Cariology Final [Fluoride Metabolism and Toxicity: Levy]
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Number of time Levy flipped to the next slide on accident
4
Elemental Fluoride (F2) is a yellowish green gas which readily
reacts to form salts:
- CaF2 (fluorite)
- Na3AlF6 (cryolite)
- Al2F2SiO4
Fluoride is ubiquitous: present in all
foods in trace amounts
Fluoride is ubiquitous: high levels in
teas and seafood
seawater is about
1 ppm F
Routes of intake
Air- as HF gas: quickly absorbed in lungs
Water
- inorganic- ~80% in 90min
- Organic or complexed (slower)
Inert physiologically - KPF6
Food
- Tea is high
- Milk is low
-- solids have slower absorption
Fluoride systemic distribution (IMAGE)
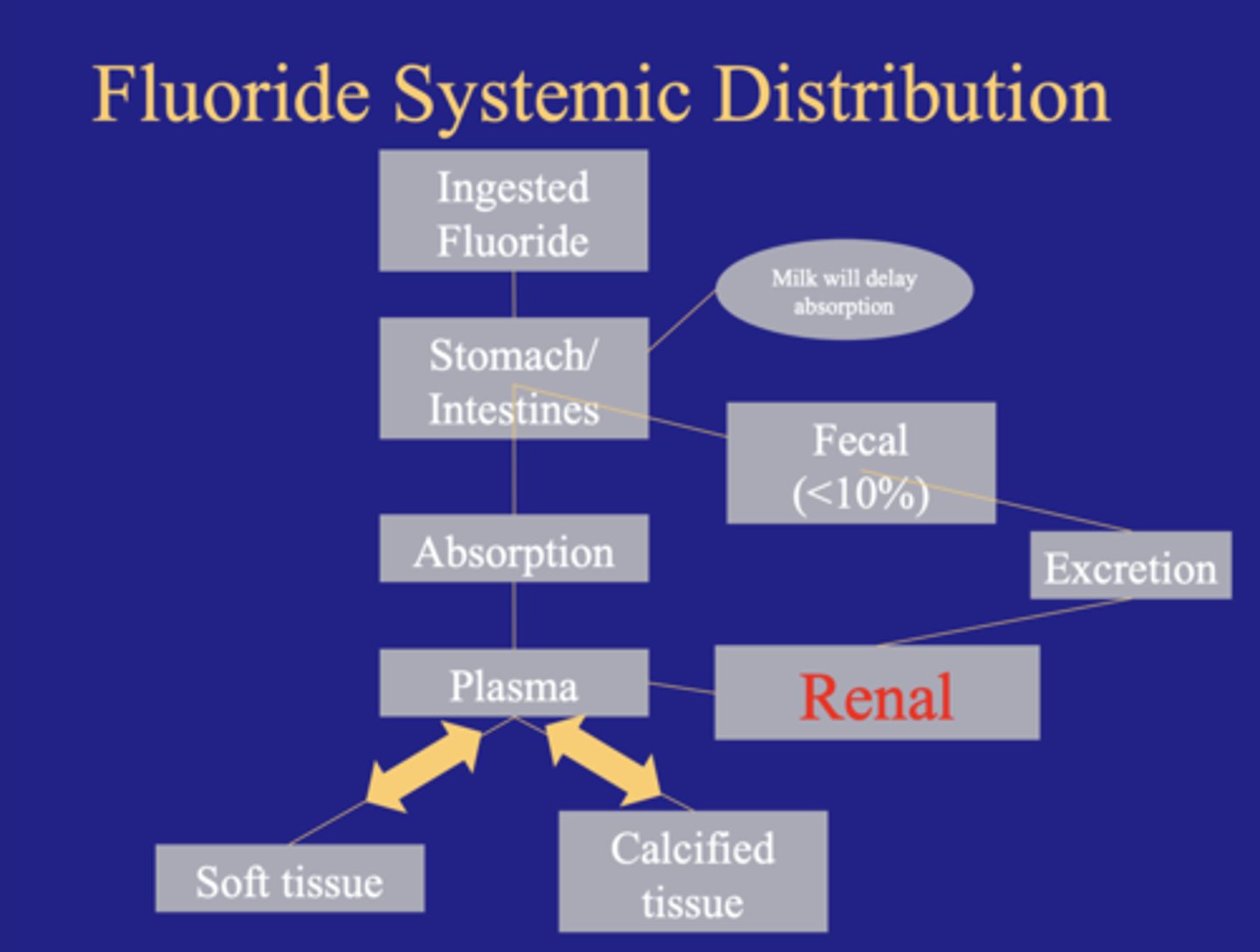
Absorption of Fluoride
Stomach and intestins
diffusion controlled
80% absorbed in 90 minutes
Need to treat overdose as fast acting poison
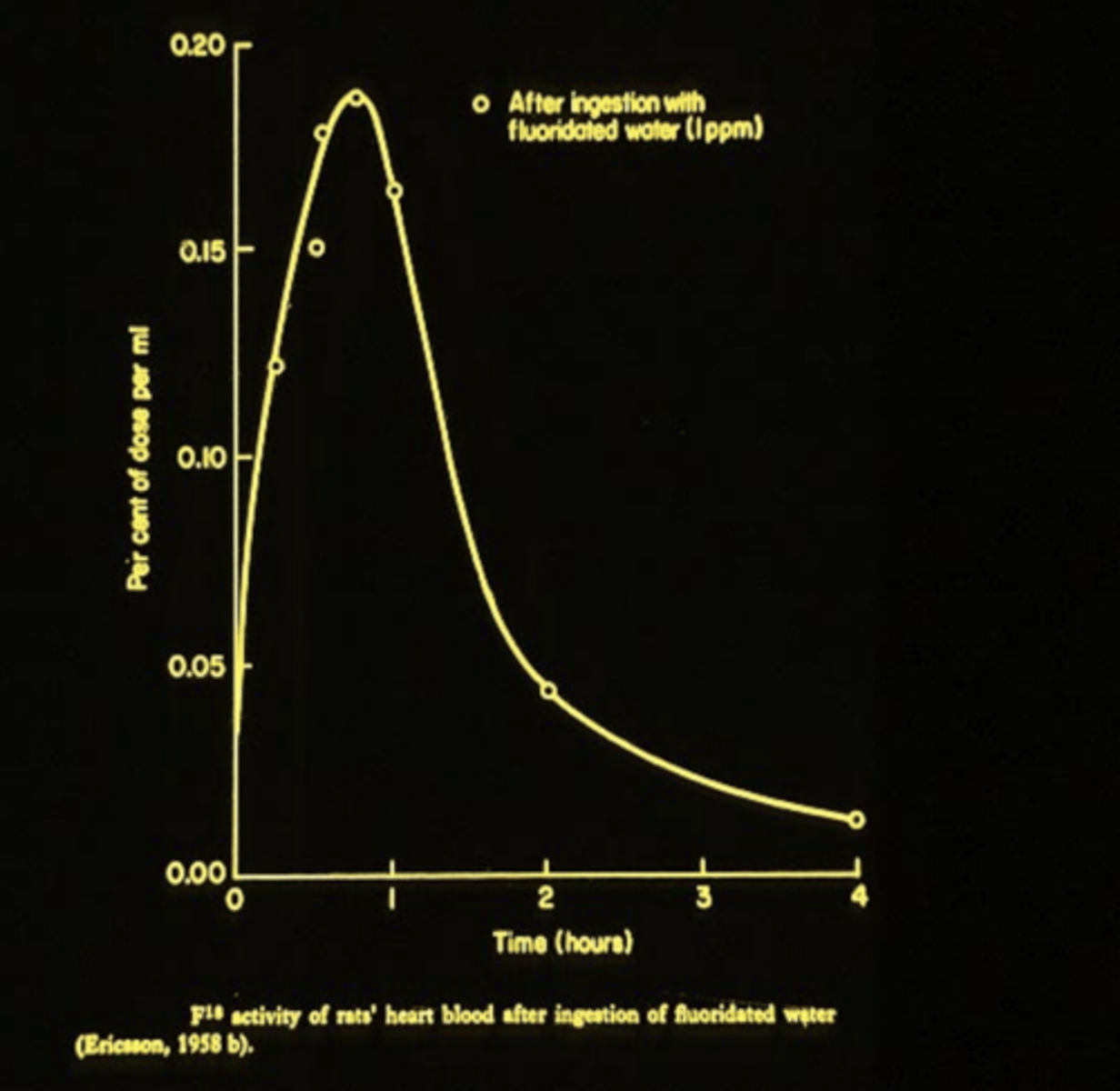
After ingestion with fluoridated water (GRAPH)
TA:
The first hour after ingestion it reaches its peak
Non-fasting fluoride absorption
- with cations only 80% absorption
- with bone meal, only 35-55% absorption
- With pablum (infant cereal) only 50% absorption
Mechanistically fluoride is complexed and therefore unavailable for absorption
Variable in Absorption
Fasting or non fasting
Liquid or solid
Rate dependent on acidity
