scrotum pathology
1/282
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
283 Terms
What are the 4 lab tests to know in this lecture?
Urinalysis
WBC
Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)
Human Chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
A urinalysis test will test for what 3 things?
Bacteria
Pus
Infection
A WBC test will test for…
Infection
For an AFP lab test:
What pathology produces AFP?
What pathology does not produce AFP?
Non-seminoma germ cell tumor
Seminoma germ cell tumor
What 2 pathologies can cause a rise in hCG levels in the blood?
Seminoma germ cell tumor
Non-seminoma germ cell tumor
Both Leydig cell tumors and Sertoli cell tumors do not make what two lab tests?
AFP
hCG
What 2 pathologies will not rise in tumor markers due to not producing AFP and hCG?
Leydig cell tumors
Sertoli cell tumors
What is an orchiectomy?
The surgical removal of the testicle
An inguinal orchiectomy is a procedure that confirms (1)_______ types and prevents the seeding of (2)____________.
Cancer types
Cancer cells
What procedure is not recommended when it comes to masses/tumors of the testicle?
Biopsy
A hydrocele is when there is (1)________ fluid found between the two layers of the tunica (2)______________.
Serous
Vaginalis
A hydrocele will displace the teste…
Posteriorly
What is normal when it comes to fluid around the testicle?
A few mL of extra testicular fluid is normal
What sonographic appearance can be seen within a hydrocele?
Low level echoes
Define idiopathic.
‘Cause is unknown’
A hydrocele is often obtained…
Congenitally
What are the 3 causes for hydrocele? (CIR)
Congenital
Idiopathic
Reactive
A reactive hydrocele can be found in the presence of what 4 pathologies?
Infection
Torsion
Trauma
Tumors
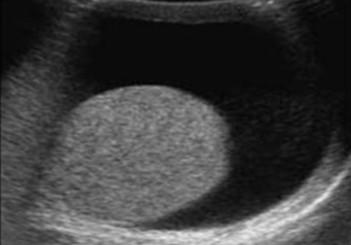
The pathology seen here has an idiopathic origin. What can be assumed here?
What sonographic finding can be seen amongst the fluid?
Hydrocele
Low level echoes
A hematocele will contain ______.
Blood
What are the 3 causes of a hematocele?
Trauma
Advanced epididymitis
Advanced orchitis
A fresh hematocele can appear (1)_________, but can often have some (2)__________ components that can be seen moving in real time.
Anechoic
Echogenic
Overtime, a hematocele can develop (1)__________ and the appearance of blood can increase in (2)__________.
Septations
Echogenicity
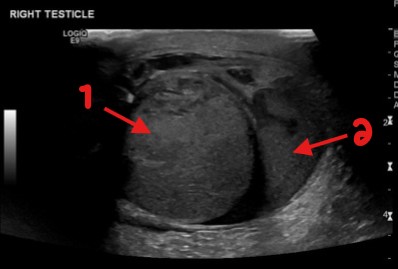
A patient has experienced trauma to the scrotum recently and this image was obtained. What can be assumed here for arrows 1 and 2?
Testicle
Hematocele
Define leukocytosis.
Elevated WBC count
A patient experiencing pyocele will present with what 2 clinicals findings?
Fever
Elevated WBC count (leukocytosis)
Pyocele is when (1)_____ fills the space between the layers of the tunica (2)________________.
Pus
Vaginalis
A pyocele on US will contain what 3 sonographic findings?
Internal septations
Loculations
Debris
Pyoceles can appear after which two occurrences?
Trauma
Surgery
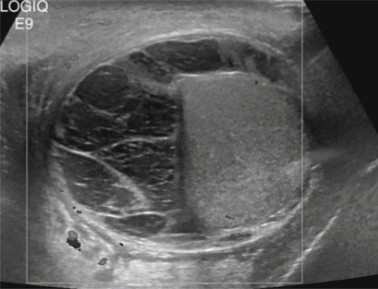
A patient recently had surgery to the testicular area and this was seen on the US. What can be assumed here?
Pyocele
What are the 6 various acute scrotal pain differentials?
Trauma
Epididymitis/Orchitis
Torsion
Appendix testes OR epididymal appendix torsion
Varicocele thrombosis
Incarcerated hernia
Patients dealing with scrotal trauma will present with what 2 symptoms?
Pain
Swelling
A scrotal rupture is a __________ emergency.
Surgical
If surgery is performed within 72 hours following a scrotal rupture, what percentage of the testes can be saved?
90%
If surgery is performed after 72 hours following a scrotal rupture, what percentage of the testes can be saved?
45%
These are the 5 sonographic findings of a scrotal rupture…
_____ alteration of the testicular parenchyma pattern
Interruption of the tunica _________
_______ testicular contour
Scrotal wall _________
______cele or ______cele
Focal
Albuginea
Irregular
Thickening
Hematocele or hydrocele
Sonographic findings of a scrotal rupture can also be seen on what 2 pathologies?
