Ops Management Midterm
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Operations Management
the management of processes used
to design, supply, produce, and deliver goods and services
Supply Chain Management
is the integration of operations
management decisions across organizational boundaries
Value Proposition
the group value dimensions that matter to a customer, with some of those dimensions qualifying the product or service for consideration and one or more dimensions distinguishing it from the competition.


Strategy Map
1. Create a comprehensive list of value dimensions customers in the firm’s market care about (not just the firm’s value prop.)
2. Organize the list in a column ordered from most important to the firm’s value to last
3. Create an x-axis
a. Poor performance = left
b. Great performance = right
4. Score the firm’s offering on each dimension and connect with the line
5. Score key competitors on each and connect with a line

Operational Capabilities
unique and superior abilities based upon the firm’s routines, skills, and processes that enable the firm to meet customer expectations and are difficult to imitate.

Operations Strategies Pillars
1. Aligns with and delivers on the firm’s value proposition
a. It is EXTERNALLY CONSISTENT
2. Develops operational capabilities that align with and reinforce one another
a. It is INTERNALLY CONSISTENT
3. Evolves maintains or extend competitive advantage
a. It is DYNAMIC

order qualifier
minimum level of value required from a set of criteria for a firm to do business

Order Winner
dimension(s) of value that differentiates one firm from another

What are the operational capabilities?

Manufacturing Environments

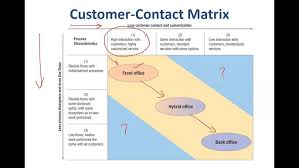
Consumer Contact Matrix
Components of visualizing a process:
1. Inputs, outputs, and “flows” – what moves through the process
a. The flow unit is the focal point of the process; the unit that the process is transforming
2. Activities
a. The task being performed
b. Transformation, inspection, storage, etc.
3. Process Structure
a. How activities are linked from beginning to end
4. Management Policies
a. How does one evaluate a process

Cycle Time
average time for completion of a unit at a production/service stage

Capacity (Throughput Time)
average number of units processed over a given time interval

Process Capacity
minimum capacity across all stages OR capacity of the stage with the longest cycle time (when no parallel processes)