topic 2 - bonding, structure and the properties of matter (flashcards)
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
types of chemical bonds
ionic
covalent
metallic
why does bonding occur?
atoms with incomplete outer electron shells are unstable. By forming bonds, atoms can completely fill their outer shell and become stable.
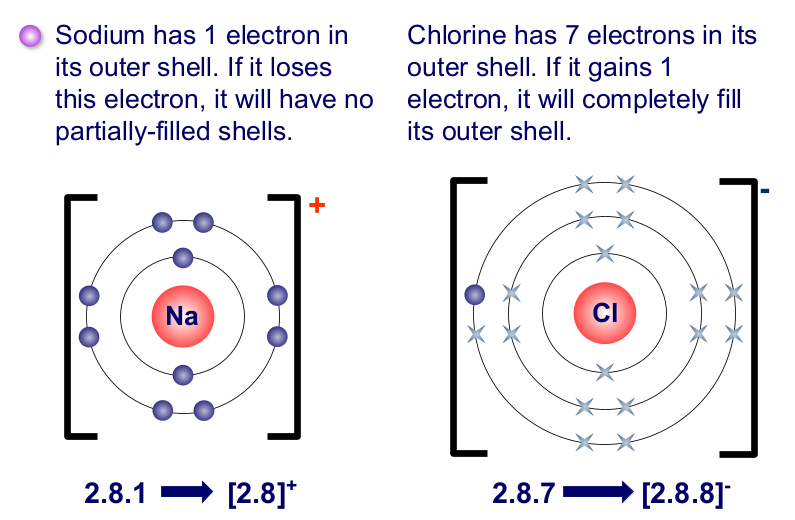
ionic bonding
metals combined with non-metals
metal atoms lose an electron to become positively charged ions → non-metal atoms gain an electron to become negatively charged ions
the oppositely charged ions are held together by strong electrostatic attractions
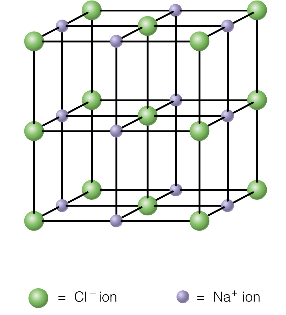
ionic compounds
millions of ions packed together in a cubic arrangement - forming a giant 3D structure called an ionic lattice
requires a lot of heat energy to break the bonds → solid at room temperature and high melting point
does not conduct electricity when solid - ions cannot move
when molten, lattic breaks and ions are free to move
ionic compounds are usually soluble in water
brittle - shatter when hit
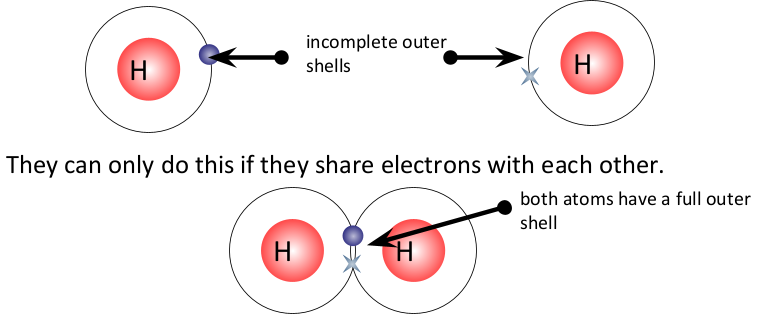
covalent bonding
occurs in non-metallic atoms, which share one or more pairs of electrons
when non-metal atoms react together, they need to gain an electron to fill their outer shell and become stable
atoms can share 2, 4 or 6 electrons
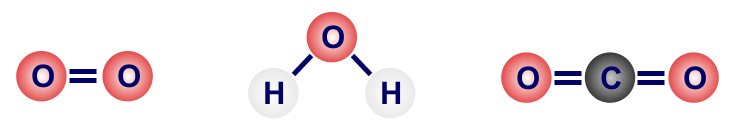
simple covalent structures
they only contain a few atoms
most molecular substances are gas or liquid at room temperature → they have weak intermolecular forces that only require a small amount of energy to break
properties of molecular substances
low melting point and low boiling point (weak intermolecular forces)
usually insoluble in water
cannot conduct electricity - no free electrons to carry an electrical charge
brittle
giant covalent structures
consists of millions of atoms joined together by covalent bonding e.g. diamond, silicon dioxide.
structure of a diamond
each atom is covalently bonded to four others
properties of diamond
very hard - each carbon atom is bonded to four others, forming a very rigid 3D structure
high melting point and boiling point - a lot of energy is needed to break many strong covalent bonds
cannot conduct electricity - no free electrons or mobile ions to carry a charge
sand (silicon dioxide)
impure form of silicon dioxide (quartz)
each silicon atom is bonded to four oxygen atoms
each oxygen atom is connected to two sillicon atoms
giant covalent structure with similar properties to diamond
structure of graphite
each carbon atom is bonded to three others
forms rings of six atoms, creating a giant structure, containing many layers - layers are held together by weak forces of attraction
properties of graphite
only three of the four electrons in the outer shell of the carbon atom are used in covalent bonds
graphite is soft and slippery - layers can easily slide over each other because the weak forces of attraction are easily broken → this is why graphite can be used as a lubricant
conducts electricity (only non-metal to do so)
high melting and boiling point
buckminsterfullerene
contains 60 carbon atoms, each bond with three others - forming two single bonds and one double bond
can be used for drug delivery into the body, in lubricants, to reinforcing materials and as catalysts
what are carbon nanotubes and their properties?
cylinder fullerenes
high tensile strength that reinforce composite materials
high electrical and thermal conductivity
graphene
form of carbon, consisting of planar sheets (one atom thick)
atoms arranged in honeycomb-shaped lattice
why are fullerenes good catalysts?
they have a large surface area compared to their volume
metallic bonding
atoms of metals are tightly packed together in a giant lattice
outer electrons separate from their atoms and become delocalised, creating a ‘sea of electrons’
atoms become positive ions and are attracted to these electrons
properties of metals
dense - metal ions are tightly packed
high melting and boiling point - metallic bonds are very strong
tough - when a metal is hit, the layers of the lattice just slide over each other
malleable - can be bent + pressed into shape
ductile - can be drawn out into wires
metals are good conductors of…
heat - they can transfer thermal energy throughout the lattice by free electrons
electricity - electrons are free to move and can carry electrical charge
nanoparticles properties
electrons can move through insulating layers of atoms
more sensitive to light, heat & magnetism
silver and able to kill bacteria
disadvantages of nanoparticles
difficult to engineer
can be dangerous