-Fluid (circular)
-Heartbeat presence (day 26)
-Embryo presence
-Presence of CL (fluid in CL)
-Foetus presence
-Placentome presence (day 33)
-Pulse in the umbilical cord (day 110)
What are some signs that the foetus has miscarried?
no heart beat
membranes flaccid
allantochorion fluid
How would you age a foetus?
Mid-sagittal section for crown-rump length
Horizontal section for biparietal distance
Transverse section for trunk diameter
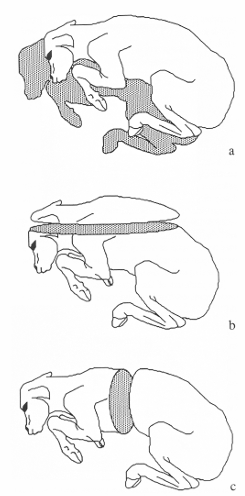
How would you sex a foetus?
genital tubercle migrates so that at about day 56 it is:
just behind the umbilicus in males
between the back of the hind legs and the tail in the female
teats and scrotum can be identified from 70 to 120 days
What are some uterine abnormalities that can be identified on ultrasound?
Cloudy fluid
Mucometra
Endometritis
Pyometra
Hard mass with bones
Mummified fetus
What is an ovarian abnormality?
granulosa cell tumour
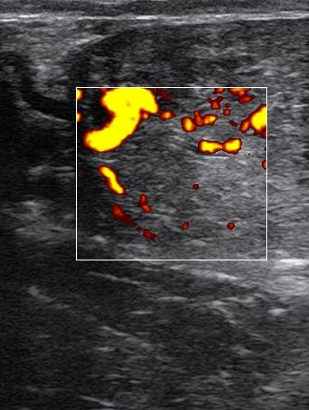
What routine should you use to pregnancy scan?
Evacuate faeces from rectum.
Insert protected and lubricated hand into rectum
lubricated scanner head cupped in palm of hand.
Use fingers to identify cervix
if necessary try to gently move tract back into the pelvic
Either move sideways from the cervix or follow the right horn round to identify the right ovary
Start on right as has 60% of ovulations and pregnancies
Obtain an image of the ovary and see if it has a CL
Scan horn towards uterine body
look for fluid, white line of amniotic vesicle and eventually fetus
If no fetus repeat process on left ovary and horn
Scan fetus from trunk towards head for heartbeat
Estimate the age the fetus
assess its size and how it is lying
decide best view to allow a measurement
freeze a good quality image and estimate age (use callipers or grid on screen)
Sexing - if old enough and the client requires it
transverse cross-section image at the umbilicus
move back, is there a hyperechoic genital tubercle behind umbilicus ?
if not move back to examine below the tail
a longitudinal midline cross-section down the fetus can also be used if the fetus is lying appropriately
What should you do if there is fluid but no fetus?
recheck both horns
is uterus over pelvic brim?
put probe over brim
placentomes? diameter?
is fluid cloudy? flecky?
any masses?
What can you identify on ultrasound relating to tendons?
injury
Longitudinal – tissue architecture
Cross-sectional – fluid accumulation
Repeat to gauge progress / prognosis
Skin preparation
What can you identify on ultrasound relating to cardiology?
Valve incompetence
Ventricular septal defects, PDA
Doppler – see direction of flow as colour
See valve motion and cardiac cycle – correlate with murmur
Pericardial effusion
Pleural fluid – U/S guided chest drain
What can you identify on ultrasound relating to the umbilical cord?
Umbilical masses
Abscess or hernia ?
Identify before incising!
Structure infected ?
Urachus – caudally
Umbilical arteries – caudally
Umbilical veins – cranially towards liver
What can you identify on ultrasound relating to the bladder and kidneys?
Urolithiasis
Is bladder intact ?
Gut motility - peritonitis
Ultrasound-guided paracentisis
Hydronephrosis
Pylonephritis
Ultrasound-guided tube cystotomy