Lecture 23: NS IX - Sensory Organs II
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/131
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:50 PM on 12/14/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
132 Terms
1
New cards
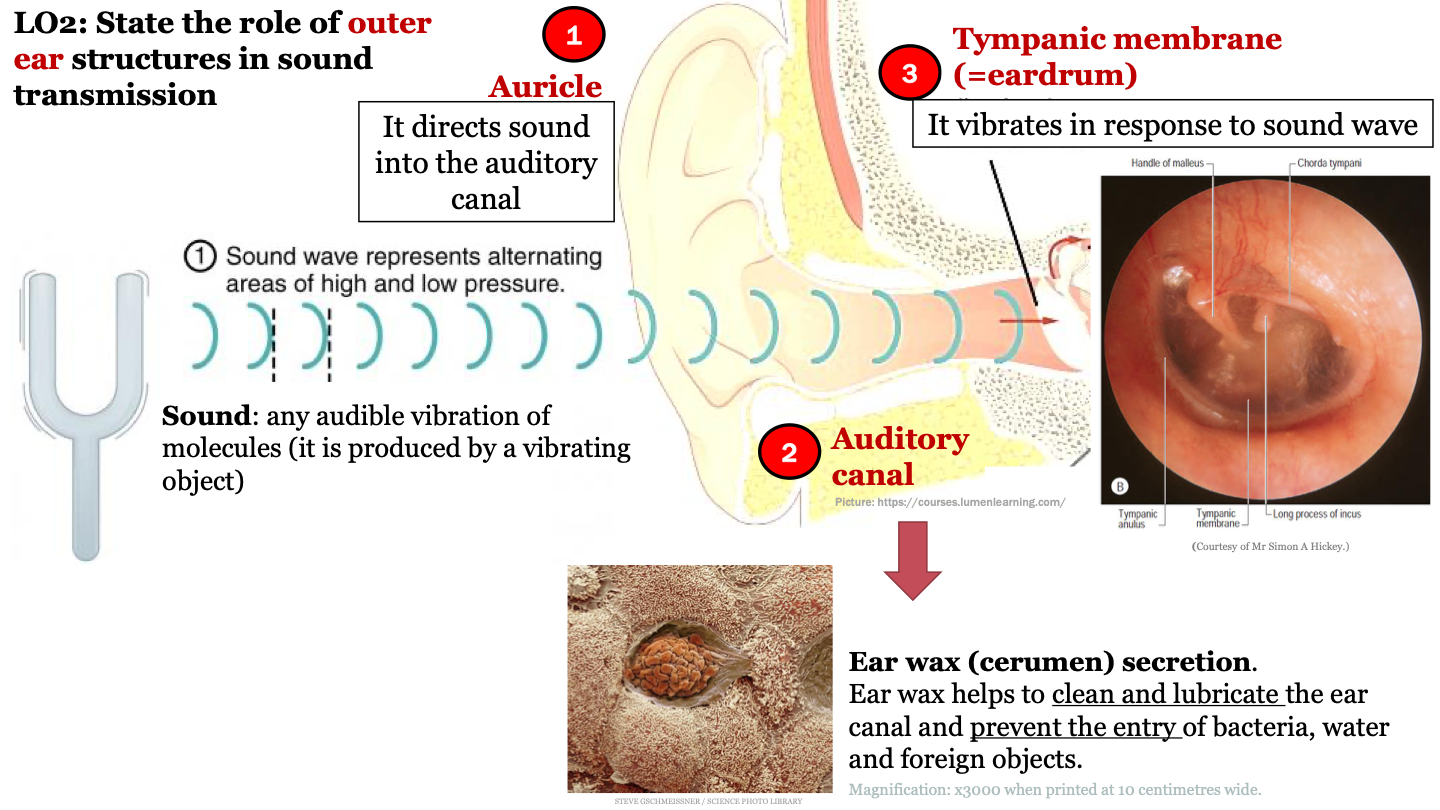
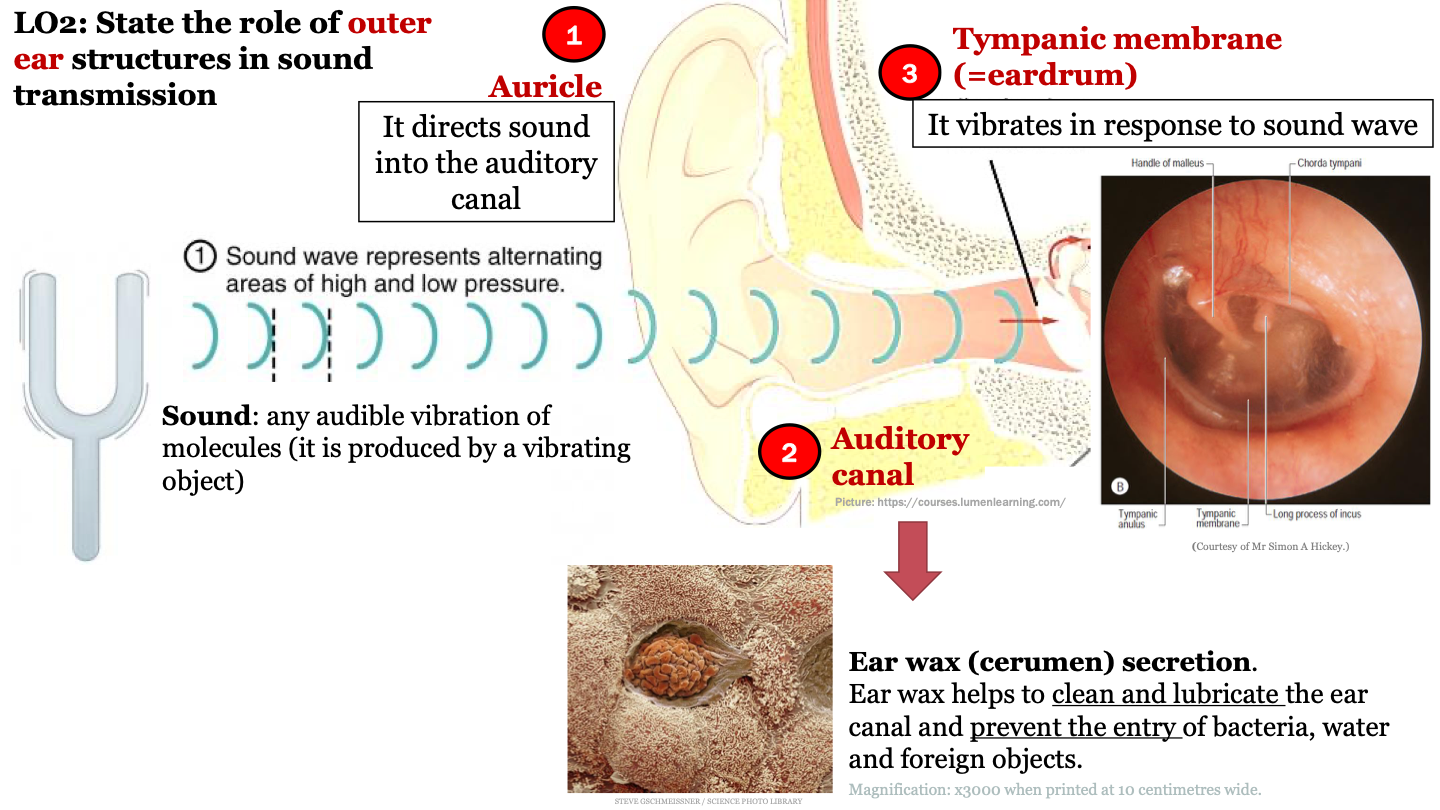
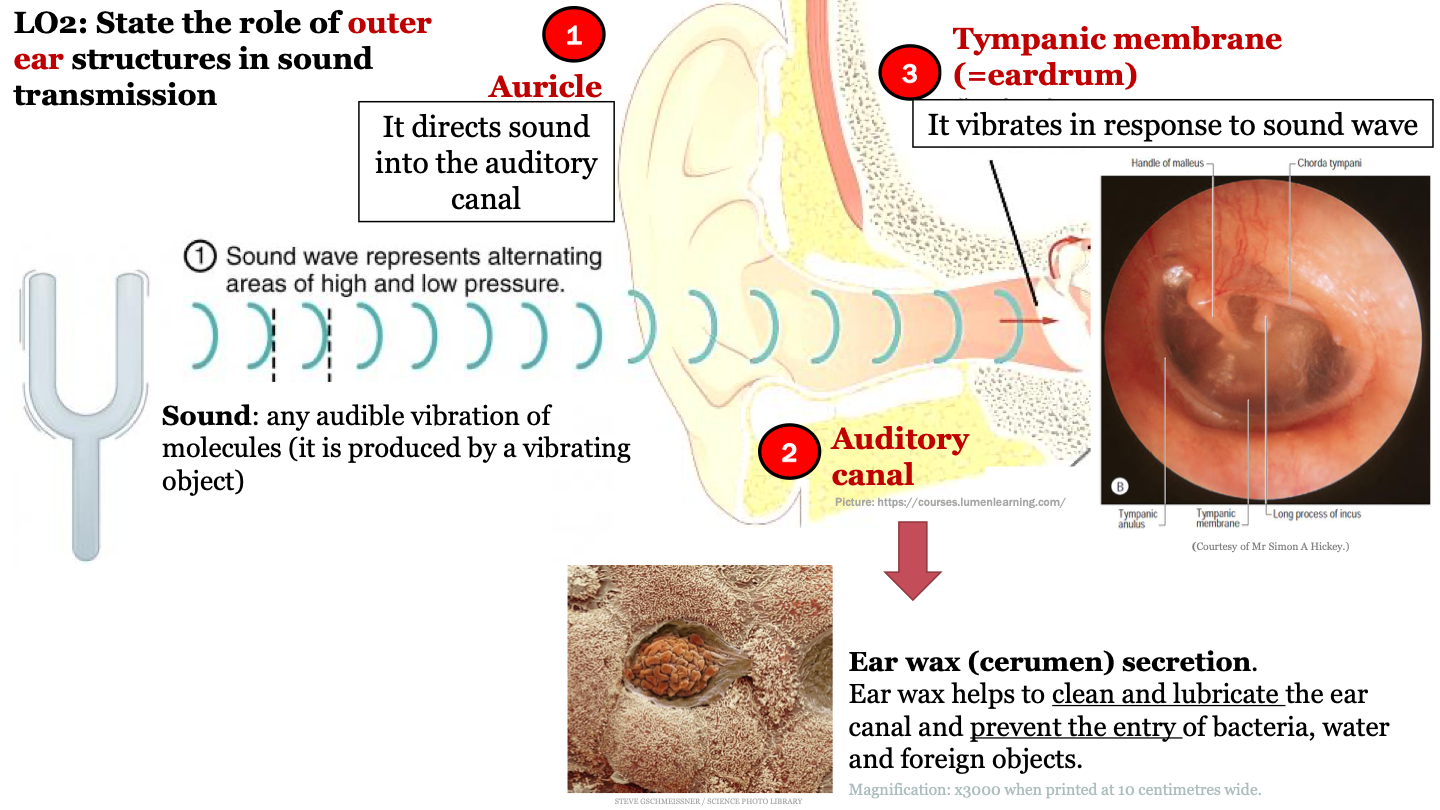
auricle function
it directs sound into the auditory canal
2
New cards
sound
any audible vibration of molecules (it is produced by a vibrating object)
3
New cards
role of earwax (cerumen) secretion
ear wax helps to clean and lubricate the ear canal and prevent the entry of bacteria, water and foreign objects
4
New cards
function of tympanic membrane (eardrum)
it vibrates in response to sound waves
5
New cards
sequence of events of sound detection
1. auricle
2. auditory canal
3. tympanic membrane
4. malleus
5. incus
6. stapes
7. oval window
8. cochlea
2. auditory canal
3. tympanic membrane
4. malleus
5. incus
6. stapes
7. oval window
8. cochlea
6
New cards
what structures are found in the middle ear?
1. ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes)
2. oval window
3. stapedius (muscle of the middle ear)
4. tensor tympani (muscle of the middle ear)
2. oval window
3. stapedius (muscle of the middle ear)
4. tensor tympani (muscle of the middle ear)
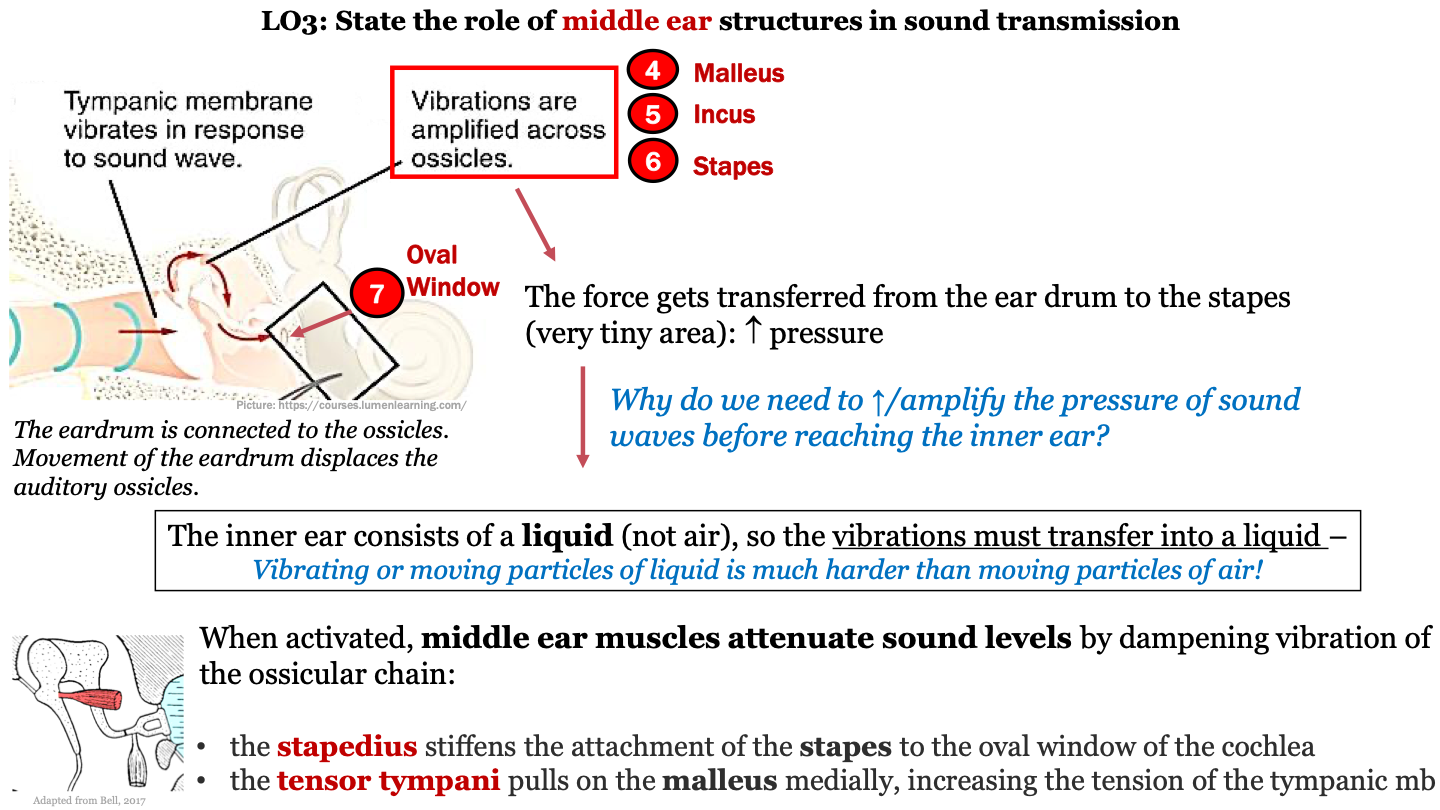
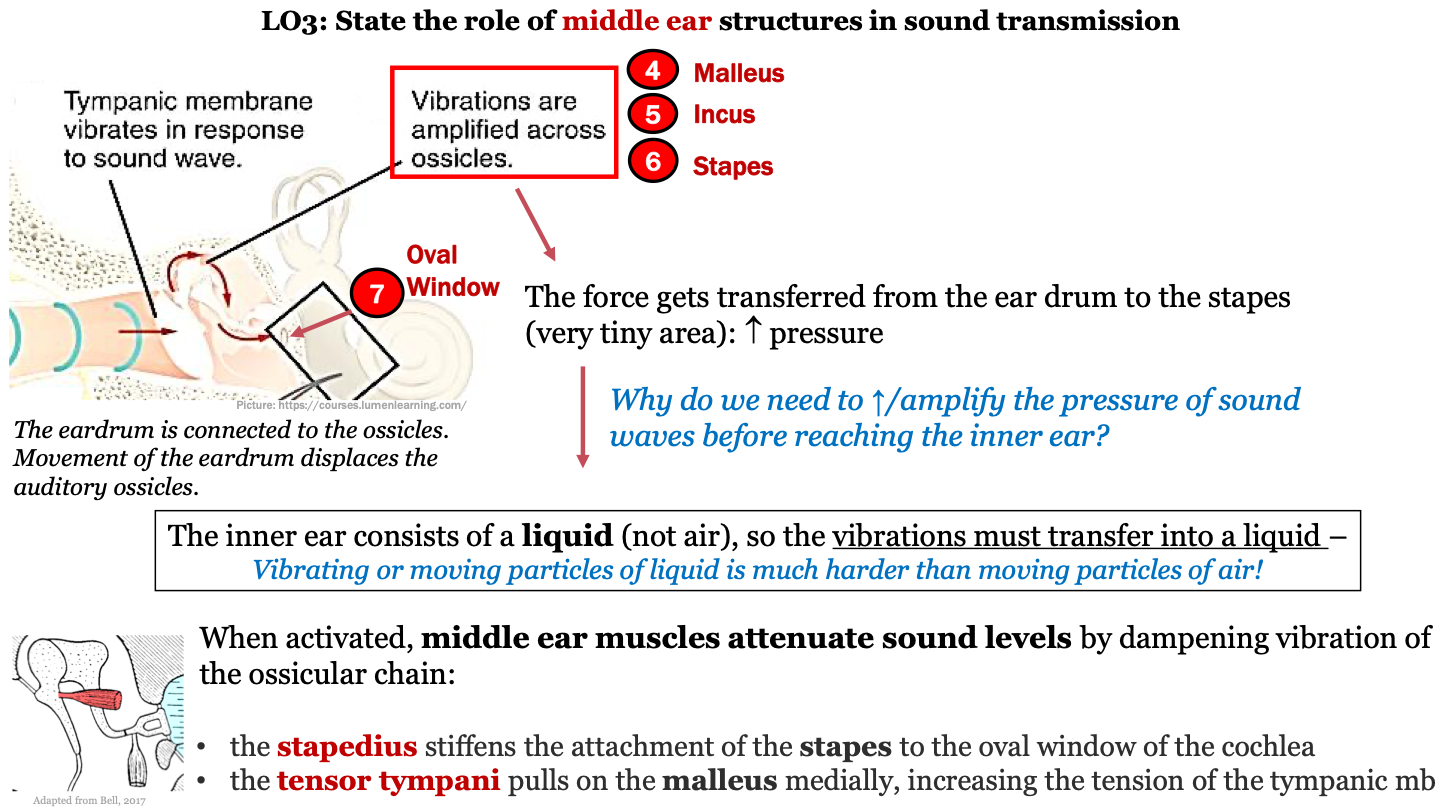
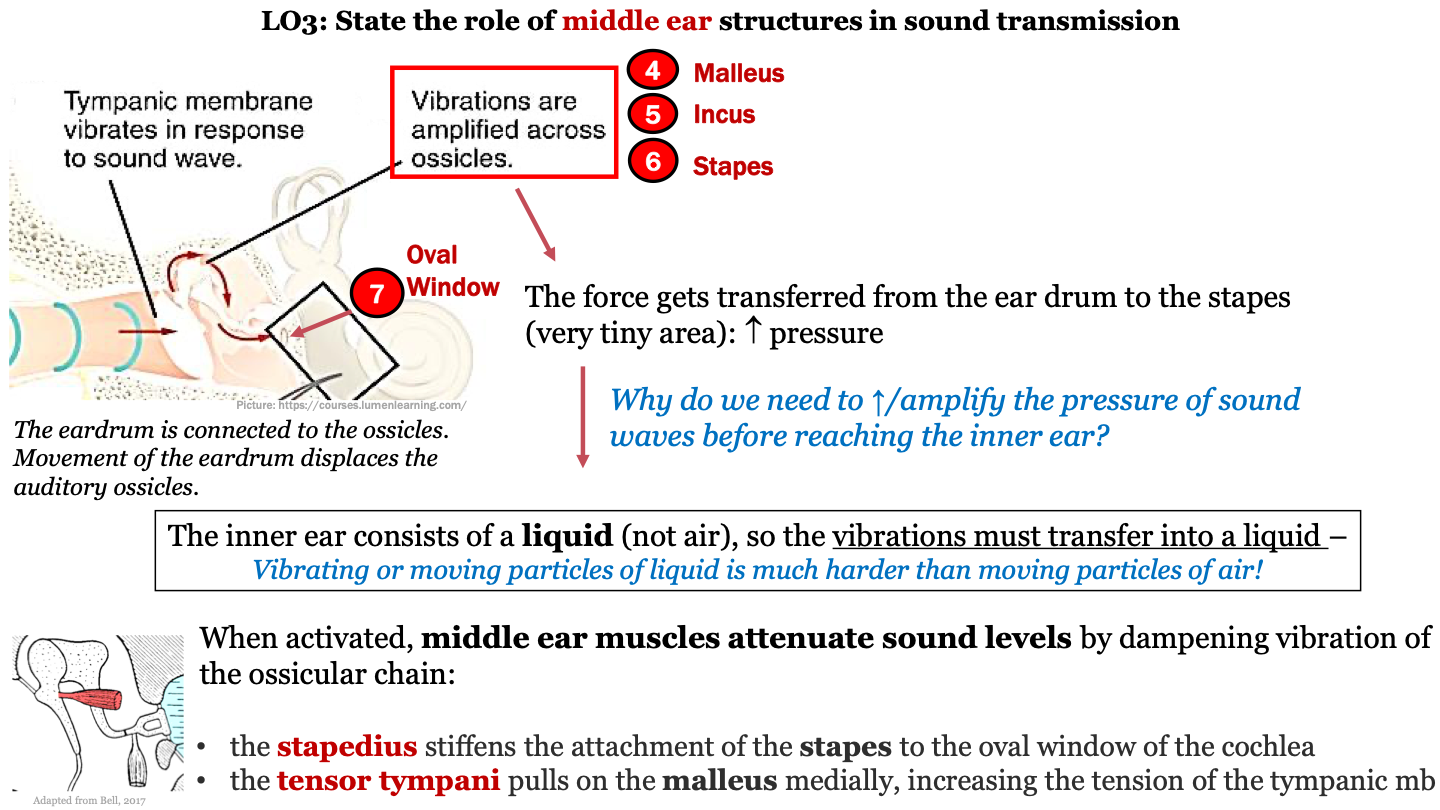
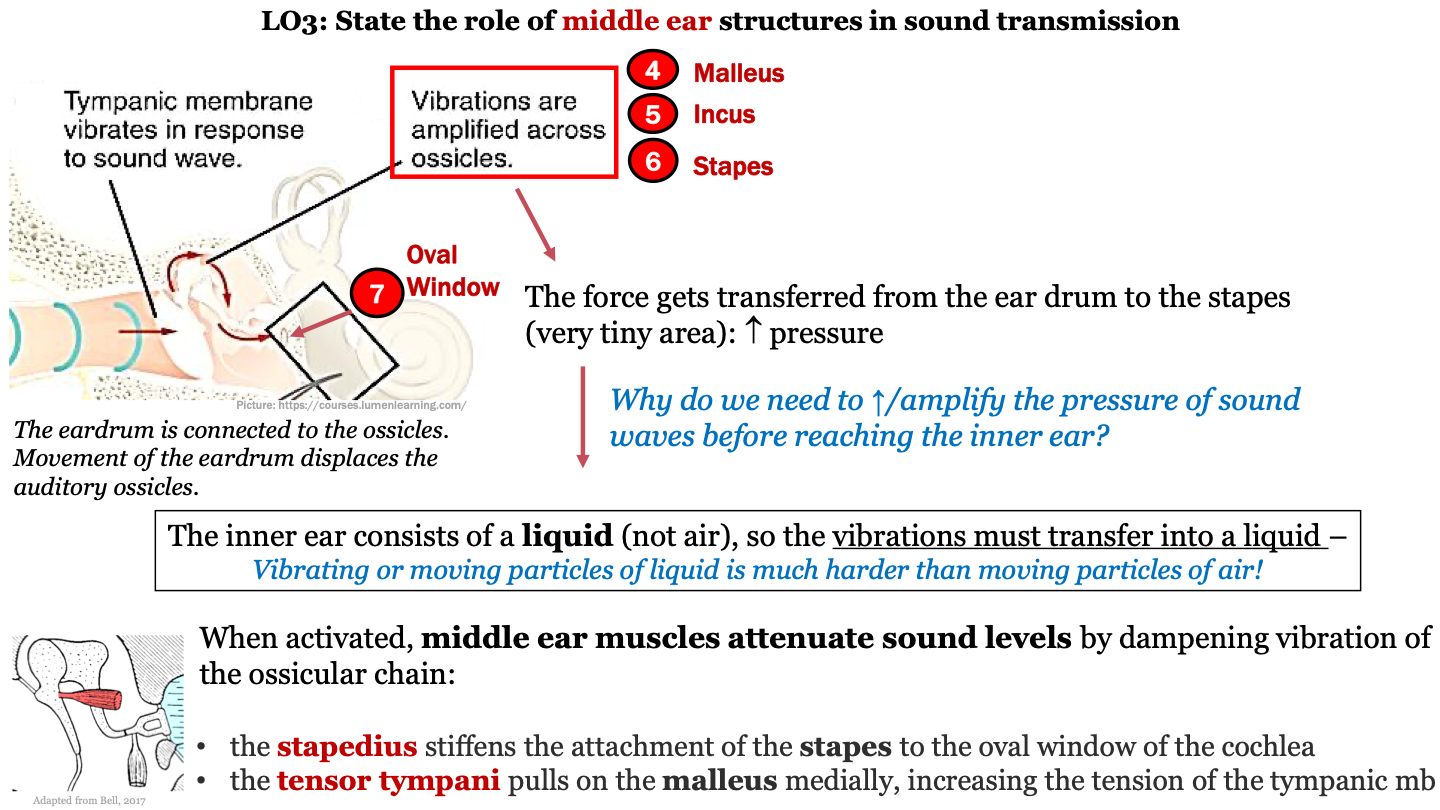
7
New cards
function of malleus, incus, stapes (ossicles)
movement of the eardrum in response to sound waves displaces the ossicles; vibrations are amplified across the ossicles; the force gets transferred to the stapes (last auditory ossicle) which increases pressure
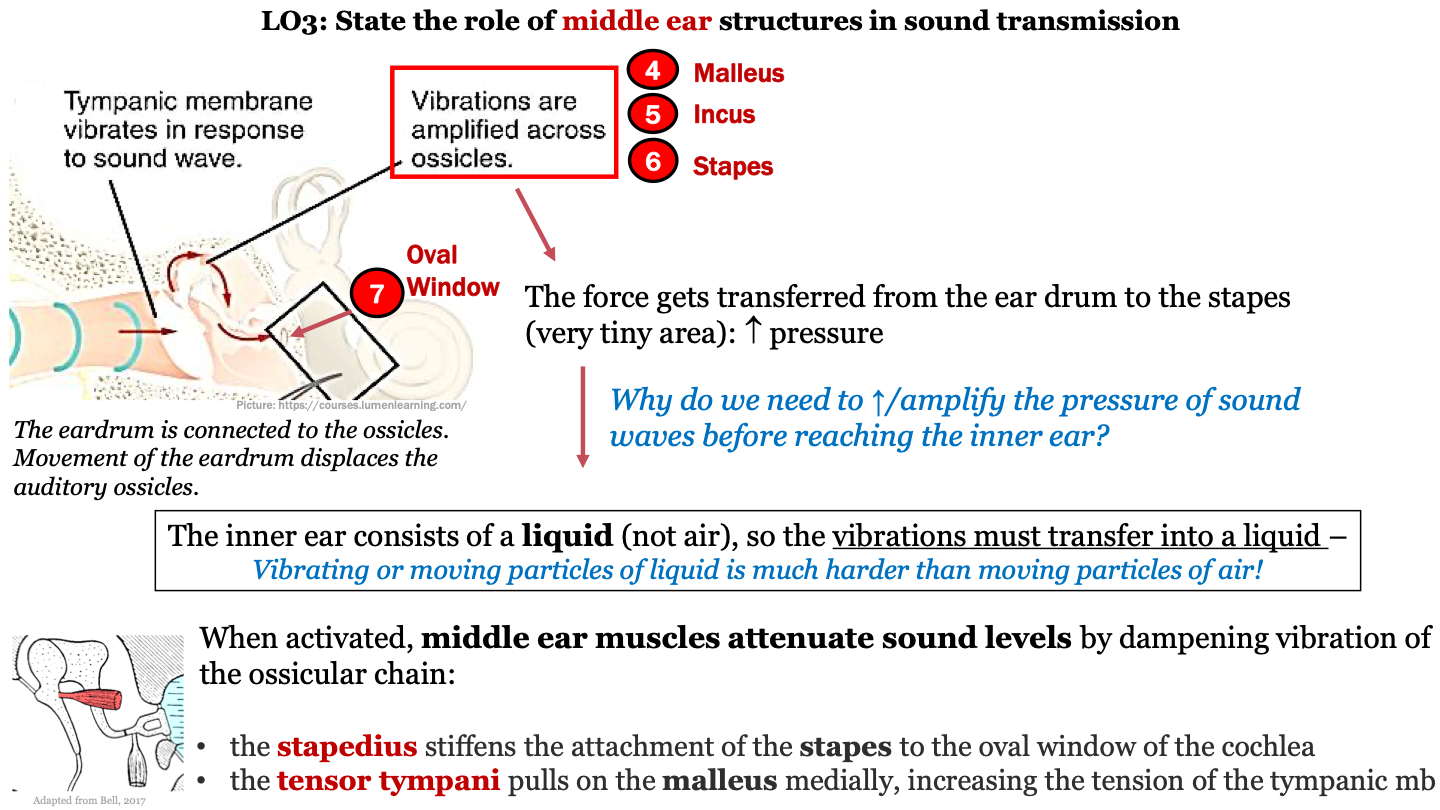
8
New cards
Why do we need to increase the pressure of sound waves before reaching the inner ear?
the inner ear consists of a liquid (not air), so the vibrations must transfer into a liquid; thus, pressure needs to increase because moving particles of liquid is harder than moving particles of air
9
New cards
what do middle ear muscles do?
