Plant Biology Test 3
1/169
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
170 Terms
short-distance transport
transport across a few cell diameters or less of distance (does not involve xylem or phloem)
long-distance transport
transport between cells that are distant from each other (involves xylem and phloem)
diffusion
movement of substances from an area of high cell concentration to an area of low cell concentration
down/with
Diffusion moves ____/____ the concentration gradient.
passive
Diffusion is a type of _____ transport.
simple diffusion
Substances move directly through the membrane
facilitated diffusion
movement of substances using a transport protein
carrier
solute binds to the transport protein
channel
allows solute to pass through
osmosis
Movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane from a high concentration to a low concentration
active transport
uses energy to transport substances up against a concentration gradient from a low concentration to a high concentration
primary active transport
What type of active transport involves transport proteins called molecular pumps that break down ATP to move substances?
secondary active transport
What type of active transport uses the energy of a gradient to move a substance up/against its concentration gradient?
proton pump
A major example for primary active transport is a ________.
proton gradient
A major example for secondary active transport is a ________.
water potential
chemical potential of water, free energy of water
psi
The symbol (Ѱ) for water potential is called ____.
heat; pressure; elevate
To increase Ѱ, you have to ___ the water, add _____, or ____ the water
solutes
Adding this to water can affect the water potential.
water potential equation
What is this?
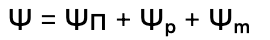
osmotic potential
Ѱⲡ stands for…
pressure potential
Ѱₚ stands for…
matric potential
Ѱₘ stands for…
pressure; water
If water is placed under pressure, the _____ potential increases, so _____ potential increases.
positive
This type of pressure causes compression.
negative
This type of pressure causes stretching/tension.
0
Pure water at 1 atm of pressure has a Ѱ of ___.
solutes
Osmotic potential is the effect of _____ on water potential.
0.0
The osmotic potential of pure water is ____ MPa.
decreases
The addition of solutes ______ the free energy of water.
negative
Osmotic potential (Ѱⲡ) for solutions is always _____.
interact; soil
Matric potential (Ѱₘ) is water’s ability to ____ with things that don’t dissolve, like ___. particles
negative
Water potential in solutions is always ____.
positive or negative
Pressure potential in solutions is always ________.
positive; negative
Water moves from a more ______ water potential to an area with a more _____ water potential.
difference
Water moves when there is a ______ in water potential.
equal; no
If the water potentials in two areas are _____, there is __net movement of water.
pairs; groups
Water potentials are observed in ____or ____.
protoplast; force
When a plant cell takes in water, the ______ swells and exerts a _____ against the cell wall.
rises
The cell wall exerts a force on the protoplast, so the pressure potential ____.
lysis
The plant cell wall inhibits ____ when the protoplast swells and exerts force.
plasmolysis
shrinking of a cell due to water loss, the protoplast pulls away from the cell wall
guard cells/stomata
involves short distance transport
shrink
At night, guard cells _____.
in equilibrium
At night, the guard cells are ________ with surrounding cells.
potassium (K+)
At sunrise, _______ ions are actively transported into the guard cells.
less
At sunrise, the surrounding cells become_____ negative.
more
At sunrise, guard cells become ____ negative.
pumped
In the morning, K+ ions are continually ____ into the guard cells.
bend; open
In the morning, water moves from the surrounding cells into the guard cells, causing them to ____, resulting in an ____ stomata
later in the morning
The net movement of water stops as equilibrium between the surrounding cells and guard cells has been reached occurs…
phloem transport
Involves long-distance transport of sugars/nutrients
Sieve tube element/member
helper → companion cell
EX. angiosperms
sieve cell
helper → albuminous cell
EX. gymnosperms
pressure-flow hypothesis
Explains the transport of phloem sap, active loading in sources, and active unloading in sinks
sources
organ/tissue that supplies material that can be transported
sink
organ/tissue that receives material transported by the phloem
leaves
main sources in plants during spring and summer
tubers; fleshy taproots
When referring to some plants that may lose leaves, their sources can be _____ or ______.
cotyledons; endosperm
For seed germination, ______ (seed leaves), and _____(tissue that can be broken down to provide nutrients for the embryo) can act as sources for an embryo.
sugars
_____ are actively transported into phloem cells when loading in sources. (step 1)
negative; negative
As phloem is loading in sources, Osmotic potential (Ѱⲡ) becomes more _____, so the water potential (Ѱ) becomes more_____. (step 2)
water
____ enters the phloem cells when phloem loads in sources. (step 3)
water and sugars; pores
When phloem is loading in sources, the solutions of ____and ____can be forced through _____ from one phloem cell to the next. (step 4)
sinks
Examples of this are growing flowers, fruits, meristems.
actively; cells
When phloem is unloading in sinks, the sap is _____ transported into ____ of the sink. (step 1)
negative
When phloem is unloading in sinks, osmotic potential (Ѱⲡ) within the phloem cells becomes less _____. (step 2)
water; sugars
When phloem is unloading in sinks, _____ flows through the _____ out into the cells of the sink.
cohesion
water’s ability to stick to itself
adhesion
water’s ability to stick to other substances
moist
With ____ soil, a plant’s roots can easily absorb the water between the soil particles (within the gaps).
dry
With ____ soil, a plant’s roots struggle to absorb the water in the film surrounding the soil particles
cohesion-tension hypothesis
As water is pulled upward by transpiration, the water molecules cohere enough to withstand tension/pulling force.
soil
1st step of water movement in the plant
root
2nd step of water movement in the plant
xylem cohesion
3rd step of water movement in the plant
leaves (veins)
4th step of water movement in the plant
evaporation of water from mesophyll cell walls
5th step of water movement in the plant
escape through the stomata
6th step of water movement in the plant
benefit
Is this a benefit or a disadvantage of an open stomata?
allows for gas exchange (CO2 can come in)
disadvantage
Is this a benefit or a disadvantage of an open stomata?
loss of water, which can lead to dehydration
soil
When rocks weather, what is produced?
rock; ions; inorganic
Soil is largely made of ____ particles, dissolved ____, and ______ components
soil
rock particles, insects, animals like earthworms, roots, plant parts, algae, bacteria, fungi
mineral nutrition
impact of minerals in a plant’s metabolism
major/macro essential elements
These elements are needed in larger amounts
major
Are these elements major or minor essential elements?
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, potassium, calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, sulfur
Minor/micro essential elements
these elements are used in trace amounts
minor
Are these elements major or minor essential elements?
Iron, chlorine, copper, manganese, molybdenum, and boron
development
The essential element is required for normal plant ______ through its complete life cycle.
substitute
The essential element is needed. No ______ is sufficient.
inside; outside
The essential element must act ____ the plant, not _____ of it.
Chlorosis
yellowing of leaves due to decreased chlorophyll
Necrosis
areas of dead tissue
physical weathering
breakdown of rock by physical forces such as wind, water, and temperature changes
chemical weathering
chemical reactions break down rock and change the chemistry of the soil that is produced
sand
large particles with large spaces between them
gas
Large spaces in sand are good for ___ diffusion.
Large spaces cannot hold water against the force of gravity, so the water/rainfall soon sinks into the groundwater
clay
small particles with small spaces between them
Small spaces hold onto water/rainfall so little sinks into the groundwater