Presence of food, milk, cations
Regulation of fluoride
Primary-skeletal tissues
Secondary-urinary excretion
F is physiologically different than other halogens
Deposited in bone
No accumulation by the thyroid
Rapid clearance by kidney
Deposition or retention of F
F is a bone-seeker - 95% found in skeleton
Steady-state occurs with constant intake
Dependent on maturation and previous exposure
Range of Plasma Fluoride
Typically follow water fluoride. as you increase water fluoride we see an increase in plasma fluoride
In adults, the water fluoride level and urinary excretion will equilibrate within ______ after introduction of fluoridated water
one week
Excretion of F
Rapid renal clearance of F
Urine 50% of intake at equilibrium
Urinary F is indicator of intake
Feces 5%
Perspiration 0-2%
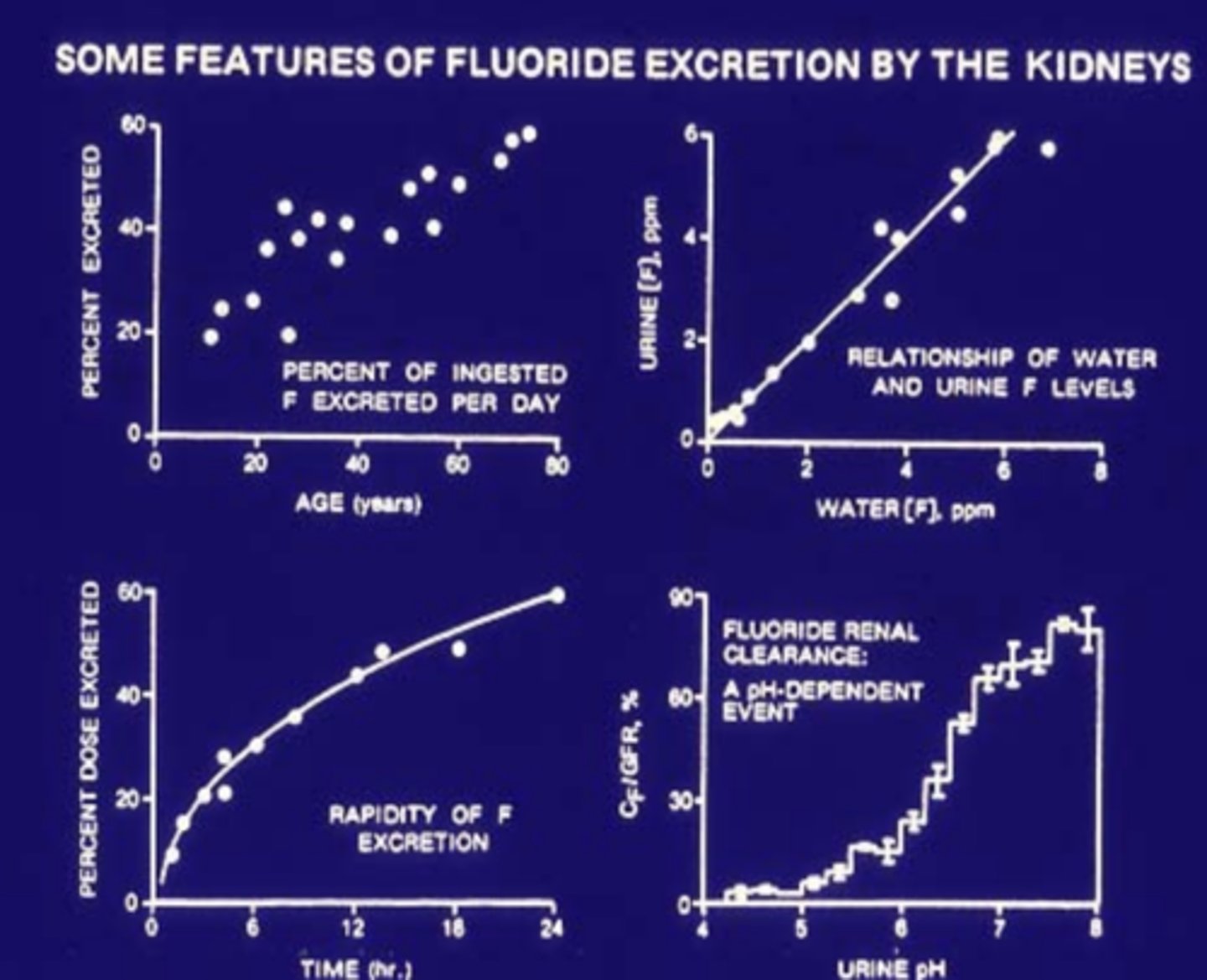
Some features of F excretion by the kidneys (GRAPHS)
TA:
as you increase water F you get more F in the urine
at low pH we get little excretion of F at higher pH we get higher excretion of F
The total amount of fluoride in the body of an adult is about ______ with 95% of this in the ___
2.6, Skeleton
TA:
- This is a very little amount
An overdose of Fluoride can cause:
Acute poisoning- Extremely rare
Crippling skeletal fluorosis - Very rare in US
Mottled enamel (severe dental fluorosis)- relatively uncommon in US