middle ear muscles attenuate sound levels by dampening vibration of the ossicular chain
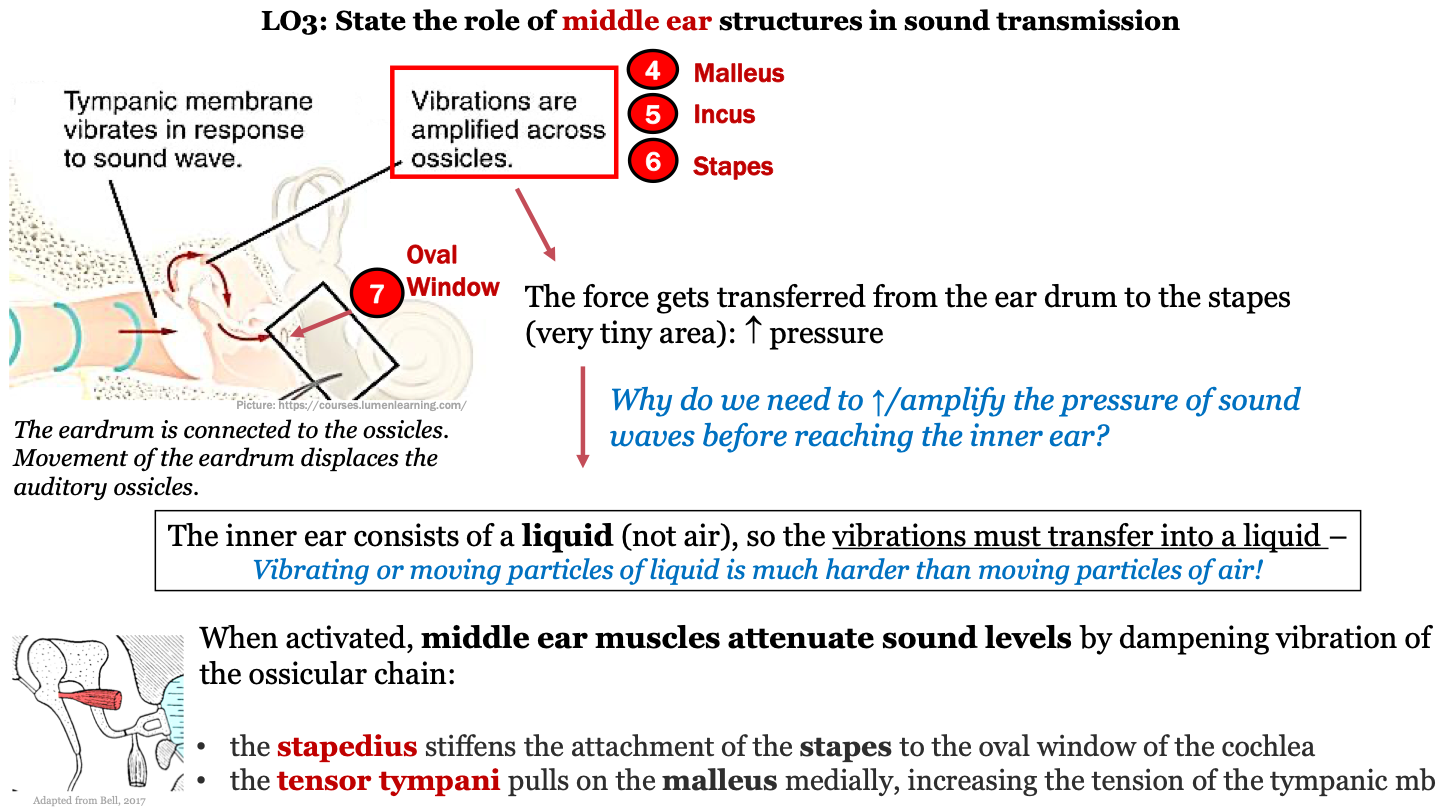
10
New cards
what does the stapedius do?
stiffens the attachment of the stapes to the oval window of the cochlea
11
New cards
what does the tensor tympani do?
pulls on the malleus medially, increasing the tension of the tympanic mb
12
New cards
what order do the ossicles go in?
from eardrum to oval window:
1. malleus
2. incus
3. stapes
1. malleus
2. incus
3. stapes
13
New cards
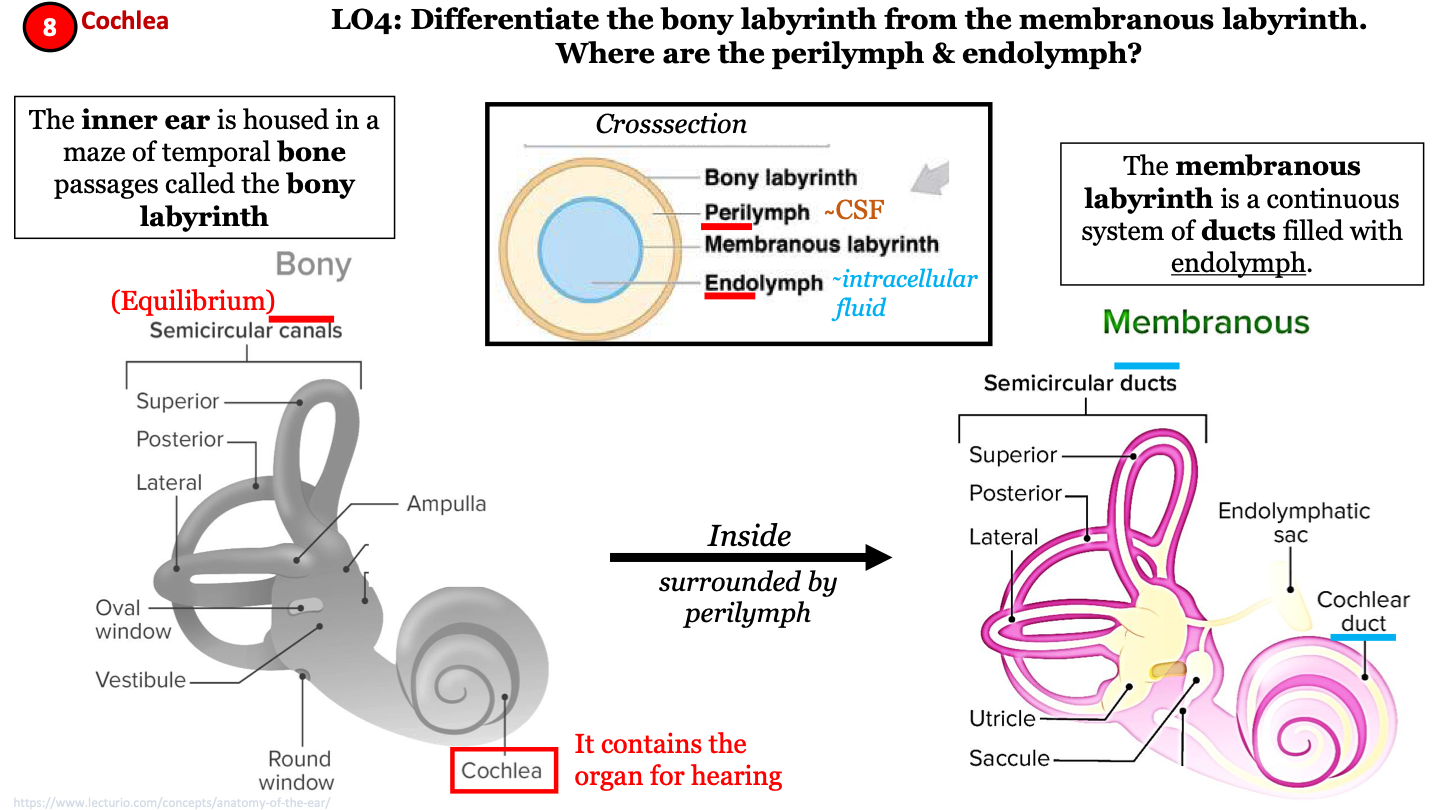
where 2 labyrinths make up the inner ear?
bony labyrinth and membranous labyrinth
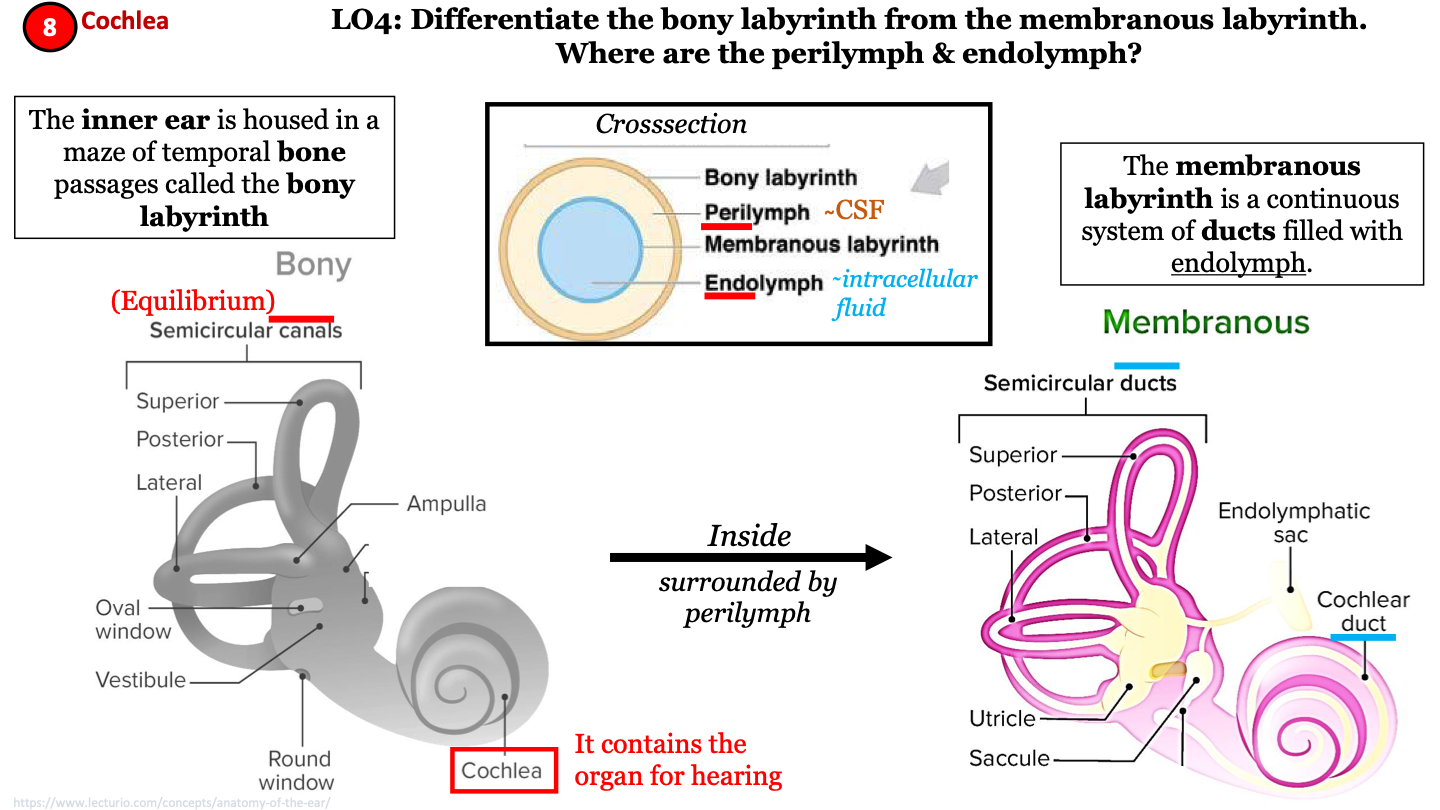
14
New cards
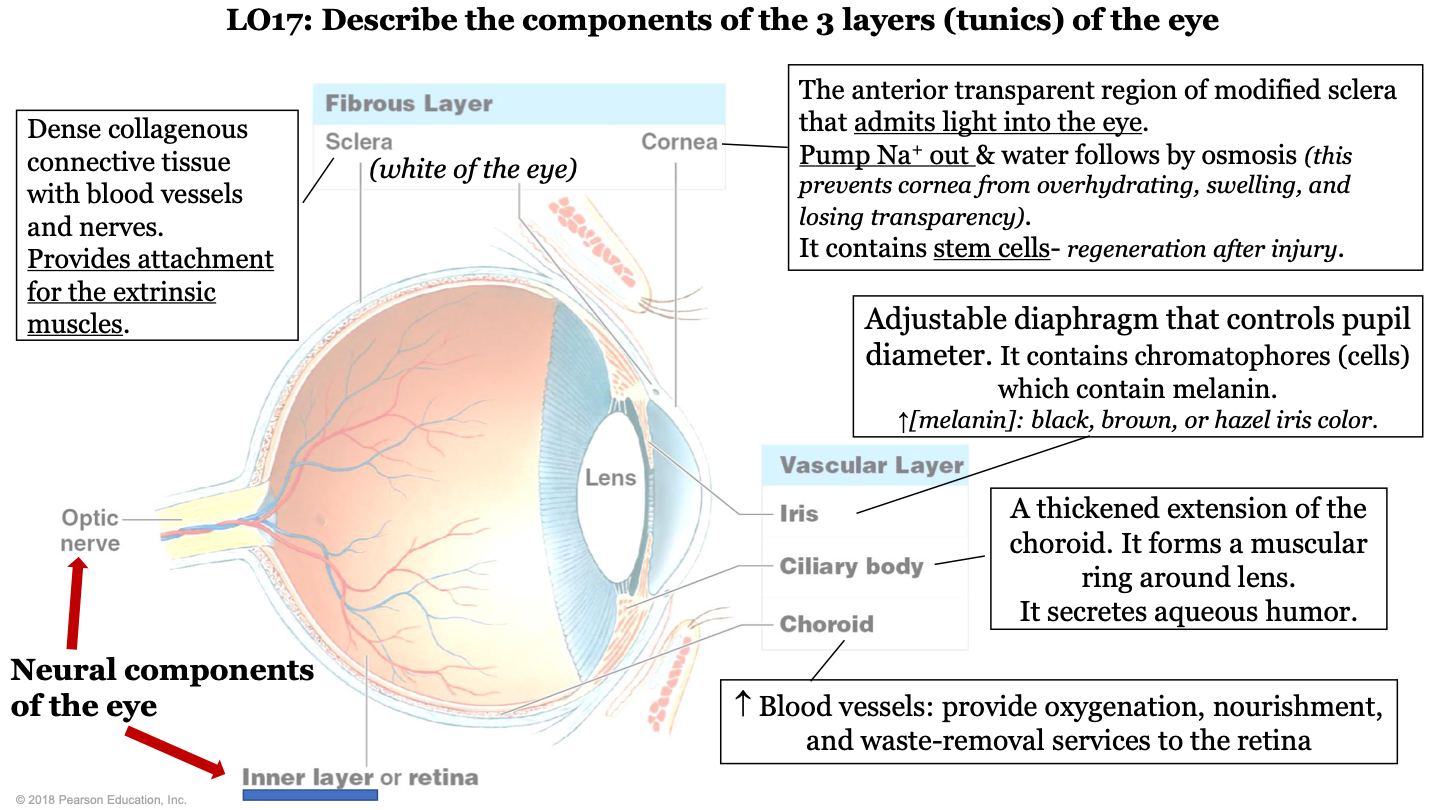
bony labyrinth
a maze of temporal bone passages; has semicircular canals and contains the cochlea; helps maintain equilibrium
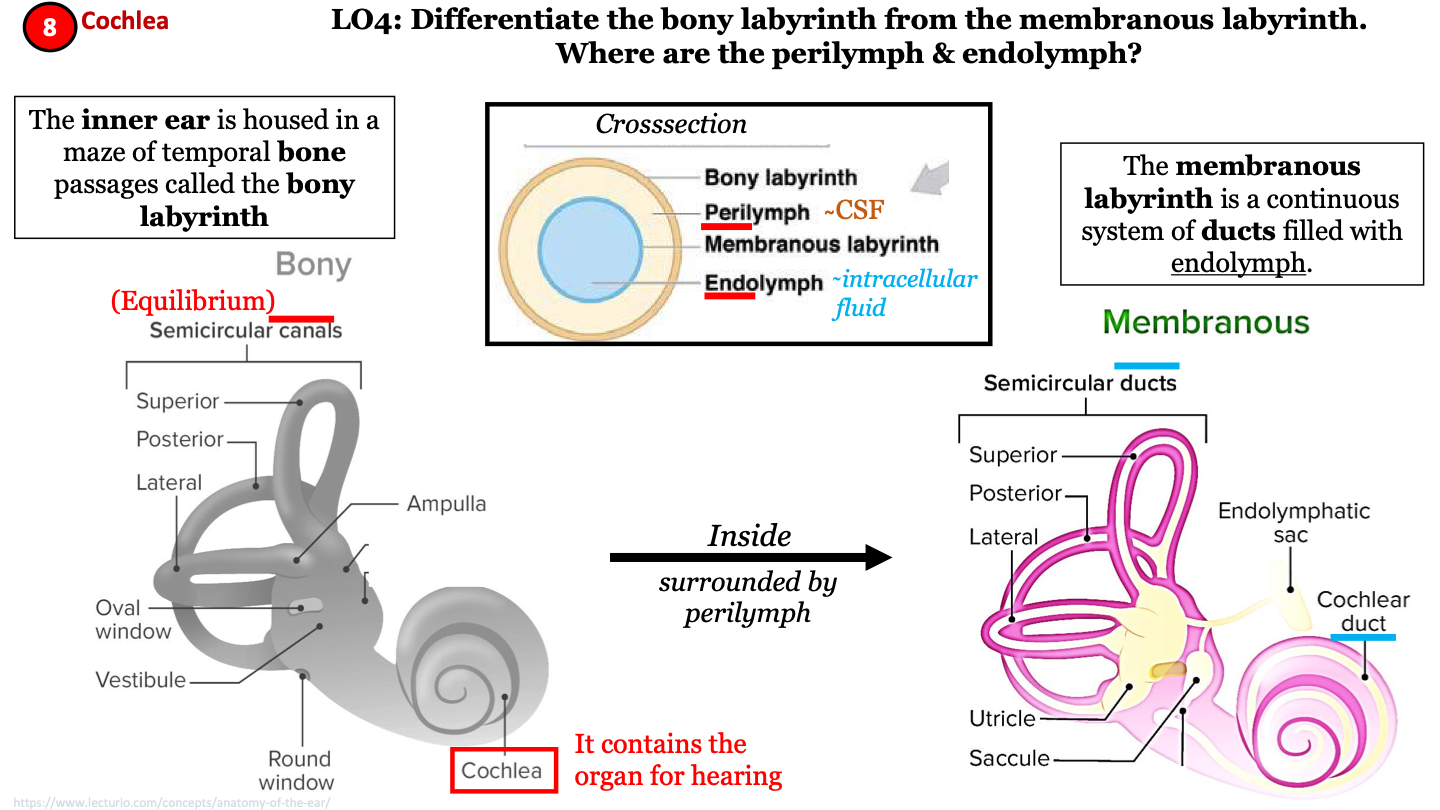
15
New cards
importance of cochlea
organ for hearing
16
New cards
membranous labyrinth
continuous system of ducts filled with endolymph; has semicircular ducts and cochlear duct; inside the bony labyrinth surrounded by perilymph
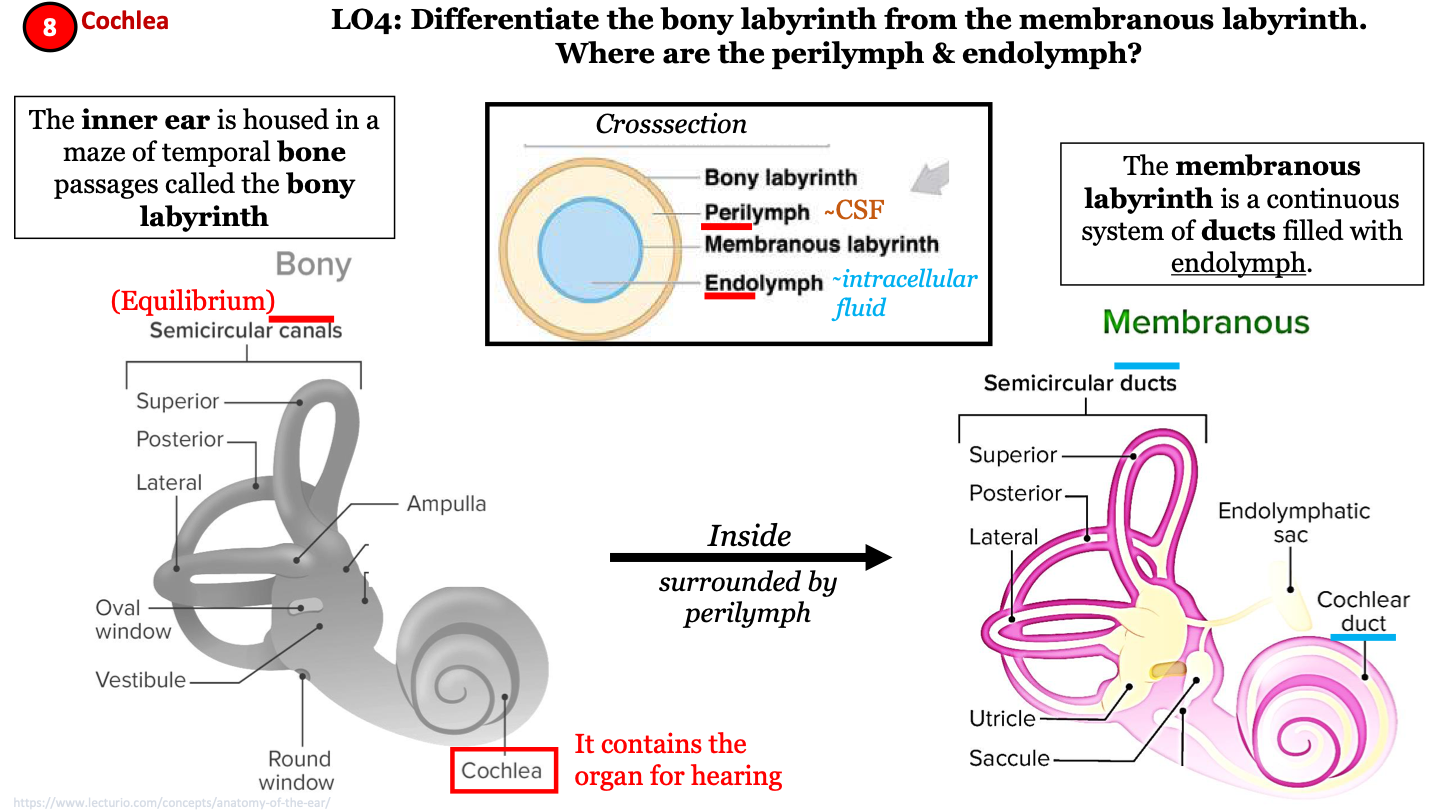
17
New cards
cross section of inner ear labyrinths
from superficial to deep:
1. bony labyrinth
2. perilymph (CSF)
3. membranous labyrinth
4. endolymph (intracellular fluid)
1. bony labyrinth
2. perilymph (CSF)
3. membranous labyrinth
4. endolymph (intracellular fluid)
18
New cards
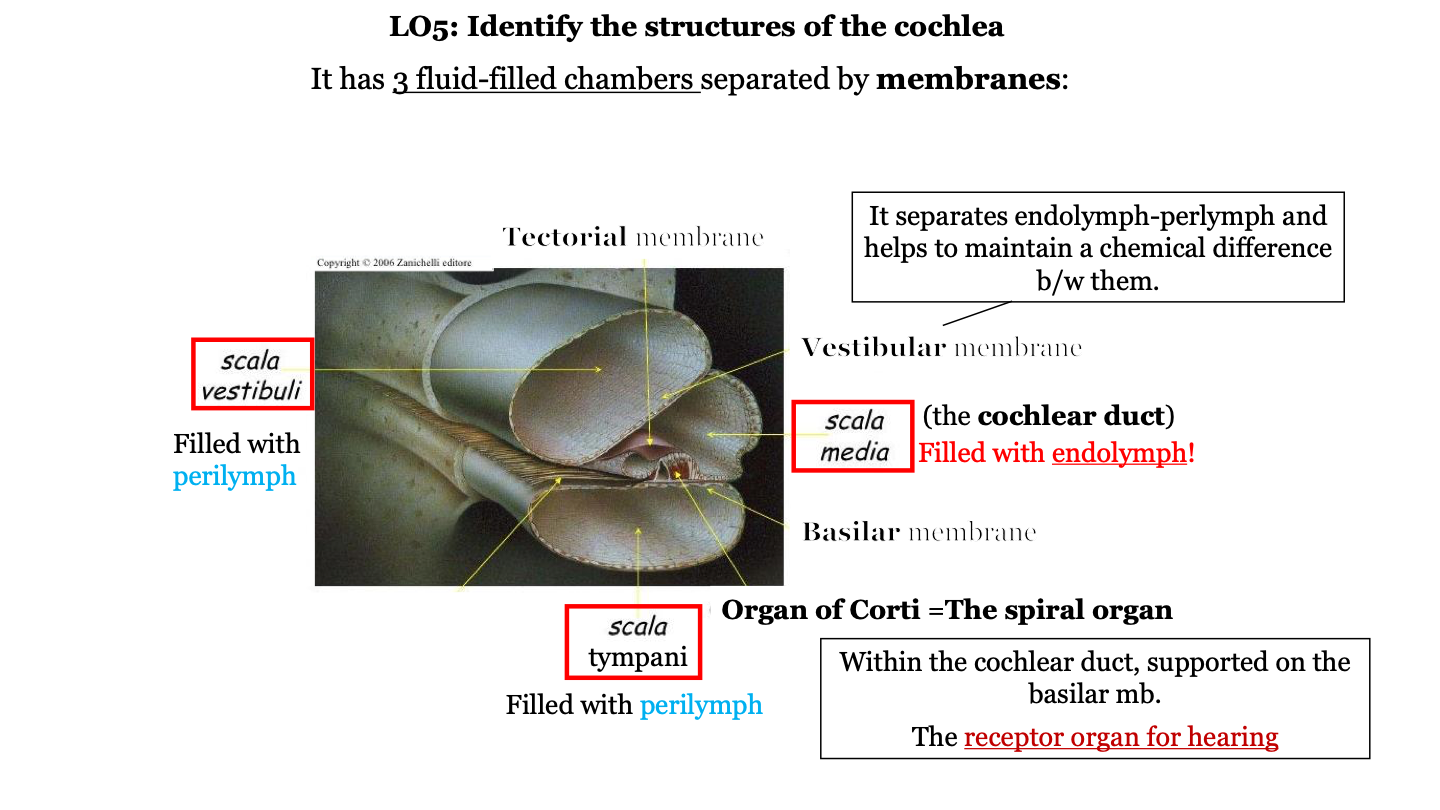
the organ of Corti (the spiral organ) is found within the _____________________ duct, supported on the __________ membrane.
