METALS
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Noble Metals
regarded as a metallic chemical element that is generally resistant to corrosion and is usually found in nature in its raw form.

Aluminum (AI)
Very light with a specific weight of 2710 kg/m3, about a third of Steel.
High Corrosion Resistance
High Electrical and Thermal Conductivity
Recyclability - can be re-melted with minimal energy requirement.
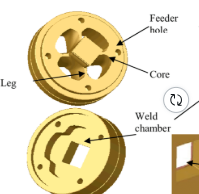
Extrusion
The process of shaping material by forcing it to flow through a shaped opening in a die.

Structural Aluminum
used in long span roofing systems where lightness is a requirement. Used in skylight primarily and secondary frames.
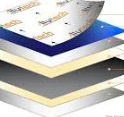
Aluminum Composite Panel
Commonly used as secondary layer of a facade or a skin system.
Aluminum Railing Components

Aluminum Curtain Wall Systems

Aluminum Doors and Windows

Aluminum Hardware

Electroplate
To plate with an adherent metallic coating by electrolysis, usually to increase the hardness, improve the durability or enhance the appearance of the base metal.

Anodize
To coat a metal, esp. Aluminum or magnesium with a hard non-corrosive by electrolytic or chemical action.

Iron (FE)
Malleable, ductile, silver, white metallic element.
Most common base for metals used in construction

Pig
An oblong mass of metal that has been poured while still molten into a mold of sand, esp. such a mass of iron from a blast furnace. Also called crude iron.

Cast Iron
Hard, brittle and non-malleable iron-based alloy.
Contains 2.0% to 4.5% carbon and 0.5% to 3% silicon.

Wrought Iron
Malleable, relatively soft iron
Contains 0.2% carbon and small amount of uniformly distributed slag.

Steel
Versatile iron-based alloy with a carbon content of less than the cast iron and more the wrought iron.
High Strength, hardness and elastic which varies according to its composition and treatment

Carbon Steel
Ordinary, unalloyed steel in which the residual elements such as carbon, manganese, phosphorous, sulfur, and silicon are controlled.

Mild Steel
A low-carbon steel containing 0.15% to 0.25% carbon. Also called Soft Steel.

Medium Steel
A carbon steel containing 0.25% to 0.45% carbon.

Hard Steel
A carbon steel containing 0.45% to 0.85% carbon.

Spring Steel
A carbon steel containing 0.85% to 1.80% carbon.

Alloy Steel
Carbon Steel to which various elements such as chromium, cobalt, copper, manganese, molybdenum nickel, tungsten or vanadium have been added to obtain particular physical and chemical properties.

Stainless Steel
Alloy steel containing a minimum of 12% chromium sometimes with nickel, manganese, or molybdenum. Highly corrosion resistant Stainless steel has a low bacterial retention capacity.

Weathering Steel
Steels that are chemically formulated to develop a protective patina layer - rust-like in appearance - that eliminates the need for paint. Can also be called corten steel.
Wide-Flange Shape
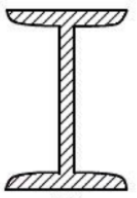
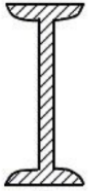
American Standard Beam
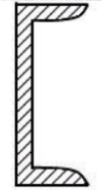
American Standard Channel
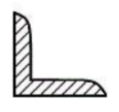
Angle
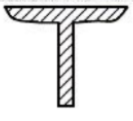
WT or ST
Pipe Section
Structural Tubing
Bars
Plates

Copper (CU)
Ductile, malleable, nonmagnetic metal with a characteristic bright, reddish-brown color.
It is highly resistant to corrosion by air and salt water.
As copper is one of the best electrical conductors, it finds tremendous use in the entire electrical field, from very fine wires to bus bars.

Tin (Sn)
Soft, ductile, malleable, bluish metal
At its refined state, Tin is corrosion resistant.
Used to coat other metals such as copper, lead, zinc or nickel

Terne Plate
is a form of tinplate: a thin steel sheet coated with an alloy of lead and tin. The terne alloy was in the ratio of -% tin and the remainder lead. The low tin content made it cheaper than other tin plates.

Zinc (Zn)
Medium hard, Bluish-white metal
Brittle and low strength
Resistant to corrosion by water
Used as coating for iron and steel, also called Galvanizing

Galvanized Iron
Iron that’s been coated with a protective zinc layer on the outside. Iron itself is susceptible to weather-related degradation.

Brass
a metal alloy of copper and zinc that typically has a golden-yellow color but can be closer to red if the alloy has high levels of copper (this is known as “red brass”)

Bronze
a metal alloy of copper and tin which varies only slightly from 90% copper and 10% tin composition.

Brass
in architecture, brass is used for
Statuary
Plaques
Medallions and other ornamentation
Finish hardware
Cladding

Chromium (Cr)
Steel-white metal which takes a brilliant polish and is harder than cobalt or nickel

Chromium Plating
Gives a thin, hard, bright, wear resistant surface which sheds water when highly polished.

Nickel
steel-white metal which takes a brilliant polish and is harder than cobalt or nickel.

Lead
Steel-white metal which takes a brilliant polish and is harder than cobalt or nickel.

Soldering
a process used for joining metal parts to form a mechanical or electrical bond. It typically uses a low melting point metal alloy (solder) which is melted which is melted and applied to the metal parts to be joined and this bonds to the metal parts and forms a connection when the solder solidifies.

Brazing
process for joining two pieces of metal that involves the application of heat and the addition of a filler metal. This filler metal, which has a lower melting point the metals to be joined, is either pre-placed or fed into the joint as the parts are heated

Welding
a fabrication process that joins materials, usually metals or thermoplastics, by using high heat to melt the parts together and allowing them to cool, causing fusion.
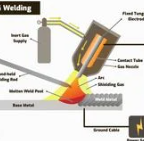
Tungsten Inert Gas Welding (TIG)
a welding process that uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to produce the weld. The weld area is protected from atmospheric contamination by an inert shielding gas, typically argon or helium.
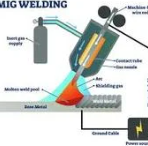
Metal Inert Gas Welding (MIG)
welding process that uses a consumable wire electrode and an inert shielding gas to create a weld. The electric arc melts the wire, which fuses with the base metal to form a strong joint.
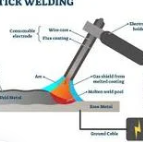
Stick Welding
welding process that uses a consumable electrode coated with flux to create an electric arc between the electrode and the metal workpiece. The heat generated melts the electrode and base metal, forming a weld joint, while the flux coating produces a protective gas shield and slag to prevent contamination.

Mechanical Fasteners
device that is used to mechanically join (or fasten or affixes) two or more objects together.