Fatal dose of Fluoridated Water would be about ___ gallons consumed at one time
625
Signs of Fluoride overdoes
Nausea
Vomiting
Diarrhea
Cramping
Larger doses of Fluoride result in
Collapse
Coma
Death ~2-4 hrs
In high concentrations fluoride is a powerful metabolic inhibitor that blocks ______ and other divalent cation dependent enzymes
magnesium
In case of accidental overdose, symptoms can be treated with
milk of magnesia or other aluminum hydroxide preparations
Equivalent Amounts of F

Topical fluoride rule of thumb

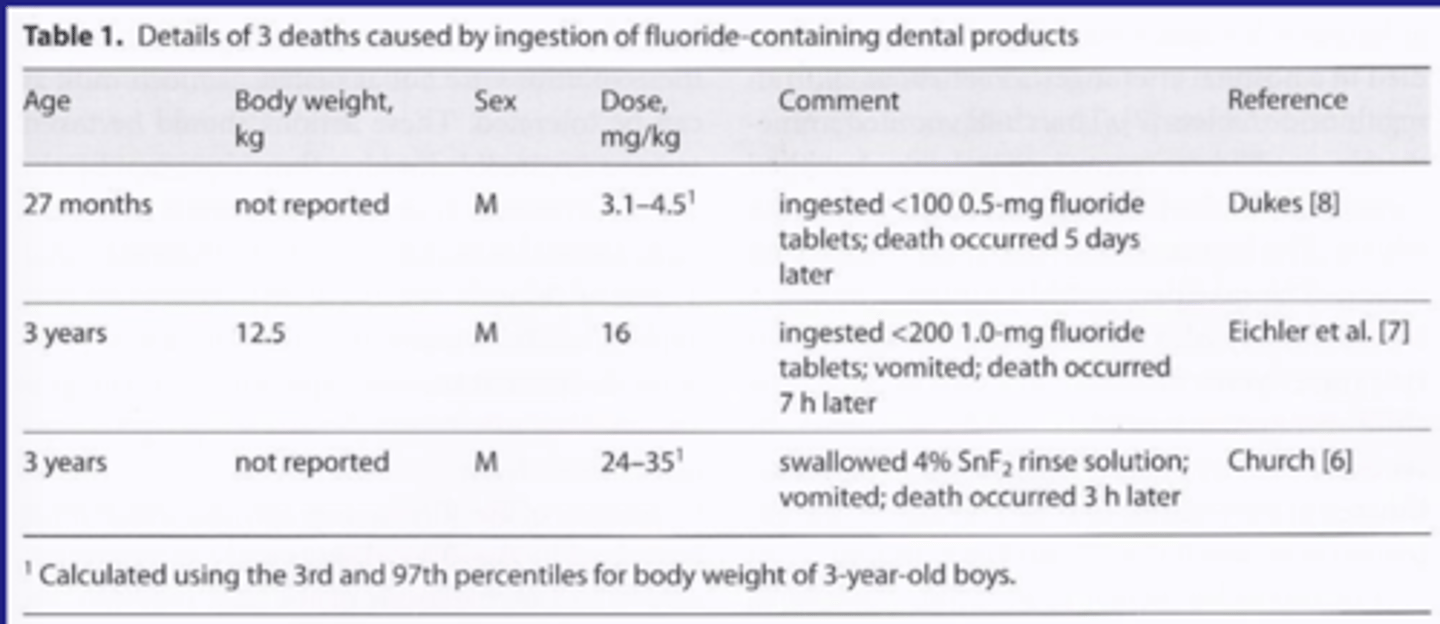
Dental death due to Fluoride
Case report: 3-yr-old male for first dental visit
Clinical findings: caries free
Preventive procedures:
- mixed pumice with F (not water) as carrier for pumice
- Washed out pumice with 4% SnF2- not water
- Demonstrated rinsing with water
- Gave 1/2 lily cup of 4% SnF2 to child
Takeaway:
Multiple application of F that were not intended
Acute overdose
3 yrs:
- 14.4 Kg
- 500mg
6yrs:
- 21.1 Kg
- 750mg
9yrs:
- 29.5 kg
-1000 mg
Based on 35mg F/kg body wt as a lethal dose
F varnish applied is ~
2.3-5.0 mg
Peak plasma F in 2hrs: 3.2-6.3
comparable to brushing with F toothpastes
Contact allergy - rare but possible
Safe Water Drinking Act (1974)
Requires EPA "to determine the level of contaminants in drinking water at which no adverse health effects are likely to occur."