semicircular/cochlear; basilar
19
New cards
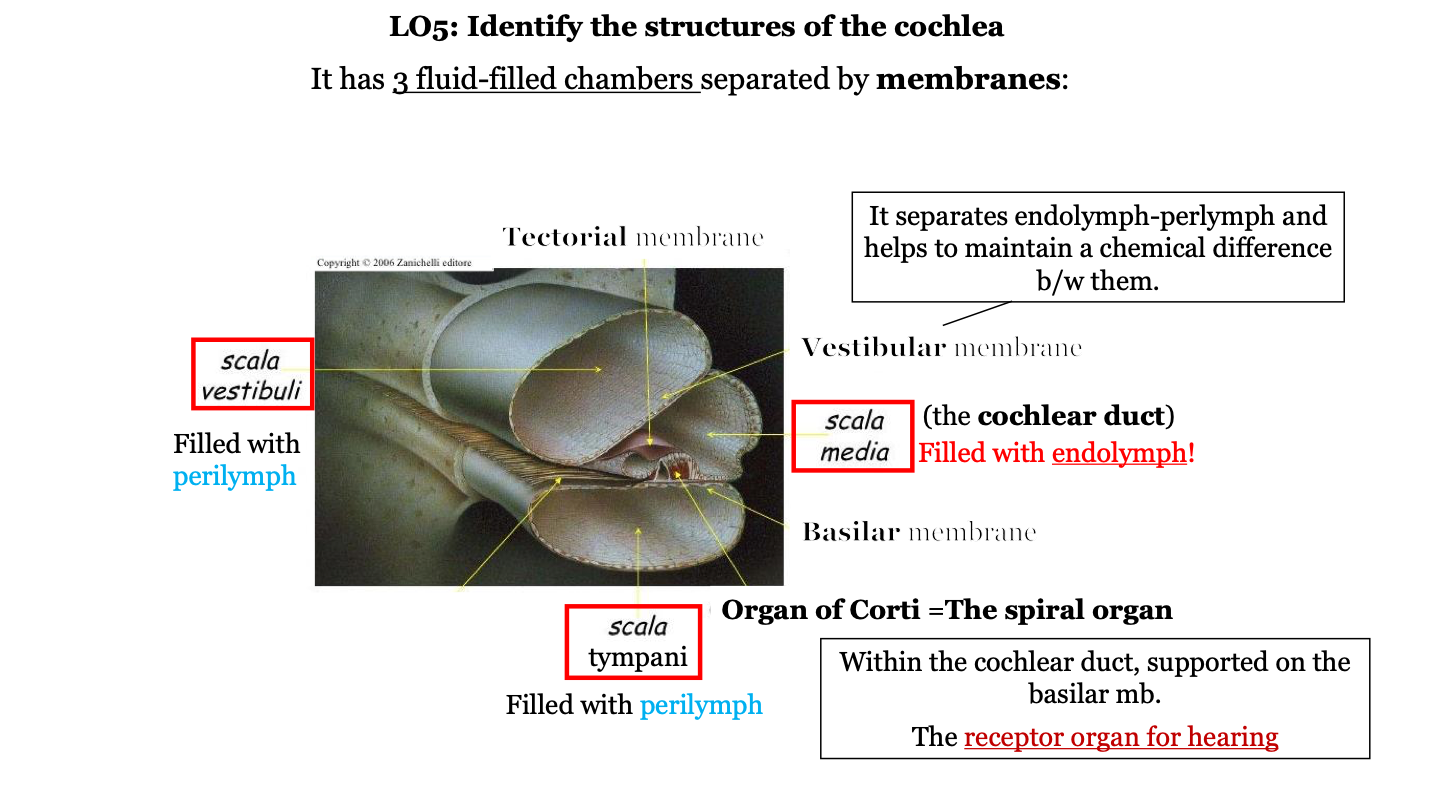
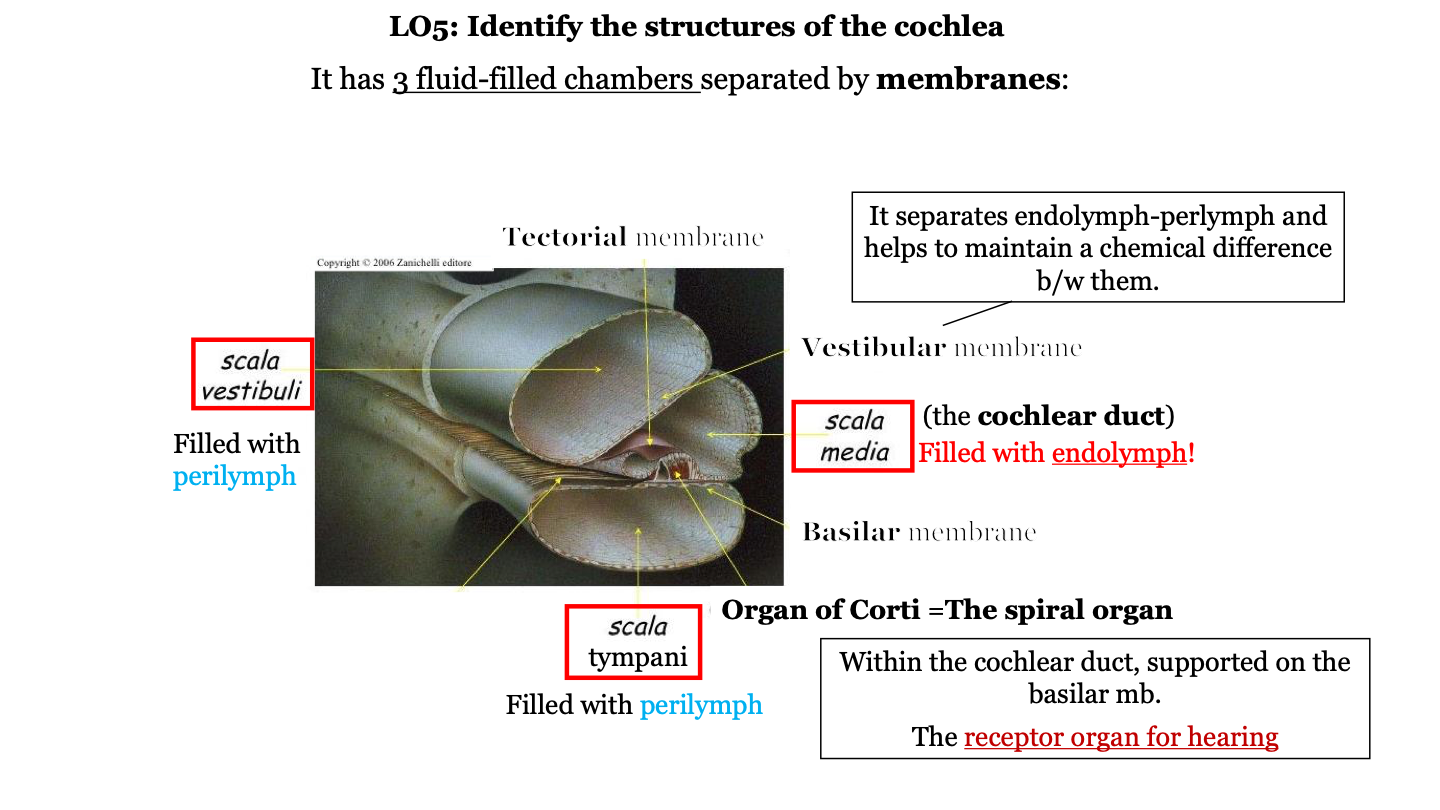
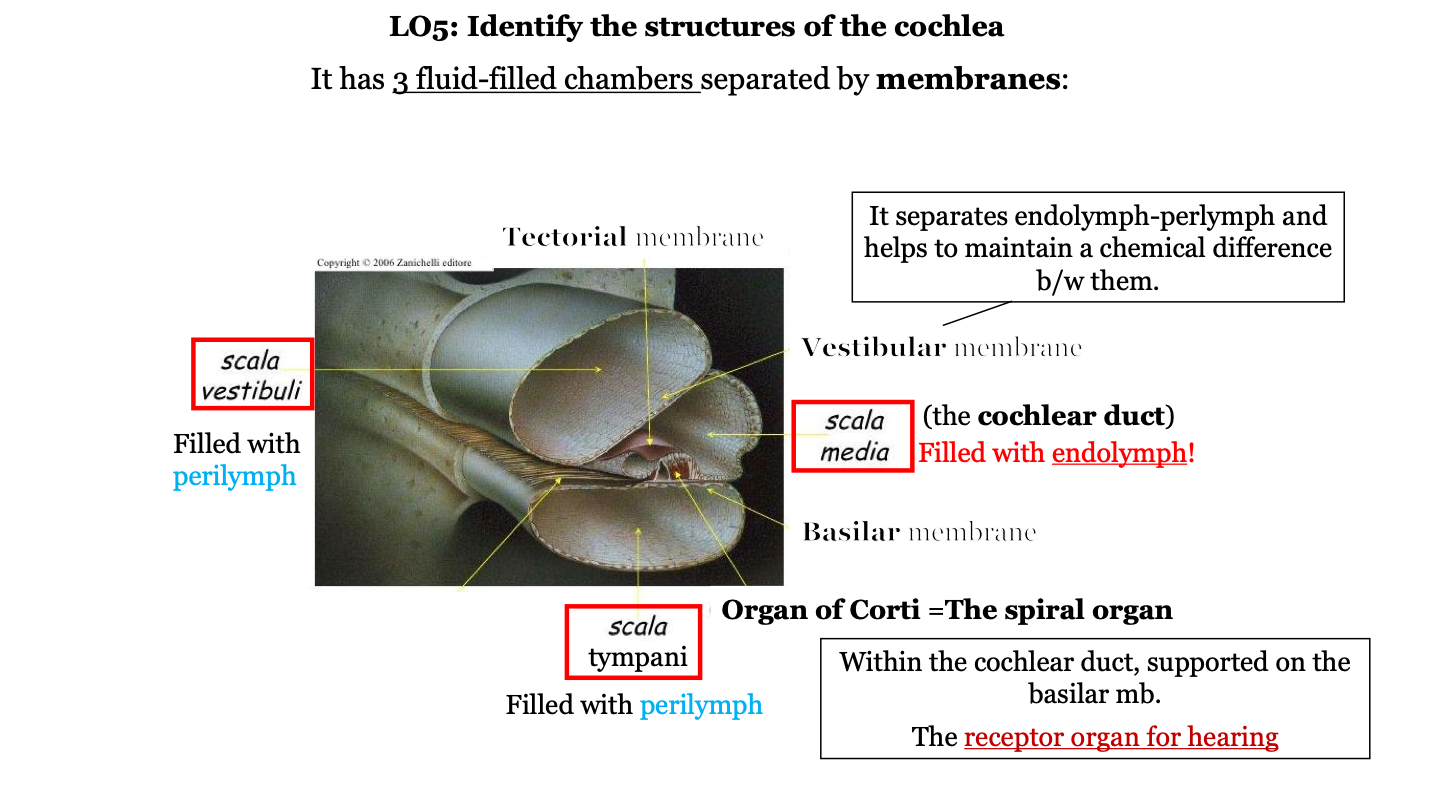
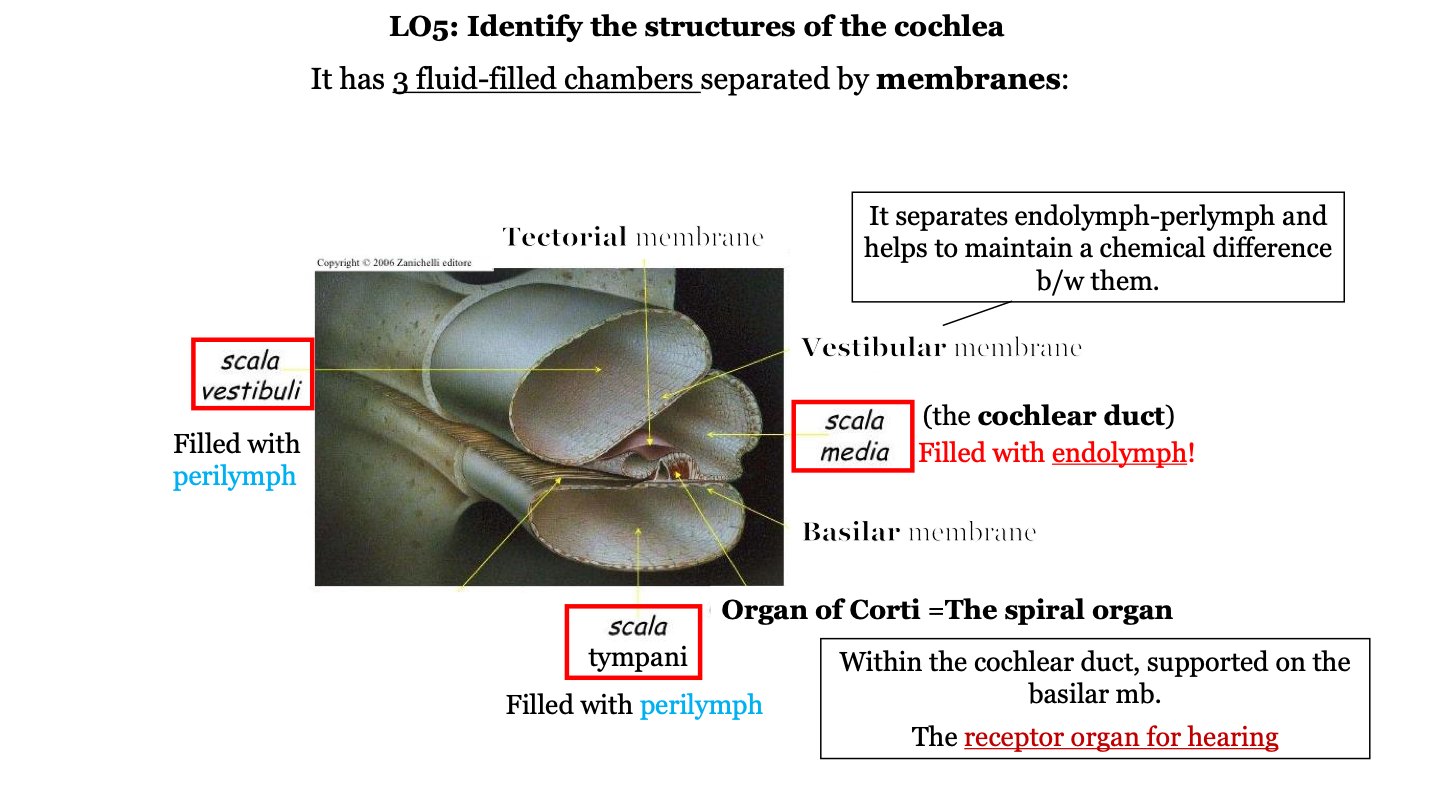
what are the three fluid-filled chambers of the cochlea?
1. the scala vestibuli
2. the scala media
3. the scala tympani
2. the scala media
3. the scala tympani
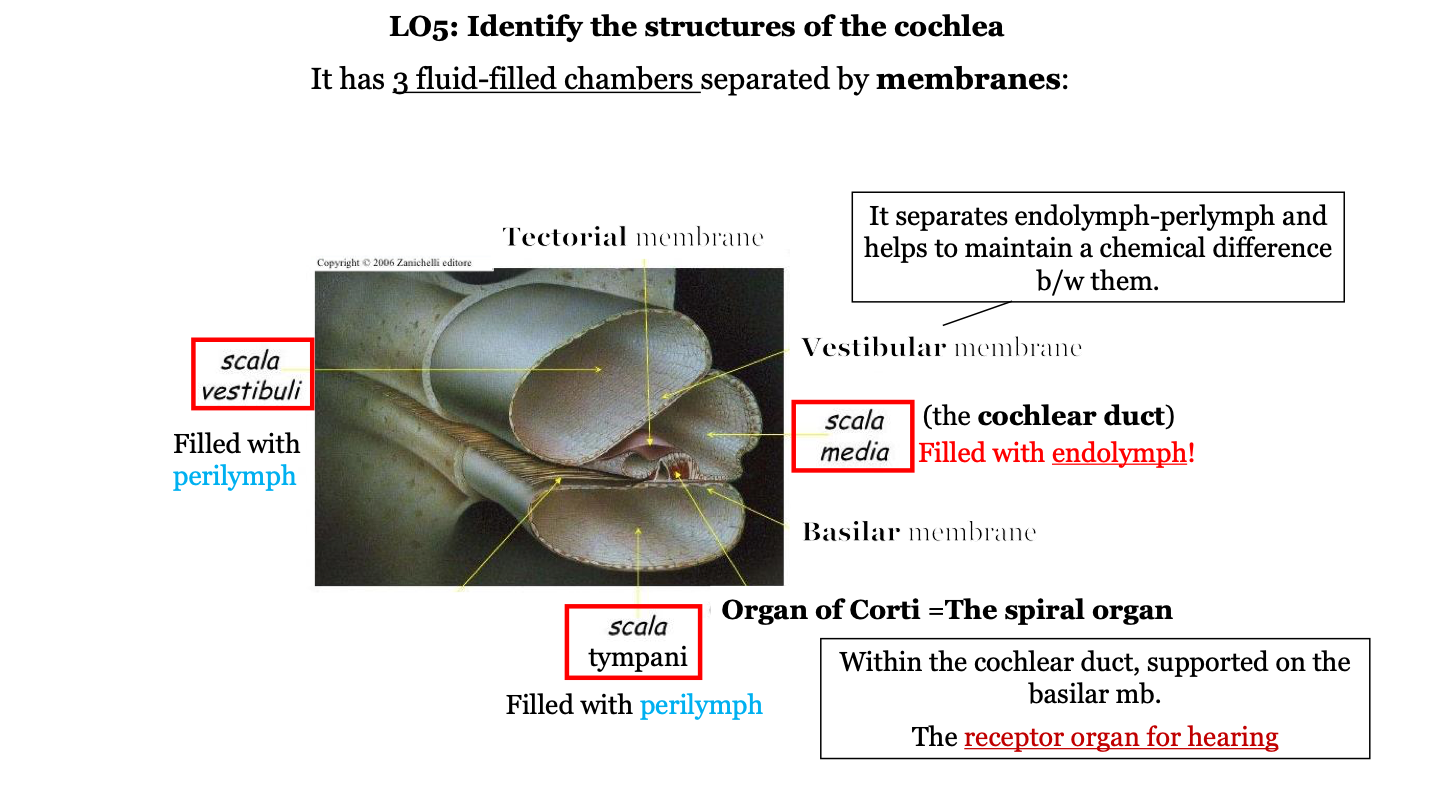
20
New cards
what fluid fills the scala vestibuli?
perilymph
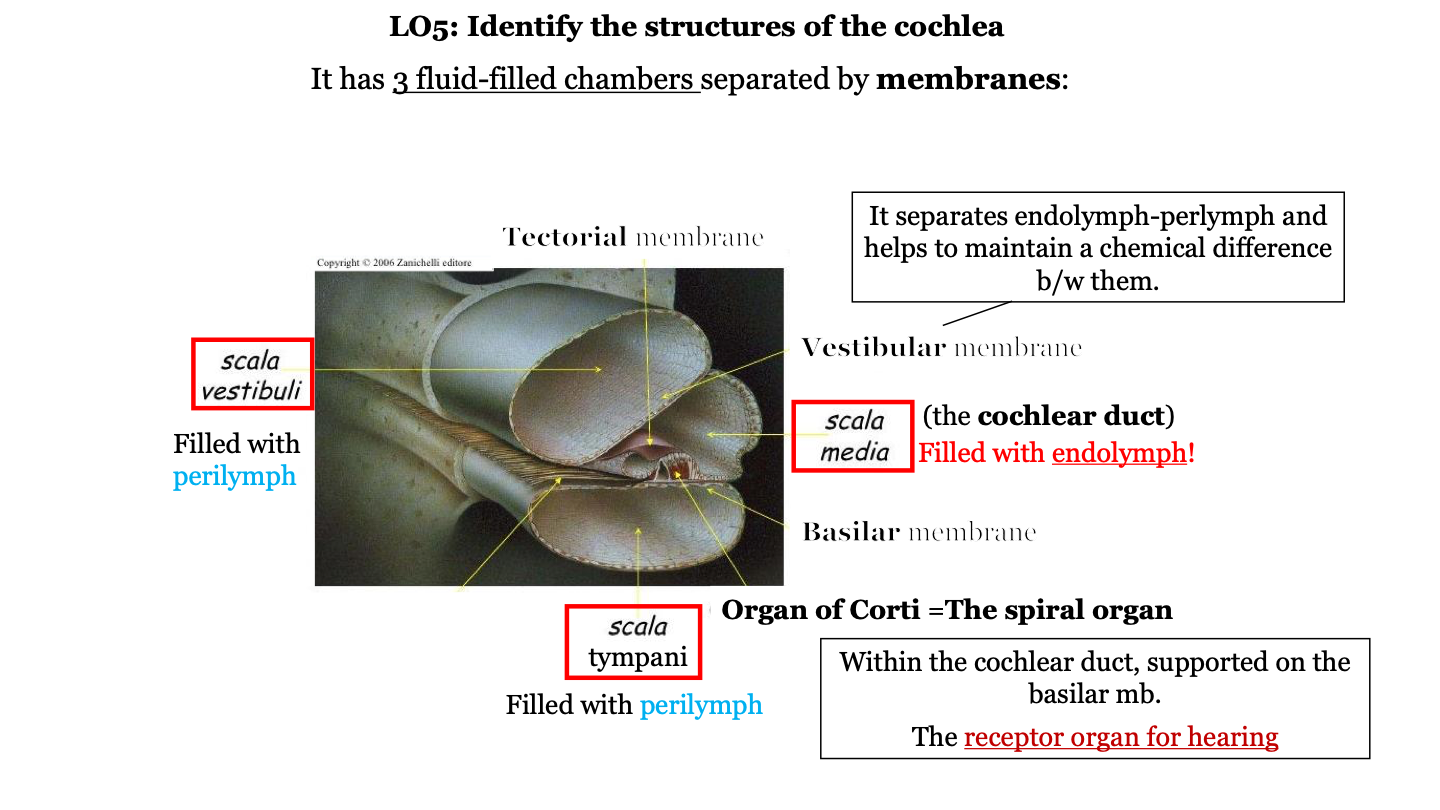
21
New cards
what fluid fills the scala media?
endolymph
22
New cards
what is the scala media AKA?
the cochlear duct
23
New cards
what fluid fills the scala tympani?
perilymph
24
New cards
what is the organ of Corti AKA?
the spiral organ
25
New cards
what does the vestibular membrane of the cochlea do?
it separates the endolymph (in cochlear duct) and perilymph (in the scala vestibuli) and helps to maintain a chemical difference between them
26
New cards
where is the organ of Corti located?
in the cochlea on top of the basilar membrane
27
New cards
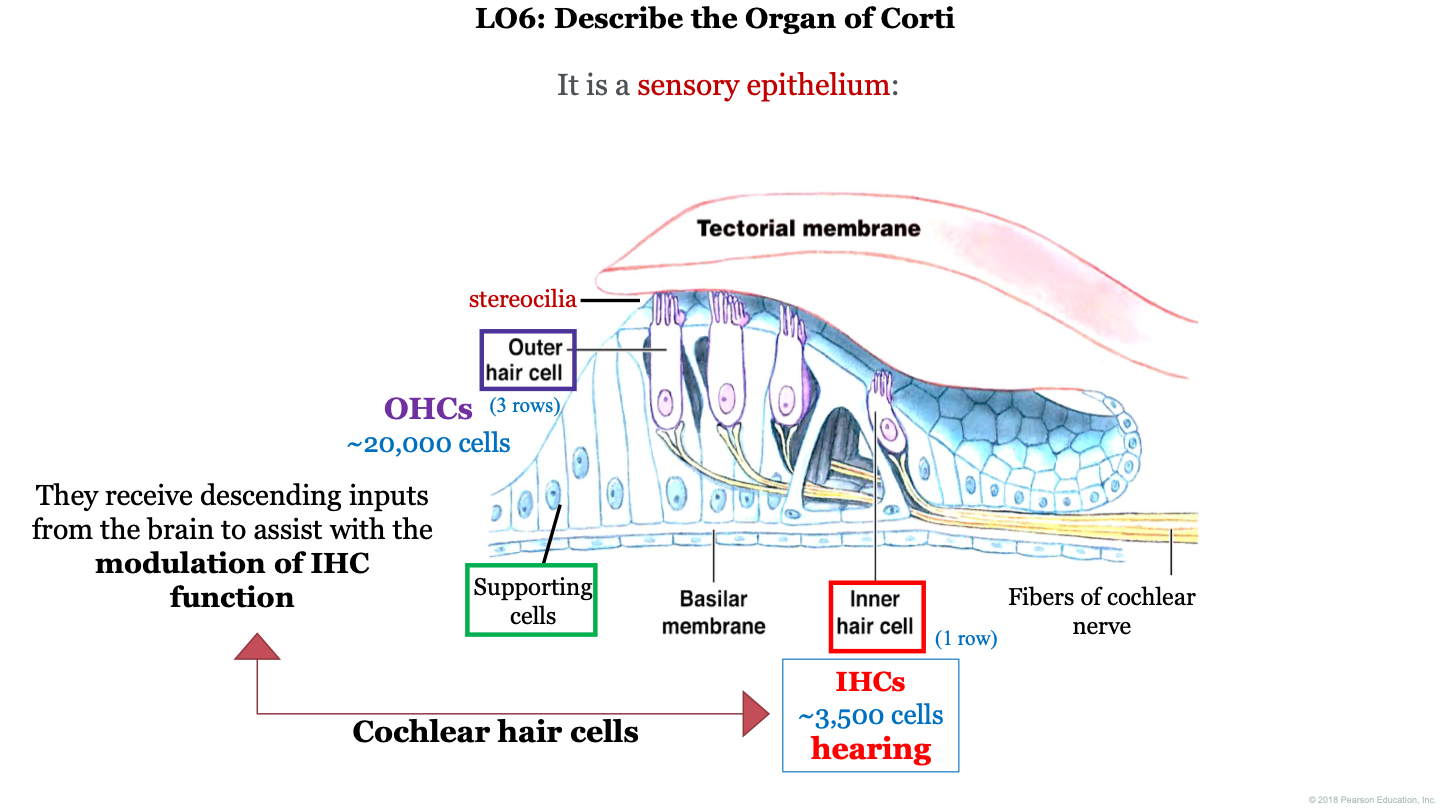
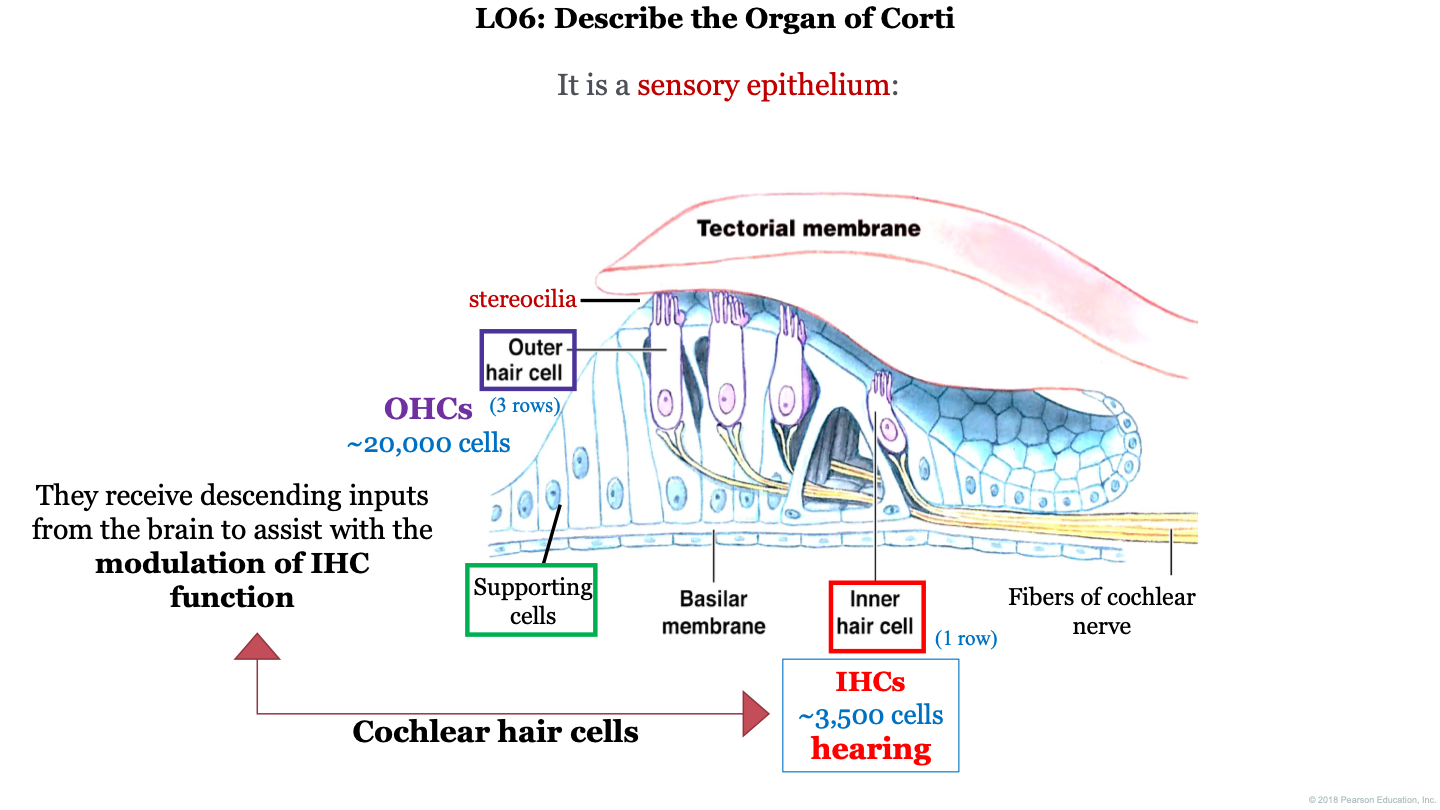
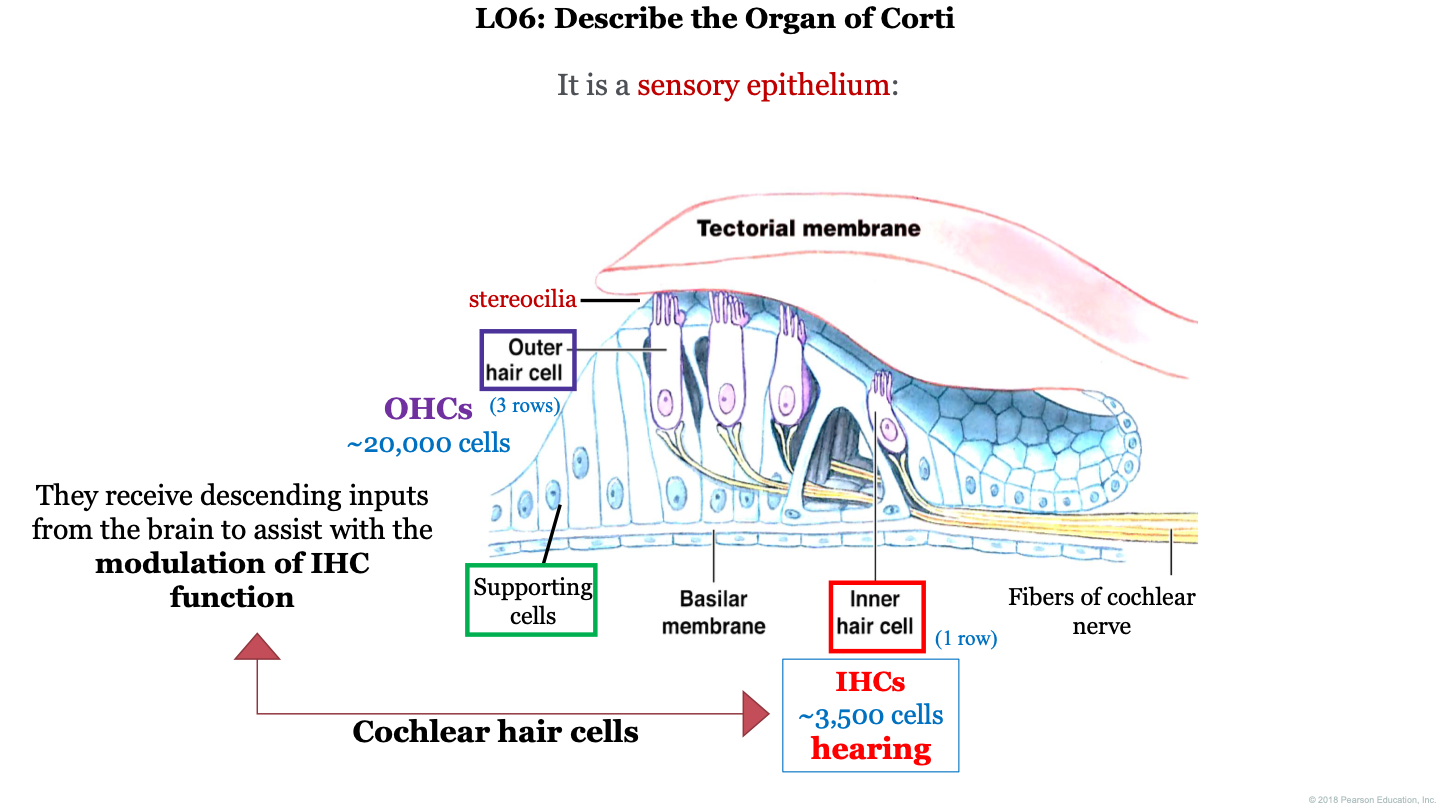
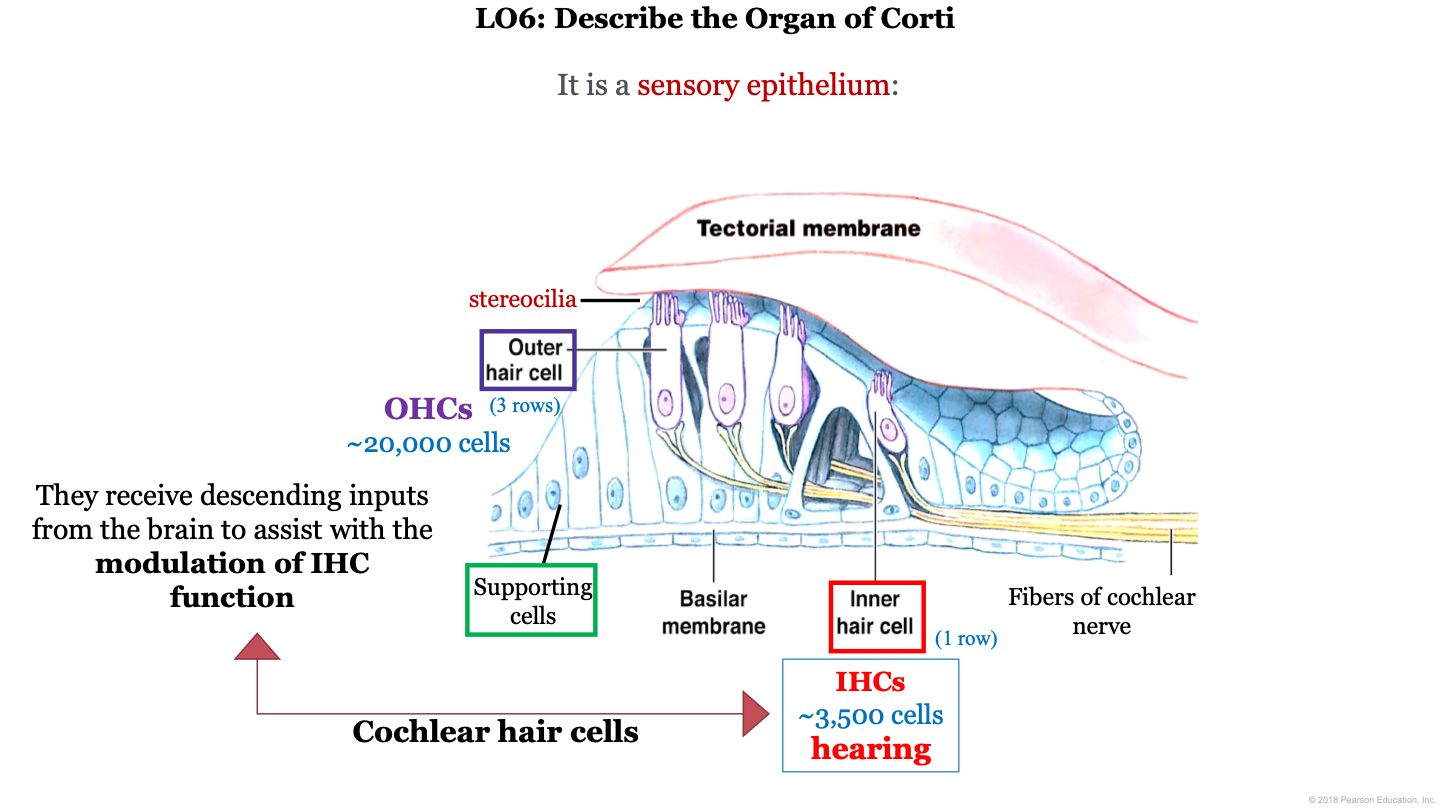
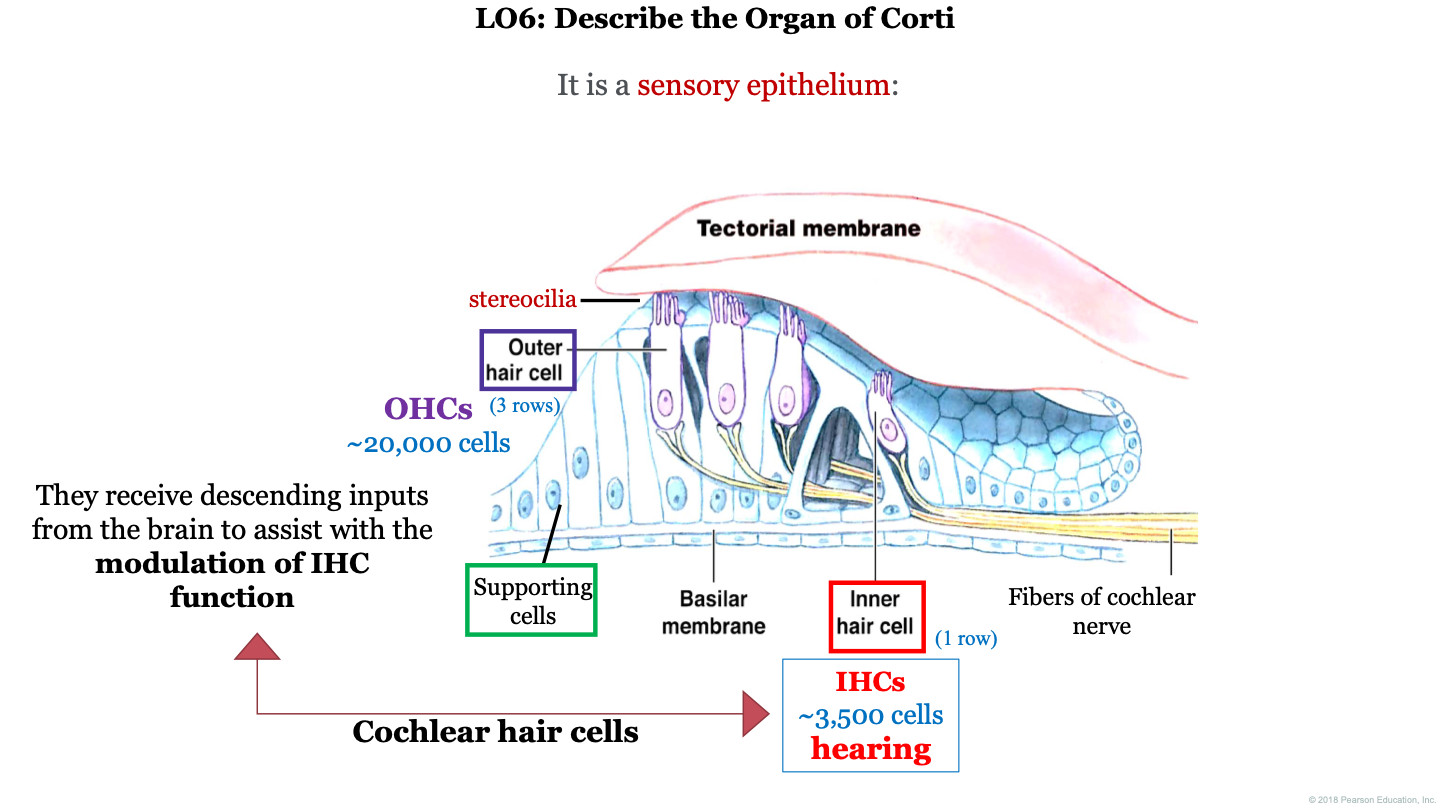
organ of Corti function
receptor organ for hearing; they receive descending inputs from the brain to assist with the modulation of IHC (inner hair cell) function
28
New cards
what is the organ of Corti?
a sensory epithelium
29
New cards
does the organ of Corti have basal/stem cells?
no so this organ can't be regenerated
30
New cards
how many outer hair cells do we have in the organ of Corti?
