APHG UNIT 1
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Thinking Geographically
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Geography
Study of where things are and why they are there
Spatial Perspective
How things are arranged in space
Spatial Patterns
Arrangement of objects on Earth
Absolute Location
Exact location (ex: latitude and longitude, address)
Relative Location
Location in relation to other places (ex: 3 miles north of…)
Site
Physical characteristics of a place (ex: climate, landforms)
Situation
Location relative to surroundings (ex: trade routes, other cities)
Distance Decay
Interaction decreases with increasing distance
Time-Space Compression
Technology reduces time it takes to travel/communicate
Friction of Distance
Distance makes interaction harder (ex: cost/time)
Distribution Types:
Density (frequency of a feature; ex: pop. per sq. mile), Concentration (clustered vs dispersed), Pattern (geometric arrangement; ex: linear, grid, etc.)
Reference Maps
Shows locations (ex: road Maps, political maps)
Thematic Maps (with examples)
Show spatial distribution of data (ex: choropleth, dot density, graduated symbol, isoline, cartogram)
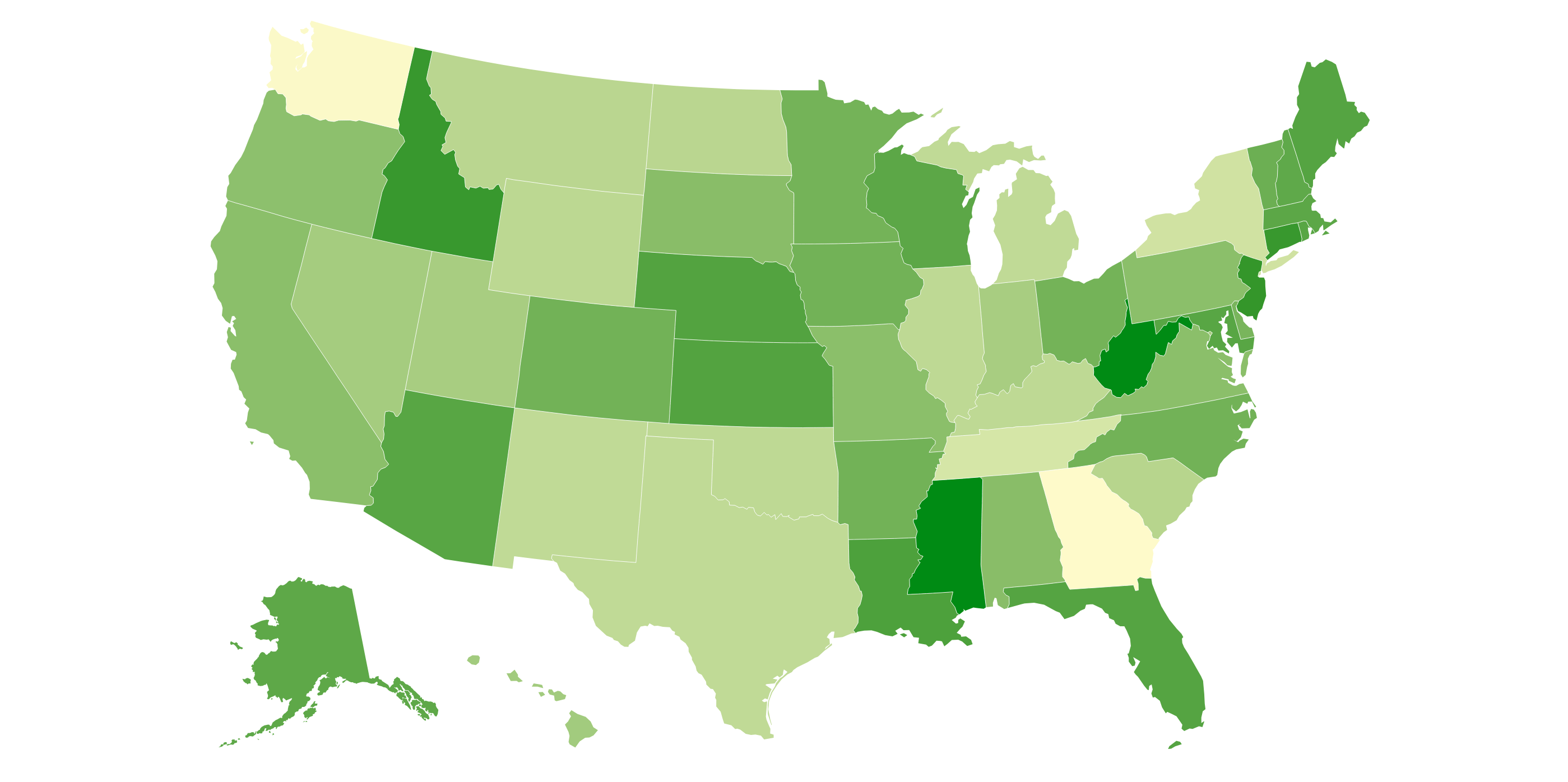
Choropleth Map
Color/shading to show values
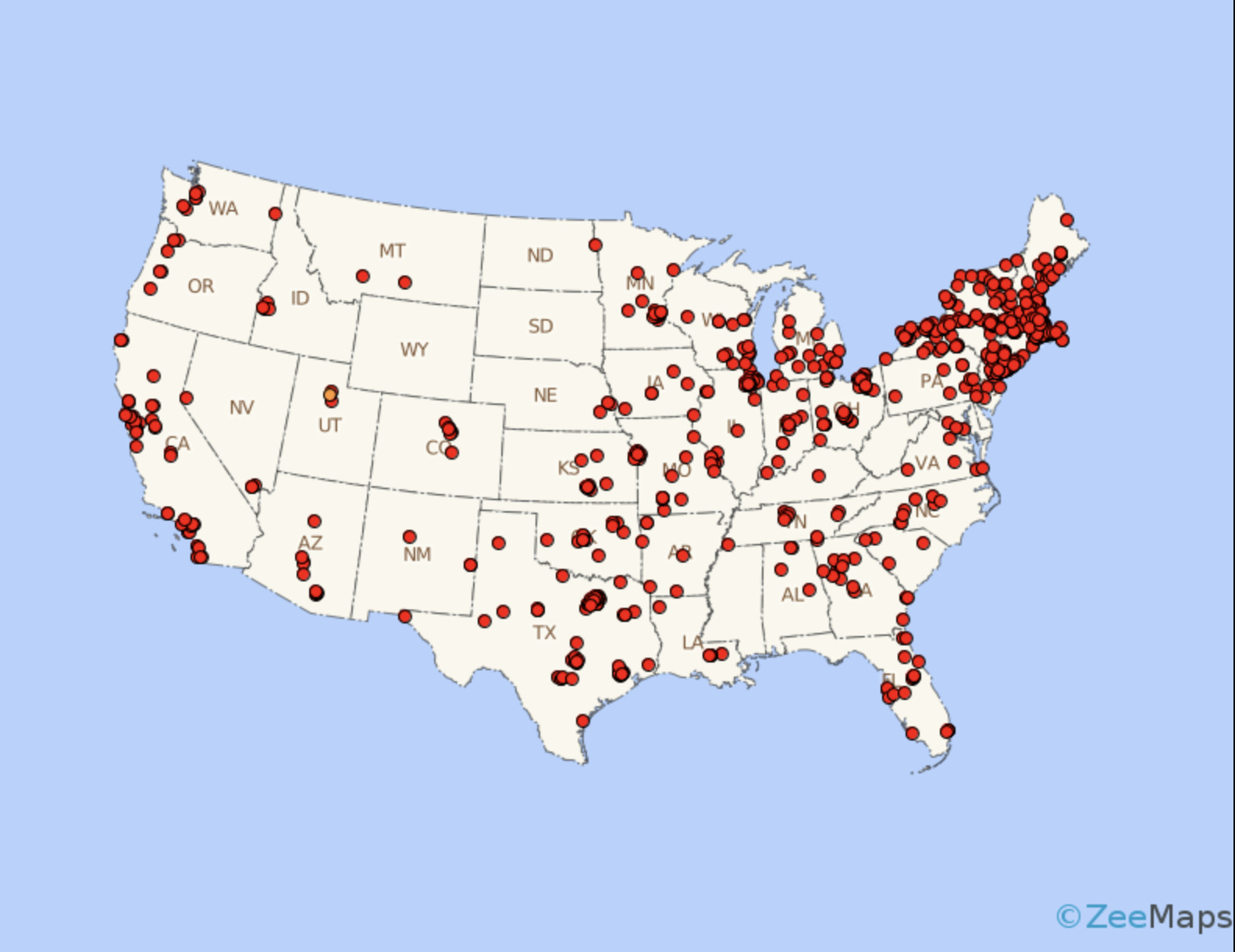
Dot Density Map