- Maximum contaminant level (MCL) at 4.0mg/L or 4.0ppm
- Water systems to remove contaminant
Balancing of the beneficial effects of protection from tooth decay and the undesirable effects of excessive exposures leading to discoloration"
- Secondary standard (SMCL) at 2.0 mg/L or 2.0 ppm
Takeaway
Maximum contaminant level is currently at 4.0mg/L or 4.0ppm
At 2.0 mg/L or 2.0 ppm have to let the consumer know every year
EPA and Drinking water main takeaway
they due reviews every so often and the never plan to do any changes
Recently (9/24/24)
- federal lawsuit against EPA ruled against EPA and said pretty much gotta look at fluoride a little more closely
Chronic effects of fluoride
Skeletal effects and bone fractures
Reproductive and development effects
Effects on the gastrointestinal system
Effects on the renal system
Carcinogenicity and genotoxic effects
Effects on IQ and related outcomes-current major emphasis
Effects of fluoride on teeth-fluorosis
Acute effects of fluoride: Gastrointestinal
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, excessive salivation, abdominal pain, and cramps
Acute effects of fluoride: Neurological
paresthesia, paresis, tetany, central nervous system depression, and coma
Acute effects of fluoride: Cardiovascular
weak pulse, hypotension, pallor, chock, cardiac irregularities and ultimate failure
Acute effects of fluoride: Blood chemistry
Acidosis, hypoglycemia, and hypomagnesemia
Toxic doses of fluoride: Probably toxic dose (PTD)
EXAM
5 mg F/kg body weight = 2.27 mg F/lb
The minimum dose that could cause toxic signs and symptoms including death and that should trigger immediate therapeutic intervention and hospitalization
Toxic doses of fluoride: Probable Lethal does (PLD)
EXAM
Death is likely. For example, in a child who ingests more than 15 mg F/kg body weight
Toxic doses of fluoride: Certainly lethal dose (CLD)
EXAM
32 to 64 mg F/kg body weight
Probably toxic dose
for a 2 year old child (average body weight 25 lbs or 10kgs
- 57 gms or 2 ounces of 1000 ppm fluoride toothpast
- 57 1.0 mg fluoride tablet
- 4.6 ml of a 1.23% APF gel
Fluoride toxicity: Acute
Levels of exposure vs the substance itself
many cases in the first half of the 20th century; rare today
Acute toxicity - is this a problem
Takeaway:
Thousands of calls to poison control
Dentifrices is the most common
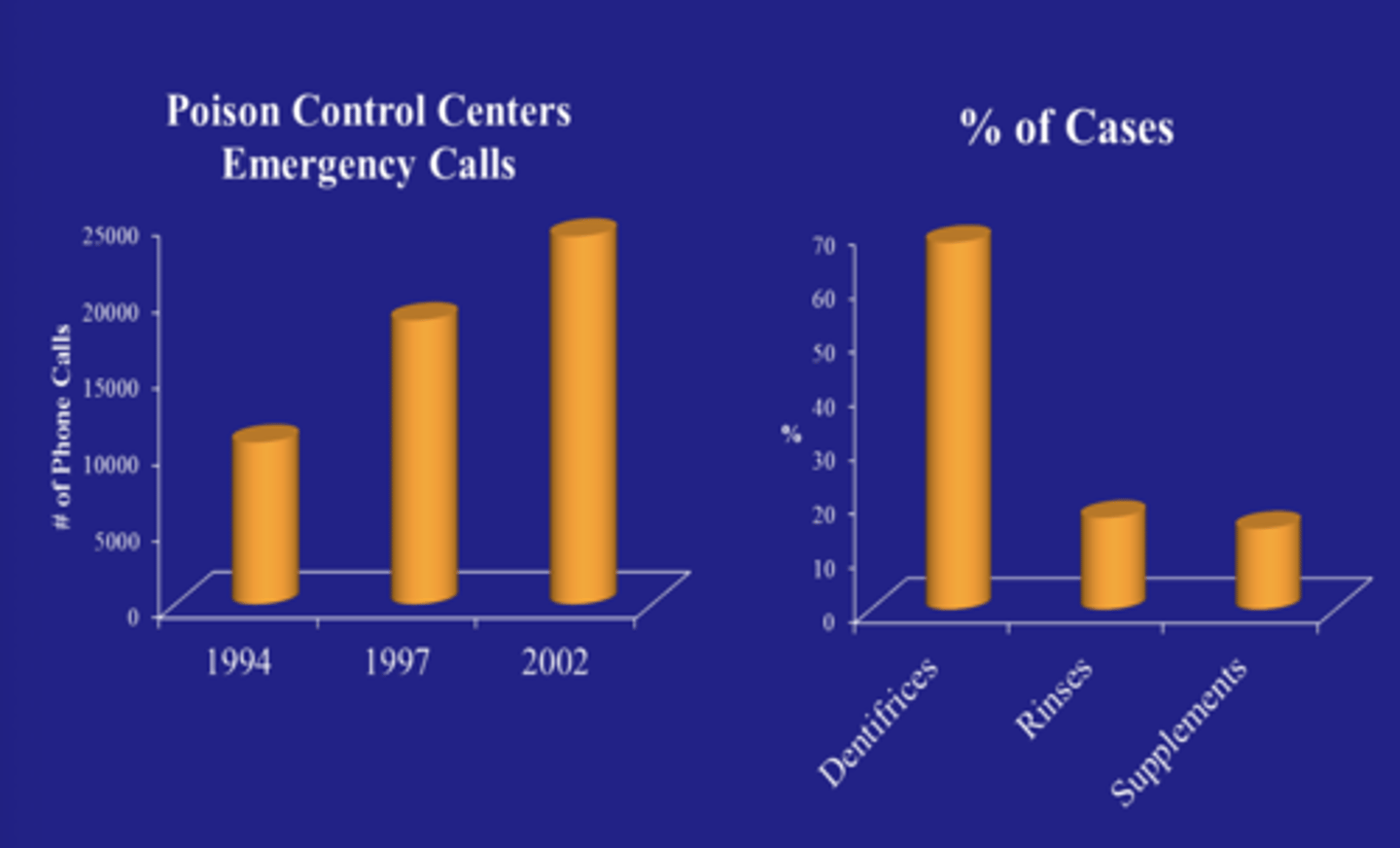
Fluoride related reports to US poison control centers
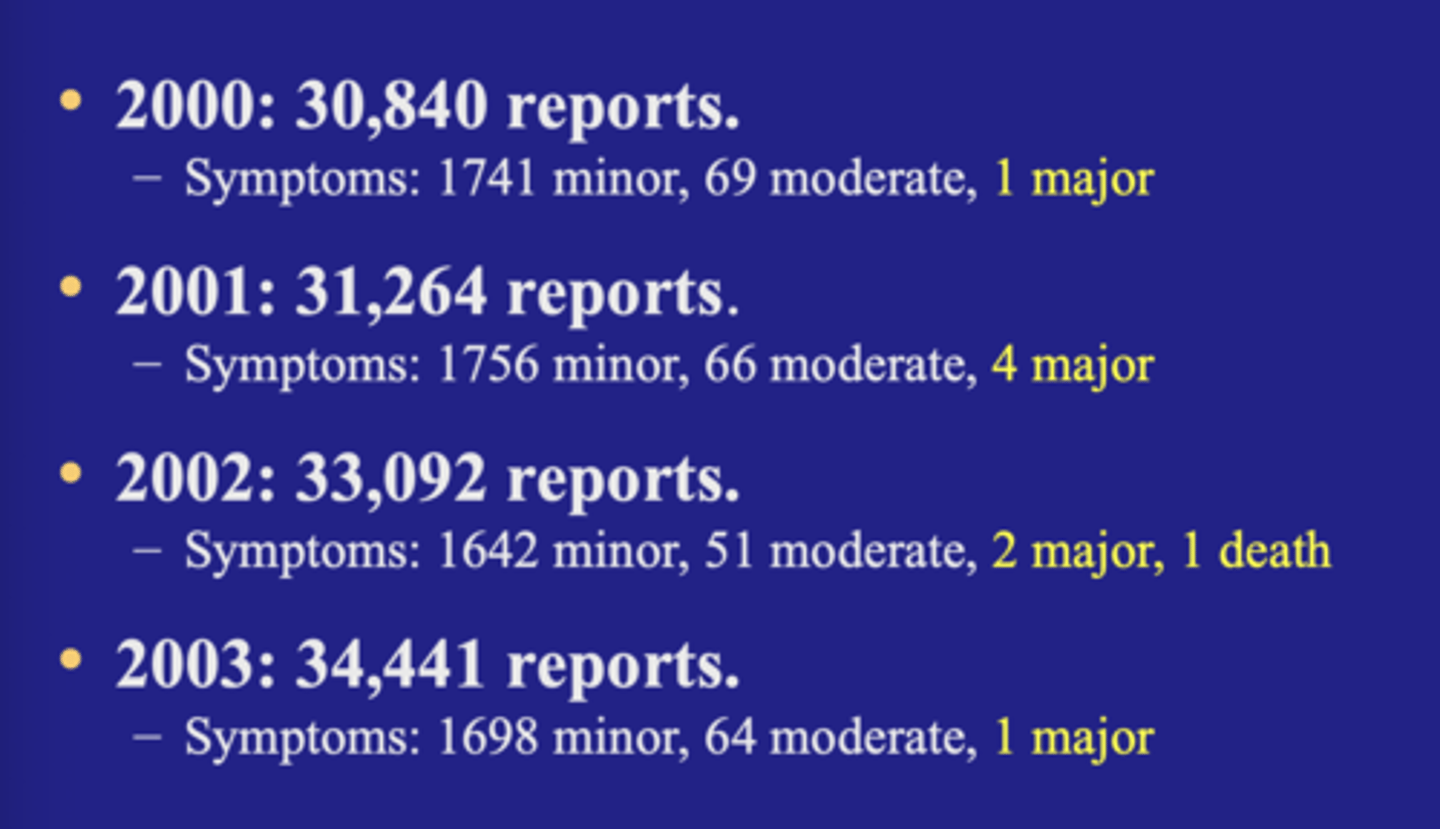
Reported fatalities
TA:
death can occur rarely and can be multiple days later
Common signs and symptoms of acute fluoride toxicity: MILD TO MODERATE
Nausea
Bloody vomiting
Diarrhea
Drop in blood calcium,
local or general signs of muscle tetany
abdominal cramping and pain
Increasing hypocalcemia and hyperkalemia
Common signs and symptoms of acute fluoride toxicity: MODERATE to severe
The three C's
- coma
- convulsion
- cardiac arrhythmias
Recommended treatment: 5.0 mg/kg
Calcium orally (milk) to relieve GI symptoms. Observe for a few hours
induce vomiting is not necessary
Recommended treatment: 5-15 mg/kg
induce vomiting
calcium orally (milk)
Hospitalize and observe
Recommended treatment: 15 mg/kg
hospitalize immediately
induce vomiting
cardiac monitoring
calcium IV (Ca gluconate)
Supportive care
Calculations

Treatment of acute toxicity
Attempt to:
- minimize absorption from GI
- Increase urinary excretion
- maintain vital signs
Induce vomiting
- unless unconscious