~20,000
31
New cards
how many inner hair cells do we have in the organ of Corti?
~3,500
32
New cards
what two structures is the organ of Corti found between?
the tectorial membrane (on top) and the basilar membrane (on the bottom)
33
New cards
what are the 3 important cell types to remember in the organ of Corti?
1. outer hair cell (with attached stereocilia)
2. supporting cells
3. inner hair cells
2. supporting cells
3. inner hair cells
34
New cards
how do cochlear hair cells transduce mechanical sound vibrations into electrical signals that are sent to the brain?
1. the cochlea contains liquid; when the stapes hits the cochlea, this causes the liquid to vibrate
2. some specialized cells in the cochlea convert these vibrations into electrical signals which will be sent to our brain
3. movement of cochlear hair cells (mechanoreceptors in the auditory system) relative to stationary structures nearby
4. for both types of cochlear hair cells (IHC, OHC), the mechanical bending of the stereocilia opens K+ channels at the tips of the stereocilia that allow depolarization of the cells
2. some specialized cells in the cochlea convert these vibrations into electrical signals which will be sent to our brain
3. movement of cochlear hair cells (mechanoreceptors in the auditory system) relative to stationary structures nearby
4. for both types of cochlear hair cells (IHC, OHC), the mechanical bending of the stereocilia opens K+ channels at the tips of the stereocilia that allow depolarization of the cells
35
New cards
what causes the stimulation of the cochlear hair cells that allows for the transduction of sound-evoked mechanical vibrations into electrical signals relayed to the brain?
a) hyperpolarization of the cells which activates glutamate release from the vesicles
b) downward movement of the tectorial membrane that compress the cells
c) detaching of the hairs of these cells
d) mechanical deformation of the hair bundle toward the longer stereocilia caused by the upward movement of the basilar membrane
a) hyperpolarization of the cells which activates glutamate release from the vesicles
b) downward movement of the tectorial membrane that compress the cells
c) detaching of the hairs of these cells
d) mechanical deformation of the hair bundle toward the longer stereocilia caused by the upward movement of the basilar membrane
d)
36
New cards
what causes stimulation of the cilia on cochlear cells of the organ of corti?
blended by the tectorial membrane (caused by the movement of the basilar mb)
37
New cards
what causes stimulation of the cilia on the hair cells of the ampullary crest?
blended by the movement of the endolymph
38
New cards
what causes stimulation of the cilia on hair cells of the macula of utricle and sacule?
blended by the heavy gelatinous mb containing otoliths
39
New cards
important concepts for utricle & saccule
1. otoliths
2. macula
3. equilibrium
2. macula
3. equilibrium
40
New cards
important concepts for the semicircular ducts
1. ampulla
2. membranous labyrinth
3. equilibrium
2. membranous labyrinth
3. equilibrium
41
New cards
When you spin while sitting in a swivel chair with your eyes closed, you can sense this movement by means of your __________.
semicircular ducts
42
New cards
important concepts for organ of corti
1. tectorial membrane
2. IHC (inner hair cells)
3. hearing
2. IHC (inner hair cells)
3. hearing
43
New cards
parasympathetic stimulation of the _____________ pupillae results in ________________ constriction of the pupil.
sphincter; constriction
44
New cards
sympathetic stimulation of the _____________ pupillae results in ________________ constriction of the pupil.
