Biochemical Tests
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
What are characteristics of PEA media?
Selective media for gram positive, reversibly inhibits DNA synthesis in gram-negative bacteria by disrupting cell membrane permeability
What are the characteristics of Eosin Methylene Blue?
Selective for Gram-negative bacteria because methylene blue and eosin inhibit gram positive. Differentiates coliforms (lactose fermenting or not)
If thick strong, growth occurs on EMB, that means the organism is…
gram negative
If no growth occurs on EMB, that means the bacteria is..
Not gram negative
If there is pink, black, purple, or metallic green growth on EMB, that means
Lactose fermentation occurred
If there was colorless growth on EMB, that means…
No lactose fermentation occurred (peptone was the nutrient source)
What are characteristics of MSA?
Selective for Staphylococcus, Differentiates mannitol fermentation, phenol red is the indicator
If MSA plate is yellow, that means
Mannitol was metabolized (acidic)
If MSA plate is fuchsia/pink, that means…
peptone was utilized (ammonia formed= basic)
If MSA plate has growth, that means
Staphylococcus genus grew
If no growth on MSA plate, that means
No staphylococcus genus
Organisms that ferment what are usually pathogenic?
Mannitol
What is catabolism versus anabolism?
Catabolism is the breakdown of molecules, whereas anabolism builds them.
After adding iodine, if there is a clearing around the growth, this means
Bacteria consumed starch, so iodine doesn’t have anything to bind to. Positive for amylase production and starch hydrolysis
After adding iodine, if there is no clearing, that means…
Bacteria could not consume the starch. Negative for amylase production and starch hydrolysis (peptone was nutrient source)
Define oxdiation
Glucose or peptone can be oxidized in the presence of oxygen to produce energy for the bacteria
Define Fermentation
Does not use or require oxygen, but can take place in the presence of oxygen
What are the ingredients of OF Glucose?
Glucose, bromothymol blue(pH indicator), agar, peptone
What can we determine with a OF Glucose test?
It is a differential test for oxidation/fermentation of glucose, determine oxygen requirements and motility
In the OF Glucose test, if yellow is present, this means
Glucose was metabolized (Oil=fermentation, No oil=oxidation)
In the OF Glucose test, if blue is present, this means..
Peptone was utilized
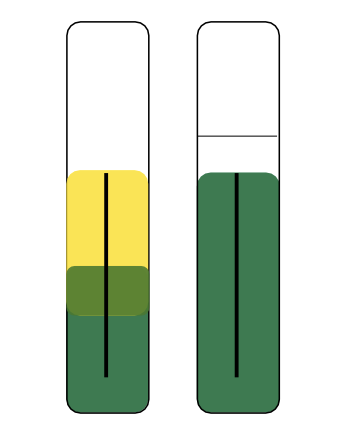
If the aerobic tube is yellow and the anaerobic tube is green, what does that mean?
Positive for glucose oxidation and negative for glucose fermentation
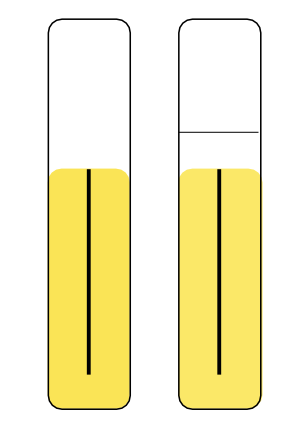
If the aerobic and anaerobic tubes are both yellow, what does that mean?
Positive for oxidation and fermentation
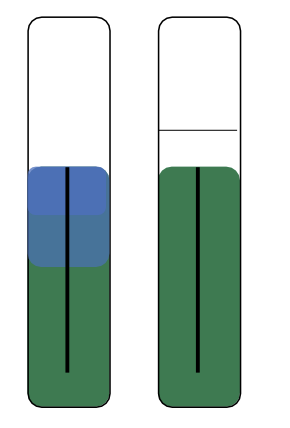
If the aerobic tube is blue or green and the anaerobic tube is green, what does that mean?
Negative for glucose oxidation and glucose fermentation
Where does lactic acid fermentation occur more?
In muscle of animals to produce energy when there is not enough oxygen.
What is the Carbohydrate fermentation test used for?
It is a differential test for the ability of the organism to ferment the specified carbohydrate
What are the ingredients of the carbohydrate fermentation test?
Carbohydrate, peptone, phenol red, and durham tube
What do Durham tubes do?
They trap gas produced during true fermentation
Why does the carbohydrate fermentation test have an idea time range?
Even if the bacteria can not ferment, the media has peptone, so they will utilize it.
What are the three things that can happen in fermentation broth?
True fermentation (acid and gas), Fermentation (acid only), Peptone utilization )No acid or gas - ammonia only)
In the fermentation test, if there is yellow color change, this means..
Fermentation occured
In the fermentation test, if there is red, pink color change and no acid/gas, this means..