calcium- can bind F due to strong affinity
- 1% calcium chloride or calcium gluconate
- or milk
Chronic: Skeletal effects and bone fracture
Skeletal fluorosis

Bone fractures:
Clinical trails with 50-80 mg NaF per day in those with osteoporosis
- 15 times higher than the intake from drinking water containing one ppm F
Epidemiological studies of bone fracture rates in fluoridated and non-fluoridated areas
conclusion:
Marginally protective in preventing vertebral fractures when the patient is adequately supplemented by calcium and Vit D along with NaF
Elevated risk of new non-vertebral fractures
Increased risk of bone fracture in populations exposed to water fluoride at 4 mg/L or greater
Reproduction and development effects
animal studies
- fluoride concentrations of 100-500 mg/L
Takeaway:
- no evidence in the literature suggesting a link
Developmental effects
fluoride concentration in fetal cord is 60% of the maternal serum concentration
- fluoride crosses the placenta
conditions studied are:
- spina bifida
- sudden infant death
- down's syndrome
takeaway:
NRC 2006 - overall developmental effects of fluoride are minimal
Child development:
Sub-study of the newburgh kingston study
complete physical examination physical measurements and laboratory and radiographic studies
takeaway:
NO difference in general health bone density hearing bunch of shit that wasn't any different
Effects on the gastrointestinal system
Animal studies:
- fluoride concentrations of 190 mg/L and higher
industrial workers with exposure to high concentration of fluoride dust
These doses are far higher than those to which typical human populations are exposed and therefore been considered of not much consequence
Effects on the renal system
Animal studies
- fluoride concentrations of 100-380 mg/L
Epidemiological studies
animal studies: Necrosis of proximal renal tubules interstitial nephritis and dilation of renal tubules
PHS: no human kidney diseases from long term non occupational exposure to fluoride concentrations in drinking water up to 8 mg/L
NRC: No human studies on drinking water containing fluoride at 4 mg/L in which gastrointestinal and renal effects were carefully documented
Carcinogenicity and genotoxic effects
Animal studies
- fluoride concentrations of 25 100 and 175 mg/L
Epidemiological studies
- NCI
PHS: the relative mortality rates from cancer including cancer of the bones and joints were similar after 20-35 years of fluoridation as they were in the years preceding fluoridation
NRC
- the evidence on the potential of fluoride to initiate or promote cancers is tentative and mixed
Several more recent high quality studies have found no association between F and osteosarcoma
Early studies of F and IQ
1) Several dozen early, low quality studies mostly from china and other places with environments very different from U.S including high F, mercury, lead, etc
2) More recent cohort studies from Mexico and Canada got more publicity since closer to US and in better journals, despite having major methodological limitations
Takeaways:
if IQ was really compromised with F (like with lead and mercury) it would be a very major concern
Early studies had a lot of other contaminants
More recent studies in places closer to the US have gotten publicity but still have major methodological limitations. Meaning their conclusions need to be taken with caution.
National Toxicology Program (NTP) Review of fluoride