dilator; dilation
45
New cards
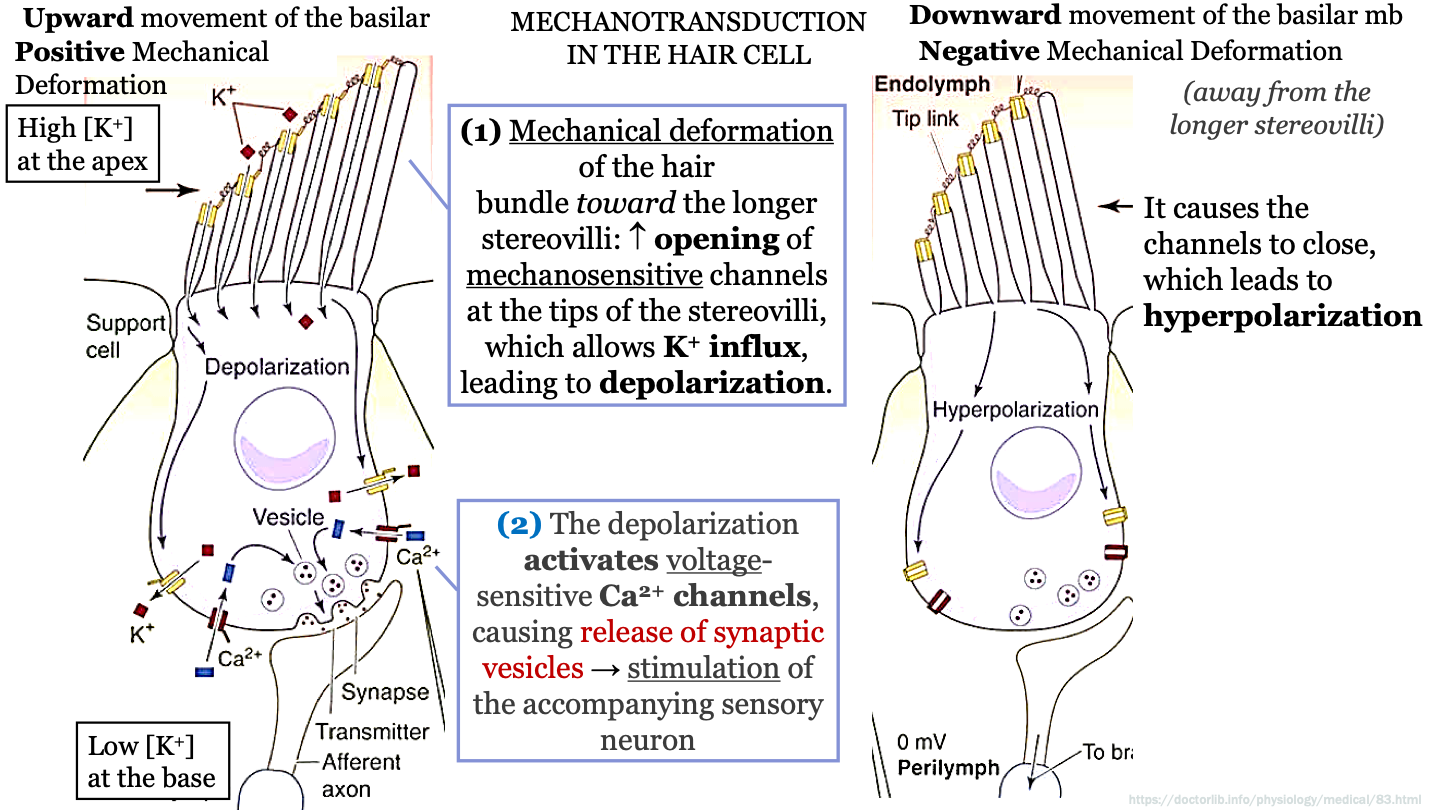
steps mechanotransduction in the hair cell - part 1
-upward movement of the basilar membrane causes positive mechanical deformation of the hair bundle toward the longer sterovilli
-this causes increased opening of mechanosensitive (activated by vibrations) channels at the tops of the stereovilli which allows K+ influx
-this leads to depolarization
-this causes increased opening of mechanosensitive (activated by vibrations) channels at the tops of the stereovilli which allows K+ influx
-this leads to depolarization
46
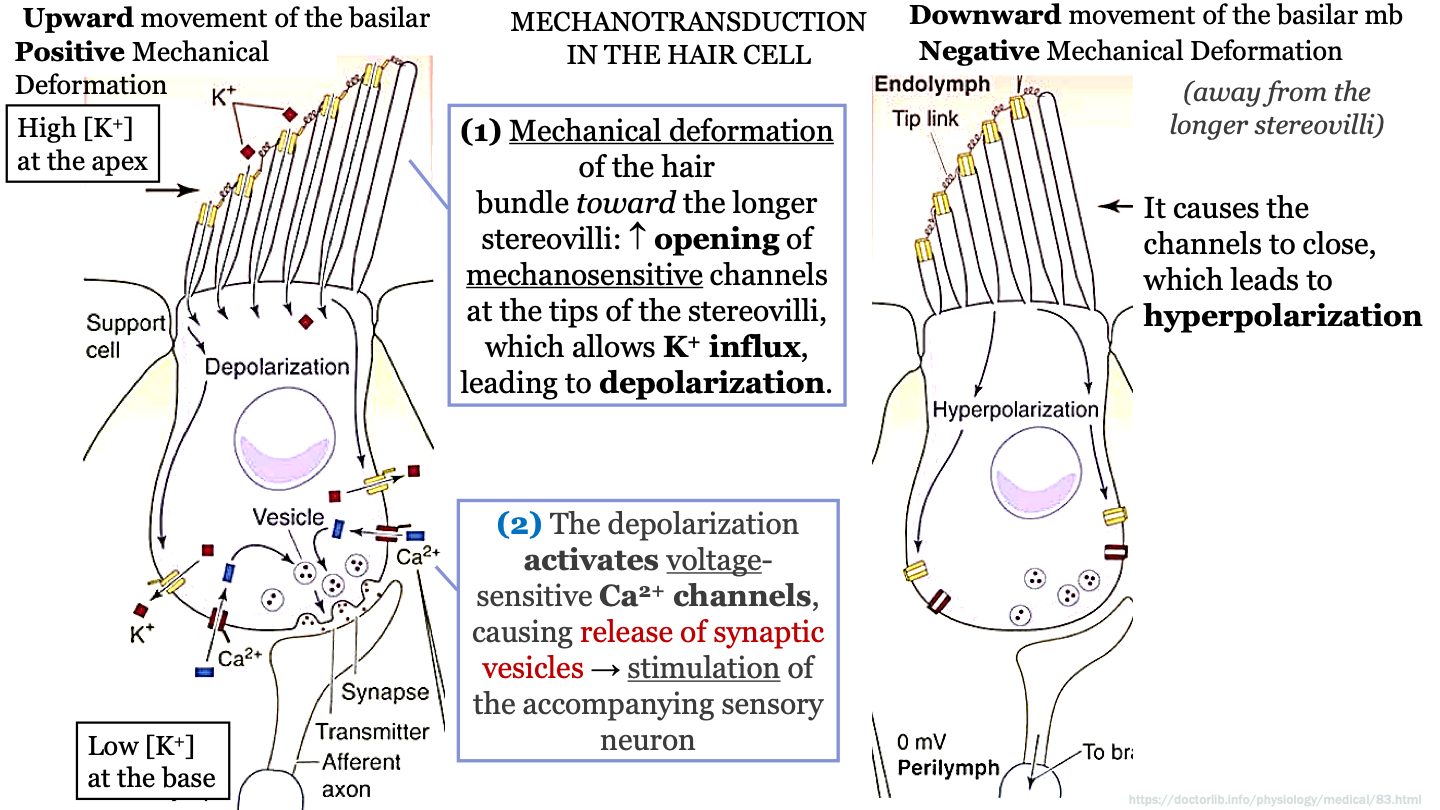
New cards
K+ concentration in hair cell/support cell
K+ concentration is high at the apex and low at the base of the support cell
47
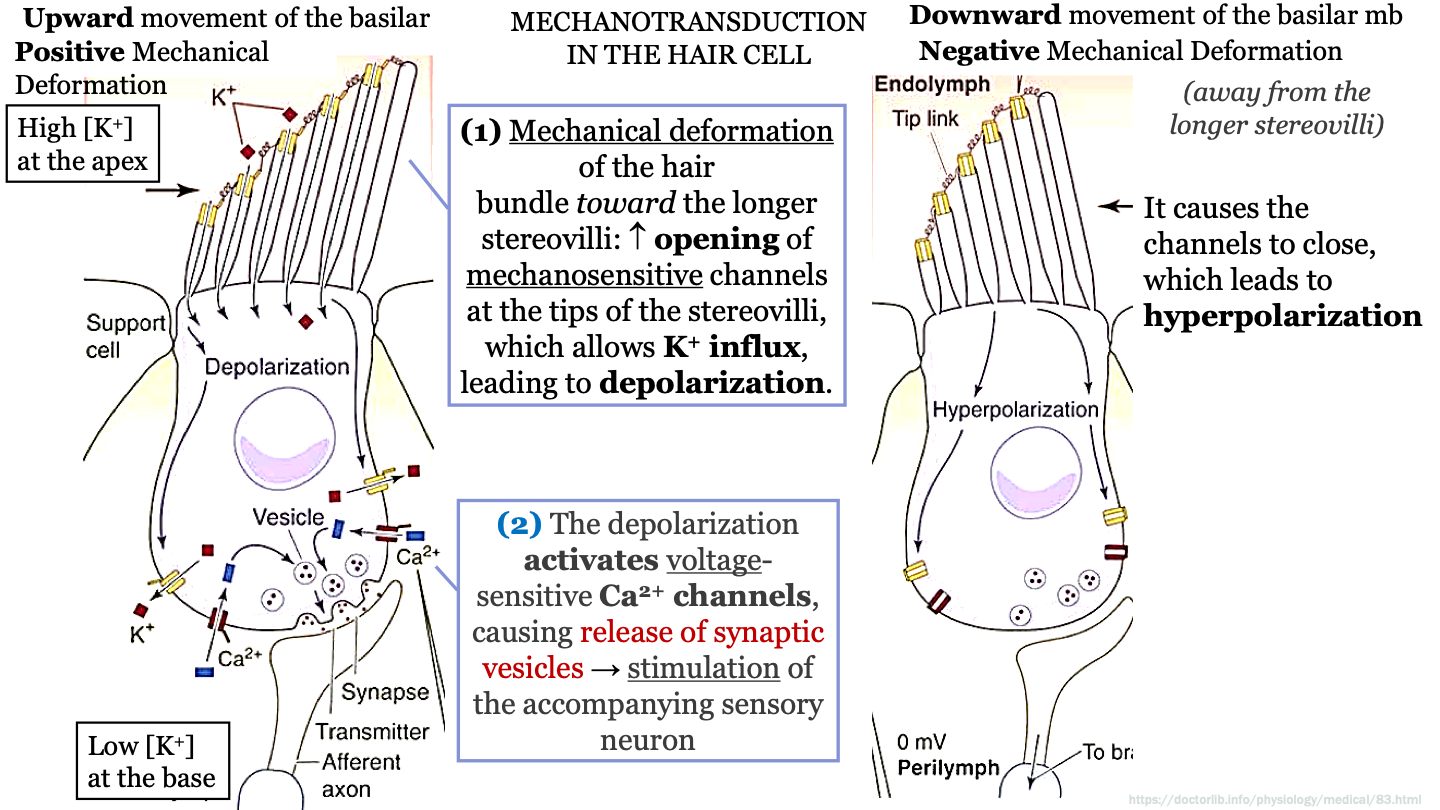
New cards
steps mechanotransduction in the hair cell - part 2
-The doplarization activates voltage-sensitive calcium channels causing release of synaptic vesicles (containing NT's)
-This causes stimulation of the accompanying sensory neuron
-This causes stimulation of the accompanying sensory neuron
48
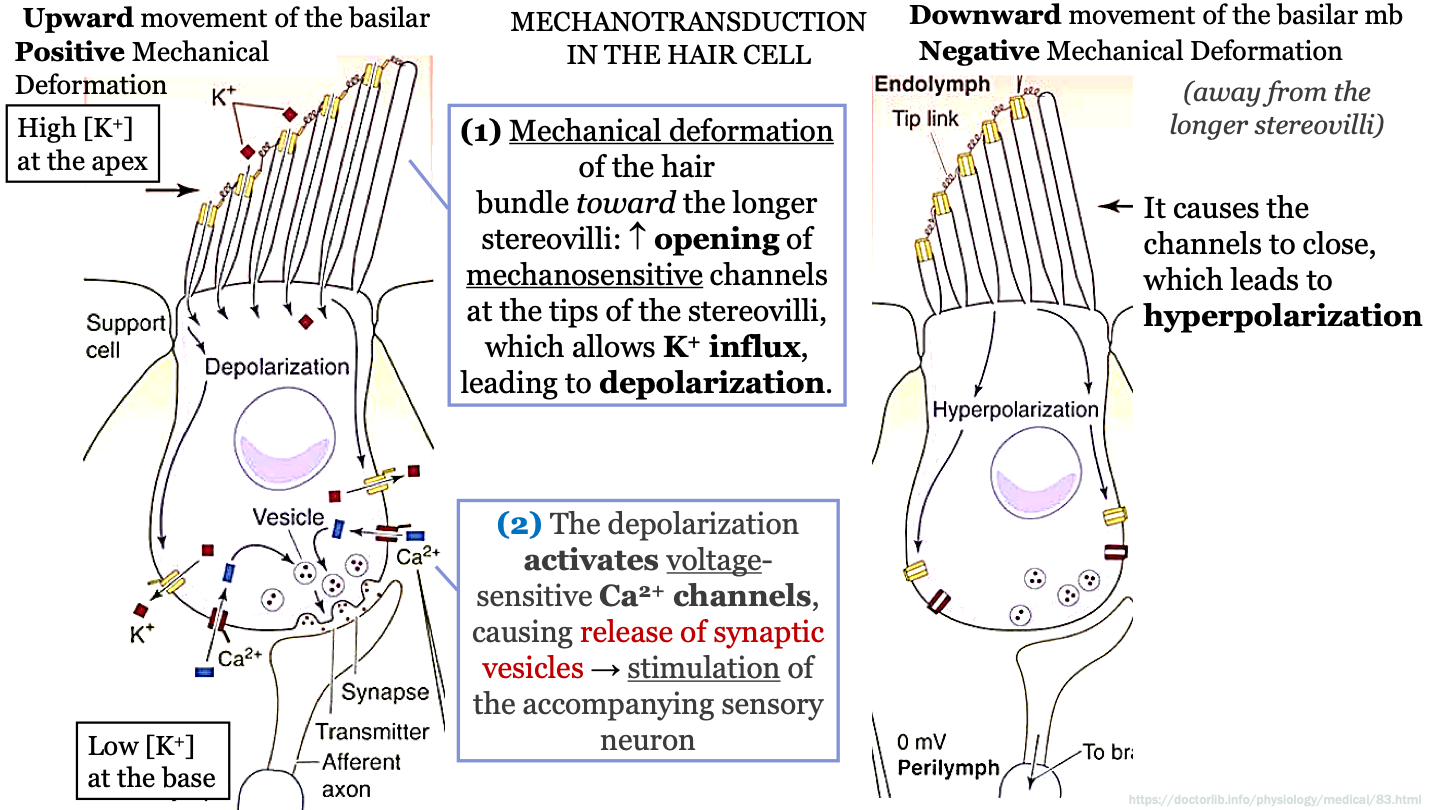
New cards
steps mechanotransduction in the hair cell - part 3
downward movement of the basilar mb causes negative mechanical deformation (shorter hairs move away from longer stereovili)
-this causes the calcium channels to close which leads to hyperpolarization
-now no NT's are being released and no signals are being sent to brain
-this causes the calcium channels to close which leads to hyperpolarization
-now no NT's are being released and no signals are being sent to brain
49
New cards
sequence of the auditory projection pathway - step 1
stimulation of hair cells activates sensory neurons
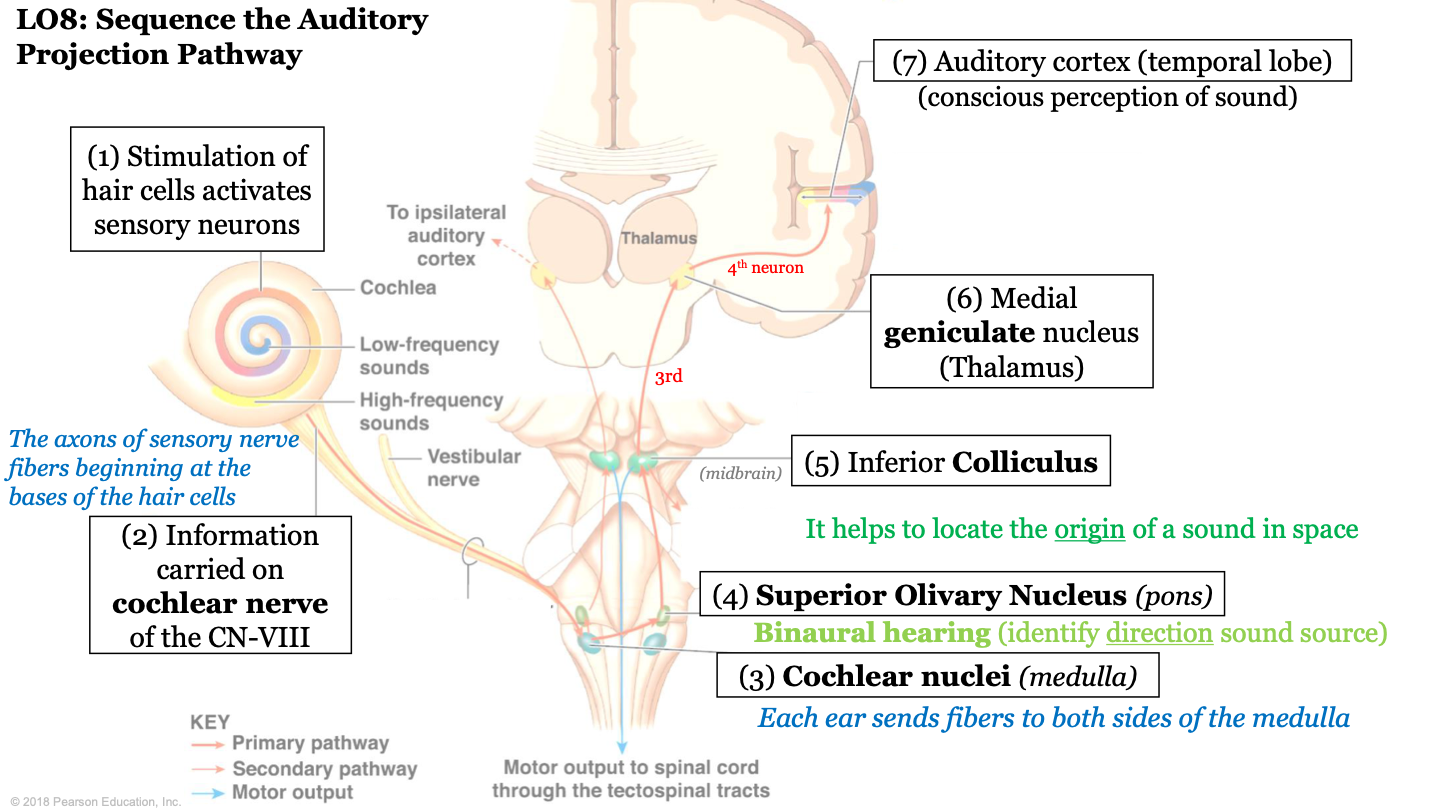
50
New cards
sequence of the auditory projection pathway - step 2
information carried on cochlear nerve of the CN VIII (the axons of sensory nerve fibers beginning at the bases of hair cells)
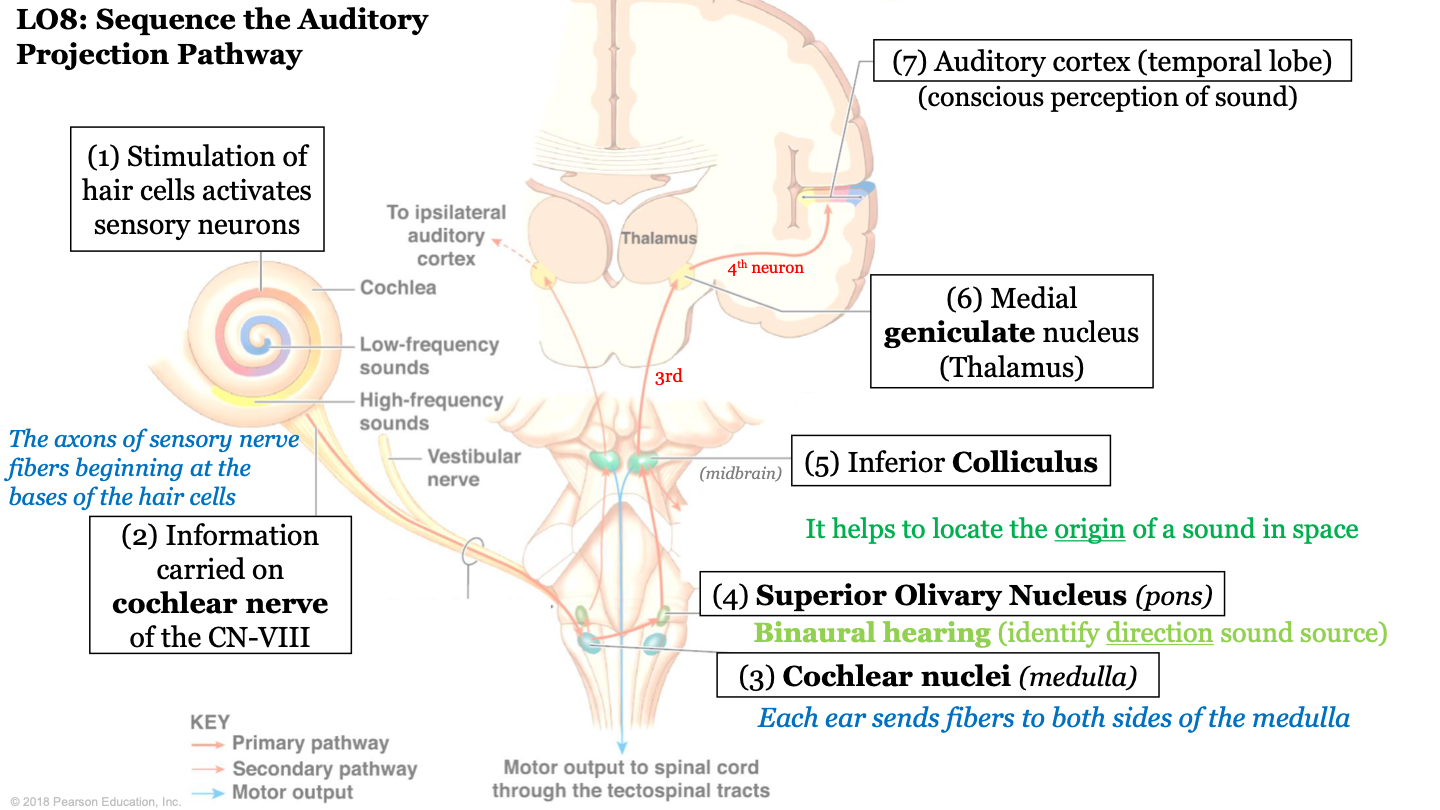
51
New cards
sequence of the auditory projection pathway - step 3
information is sent to the cochlear nuclei (found in medulla); each ear sends fibers to both sides of the medulla
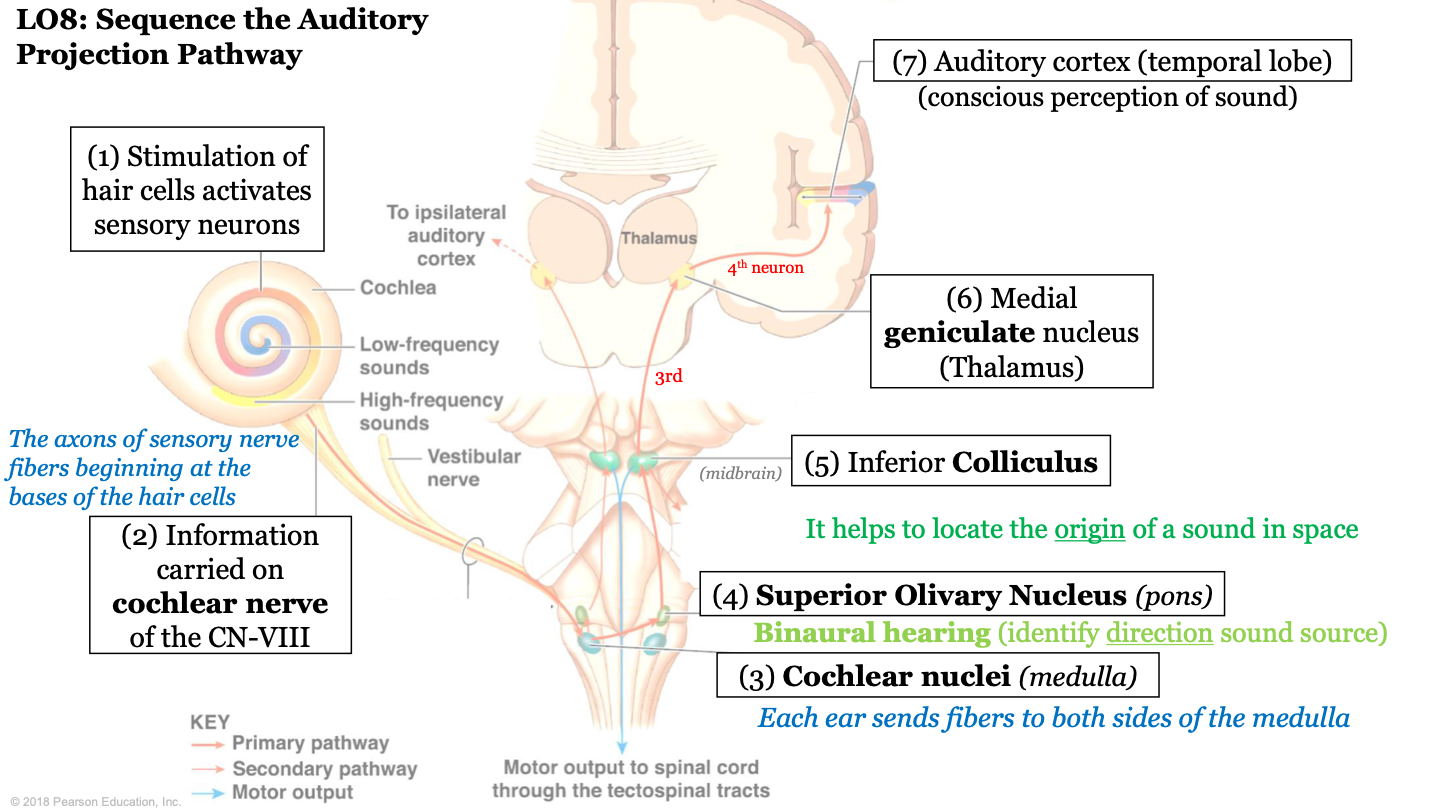
52
New cards
sequence of the auditory projection pathway - step 4
information is sent to the superior olivary nucleus (located in pons); biaural hearing (allows us to identify direction of sound source)
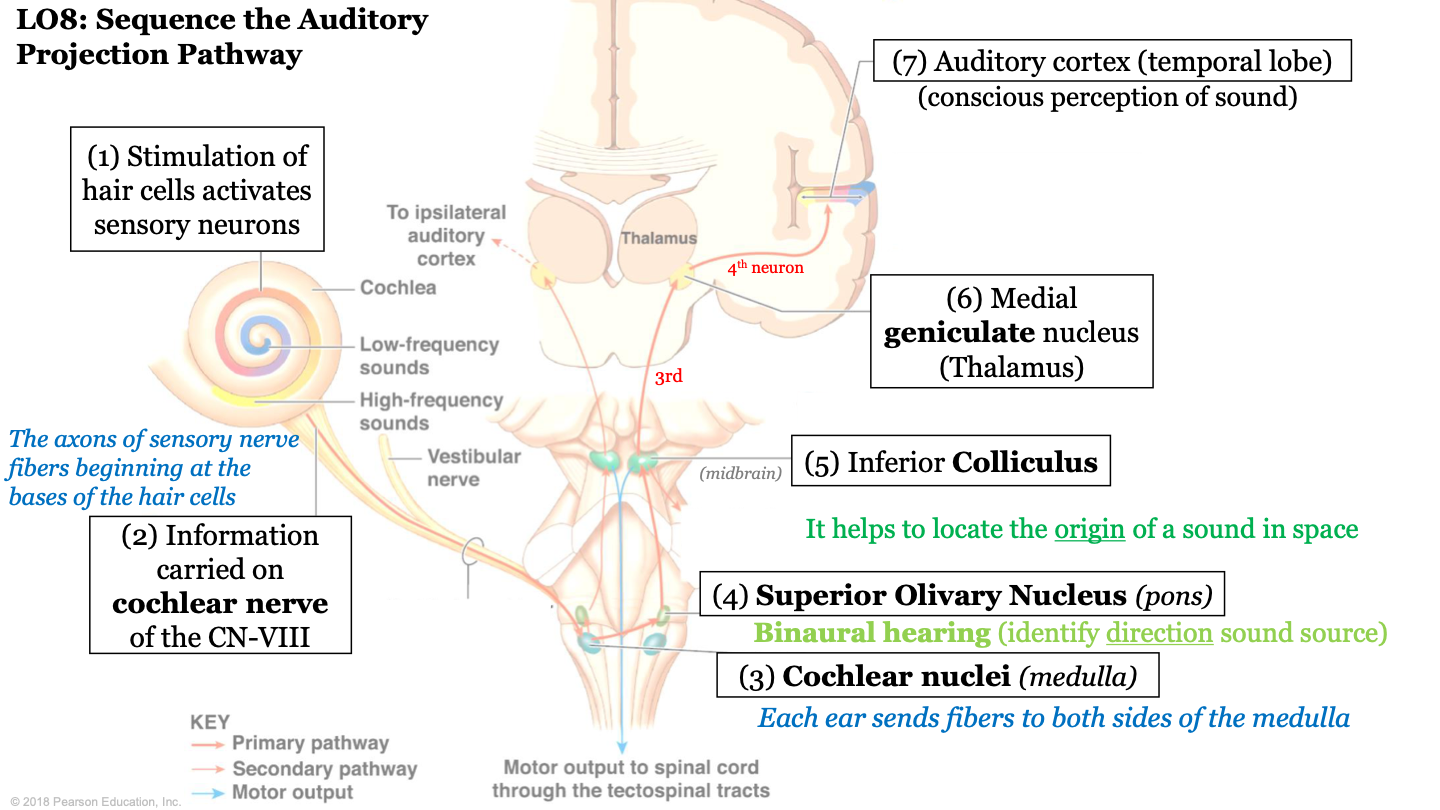
53
New cards
sequence of the auditory projection pathway - step 5
information is sent to the inferior colliculus; it helps locate the origin of a sound in space
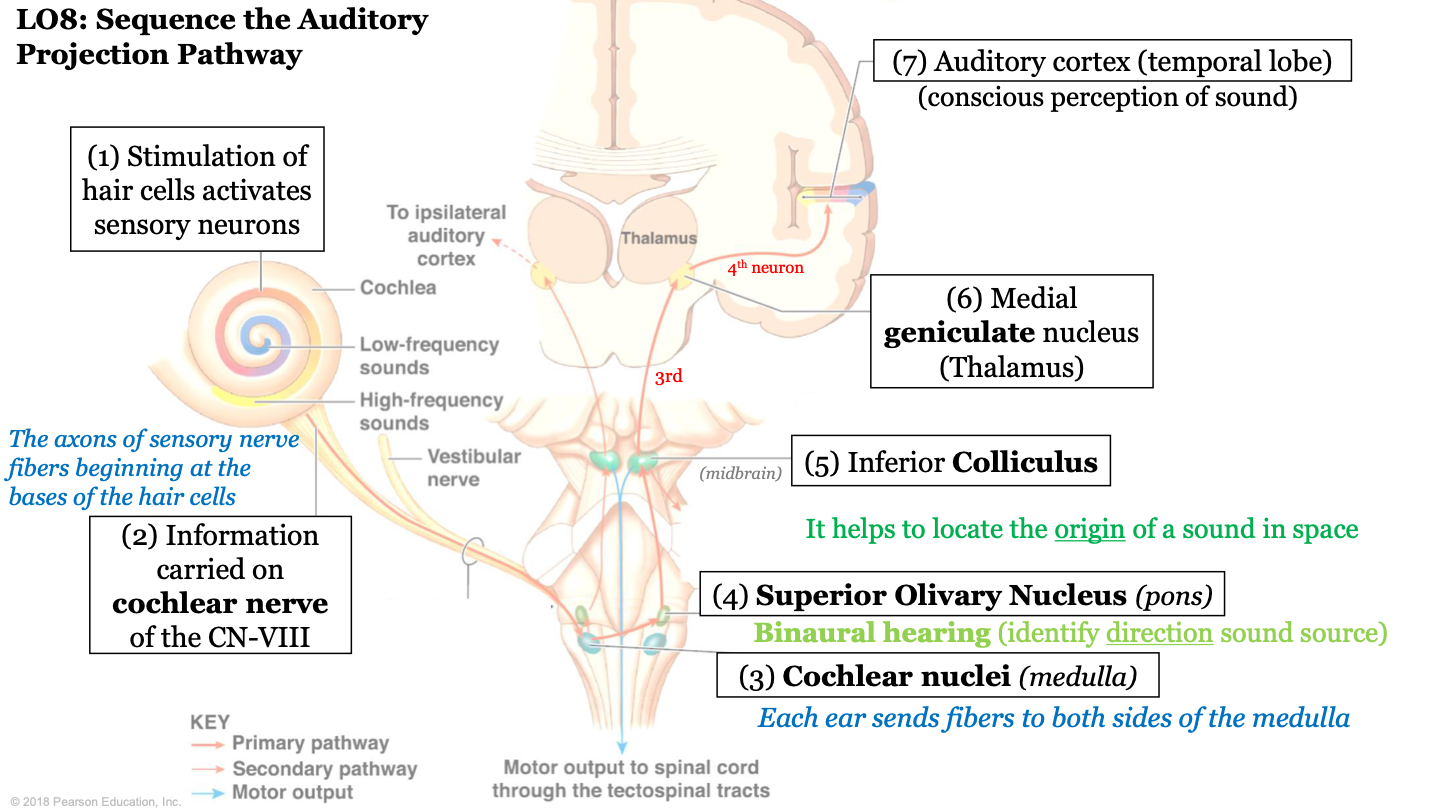
54
New cards
sequence of the auditory projection pathway - step 6
information is sent to the medial geniculate nucleus (located in the thalamus); Making Good Noise!
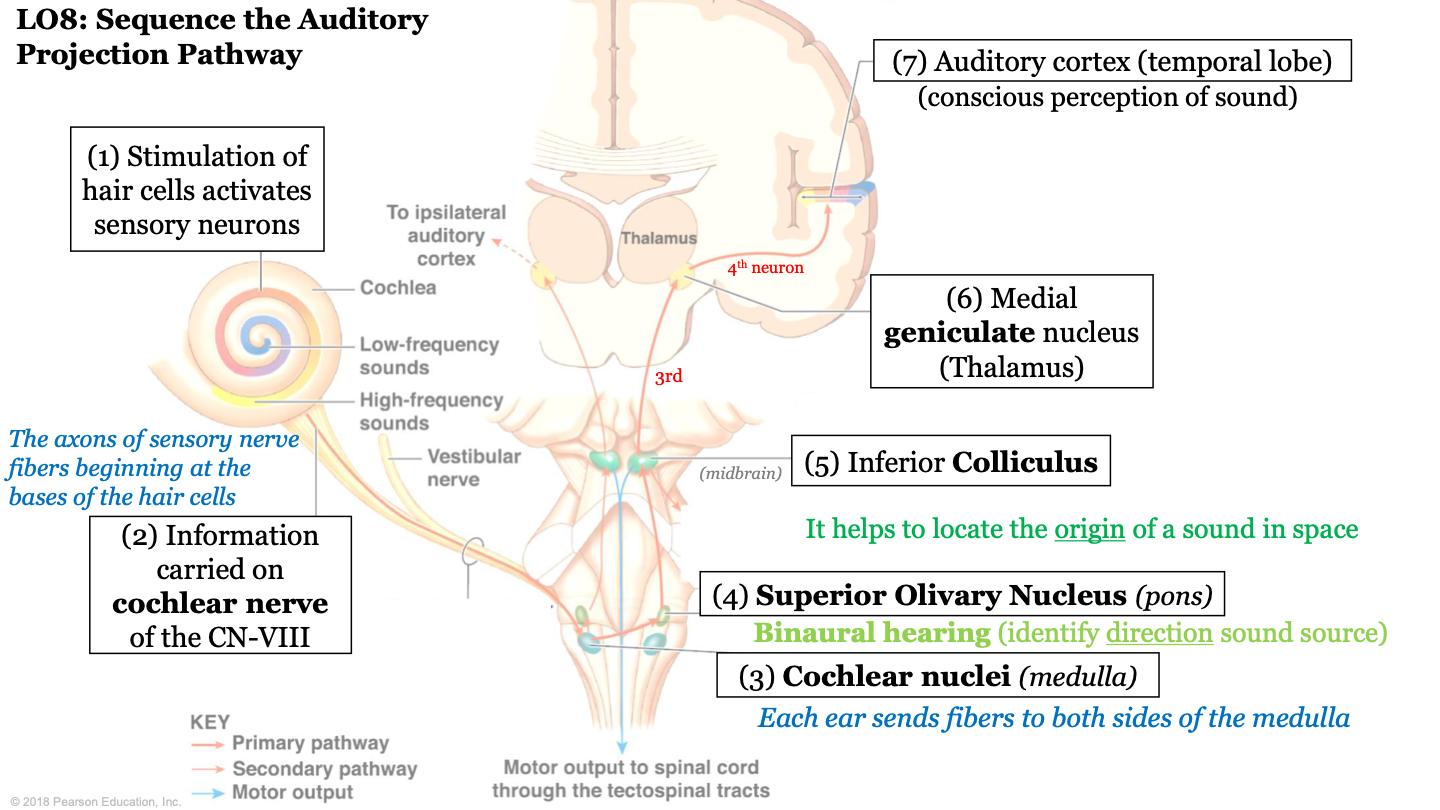
55
New cards
sequence of the auditory projection pathway - step 7
information is sent to the auditory cortex (temporal lobe); conscious perception of sound
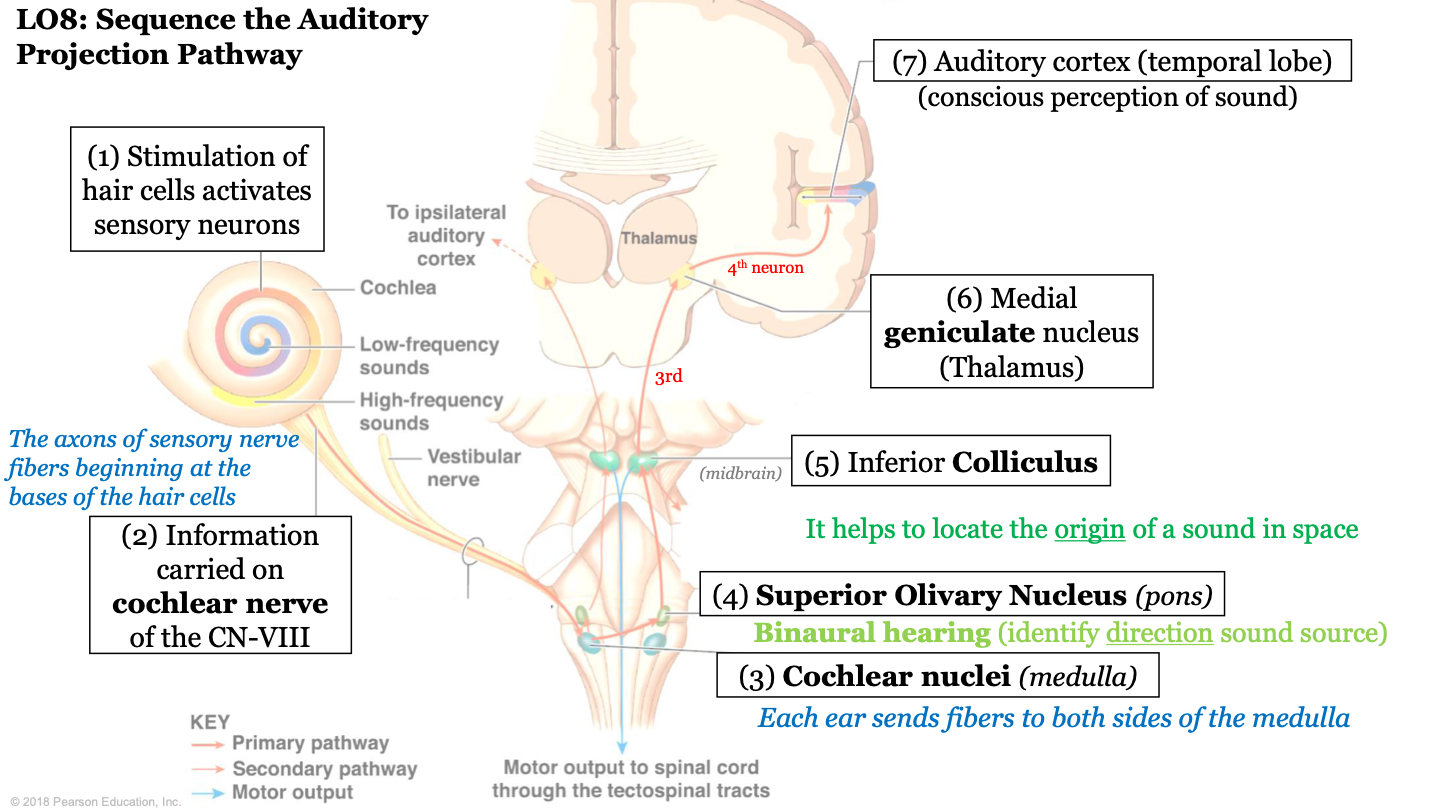
56
New cards
components of vestibular apparatus/complex
-3 semicircular ducts
-2 chambers (otolith organs): utricle and saccule
-2 chambers (otolith organs): utricle and saccule
57
New cards
purpose of vestibular apparatus/complex
maintains balance and awareness of the body's spatial orientation
58
New cards
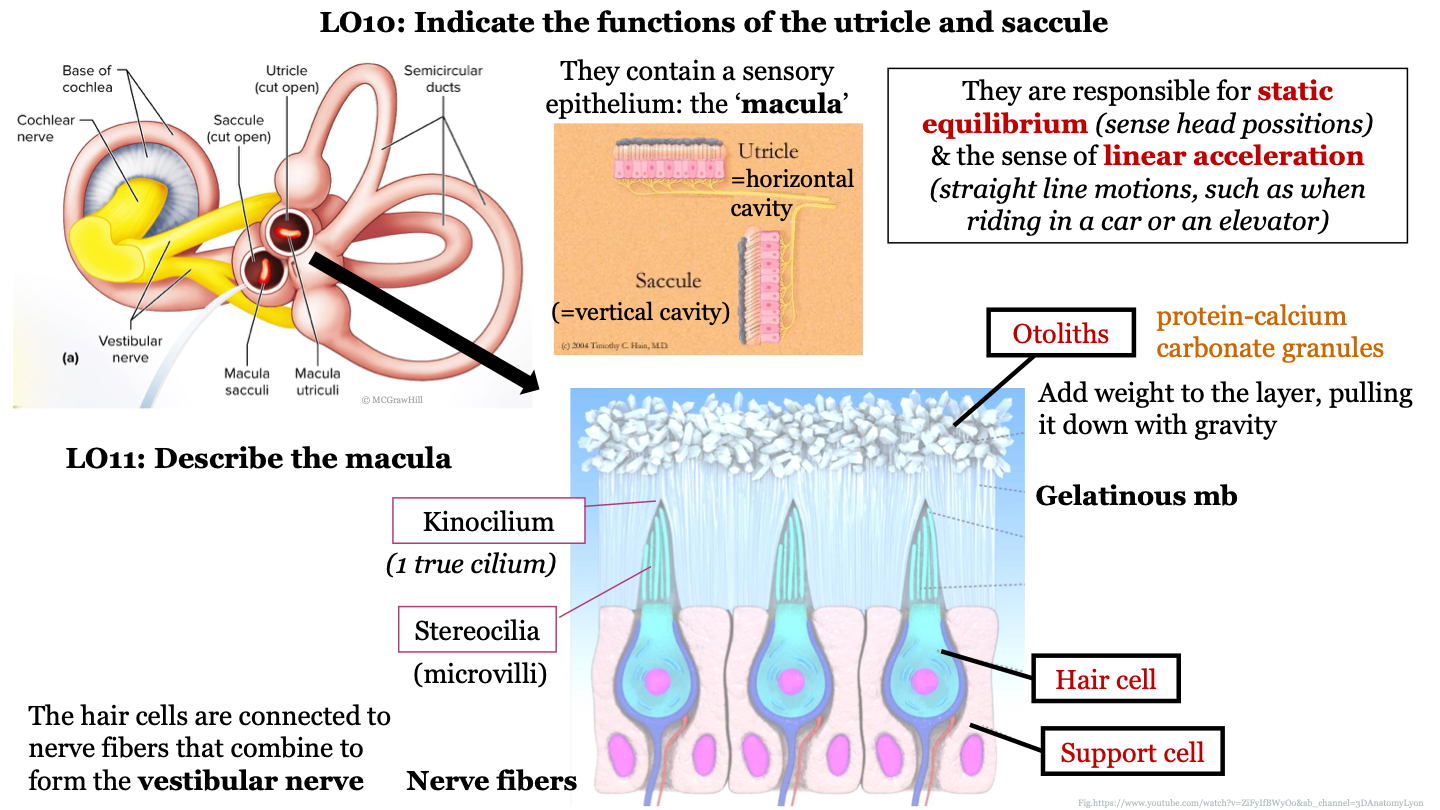
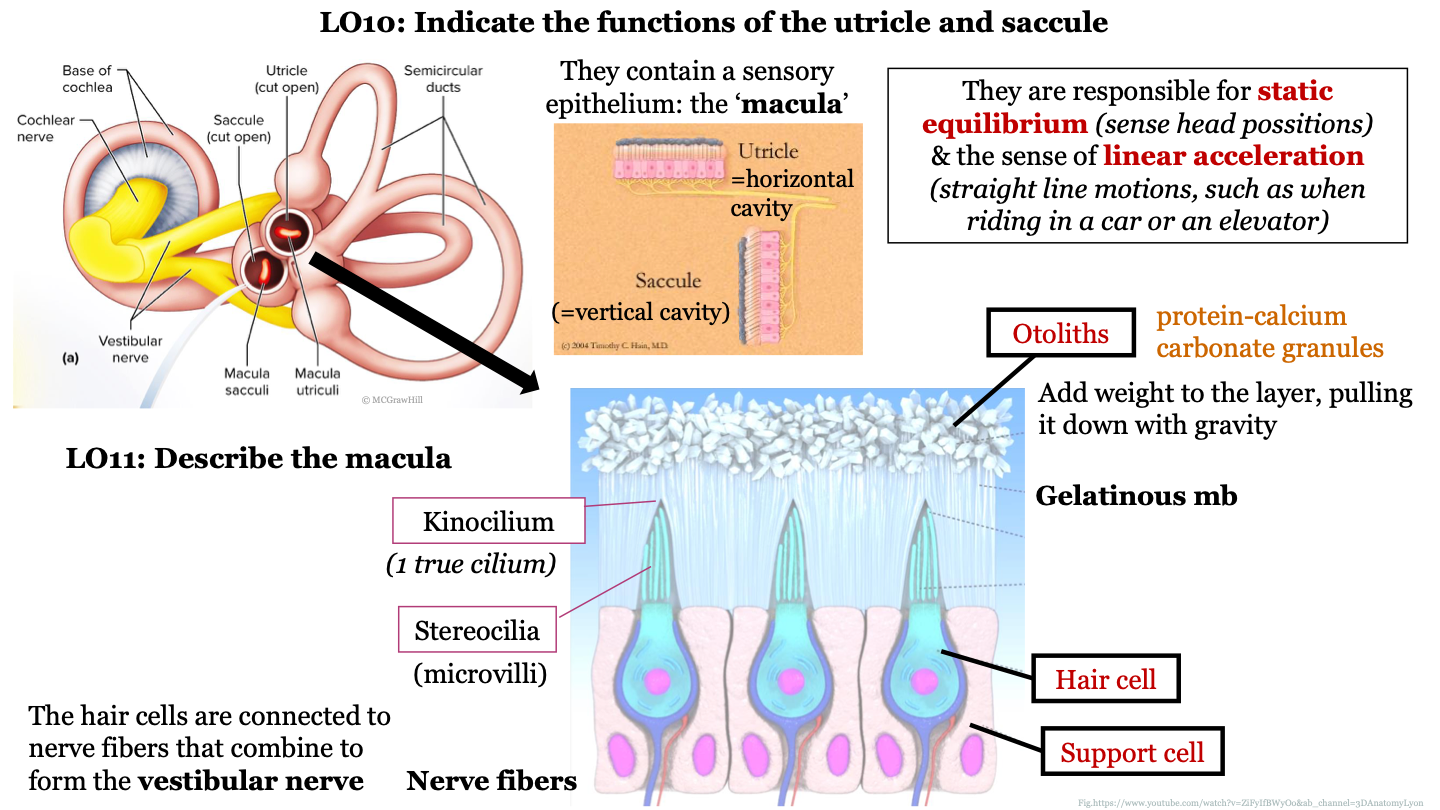
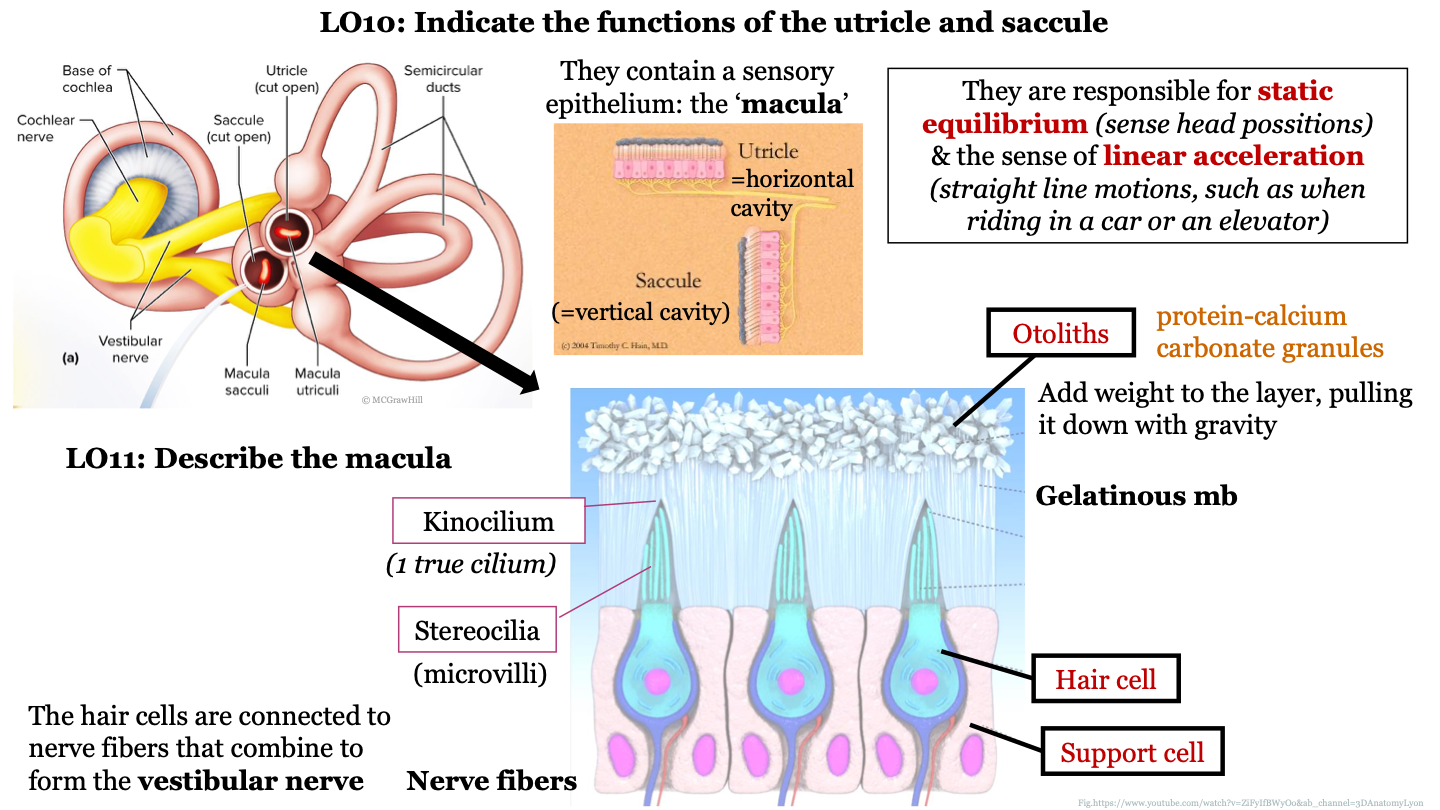
what is the macula?
sensory epithelium found inside the utricle and sacule
59
New cards
the utricle is a horizontal/vertical cavity?
