Physics paper 3 questions I keep getting wrong
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Definitions and explaing questions that I find difficult in the AQA spec
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What is meant by dielectric constant? (1)
Permittivity of medium/permittivity of free space
How do polar molecules cause a change in capacitance? (3)
Align with their positive side facing the negative plate
Produces a counter electric field
V between plates decreases but Q stays the same so C increases as C=Q/V
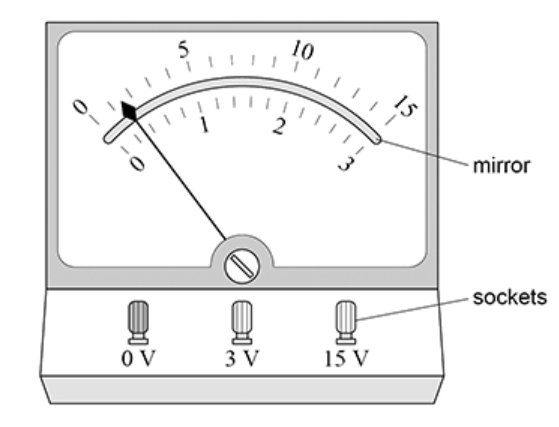
Explain the use of the mirror when reading the meter. (2)
Move position until the needle has aligned with its reflection
Reduces parallax error
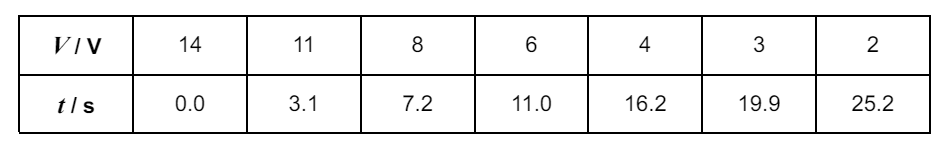
Suggest 2 reasons why the student selected the values of V shown in the table and explain. (4)
V recorded to nearest volt - due to low scale resolution
Decreasing intervals between values of V - to make intervals between t readings about the same
No readings for V<2V - needle is moving too slowly to judge
V recorded over wide range - to maximise evidence available
No readings for V>14V - capacitor can discharge before starting stopwatch
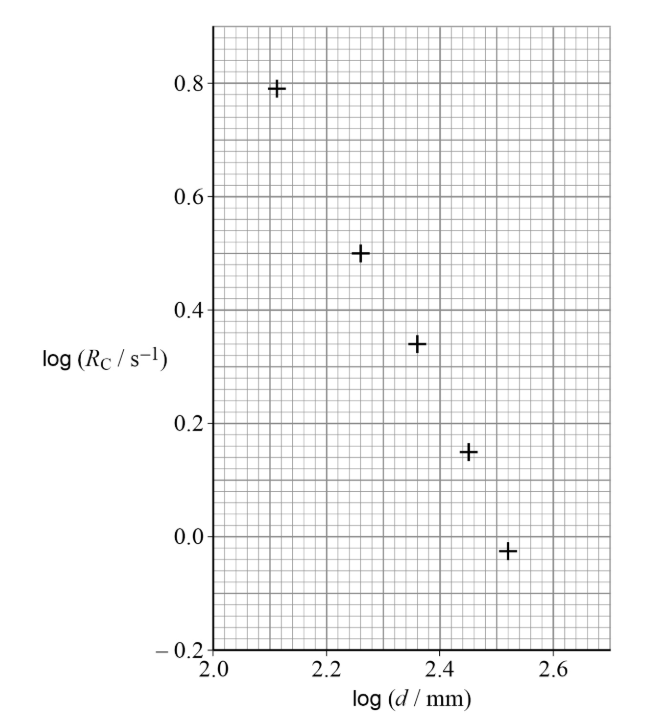
Explain how the student could confirm whether the graph supports the prediction Rc=k/d² (3)
Plot graph of logRc = -2logd +logk
Draw line of best fit and measure gradient
If gradient is about -2, prediction is confirmed
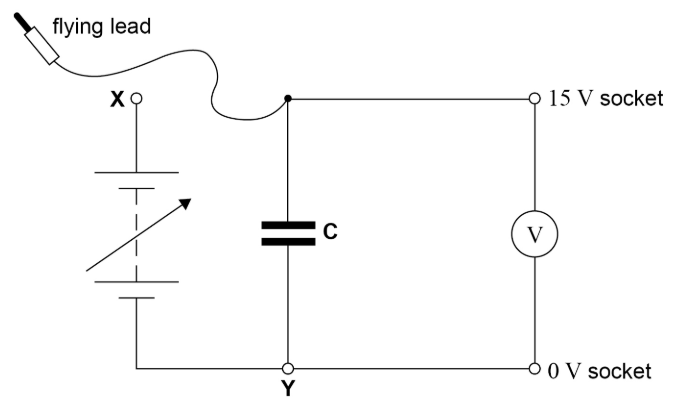
The student thinks that the time constant of the circuit is directly proportional to range of the meter. To test her theory, she repeats the experiment with the voltmeter set to the 3V range. She expects half-life to be about 2.5s.