No fermentation, and positive for peptone utilization
In the fermentation test, if there were significant sized bubbles in the durham test, this means…
Positive for gas production
In the fermentation test, if there are tiny bubble or no bubbles in durham tube, this means…
Negative for gas production
What is the gelatin hydrolysis test for?
It is a differential test that determines if bacteria can catabolize gelatin using exoenzyme gelatinase
Can a gelatin hydrolysis test be put in the incubator?
No
If gelatin liquifies, this means..
positive for gelatinase
What does the phenylalanine slant test for?
Production of endoenzyme deaminase (differential test)
After incubation, what is added to phenylalanine slant?
10% ferric chloride
If there is dark green color change after 10% ferric chloride, what does this mean?
positive for phenylpyruvic acid and deaminase
If there is no color change after 10% ferric chloride, what does this mean?
negative for phenylpyruvic acid and deaminase
What is the purpose of the MIO test?
Differential test to determine if an organism is motile, can decarboxylate ornithine (amino acid), and can produce indole from tryptophan
What indicator is used for MIO deep test?
Bromocresol purple
What is indole?
Organisms that produce endoenzyme tryptophanase breakdown tryptophan, producing indole
How is indole detected in MIO?
A red ring after adding Kovac reagent
What is ornithine?
Organisms that produce endoenzyme ornithine decarboxylase decarboxylate ornithine, resulting in alkaline end products
What is a positive test for ornithine look like?
Dark purple(putrescine)
If red fluid layer forms after Kovac’s reagent in MIO, this means..
+ for indole and tryptophanase
If yellow fluid layer after Kovac’s reagent in MIO, this means…
- for indole and tryptophanase
If dark purple color change in MIO, this means
+ for ornithine decarboxylation and ornithine decarboxylase
What amino acids have sulfur?
Methionine and Cysteine
What is peptone iron deep test?
Differential test for hydrogen sulfide (H2s) production
If there is a black color change in peptone iron deep, this means..
+ for hydrogen sulfide and cysteine
If there is no black color change in peptone iron deep, this means..
- for hydrogen sulfide and cysteine
What is oxidase test?
Differential test for endoenzyme cytochrome C to investigate aerobic respiration. Needs oxidase strip
Who has cytochrome C?
Only strict aerobic bacteria
If oxidase strip turns blue, purple, or black in 30 seconds, this means…
+ for cytochrome c
If no color change on oxidase in 30 seconds, this means…
- for cytochrome c
What is the catalase test?
Differential test for endoenzyme catalase to investigate aerobic respiration.
If bubbles form in catalase test, this means..
+ for catalase
If no bubbles form in catalase test, this means…
- for catalase
What is the difference between oxidase test and catalase test?
Only strict aerobic organisms can produce cytochrome c, whereas strict aerobic and facultative anaerobic organism can produce catalase.
Is nitrate reduction test aerobic or anaerobic?
Anaerobic respiration
What enzyme reduced nitrate to nitrite?
Nitrate reductase
What enzyme reduces nitrite to nitrous oxide?
Nitrite reductase
What enzyme reduces nitrous oxide to nitrogen gas?
Nitrous oxide reductase
What do Nitrate A and Nitrate B react with to form a red color?
Nitrite
If no red/orange color forms after addition of Nitrate A and B, what does this means…
Nitrite is not present, but three other possibilities
What are the three possibilities if nitrite was not shown to be present?
Nitrate was not reduced and is still present, it was reduced to nitrous oxide and left as gas, or it was reduced to nitrogen gas and left as a gas
What is used to determine which of the three possibilities is correct?
Zinc
Once adding zinc, what do the results mean?
If a red color change occurs, zinc reduces nitrate to nitrite. If no color changes, nitrate was reduced to nitrous oxide or nitrogen gas by the bacteria
What 4 test make up IMViC?
Indole, Methyl red, Voges-Proskauer, Citrate
What is used to conduct indole test?
Tryptone Broth
What purposes does the MRVP broth serve?
It can detect stable acid from glucose or unstable acid (acetoin) from glucose
What reagent detects stable acid?
Methyl red
What reagent detects unstable acid?
VPI and VPII
What is the purpose of methyl red test?
It is a differential test that identifies organism capable of producing stable acid
If red color change occurs after adding methyl red, this means…
+ for stable acid
What is the purpose of the Voges-Proskauer Test?
Differential test for organisms capable of producing acetoin
If a cherry red color change occurs 20-30 minutes after adding VPI and VPII, this means…
+ for acetoin
If gray, brown, or no color change occurs after adding VPI and VPII, this means…
- for acetoin
What must you do after adding VPI and VPII?
Leave the cap off
What is the purpose of citrate test?
Differential test that determines whether an organism can use citrate as its sole carbon source and whether an organism can produce exoenzyme citrase
If there is a blue color change in the citrate test, this means…
+ for citrase and citrate utilization
If there is green or no color change in citrate test, this means…
- for citrase and citrate utilization
What type of reaction is the citrate test?
Aerobic
What is the pH indicator for citrate test?
Bromothymol blue