horizontal; detects linear accelerations and head tilts in the horizontal plane
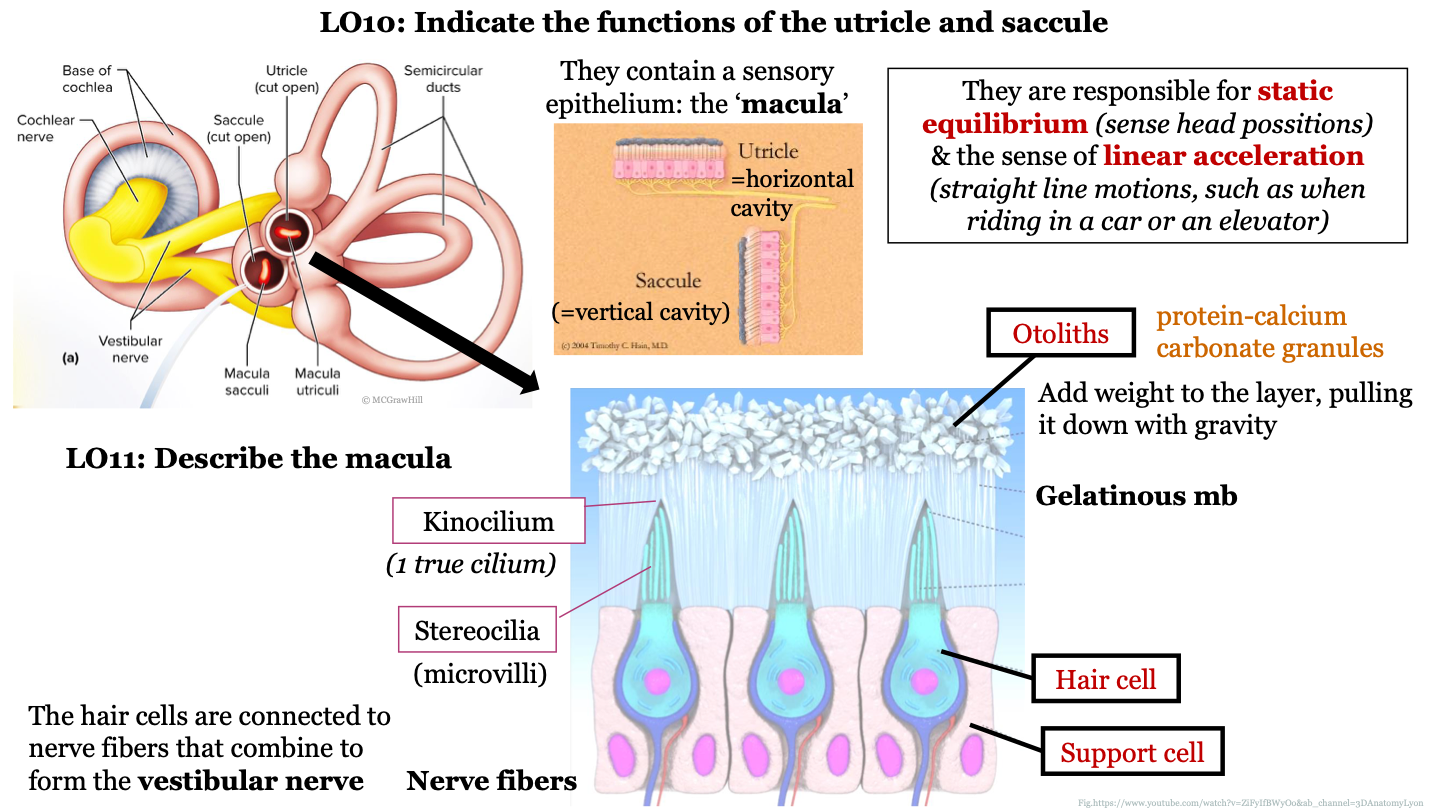
60
New cards
the saccule is a horizontal/vertical cavity?
vertical; detects vertical accelerations and head tilts in the vertical plane
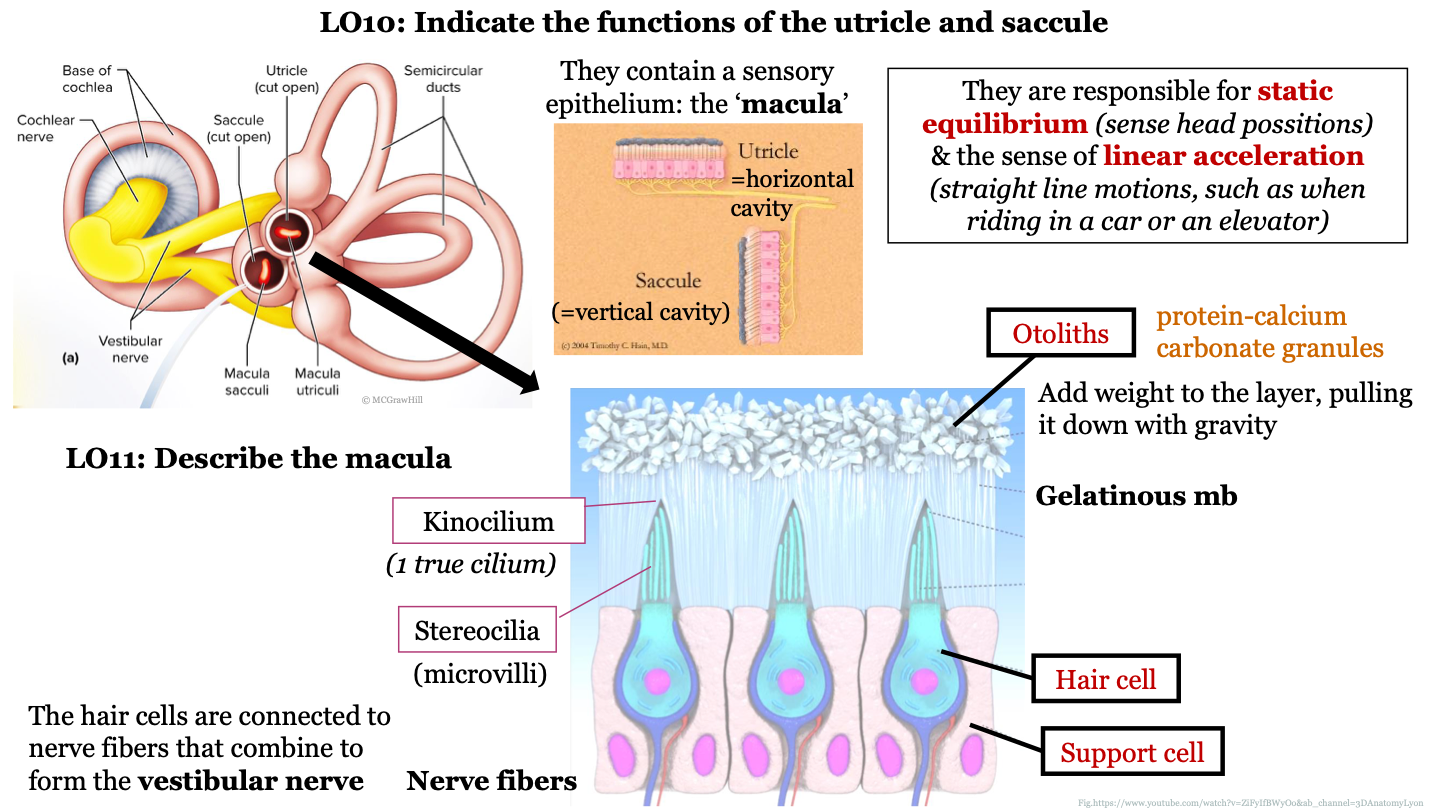
61
New cards
function of utricle and saccule
they are responsible for static equilibrium (sense head positions) and the sense of linear acceleration (straight line motions, such as when riding in a car or on an elevator)
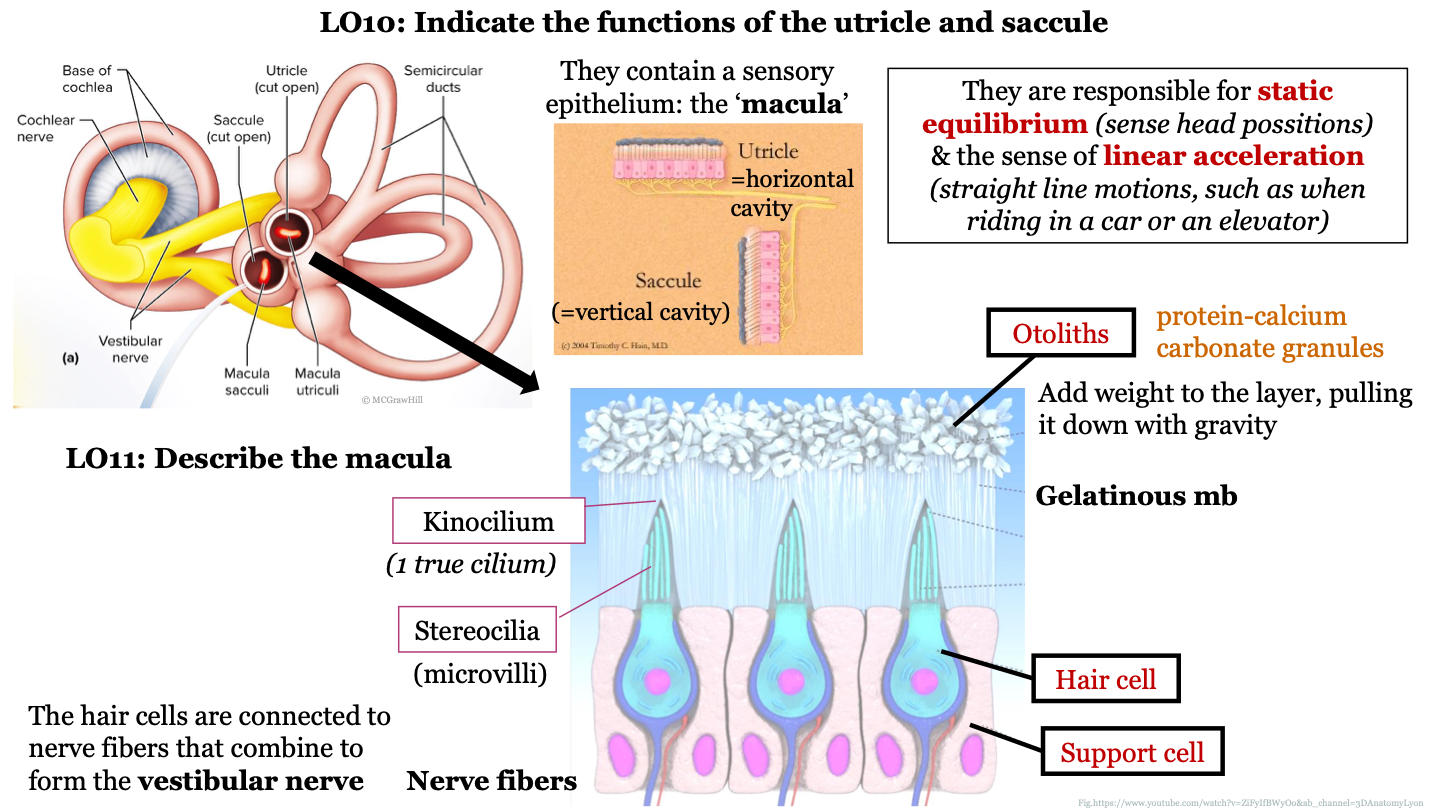
62
New cards
structure of macula
epithelium that contains hair cells that are embedded in support cells; the hair cells are connected to nerve fibers that combine to form the vestibular nerve; the hair cells have stereocilia at their surface which are surrounded by a gelatinous membrane; the tips of the stereocilia are called kinocilium; otoliths are found on top of the gelatinous membrane
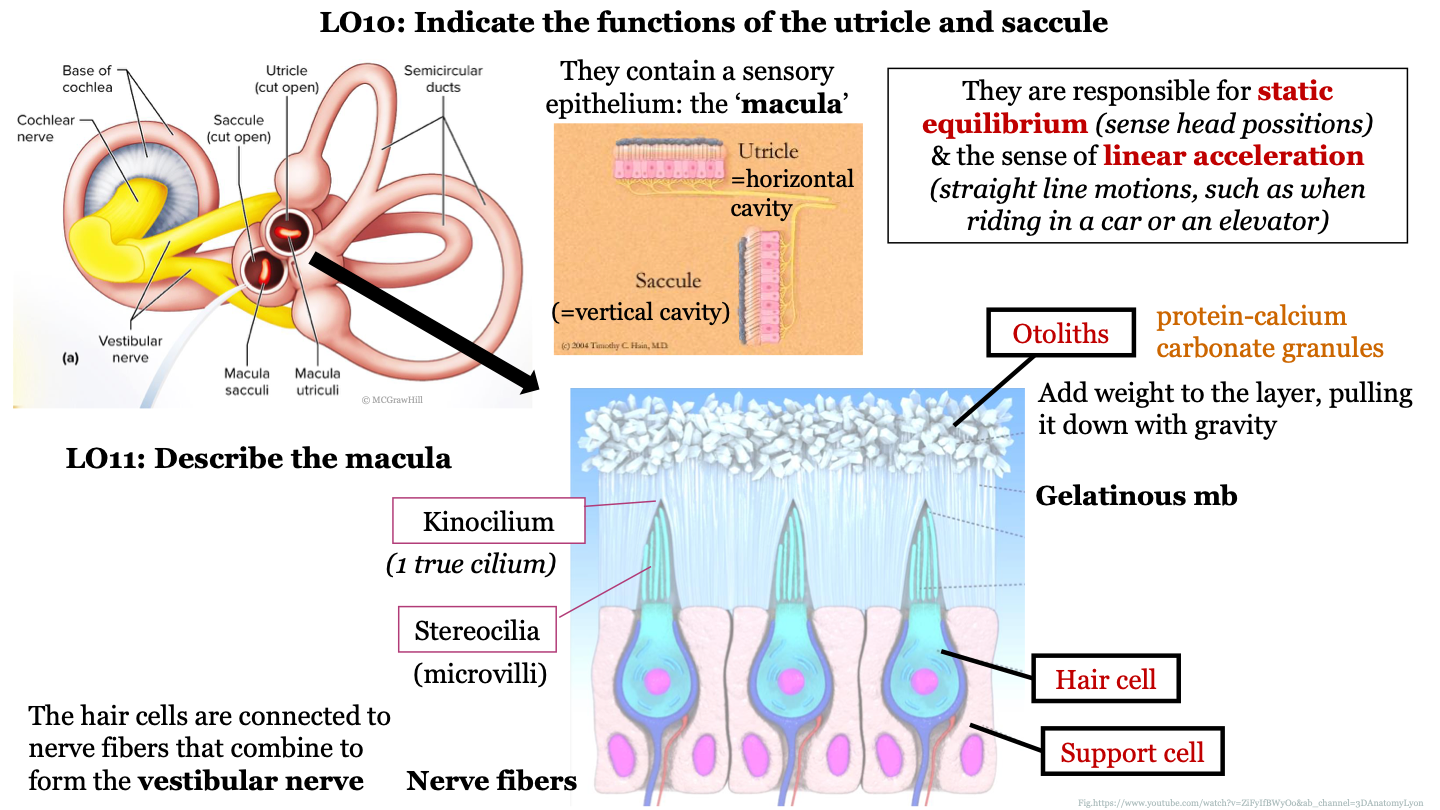
63
New cards
what are otoliths?
protein-calcium carbonate granules
64
New cards
what do otoliths do in the macula?
they add weight to the layer, pulling it down with gravity
65
New cards
1 true cilium
kinocilium
66
New cards
what are stereocilia AKA?
microvilli
67
New cards
how does the macula and utriculi detect head tilt?
when you tilt your head down to read a book, the heavy gelatinous mb (containing otoliths) is pulled downwards by gravity and this bends the stereocilia, stimulating the hair cells
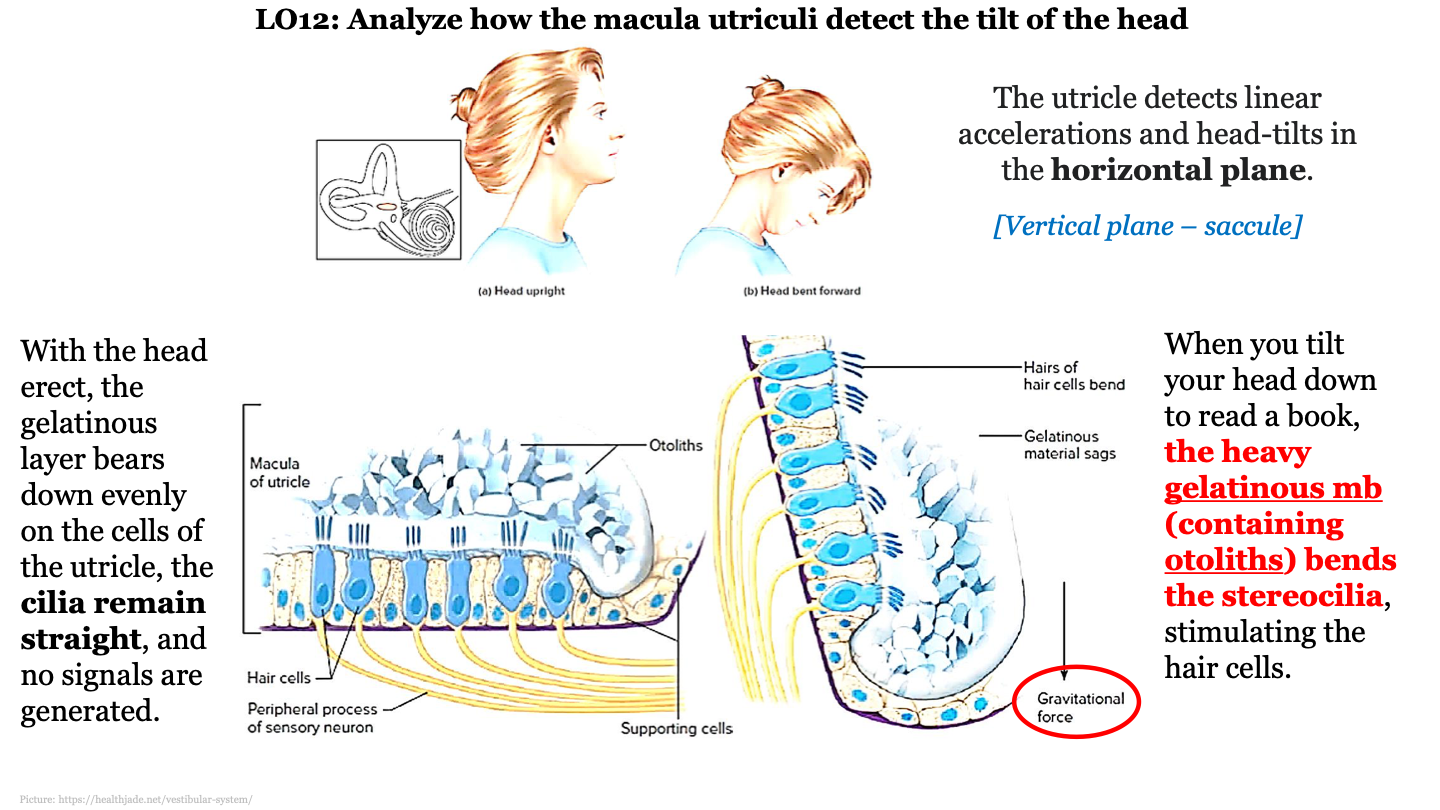
68
New cards
what does the macula do when we aren't tilting our head?
with the head erect, the gelatinous layer bears down evenly on the cells of the utricle, the cilia remain straight and no signals are generated
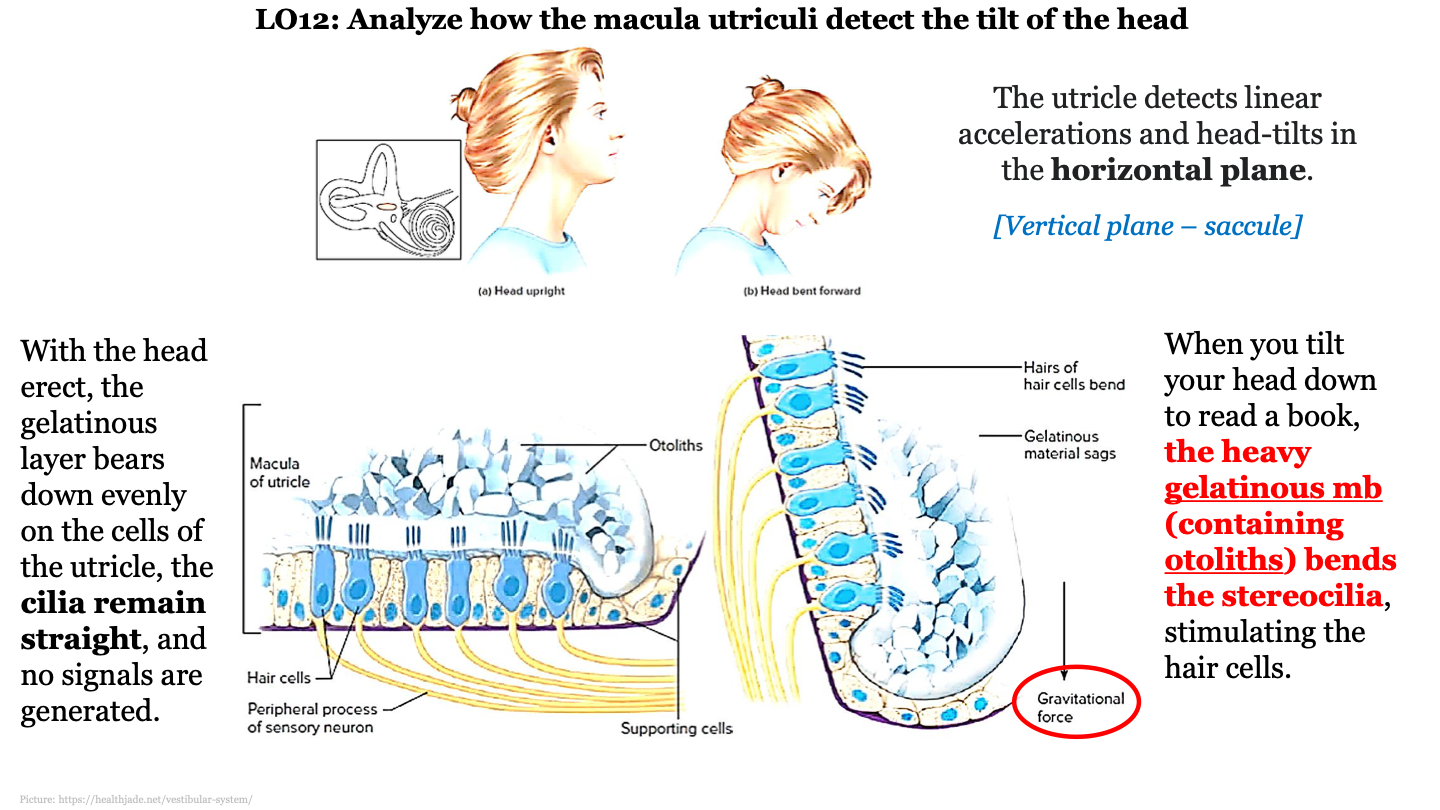
69
New cards
what is the ampula?
a bulbous expansion at the base of each semicircular canal
70
New cards
what does the ampula house?