Dots show freqency
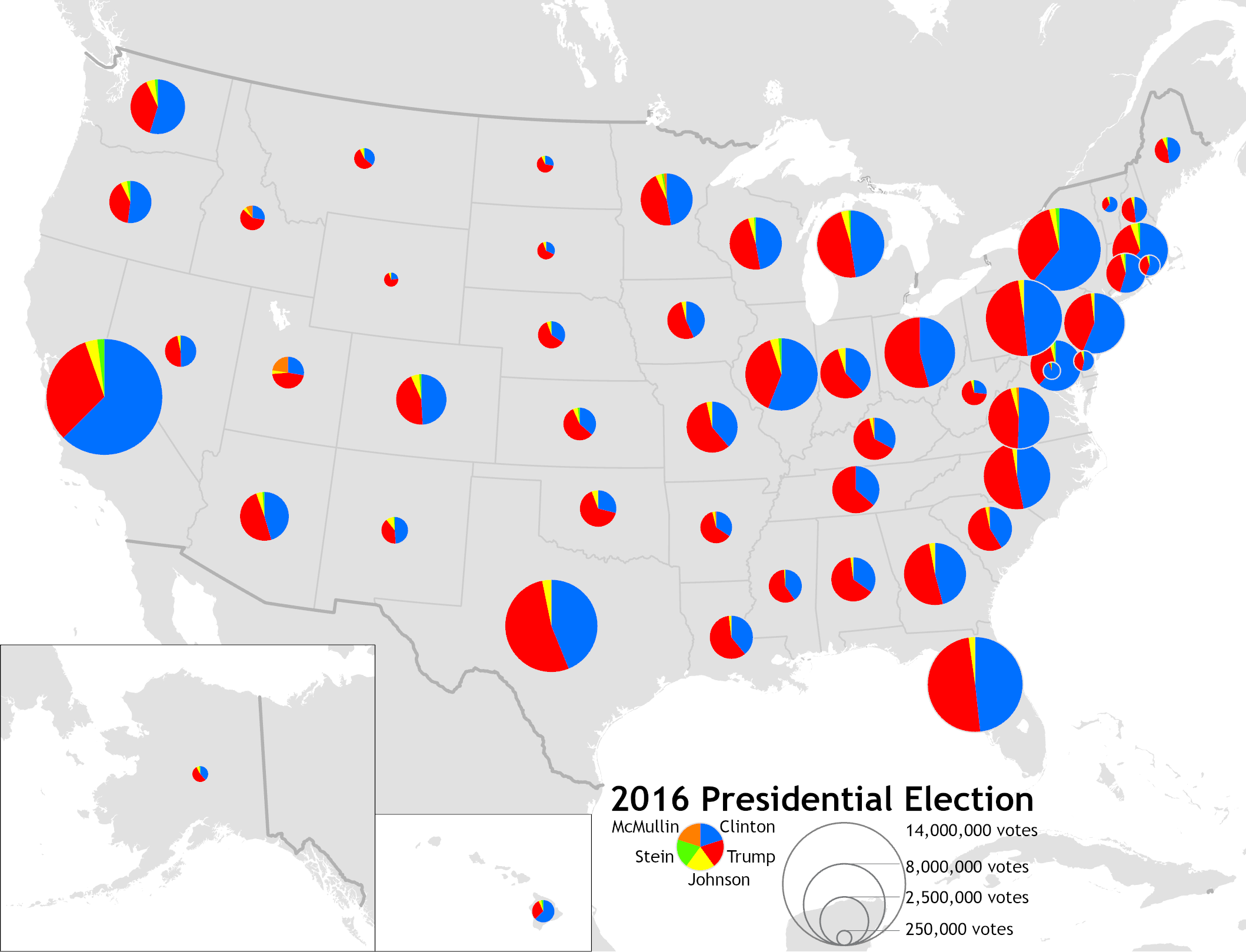
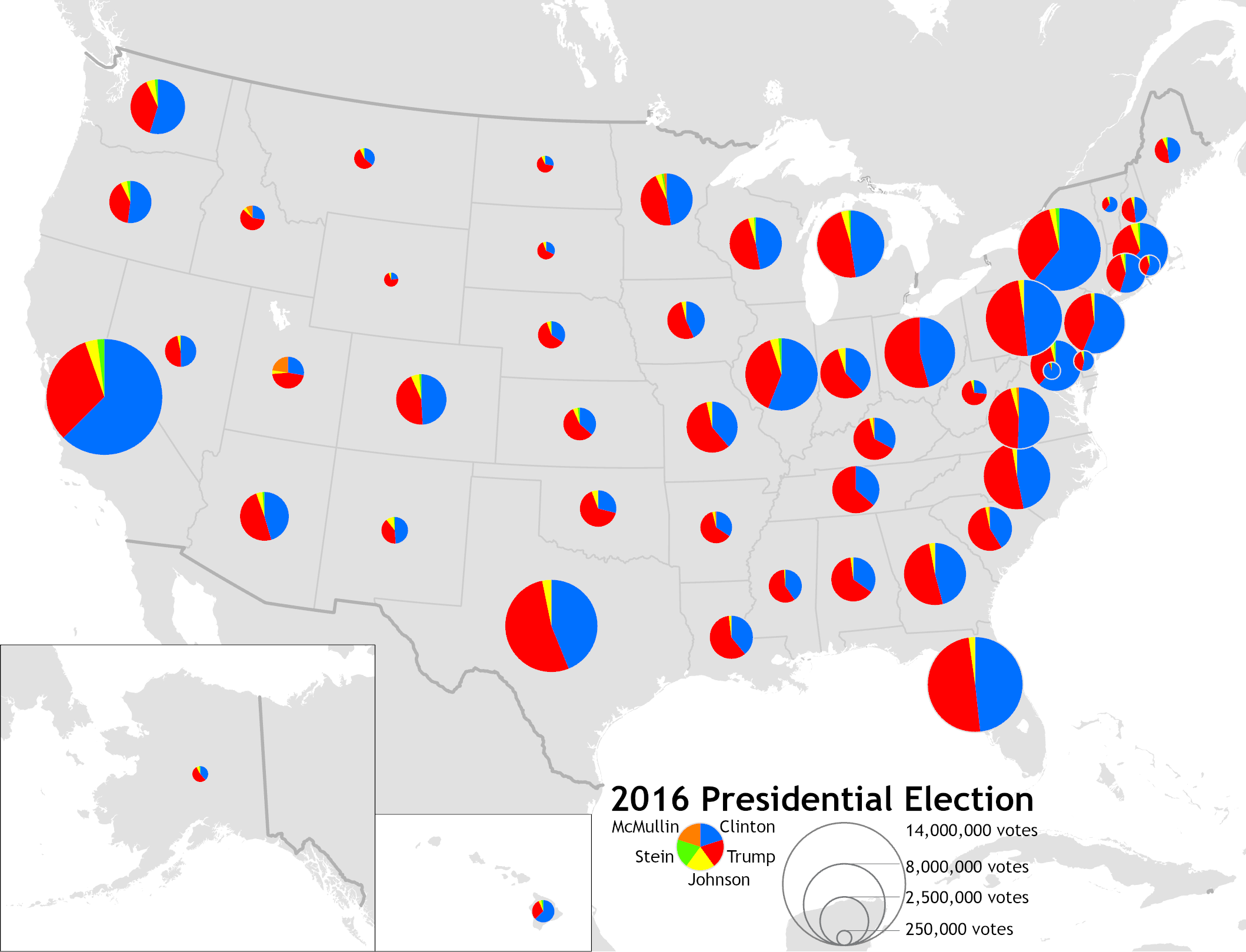
Graduated Symbol Map
Symbols sized by value
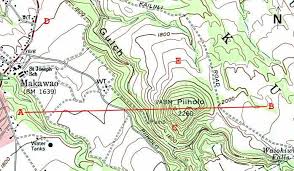
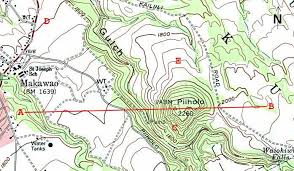
Isoline Map
Lines connect equal values (ex: topography, weather)
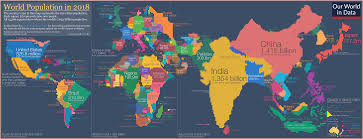
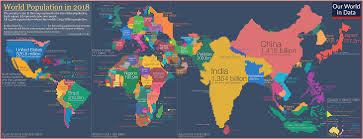
Cartogram Map
Size of area scaled by data (ex: pop. cartogram)