Abscess
Tumor
The presence of abscess, tumors, or any other clinical conditions combined with a history of _______, can result in rupture.
Trauma
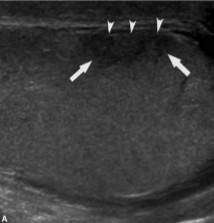
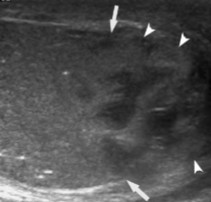
This scan was performed on a patient whose been feeling pain and swelling around the area. What can be assumed here?
Scrotal trauma
This scan was performed on a patient whose been feeling pain and swelling around the area. What can be assumed here?
Scrotal trauma
What pathology is associated with scrotal trauma?
Hematomas
How will a hematoma on a patient with scrotal trauma appear on US?
Heterogenous area
A hematoma can become more (1)_______ overtime and develop (2)_____ components.
Complex
Cystic
Hematomas seen on patients with scrotal trauma can involve the (1)______ and (2)__________ and will be contained in the (3)_______ wall.
Testes
Epididymis
Scrotal
Define avascular.
No internal blood flow
What kind of vascularity do hematomas have?
What US feature is helpful in identifying them?
Avascular
Color doppler
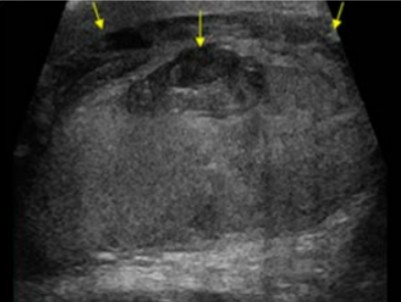
The pathology seen here was seen on a patient whose had trauma to the area. It has become more complex as it sits there. What can be assumed here?
Hematoma
What are the 2 most common conditions causing acute scrotal pain in adults?
Epididymitis
Epididymo-Orchitis
Epididymitis is a result of what 3 pathologies?
Infection
STI
Trauma
What 6 sonographic findings can be seen on a scan of epididymitis?
Enlarged epididymis
Hypoechoic
May contain hyperechoic areas
Heterogenous texture
Hyperemic blood flow
Possible scrotal wall thickening
If epididymitis is isolated to just the epididymis, how will the testes appear?
Normal
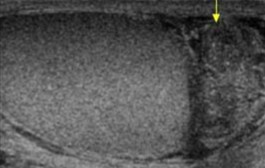
This scan was performed on a patient who has STIs. What can be assumed here?
Is this pathology isolated or spread?
Epididymitis
Isolated, testes appear normal
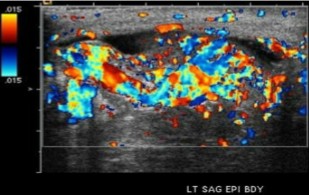
This scan was performed on a patient who currently has an infection at the testicles. What can be assumed here?
What sonographic finding can be seen here?
Epididymitis
Hyperemic blood flow
With orchitis, the affected testes will be __________.
Enlarged
Define focal.
Affects one part
Define diffuse.
Affects entire teste
Orchitis infection can be (1)________ or (2)________.
Focal
Diffuse
Infected areas of orchitis may appear as what echogenicity compared to the surrounding tissue?
Hypoechoic
A diffusely infected teste (orchitis) will appear (1)________ with a (2)________ echogenicity.
Enlarged
Hypoechoic
How does arterial resistance appear on a scan of orchitis?
Decreased
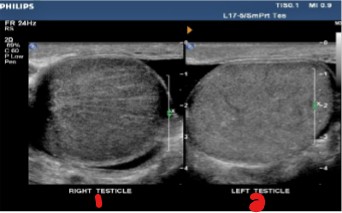
Which testicle has pathology?
What pathology can be assumed?
Right testicle
Orchitis
What is epididymo-orchitis?
When both epididymis and testicles are infected
What is the most common cause of epididymo-orchitis?
Lower UTI via the spermatic cord
What are 5 less common causes of epididymo-orchitis? (MTVTC)
Mumps
Tuberculosis
Various viruses
Trauma
Chemical causes
In cases of epididymo-orchitis, which part of the scrotum is most often involved with the infection?
Epididymis
In 20-40% of cases of epididymo-orchitis, where will it typically begin?
Where will it then spread to?
Epididymis
Testes
What are the 3 clinical findings of epididymo-orchitis? (PFD)
Pain
Fever
Urethral discharge
Epididymo-orchitis will appear…
______ epididymis and testicles
_______ flow
Scrotal wall _________
_______
Enlarged
Hyperemic
Thickening
Hydrocele
What US features are key tools in differentiating between epididymo-orchitis vs. torsion?
Color doppler
Spectral doppler
A color doppler of epididymo-orchitis will show what kind of blood flow?