NTP from 2015-2024 reviewed animal and human evidence about F and neurodevelopment
- Part of the federal government-
Early draft shared with National academics of science, engineering and medicine (NASEM)
Final report
changed from original to a state of the science concerning fluoride
Takeaway:
The initial draft called fluoride a neurotoxicant (messing up the brain development)
Final report
- changed from original
- Removed the wording of neurotoxicant
- Did not properly consider the study biases nor separately consider high vs low F levels
Lot of deficiencies
Federal Court case against CWF
- Plaintiffs sues EPA : Wanted the court to rule there could not be water fluoridation allowed by the EPA due to reductions in IQ and other health concerns
- Judge kept delaying it. Waiting for the NTP report
- Judge decided that the EPA needed to respond the possible safety concerns even though the science was far from settled
EPA appealed the court decision on 1/17/25
takeaway:
Even though there was not proof of risk judge decided there's enough questions and concerns about water fluoridation.
EPA is reviewing the science now
JAMA Peds Meta-analysis and editorials (published online on 1/6/25)
Fluoride exposure and children's IQ scores: a systamatic review and meta-analysis - original investigation: Kyla W. Taylor et al
Takeaway:
reported inverse associations and a dose response association between fluoride measurements in urine and drinking water and children IQ
Limited data and uncertainty in the dose-response association between fluoride exposure and children's IQ when Fluoride exposure was estimated by drinking water alone at concentrations less than 1.5 mg/L
Had some bias
70% of the studies were rated high risk of bias
Had tons of data and looks impressive but since it was all observational studies it is suggested that it should be used to generate hypotheses only about future research not for strong statements that affect policy
JAMA Peds Meta-analysis and editorials (published online on 1/6/25)
Caution needed in interpreting the evidence base on Fluoride and IQ : Steven M Levy
wrote an editorial reviewing an article. was told the manuscript was conditionally accepted and that they already had an editorial to endorse it and wanted Levy to let them know his thoughts.
Told them he couldn't endorse it because it had some major problems
Takeaway:
Contacted them and said that he would not write a favorable report and that the authors needed to look at some of their major problems
Later was told they disregarded another colleagues comments as well.
within 24 hours it was still accepted
They were more interested in publicity rather than the best science
main conclusion:
- There was very few valid data from which to include that community water fluoridation benefits should be taken away
JAMA Peds Meta-analysis and editorials (published online on 1/6/25)
Time to reassess systemic fluoride exposure, again- editorial: Bruce P. Lanphear et al
These authors did a good job. Told a good story emphasized several things that were true but also misleading:
Said we didn't need water fluoridation because fluoride is mostly topical (well water fluoridation is topical as well)
They are essentially saying in this that we should stop water fluoridation until we know it is entirely safe (want to stop and reevaluate) the problem is that if we stop we might not ever get it going again and the current science is saying we are chilling and don't need to stop so why risk that.