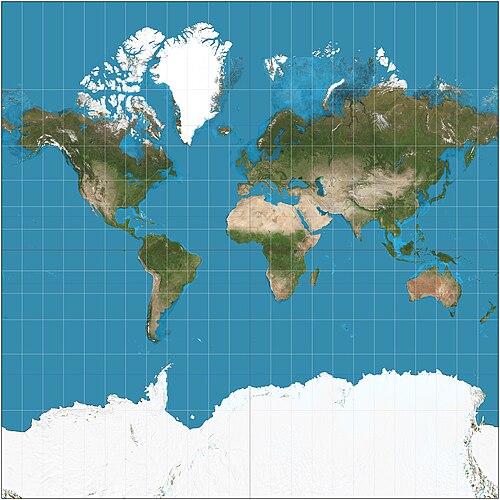
Mercator Projection
Presserves direction, distorts size (makes Greenland HUGE)
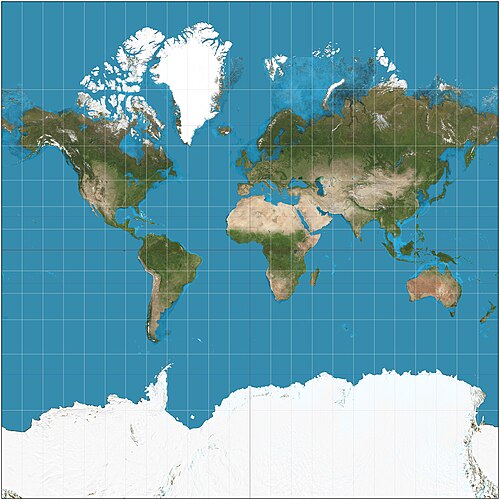
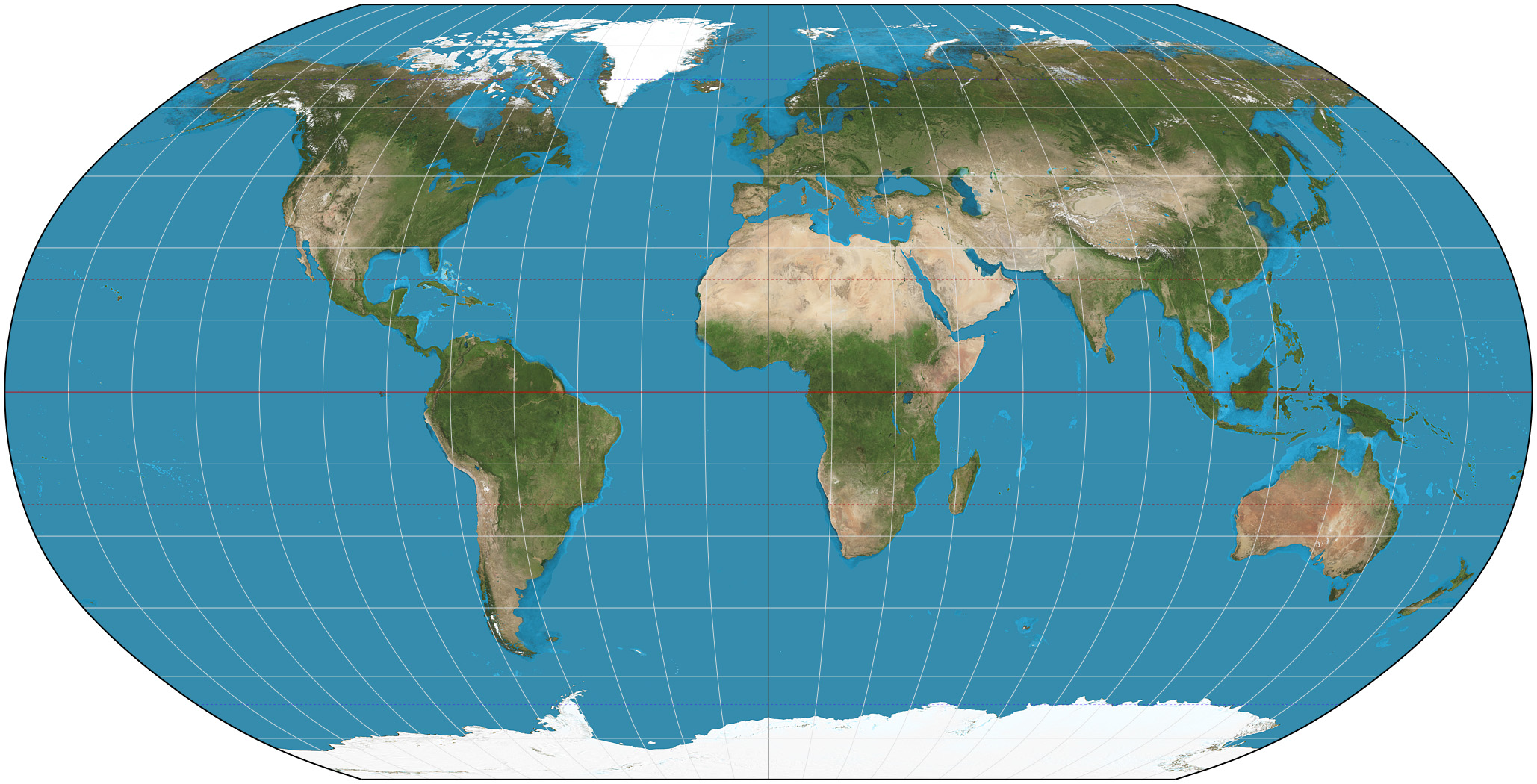
Robinson Projection
Balanced distortion, good for general use
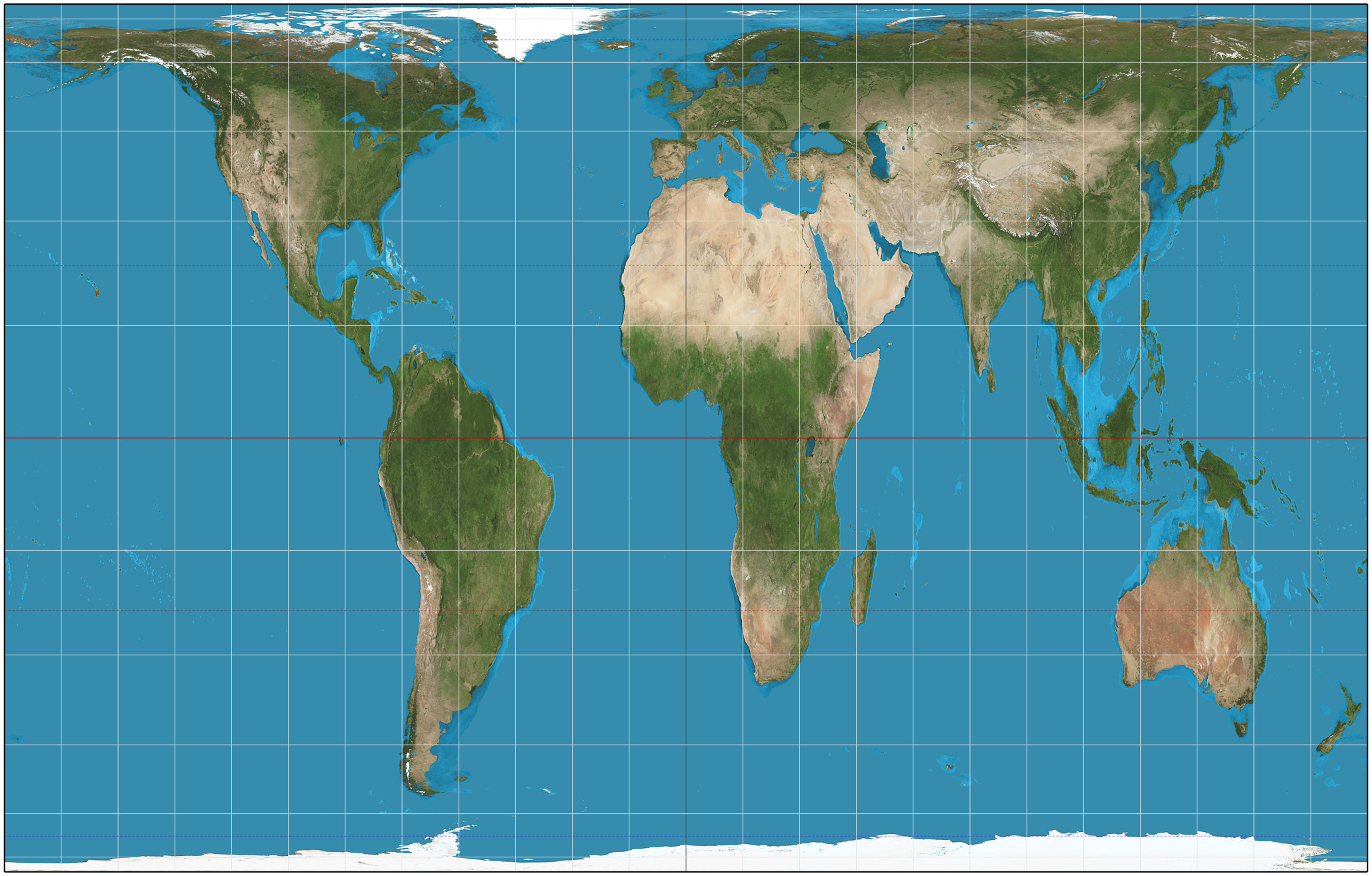
Gall-Peters Projection
Equal area, has accurate size but distorts shape
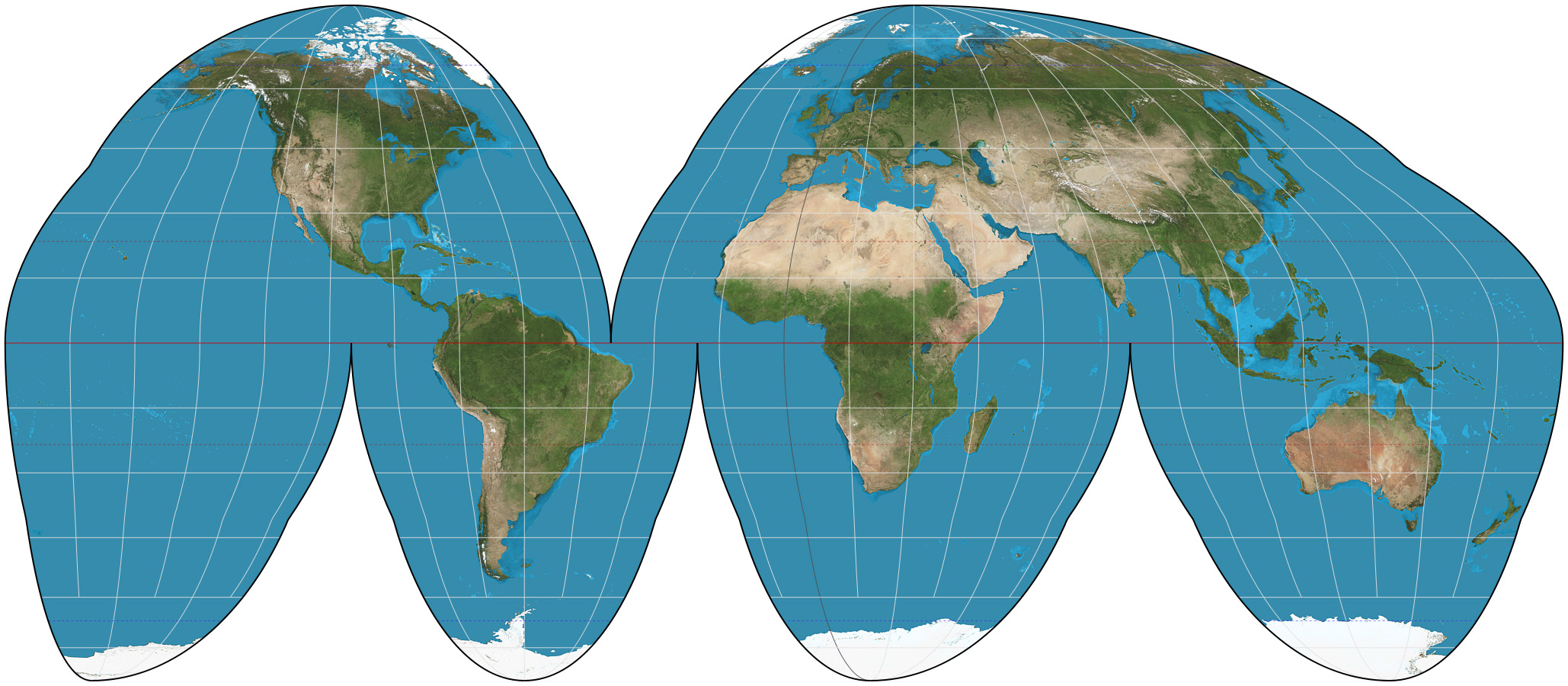
Goode Homolosine Projection