the sensory epithelium or crista, that contains the hair cells
71
New cards
what fills the ducts of bony semicircular canals?
endolymph
72
New cards
which type of movement does the semicircular ducts and ampulla detect?
rotational movement (angular acceleration); rotation of the head in different planes stimulates a different duct
73
New cards
what causes stereocilia to move in the ampulla?
the movement of endolymph through the duct (caused by rotation of the head) will move the stereocilia in the hair cells of the ampulla
74
New cards
ampulla structure
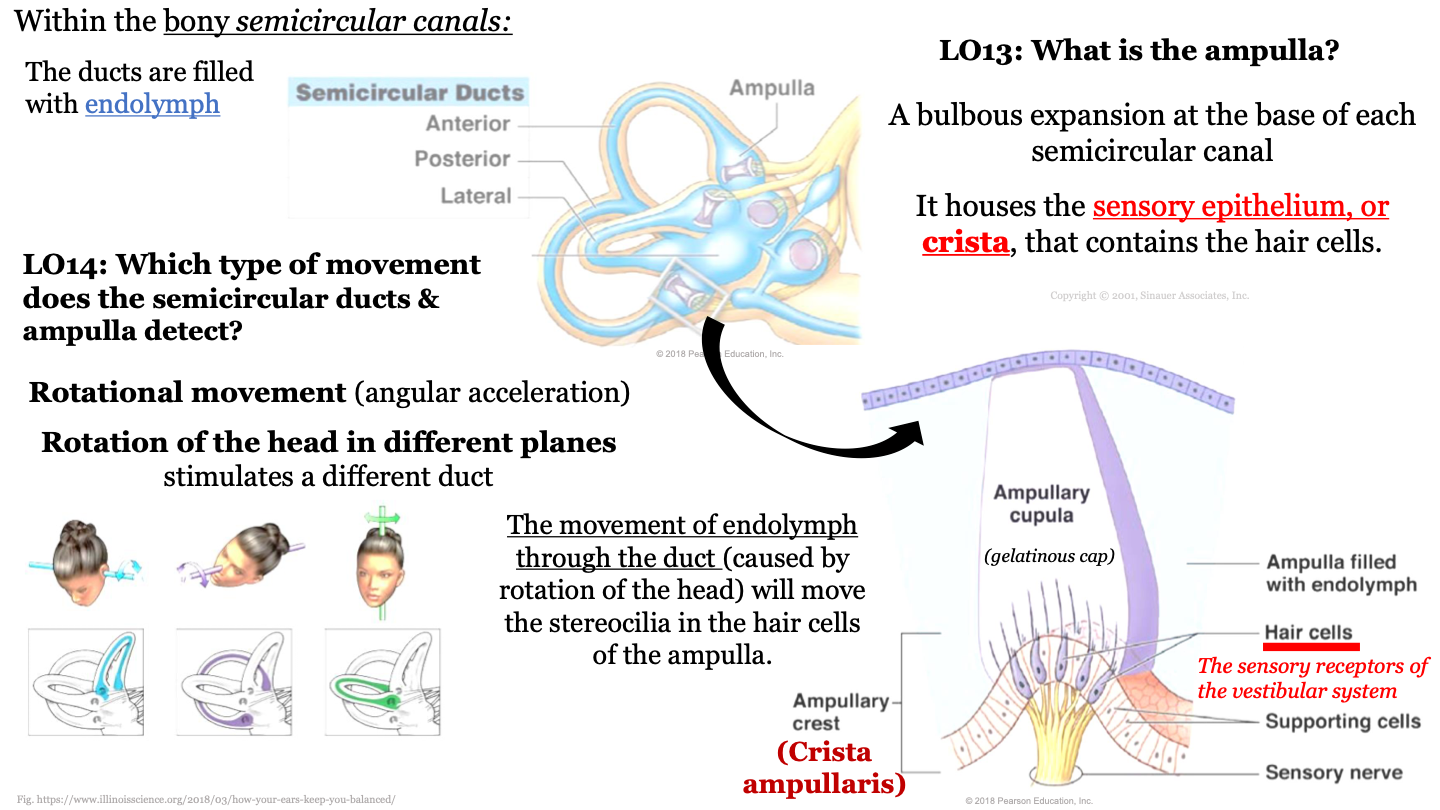
75
New cards
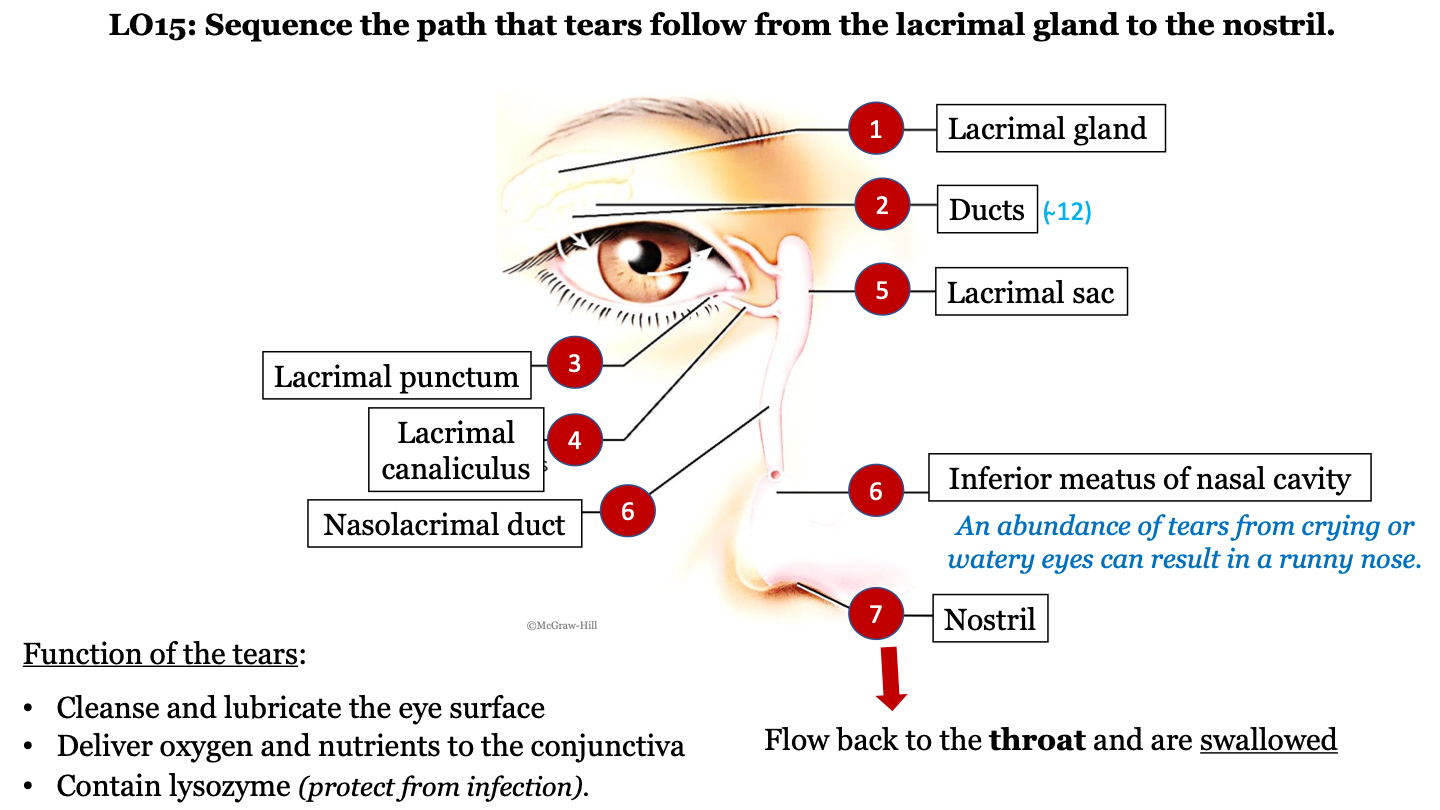
tear pathway - 1
lacrimal gland
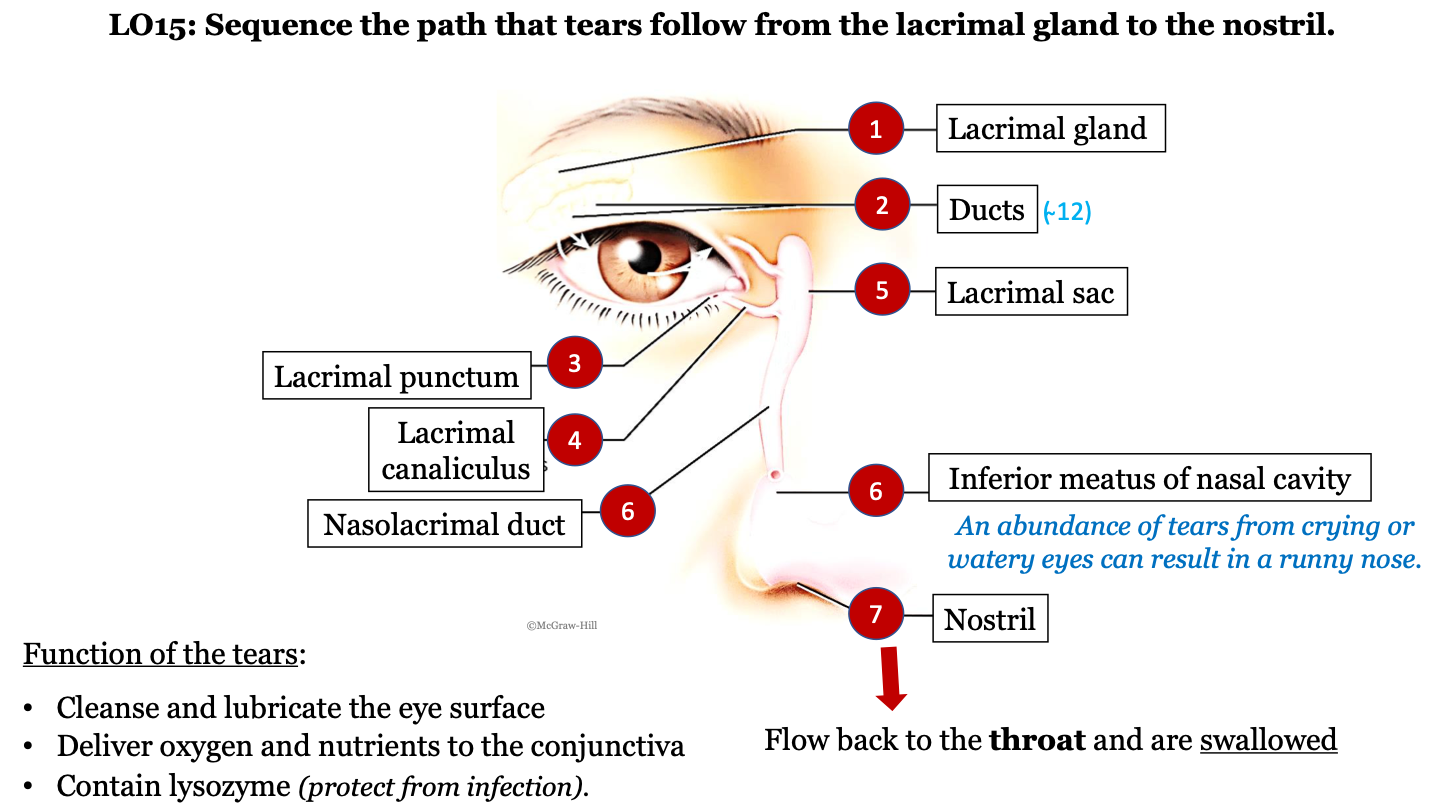
76
New cards
tear pathway - 2
ducts (there are ~12)
77
New cards
tear pathway - 3
lacrimal punctum
78
New cards
tear pathway - 4
lacrimal canaliculus
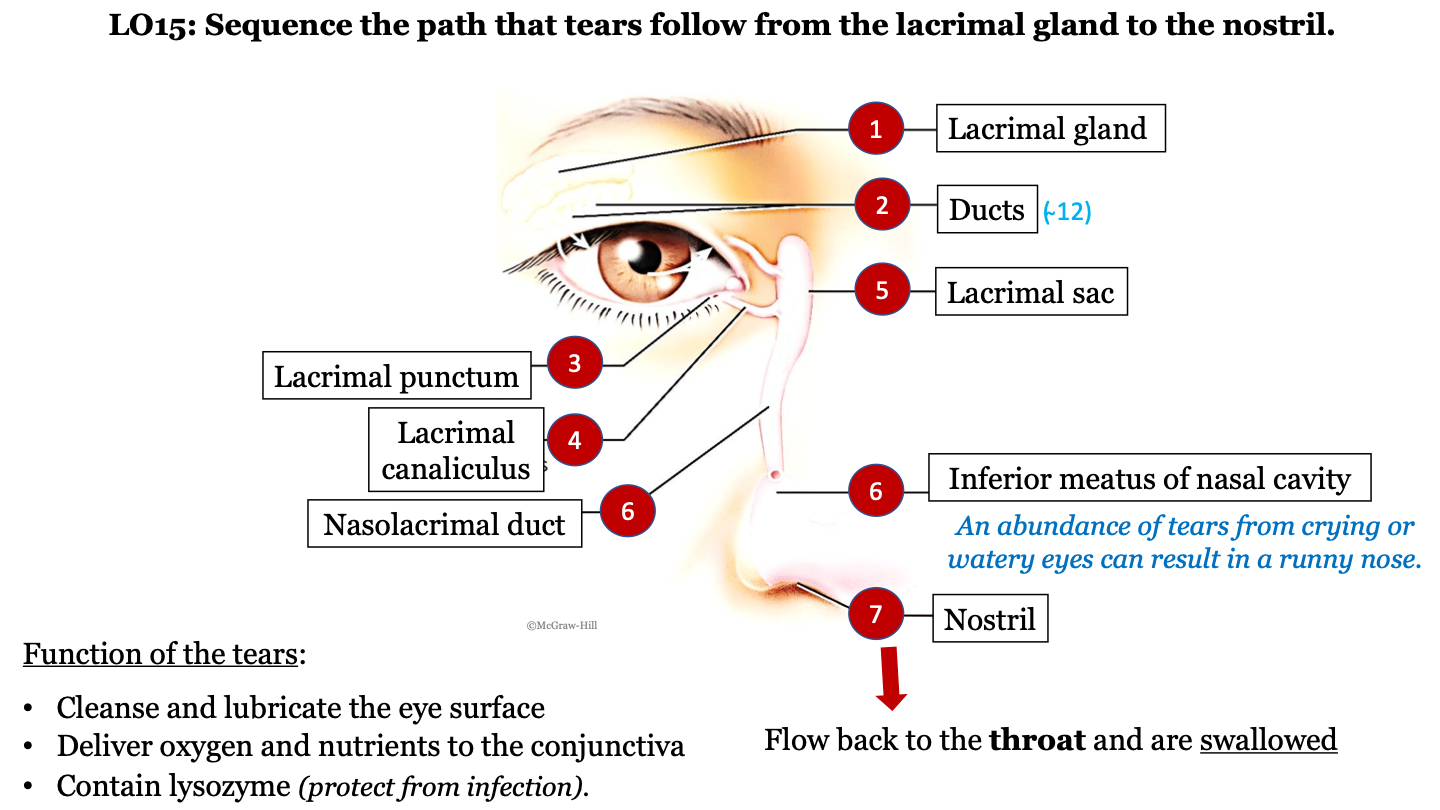
79
New cards
tear pathway - 6
nasolacrimal duct
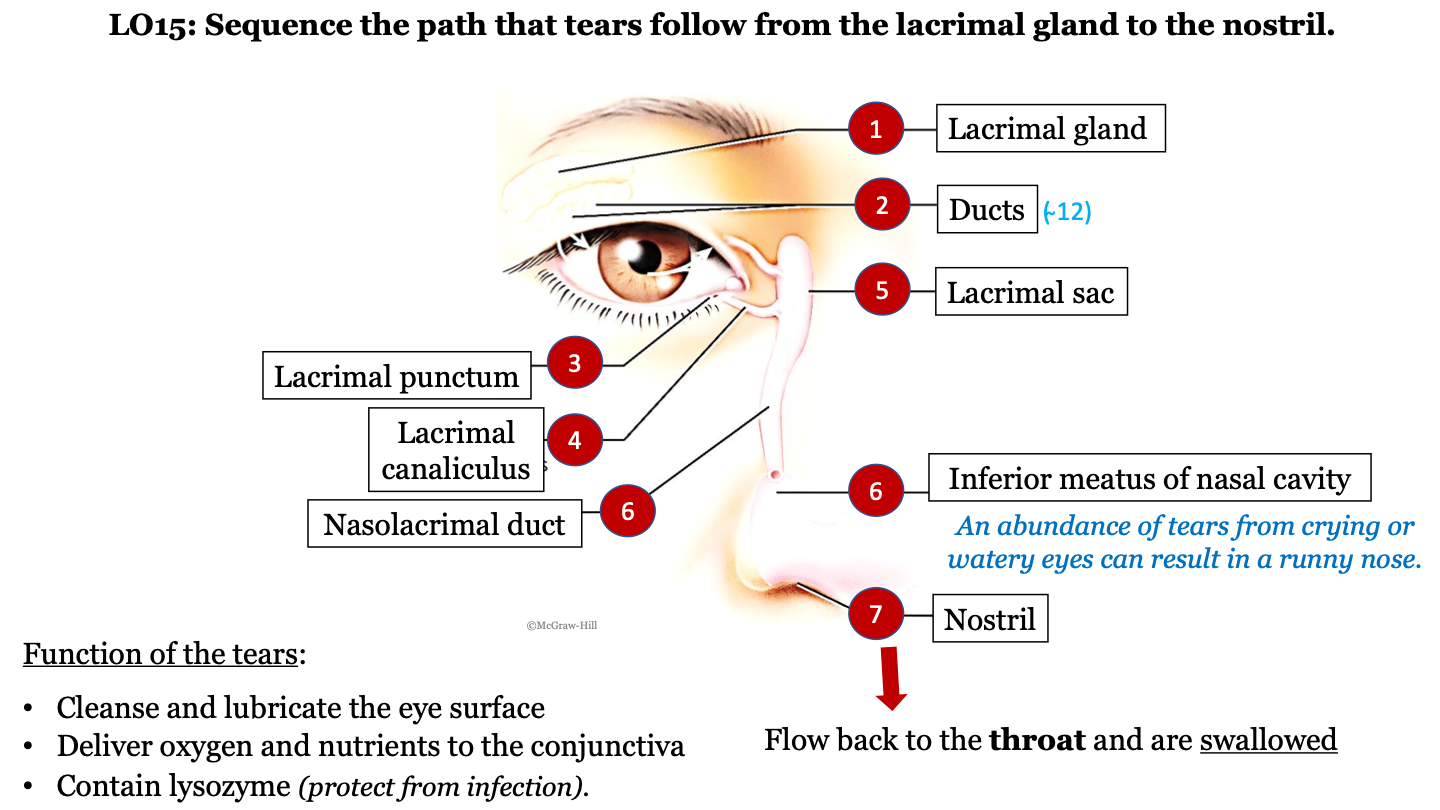
80
New cards
tear pathway - 7
inferior meatus of nasal cavity; an abundance of tears from crying or watery eyes can result in a runny nose
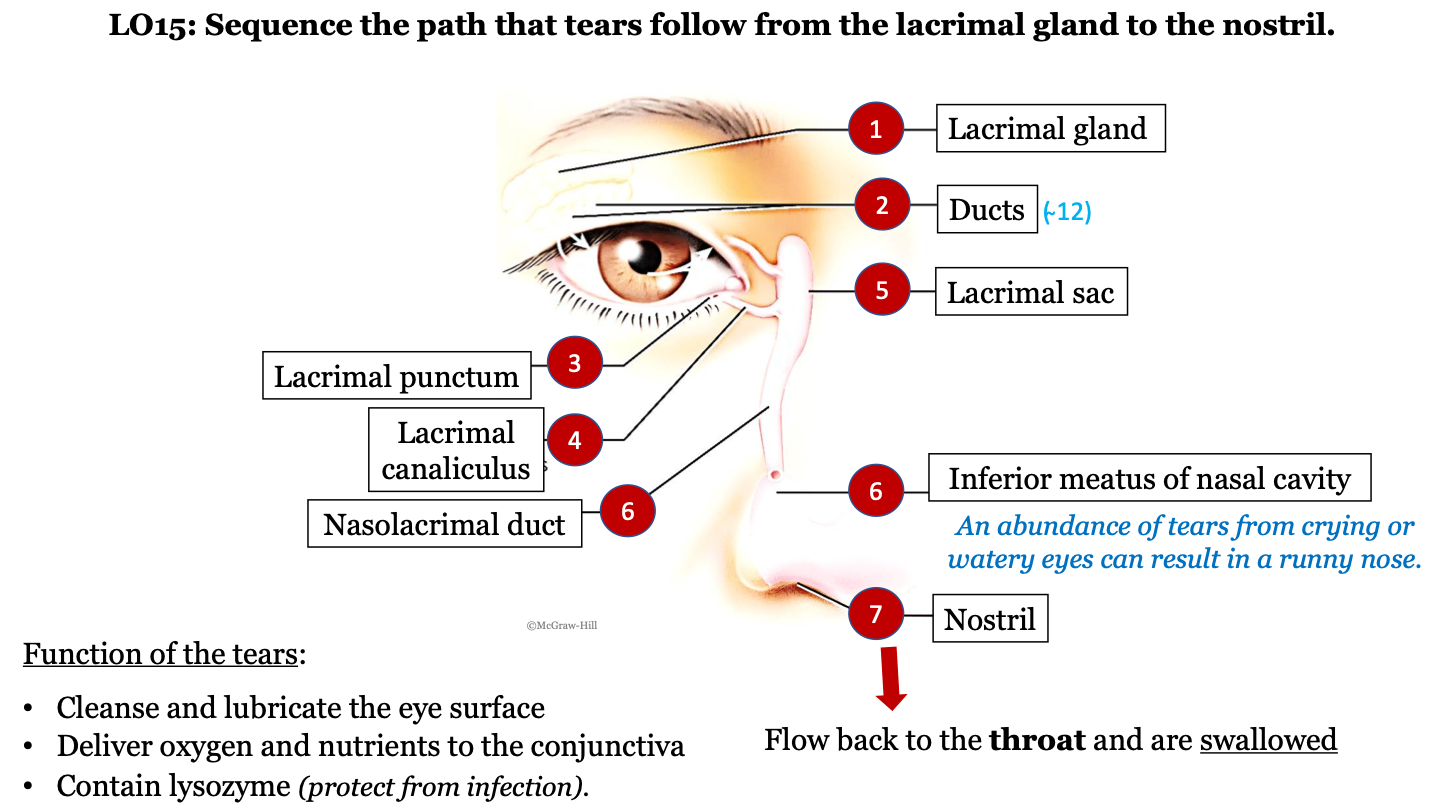
81
New cards
tear pathway - 8
nostril
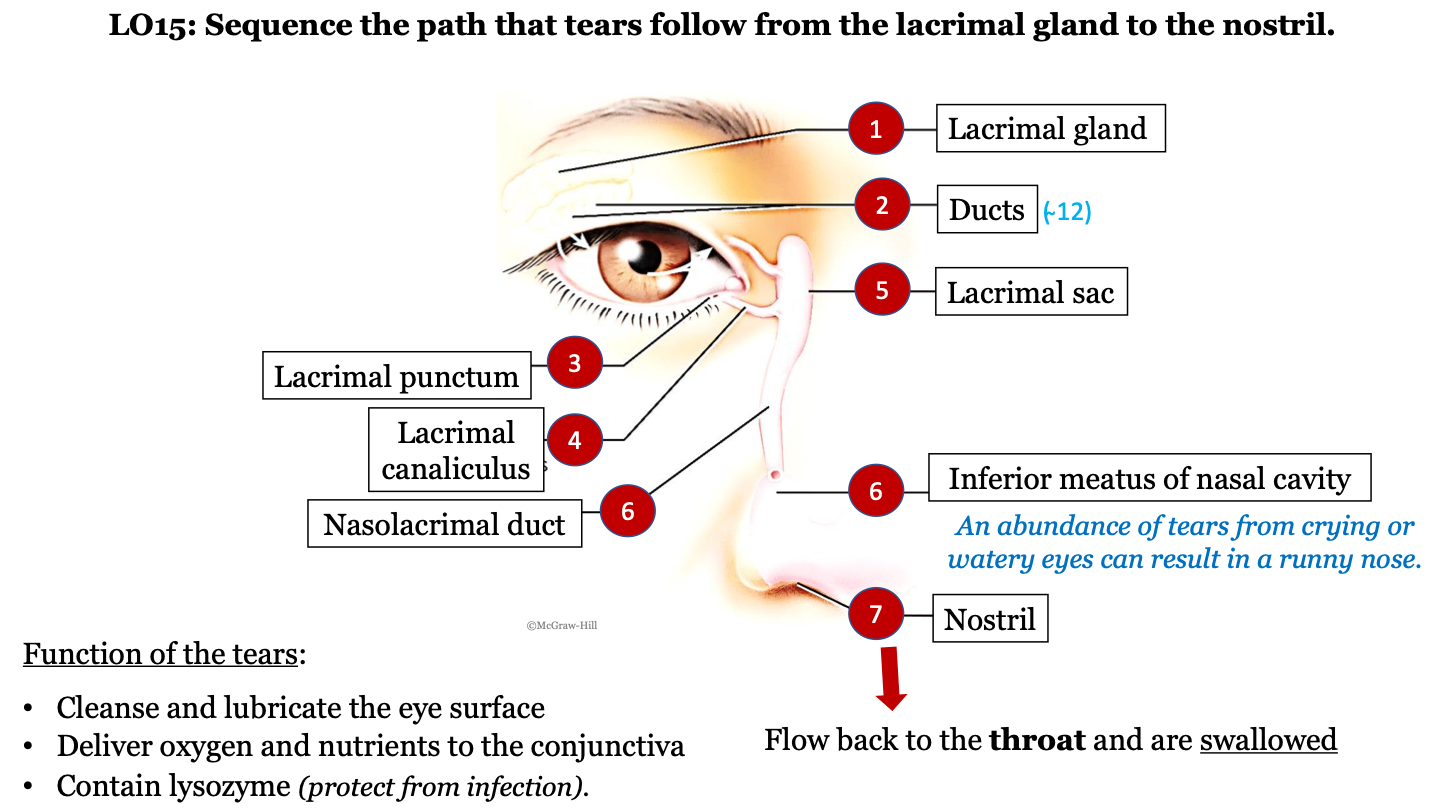
82
New cards
tear pathway - 9
tears flow back to the throat and are swallowed
83
New cards
function of tears
-cleanse and lubricate the eye surface
-deliver oxygen and nutrients to the conjunctiva
contain lysozyme (protect from infection)
-deliver oxygen and nutrients to the conjunctiva
contain lysozyme (protect from infection)
84
New cards
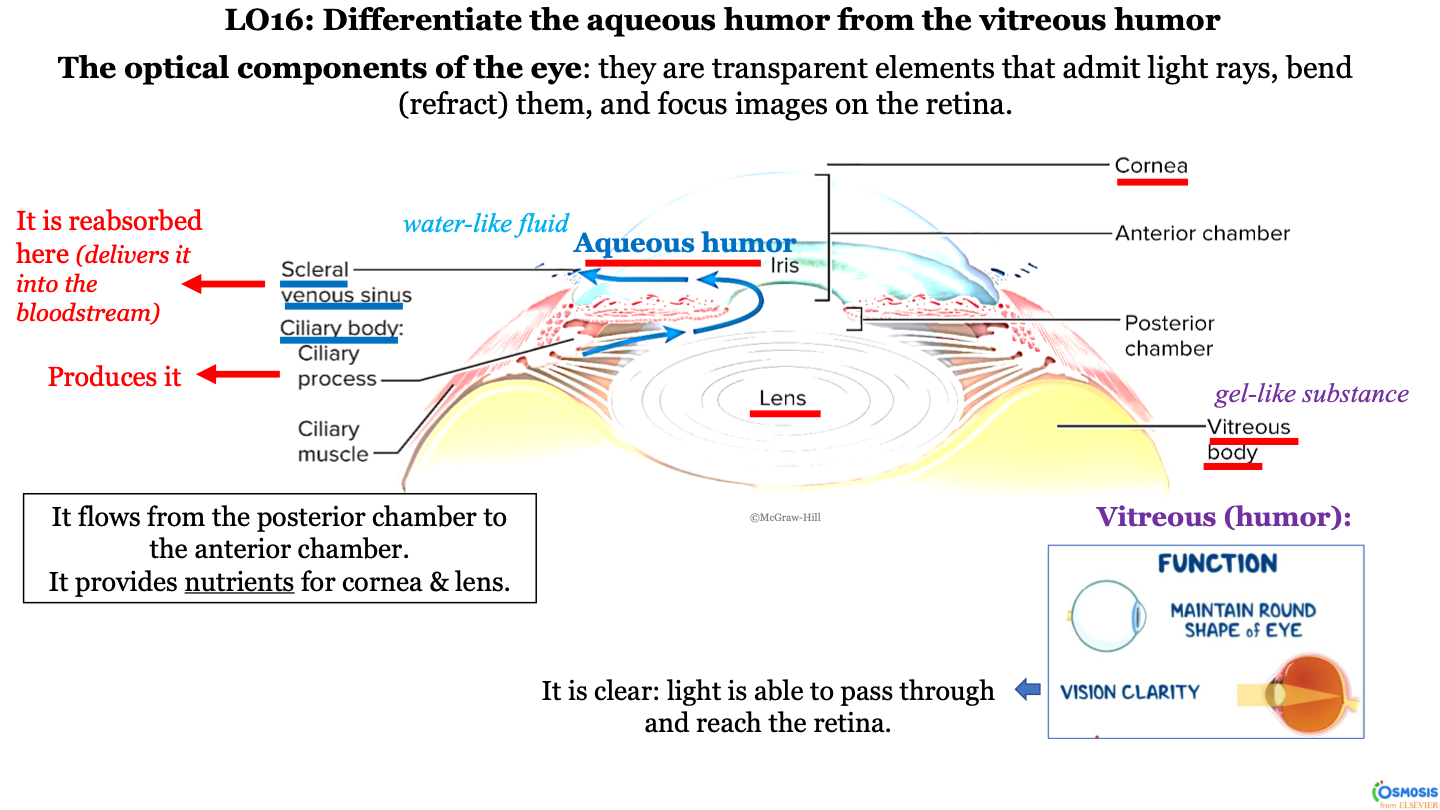
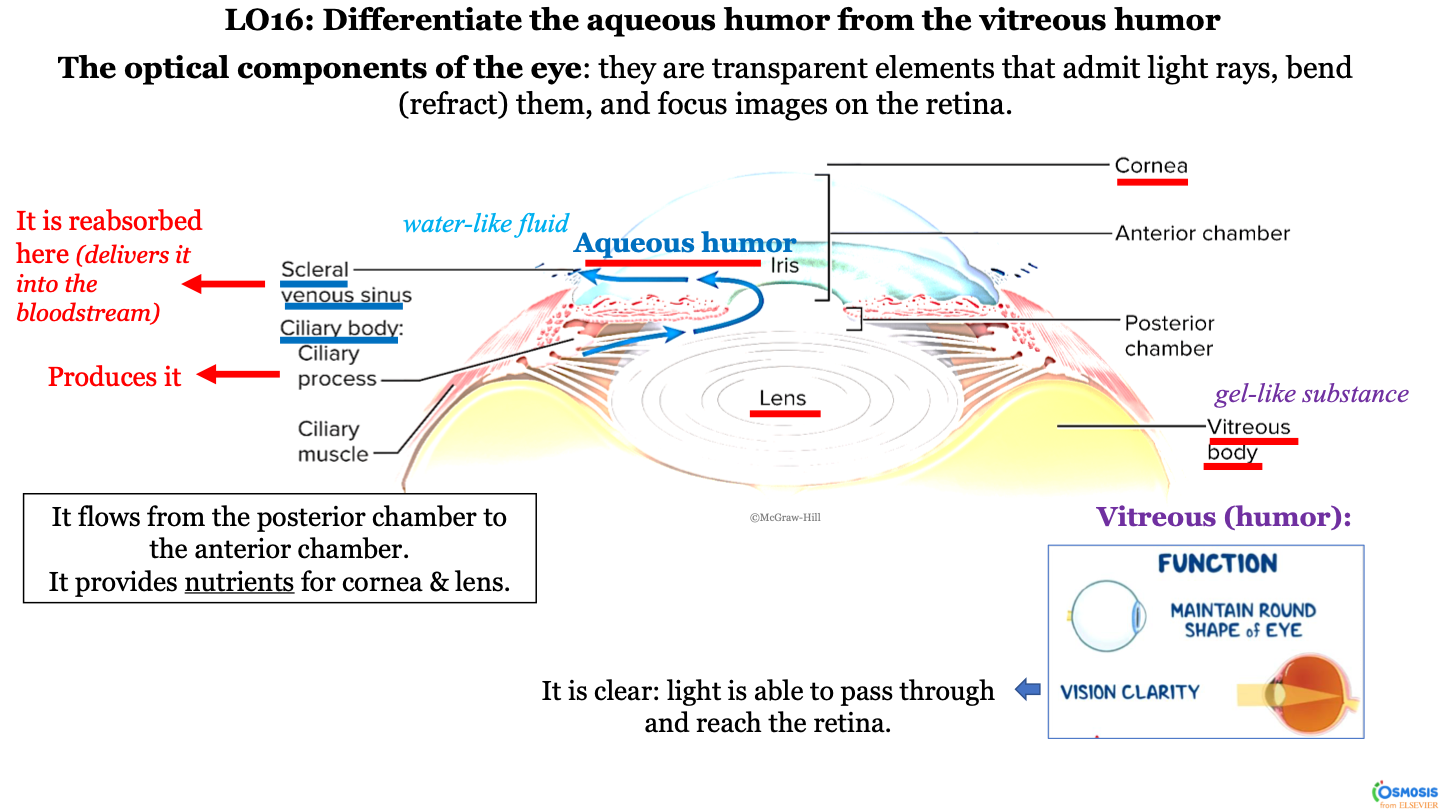
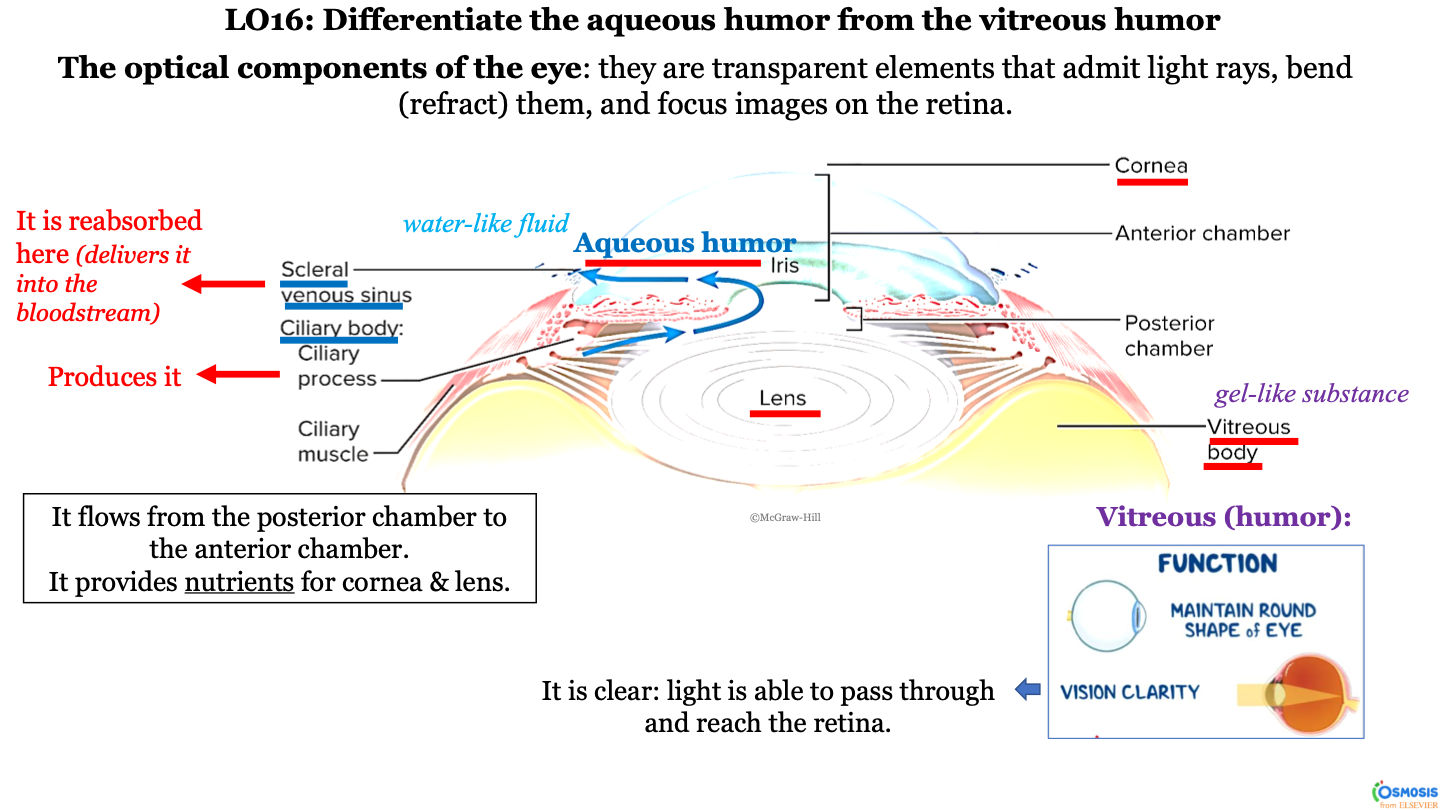
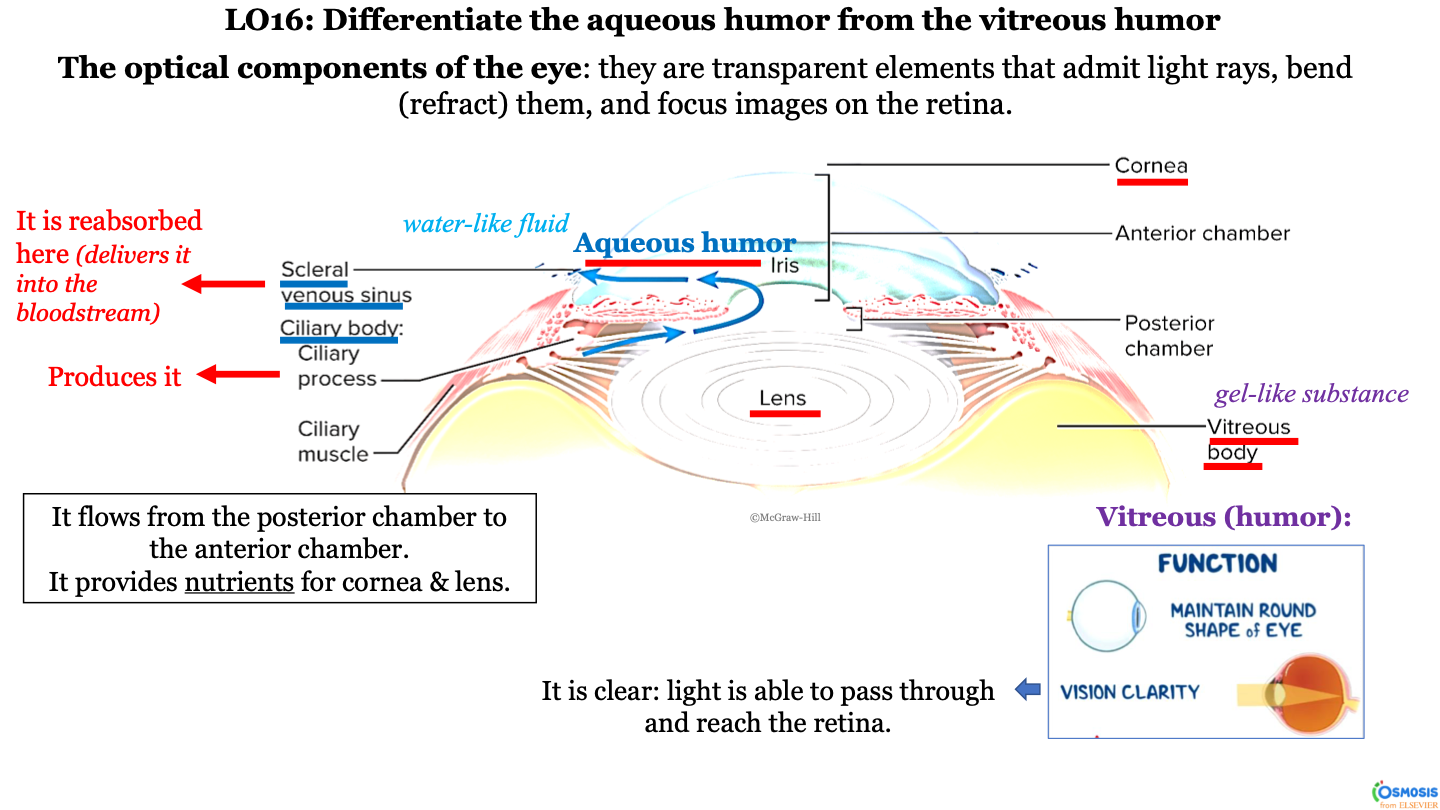
optical components of the eye
they are transparent elements that admit light rays, bend (refract) them, and focus images on the retina
85
New cards
what produces aqueous humor?