Two recent articles of importance:
- A well done cohort study - from Spain:
Found better IQ in boys with more F
Another excellent cohort study- from Australia
- Slightly higher IQ levels for both those with lifelong CWF and partial CWF than those with none
Takeaway
The study provided consistent evidence that early childhood exposure to fluoride does not have effects on cognitive neurodevelopment
Kumar et all Meta-analysis (2023)
They properly separated F levels relevant to CWF from much higher ones to analyze separately
Found no association of lower IQ with F in areas with levels close to CWF levels
Possible elevated risk only in high F situations
Takeaway
Did a good job separating cofounding factors from flouride and showed that F at the proper concentration didn't cause lower IQ
Kumar Continued: GRAPH
Consistant evidence when we are talking about non-fluoridated and fluoridated that there is no concerned
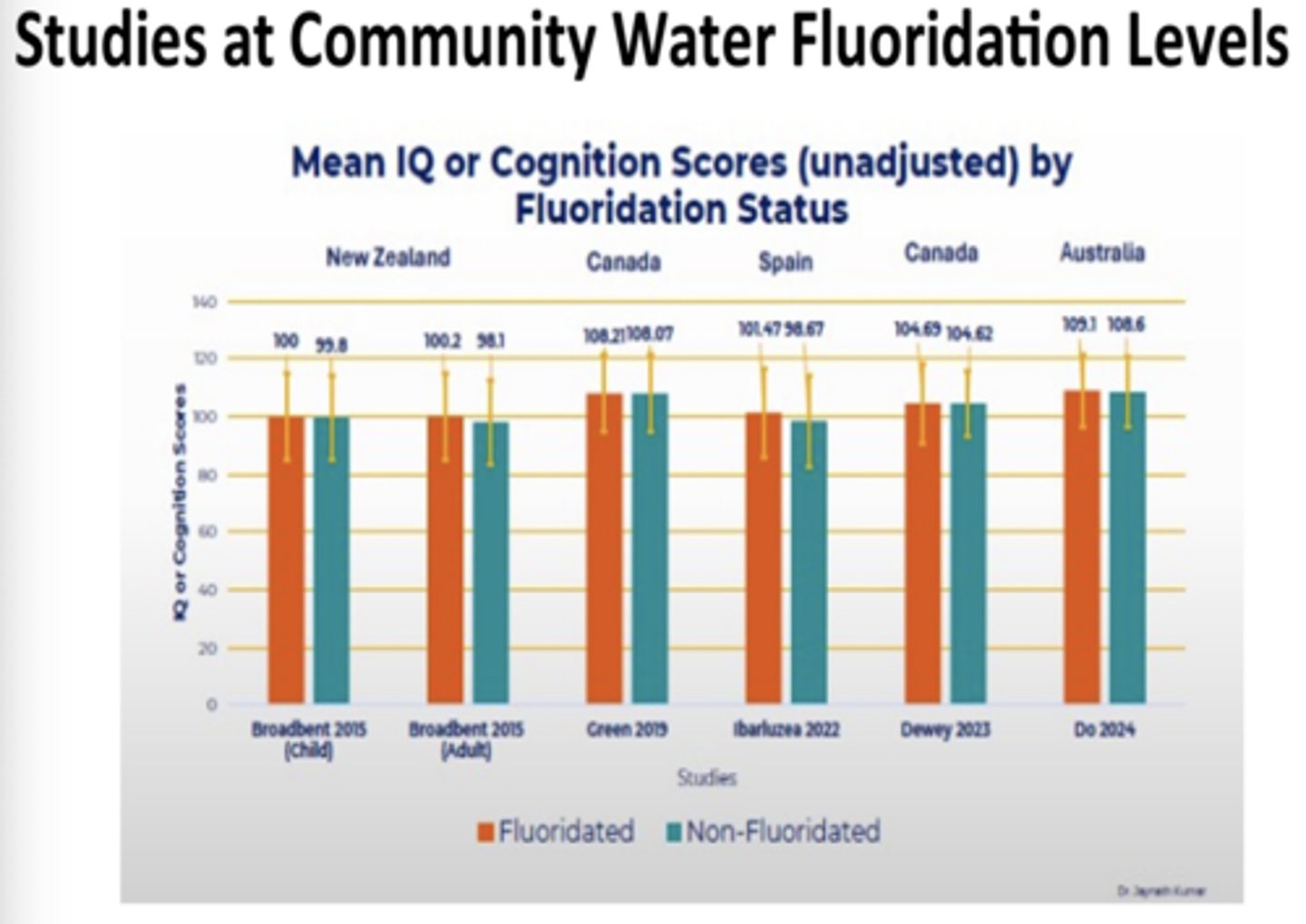
Some efforts/ results in progress
Levy, Kumar, Warren (UNPUBLSIHED, 2025)
Only the high fluoridation has the reduction. Leading to high urinary fluoride.