Interrupted, minimizes distortion but splits oceans
GIS (Geographic Information System)
Layers geographic data
Remote Sensing
Data from satellites (ex: land cover, urban sprawl)
GPS
Pinpoints exact location
Census Data
Population data (used for policy, redistricting)
Fieldwork
Observing and recording data on location
Scale of Analysis
Global = whole world, regional = larger area (ex: Latin America), national = country, subnation = state or province, local = city or neighborhood
Formal (Uniform) Region
Shared trait (ex: French-speaking region, political boundaries)
Functional (Nodal) Region
Organized around a node (ex: Newspaper circulation, metro area)
Perceptual (Vernacular) Region
Defined by cultural perception (ex: “The South”)
Relocation Diffusion
People move and carry ideas (ex: migration of Christianity)
Expansion Diffusion (with types)
Idea spread outward, stays strong at hearth (hierarchical, contagious, stimulus)
Hierarchical Diffusion
Spread via authority/elite (ex: fashion trends)
Contagious Diffusion
Rapid, widespread (ex: viral videos)
Stimulus Diffusion
Idea spreads, but is adapted (ex: McDonald’s in India)
Cultural Landscape
Built environment = interaction of humans and nature
Subsequent Occupance
Layers of history in landscape (ex: Rome = Roman ruin + modern city)