A color doppler of torsion will show what kind of flow?
Hyperemic blood flow
No blood flow
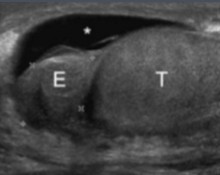
This scan was done on a patient whose recently come down with a fever. What can be assumed here?
Epididymo-orchitis
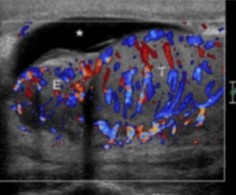
This scan was done on a patient whose had symptoms of urethral discharge. What can be assumed here?
Epididymo-orchitis
In severe cases of orchitis, what pathology can occur?
Testicular infarction
Color doppler of testicular infarction will show what kind of flow compared to contralateral testicles?
Decreased or absent flow
Decreased flow seen on testicular infarction, will show what kind of waveforms on spectral doppler?
High resistance with little to no diastolic flow
A spectral doppler waveform with reversed diastolic flow of testicular infarction will be what kind of indication?
Serious indication for threatened testicular infarction
Areas of testicular infarction will be…
________ to surrounding testicular parenchyma
_______ shaped
________
_________ lesion
Varies with ____ of infarction
Hypoechoic
Triangular
Avascular
Intratesticular
Age
When the entire testicle is infarcted, findings cannot be differentiated from what other pathology?
Testicular torsion
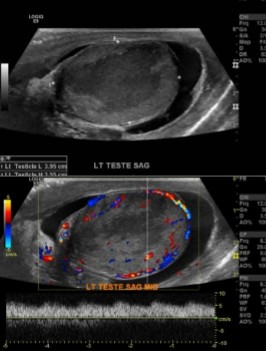
What pathology is seen here based on the images?
What area is presumably the area of pathology?
Testicular infarction
Hypoechoic area
What pathology is most commonly a complication of epididymo-orchitis?
Scrotal abscess
What are the 2 clinical findings of a scrotal abscess?
Pain
Swelling
Fourneir Gangrene is a rare life threatening (1)_______ infection of the (2)___________.
Bacterial
Scrotus/penis
Scrotal abscess is often associated with what pathology?
Fourneir gangrene
These 4 sonographic findings can be seen on a scrotal abscess…
________ fluid collection
_______ borders
________ around the periphery
____ may be present, which can cause echogenic shadowing with ring down artifact
Complex
Irregular
Hyperemia
Air
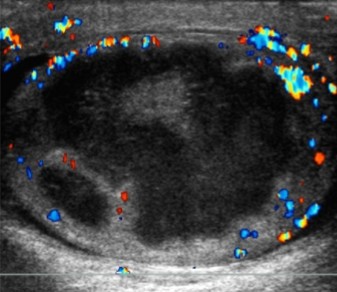
The pathology seen here can be a complication of epididymo-orchitis and can have symptoms of swelling. What can be assumed here?
Scrotal abscess
What is another term for torsion?
Intravaginal testicular torsion
Because torsion is considered a surgical emergency, what should be done as the sonographer?
Images should be obtained as quickly as possible
How does torsion occur?
When the testis and epididymis twist within the scrotum
How will torsion affect the blood supply of the spermatic cord?
Cuts off the vascular supply
Up to 60% of torsion cases will have anatomic _________ on both sides.
Anomalies
Undescended testicles are 10 times more likely to be affected by what pathology?
Torsion
What pathology is 10 times more likely to be affected by torsion?
Undescended testicles
What flow is affected first by torsion?
As torsion continues, what occurs from there?
Venous flow
Arterial flow is obstructed and testicular ischemia follows
What 2 US features can be used when documenting torsion?
Decrease PRF (scale)
Utilize power doppler for slow flow and rule out complete torsion
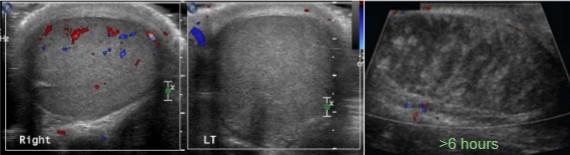
What is different about the right and left testicles?
What can be interpreted of the image on the far right?
What pathology can be assumed happening in these pictures?
The left testicle no longer has flow
That no flow to the testicle after six hours will cause the testicle to have that appearance
Torsion
The bell clapper deformity is a _________ abnormality.
Congenital
What is the most common cause of torsion?
Bell clapper deformity
The bell clapper deformity puts the patient more at risk for torsion because they lack the normal (1)______________ of the testis and (2)__________ to the scrotal wall.
Posterior fixation
Epididymis
The bell clapper deformity is (uni/bi)lateral in most cases.
Bilateral
What are the percentages of salvage rate with torsion for each of the following times:
Within the first 6 hours:
Within 6-12 hours:
Within 12-24 hours:
100%
70%
20%