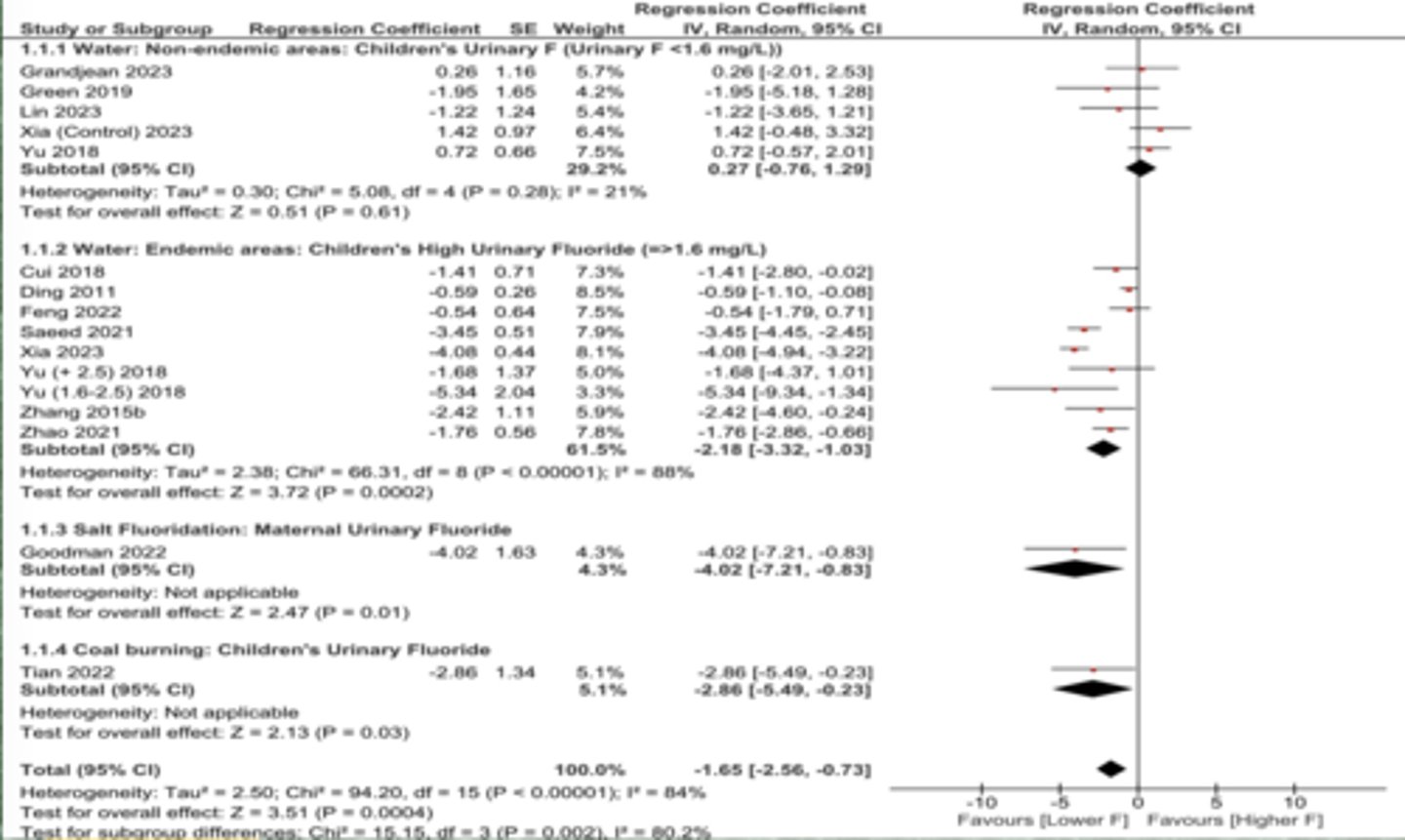
Kumar, Levy, and Warren unpublished
Subgroup analysis shows that there is no association between urinary fluoride and IQ in non-endemic areas
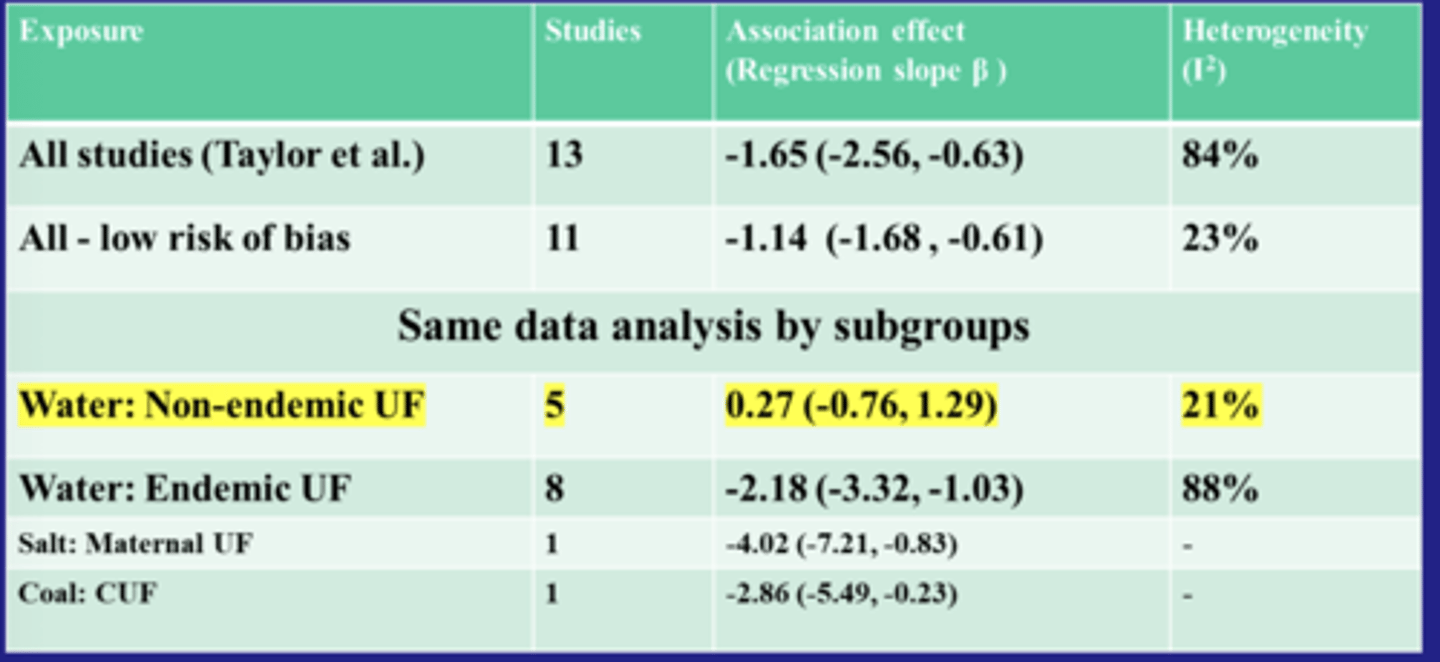
Summary of everything:
No clear negative health effects from doses used in community water fluoridation
Only effects:
- Caries reduction
- Mild dental fluorosis risk