Explain:
what she should do before connecting C to the 0V and 3V sockets to avoid exceeding the full-scale reading on the voltmeter
how she should develop her procedure to get an accurate result for time constant
how she should use her result to check whether her theory is correct (4)
Discharge C
Reduce output pd to <3V
Increase timing interval in measuring V
Repeat to calculate mean
Check + compensate for 0 error
Check for systematic error
Theory will be correct if half-life is 1/5 of previous value
Explain why moment of intertia about axis of rotation decreases when radius decreases. Explain the effect this has on angular speed. (3)
More mass closer to axis of rotation
Angular momentum constant as there is no external torque
Since moment of intertia decreases, angular speed increases
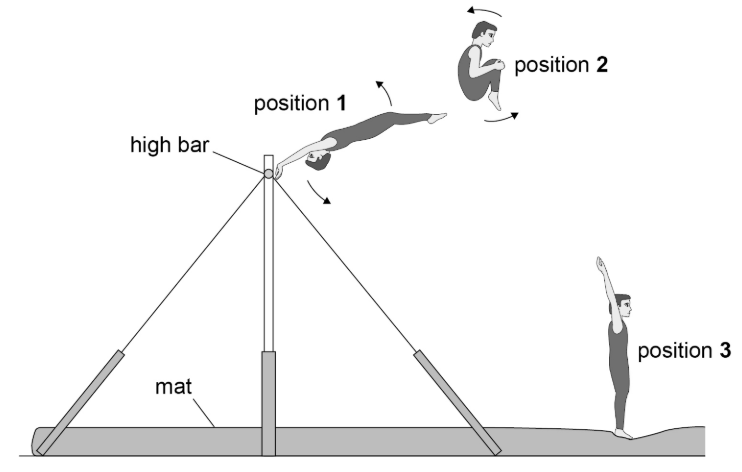
Without increasing height of bar, state and explain 2 actions the gymnast can take to complete more rotations during the dismount. (4)
Build up a greater initial angular speed around the bar - he will reach a greater height
Release at a greater angle from the horizontal - he will reach a greater height
Get into tuck position earlier - he will be turning for longer
Get into a tighter tuck position - moment of intertia will decrease so angular speed will increase
How do you calculate overall efficiency and why is it important for an engineer to know? (2)
Overall efficiency = brake power/input power
It gives an idea of how well energy in fuel is converted into useful work output
How do you calculate thermal efficiency and why is it important for an engineer to know? (2)
Thermal efficiency = indicated power/input power
Gives an idea of how well calorific value is converted into work in the engine
How do you calculate mechanical efficiency and why is it important for an engineer to know? (2)
Mechanical efficiency = brake power/indicated power
Gives an idea of work used in overcoming friction inside the engine and work done to operate valves
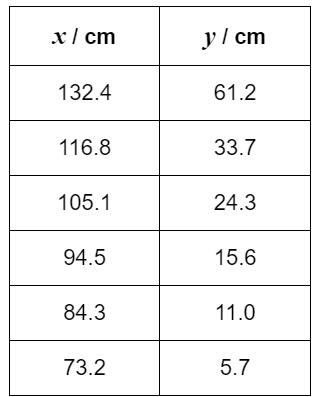
Suggest why the student chose to make all measurements of x greater than 70cm. (1)
Percentage uncertainty too large
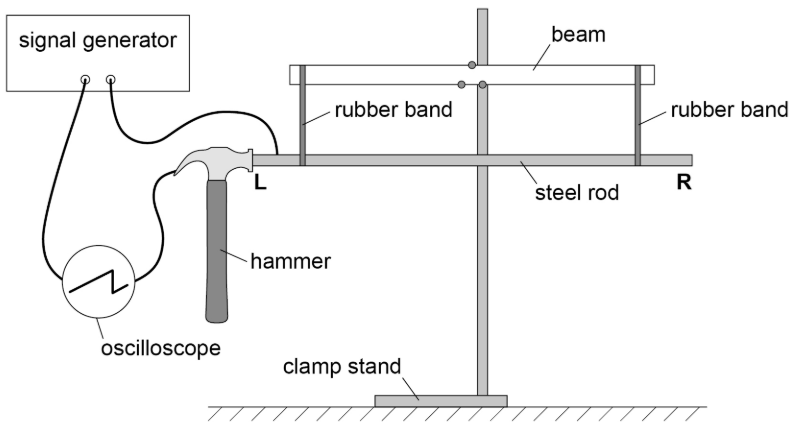
A student repeats the experiment using a steel rod of twice the length.