ciliary process (within the ciliary body)
86
New cards
what structures does the aqueous humor travel between?
it flows from the ciliary body (posterior chamber) to the scleral venous sinus (anterior chamber); it passes the lens, iris, and then cornea
87
New cards
what is aqueous humor?
a water-like fluid
88
New cards
what does the aqueous humor provide?
it provides nutrients for the cornea and lens
89
New cards
what happens to the aqueous humor at the scleral venous sinus?
it is reabsorbed here (delivered into the bloodstream)
90
New cards
what is the consistency of the vitrous body?
gel-like substance
91
New cards
function of vitreous body/humor
-maintain round shape of eye
-vision clarity (it is clear; light is able to pass through and reach the retina)
-vision clarity (it is clear; light is able to pass through and reach the retina)
92
New cards
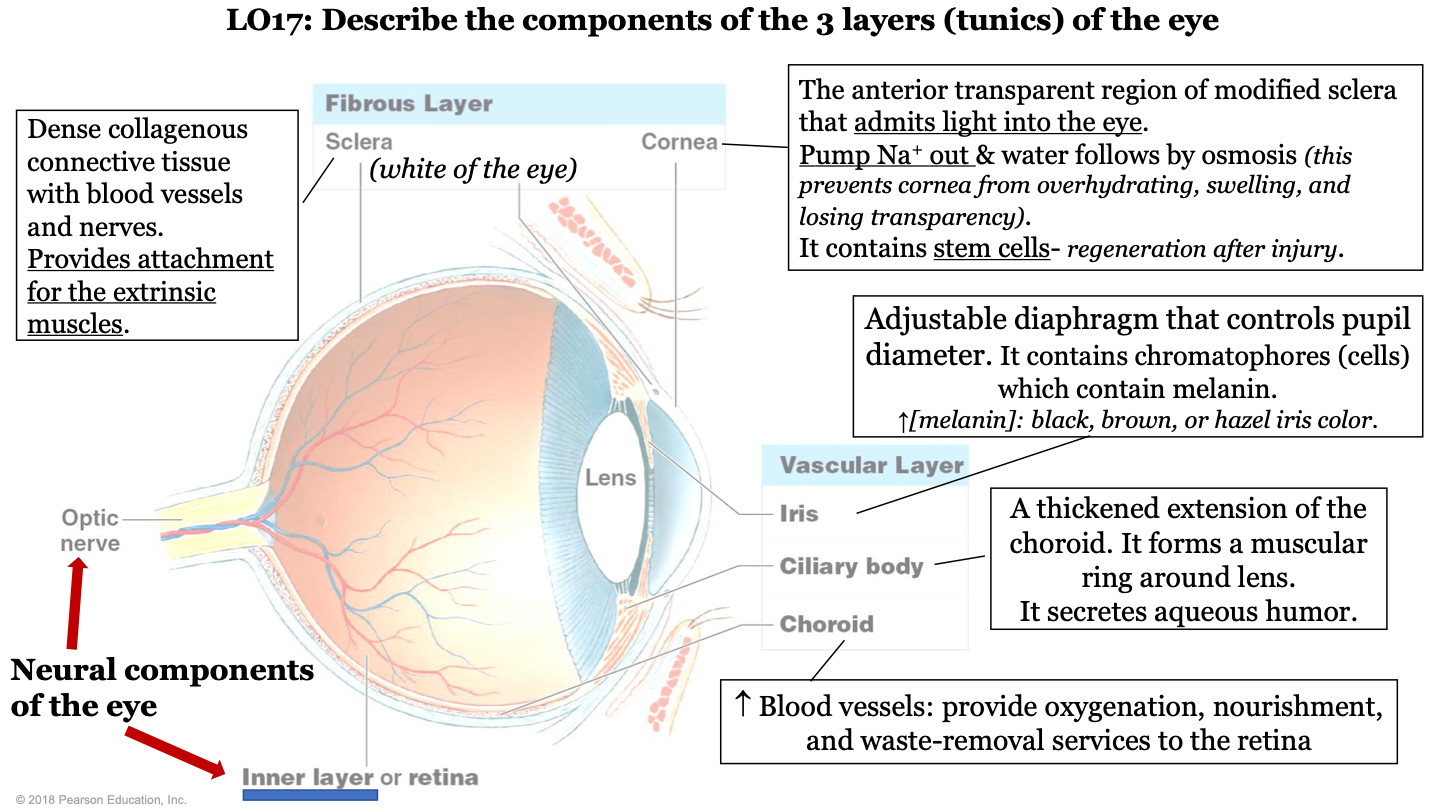
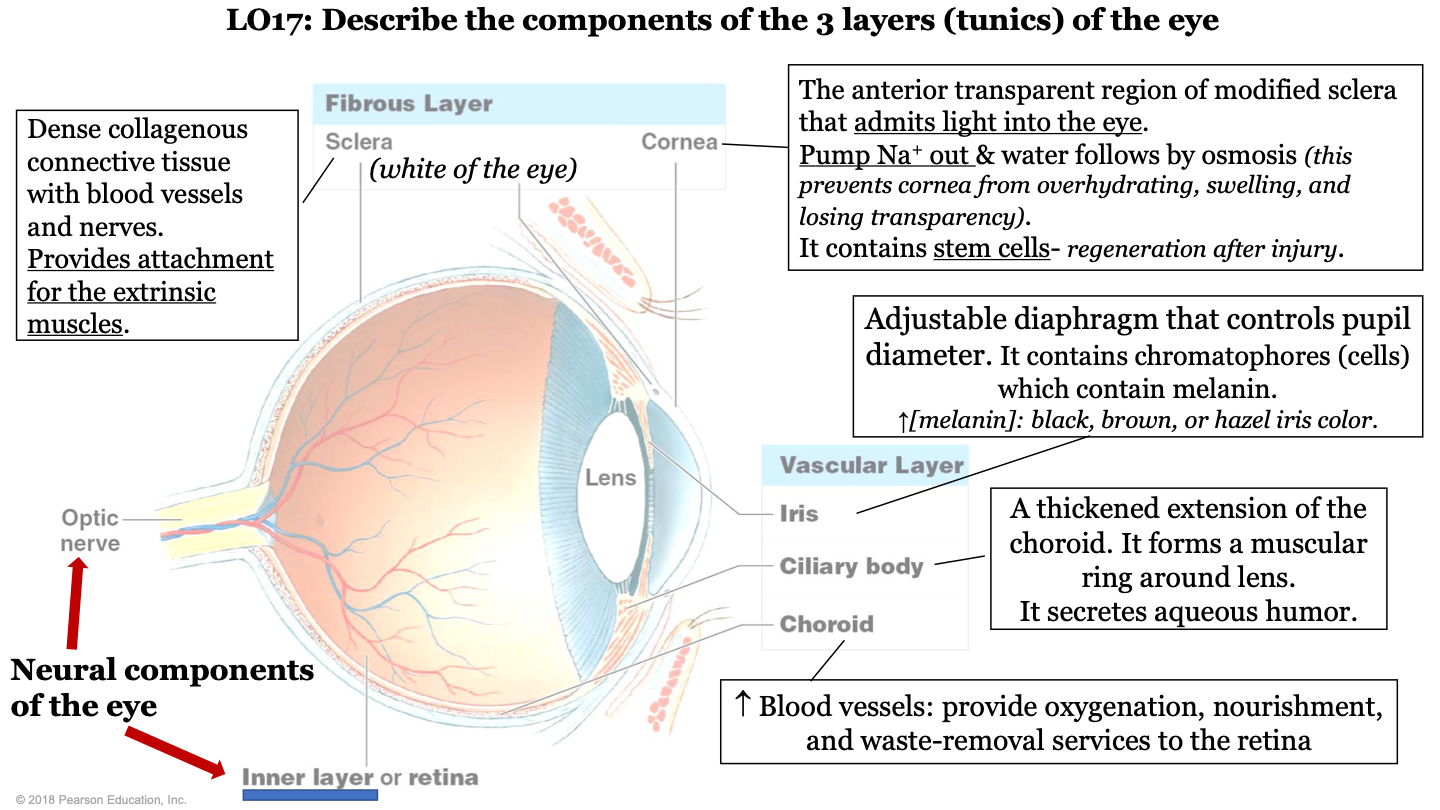
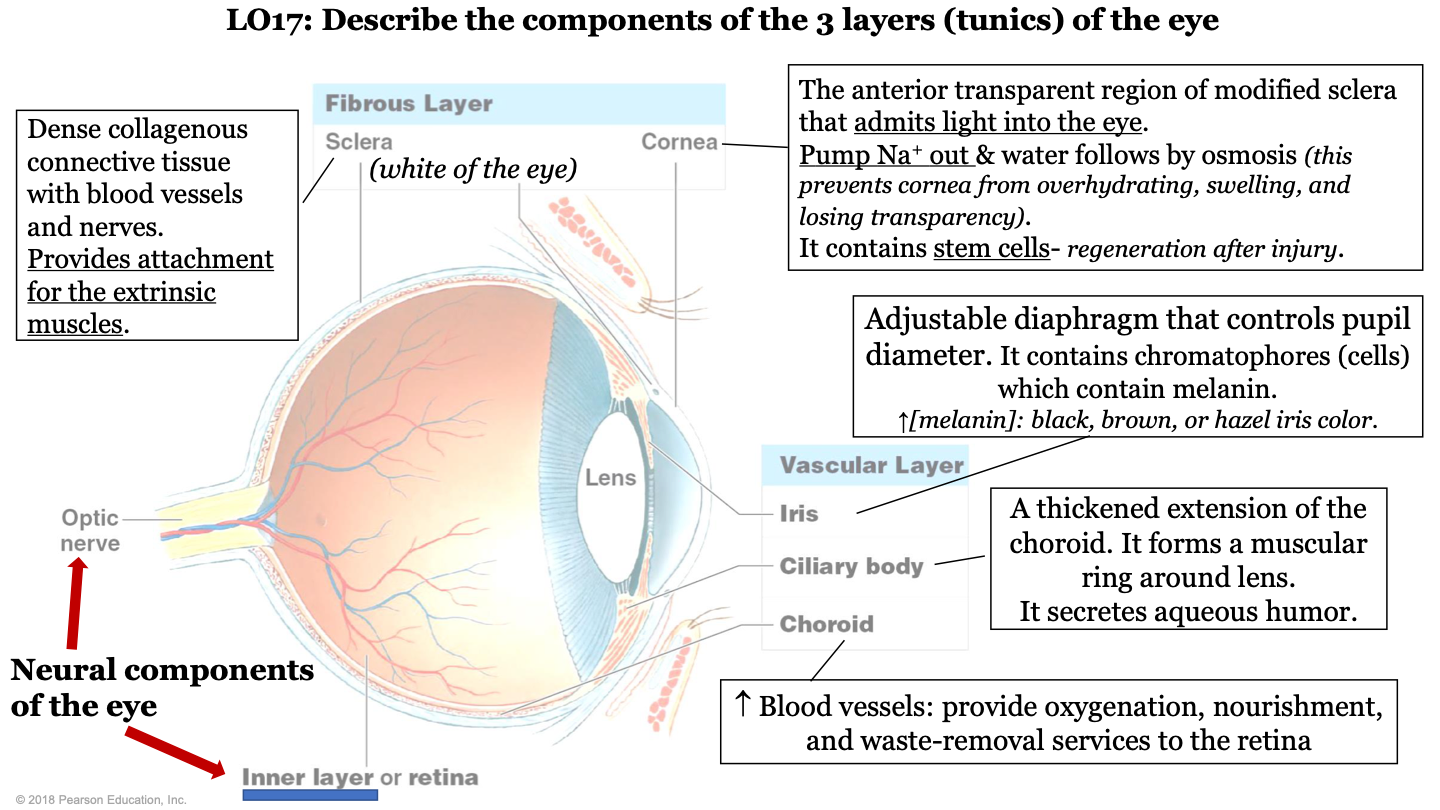
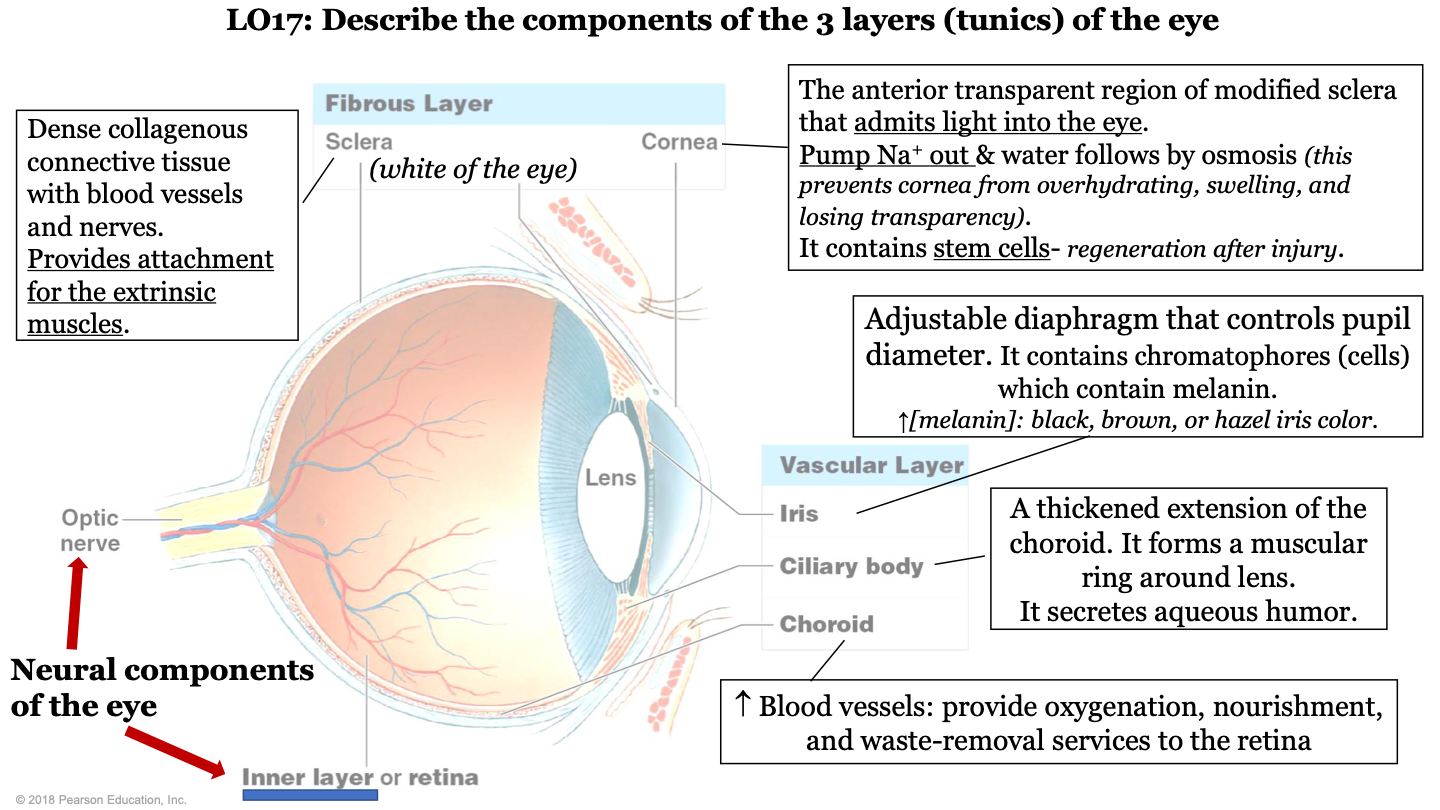
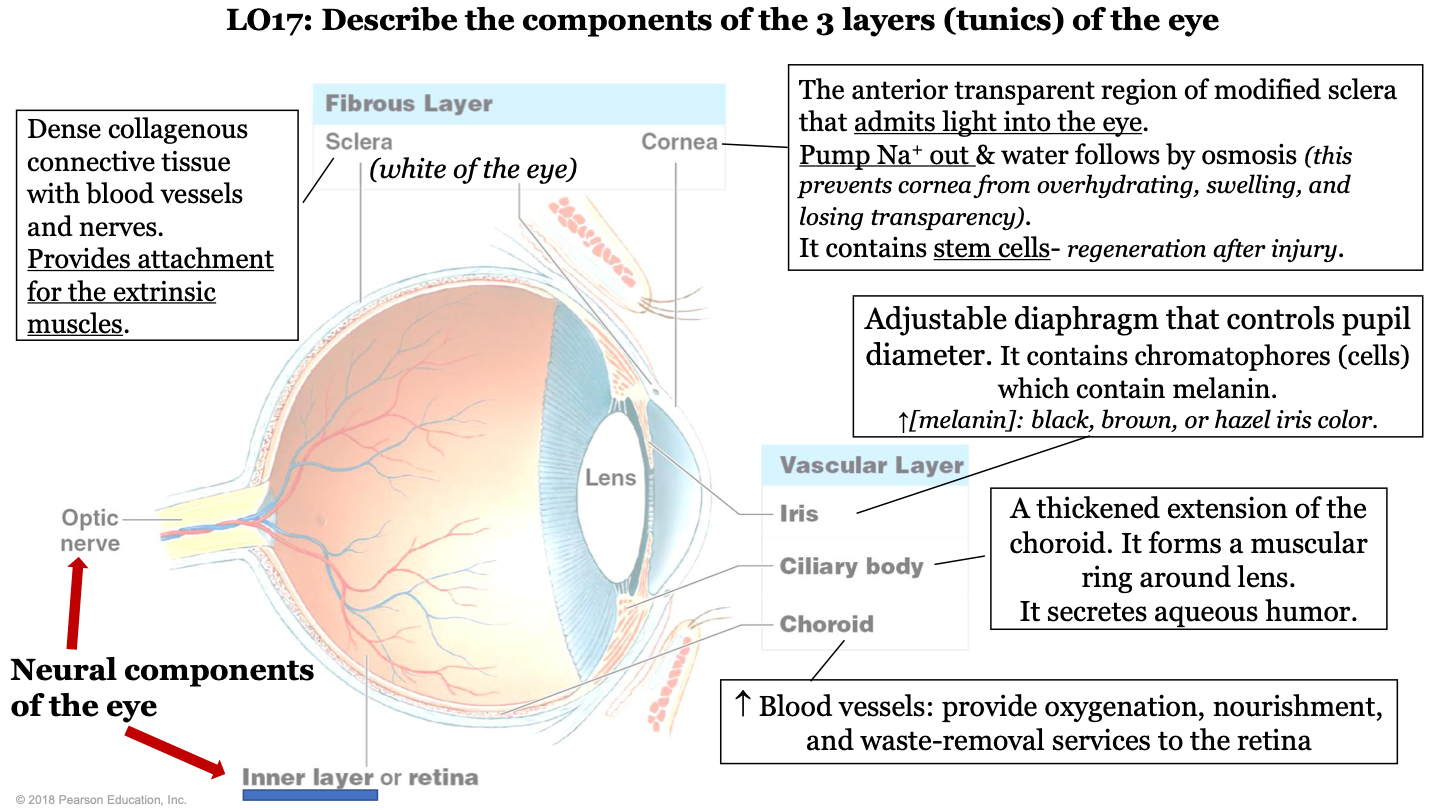
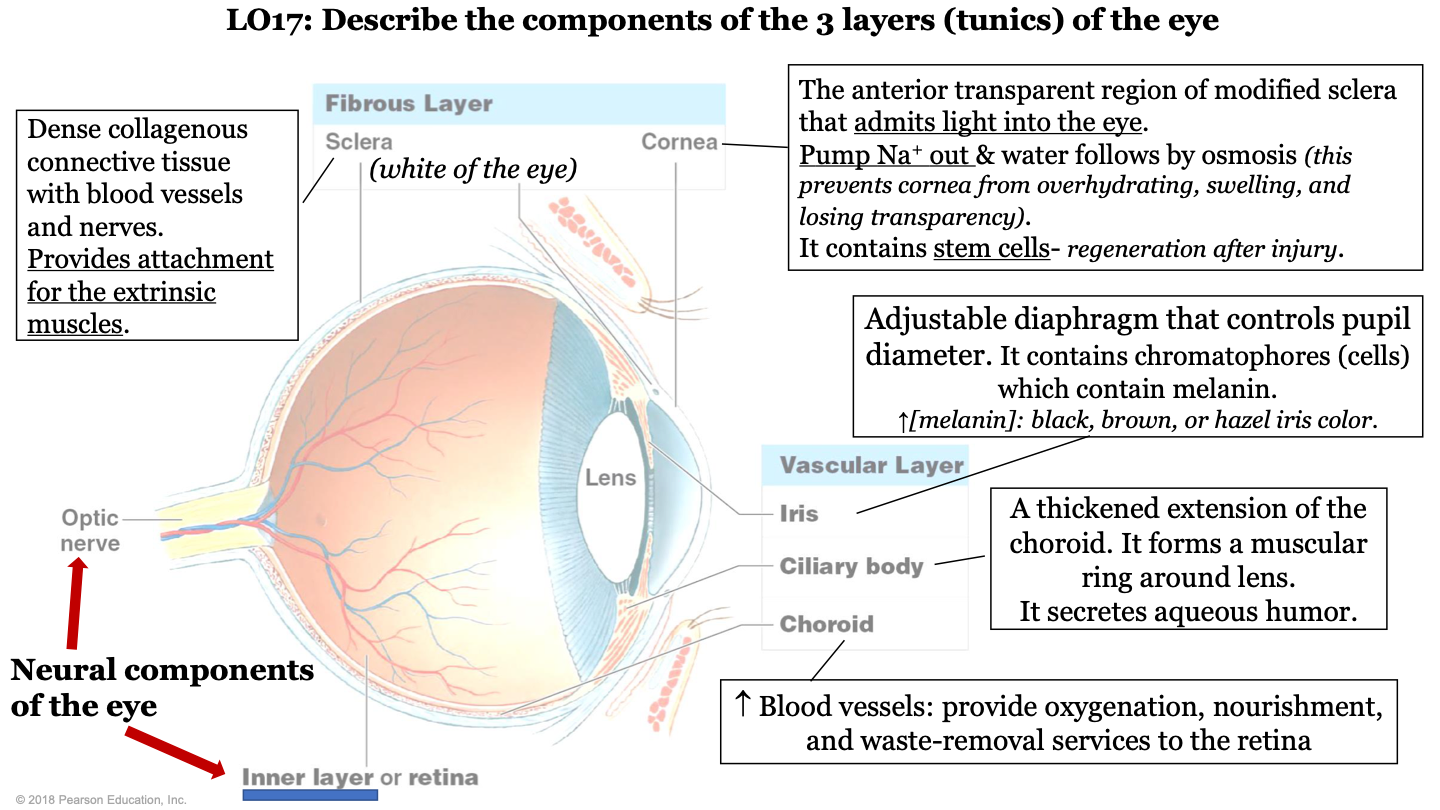
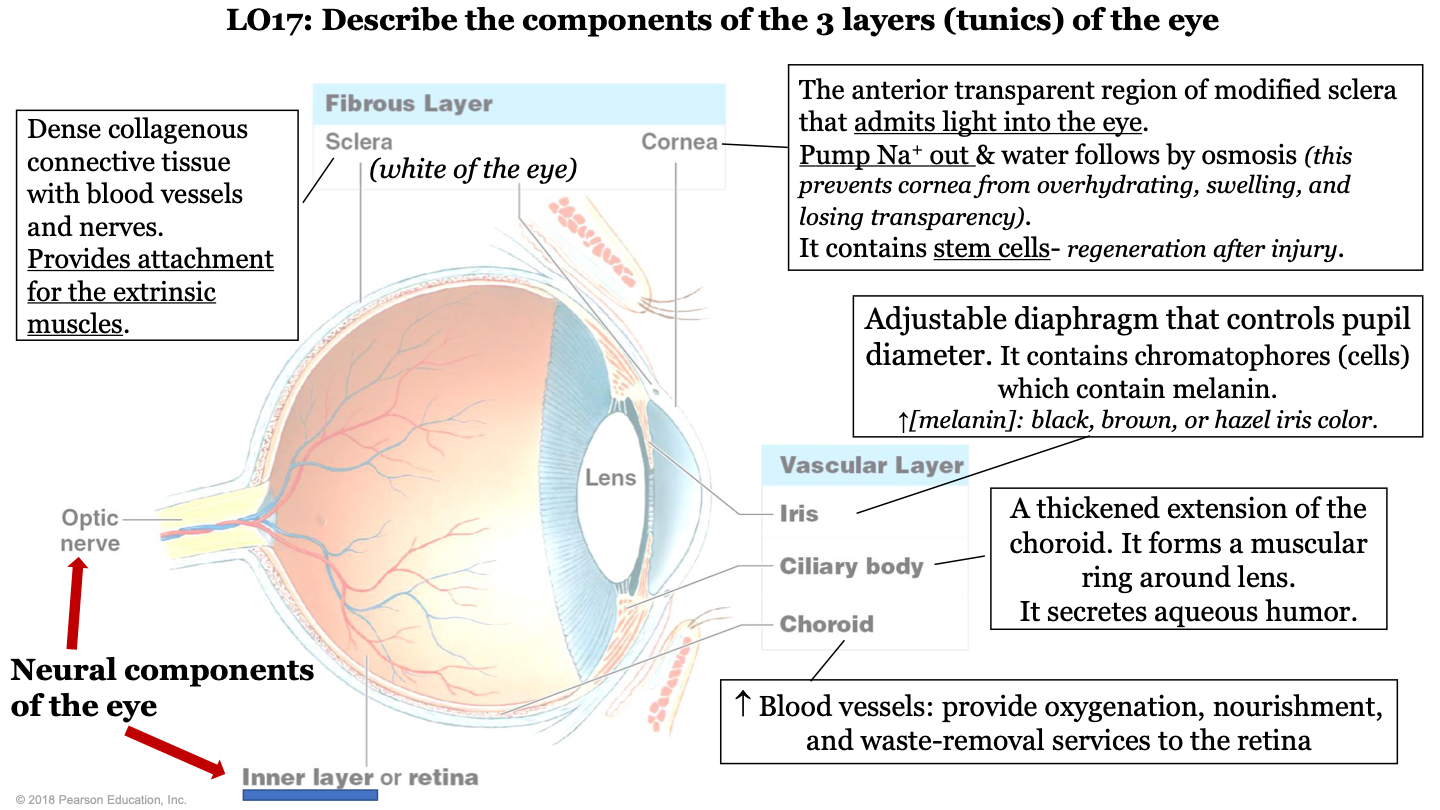
what are the 3 layers (tunics) of the eye?
-fibrous layer
-vascular layer
-inner layer
-vascular layer
-inner layer
93
New cards
what structures make up the fibrous layer/tunic of the eye?
sclera and cornea
94
New cards
what structures make up the vascular layer/tunic of the eye?
iris, cilliary body, and choroid
95
New cards
what are the neural components of the eye?
optic nerve and inner layer/retina
96
New cards
what does the choroid of the eye do?
part of vascular layer; it has lots of blood vessels which provide oxygenation, nourishment, and waste-removal services to the retina
97
New cards
what does the cilliary body of the eye do?
part of the vascular layer; it is a thickened extension of the choroid. It forms a muscular ring around the lens and it secretes aqueous humor
98
New cards
what does the iris of the eye do?
part of the vascular layer; it is an adjustable diaphragm that controls pupil diameter. It contains chromatophores (cells) which contain melanin (increased melanin gives a black, brown, or hazel eye color).
99
New cards
what does the cornea of the eye do?
part of the fibrous layer; is is the anterior transparent region of modified sclera that admits light into the eye. Pumps sodium out and water follows by osmosis (this prevents the cornea from overhydrating, swelling, and losing transparency); also contains stem cells (so it can regenerate after injury)
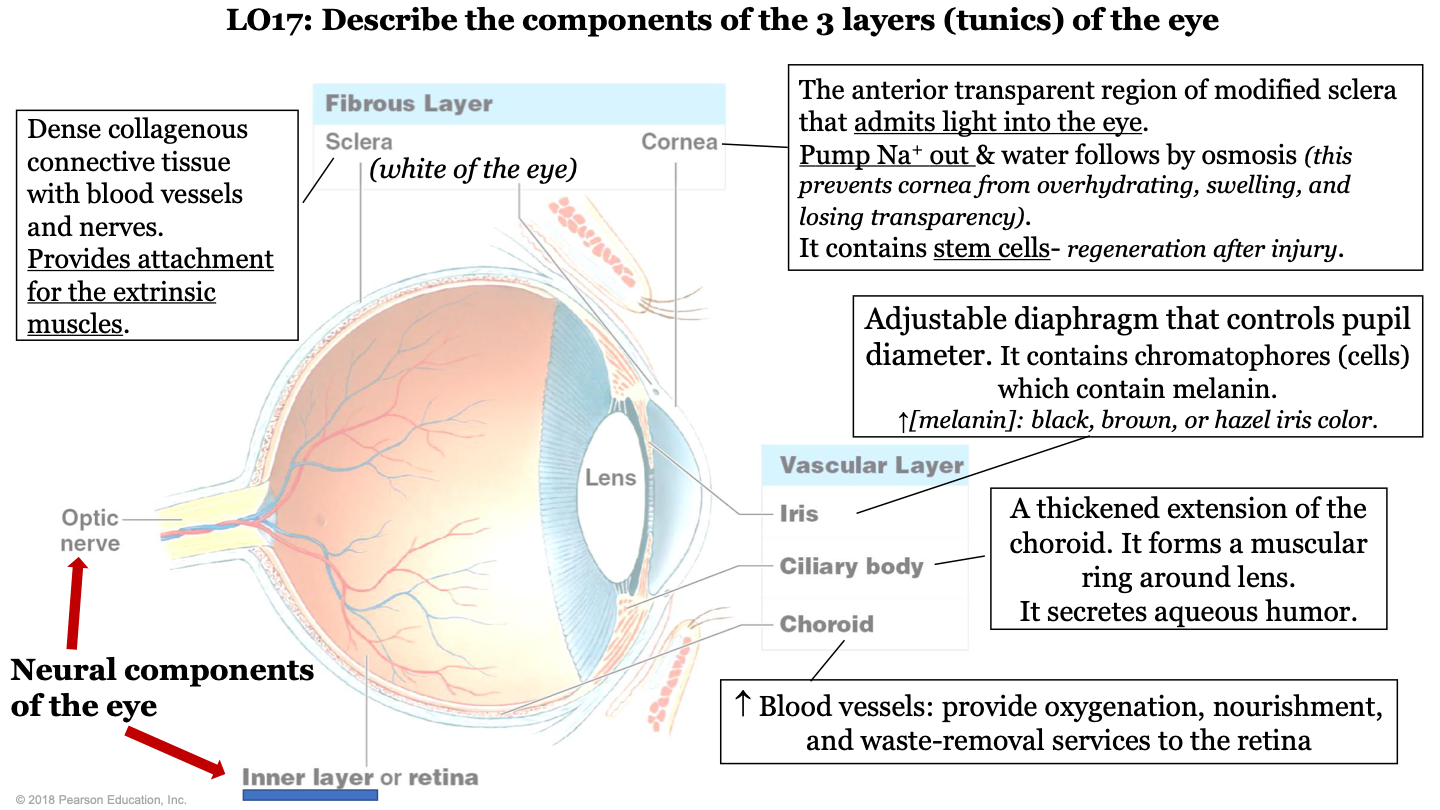
100
New cards
what is the sclera of the eye?
part of the fibrous layer; it is a dense collagenous connective tissue with blood vessels and nerves. It provides attachment for the extrinsic muscles; white part of the eye