Explain
how using the longer rod affects the waveform displaed
any changes needed to get an accurate result for the speed
Include numerical detail. (4)
Contact time with rod is doubled
Number of cycles produced is doubled
Waveform would not be fully displayed
Adjust time-base
To 0.1ms
Suggest 2 advantages of keeping a flywheel connected to the driving whells of a tram travelling downhill. (2)
Potential energy of tram can be converted to kinetic energy so less energy will be transferred to the brakes and the tram will not reach a high speed
Fly wheel stores energy which can be used later
Discuss the design features of a flywheel that will enable it to store more energy without increasing mass of the system.
Consider:
design of flywheel
how choice of materials is influenced by design and maximum angular speeds
other design aspects that allow for high angular speeds (6)
Ek is proportional to ω2 and I
I depends on mass and distribution of mass around the axis
Arrange more mass at the outer edge of the flywheel as I=Σmr2
Use a heavy rim and spokes
increase radius
use material of higher density at the rim
use material of higher strength
For higher speeds without breaking
E.g. titanium
Increase ω by decreasing friction at bearings
Use lubricant or roller bearings
Use materials with smooth outer surfaces
A small increase in ω will create a large increase in Ek
Explain what is meant by an adiabatic change (1)
no heat energy transfer to or from the system
Explain why the compression ratio for a diesel engine must be greater han the compression ratio for a petrol engine. (2)
Diesel engine requires a larger compression ratio to create a high enough temperature to ignite fuel
Petrol vapour-air mixture ignited by spark at a lower temperature or pressure
Explain 2 differences between the ideal cycle and the indicator diagram for the real diesel engine cycle. (2)
Curved corners - valves take finite time to open and close
No constant volume processes - engine would have to stop
Compression and expansion not adiabatic curves - energy lost by heat transfer
Pumping loop open - engine needs to draw in and expel air
Heating is not at a constant pressure - fuel injection and combustion not exactly controlled
Area of diagram decreases - due to energy lost by heat transfers
Pressure decreases - incomplete combustion of fuel not fully released
A student suggests that setting the time-base on an oscilloscope to a 0.2ms division-1 from 0.5 might reduce uncertainty in the determination of the time constant.
State and explain any possible advantage or disadvantage in making this suggested adjustment (3)
Waveform will stretch horizontally
By a factor of 2.5
Resolution will increase
Measuring larger distance reduced % uncertainty in reading time
Compare the work done in an adiabatic compression and an isothermal compression (3)
Isothermal compression pressure not as high
So the area under a p-V graph is smaller
So less work is done
Compare the theoretical and real engine cycles. In your answer you should:
State and explain the differences between the cycles
Explain why the work outpuf per cycle of the real engine is less than predicted by an analysis of the theoretical cycle (6)
Real engine needs induction and exhaust strokes - ideal cycle uses same air repeatedly
Corners rounded on real cycle - valves take finite time to open and close
Heating/cooling cannot occur at constant volume in real cycle - piston would have to stop
expansion and compression not adiabatic in real cycle - heat transfer takes place to cooling medium
some exhaust gas is present in real cycle - only air taken through cycle in ideal
max pressure is lower in real engine - fuel may not be completey burnt
Area of loop is smaller for real engine so less work done per cycle
Area of pumping loop has to be subtracted from the main loop, reducing work done
Friction between moving surfaces
Energy expended in driving oil and water pumps, opening and closing valves, etc
State the law of conservation of momentum (1)
Total angular momentum remains constant provided no external torque acts on the system

The table shows the average power requirements for a large paper-manufacturing business.
National Grid is supplied mainly from power stations which have overall efficiencies of up to about 40%.
The paper mill can either:
take all of its energy from the National Grid
install an electrical generator of output 60MW driven by a gas turbine of efficiency 36% as part of a combined heat and power (CHP) scheme. The hot exhaust gaes from the rubine are used to produce steam at high temperatures and pressure for heating.
Explain why the maximum theoretical efficiency of a heat engine is much less than 100%.
Compare the 2 options using the numerical data.
All heat engines must obey 2nd Law of thermodynamics
They must reject energy to surroundings
Maximum efficiency determined by source and sink temperatures
100% efficiency would require Tc=0K
Inefficiencies from nature of working cycle - friction
60MW will cover electrical need
Input power = 60/0.36 = 167MW
Max heat available for heat requirement = 107MW
And likely will be less than this
Which is not enough for heating requirement
34MW will need to come from National Grid
Power station input to give 198MW to mill = 495MW
Energy that would otherwise be wasted is utilised
Explain why it is important to use a voltmeter with very high resistance. (1)
Capacitor must not lose charge