Vesicular Transport
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
3 vesicular transport pathways
biosynthetic
retrieval
endosomal
biosynthetic pathway refers to cargo being made in the cell and its vesicular transport “forward,” post-ER - and - pathways
secretory, endosomal-lysosomal
retrieval pathway refers to return of cargo to the -
original donor compartment
endosomal pathway refers to - vesicles bringing cargo into the cell from -
endocytic, extracellular space
biosynthetic pathway refers to the delivery of newly synthesized proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids to - or - of cells, and proteins can be - along the way
appropriate cell compartments, exterior, modified
endocytic pathway refers to - from extracellular space, - and -
metabolites, PM receptors, bound ligands
retrieval pathway refers to the recycling of - back to the PM or golgi or the retrieval of molecules “accidentally” packaged into -
transport receptors, vesicles
in the endocytic pathway, endocytic vesicles fuse with -, which will evolve into -
early endosomes, lysosomes
endosomes are the compartment where - and - cargo can meet
inside, outside
proteins made on RER are sent to the golgi, then the PM or extracellular space via -pathways
they can also be sent to lysosomes via -
biosynthetic secretory, endosomes
retrieval pathway - or - molecules, ensuring that ER and golgi - or endocytosed - are returned to these compartments
redistributes, recycles, resident proteins, PM receptors
biosynthetic cargo is delivered from the RER to golgi to PM/lysosomes via -
fusion of exocytic vesicles with the PM delivers proteins in the vesicle membrane into the - and releases soluble biosynthetic cargo into the -
vesicular transport
PM, extracellular space
endocytosis delivers outside cargo into the cell via -
endocytic vesicles
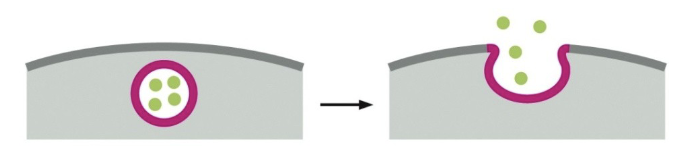
this image depicts endocytosis or exocytosis?
exocytosis
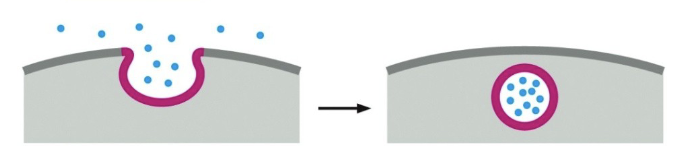
this image depicts endocytosis or exocytosis?
Endocytosis
vesicular transport steps
- form in regions of cytosolic side
budding of membrane containing soluble cargo or membrane proteins → -
- and - of vesicle to target compartment
- of vesicle and target compartment = - of soluble cargo or membrane proteins
protein coated pits, vesicle, binding, recognition, fusion, delivery
3 major types of protein coats
COPII
COPI
clathrin
COPII coats vesicles budding from - en route to -
ER, golgi
COPI coats vesicles budding from - to -, for -
golgi, RER, retrieval
clathrin coats
endocytic vesicles budding from -
transport vesicles moving between - and -
secretory retrieval vesicles moving back to -
PM, golgi, endosomes, golgi
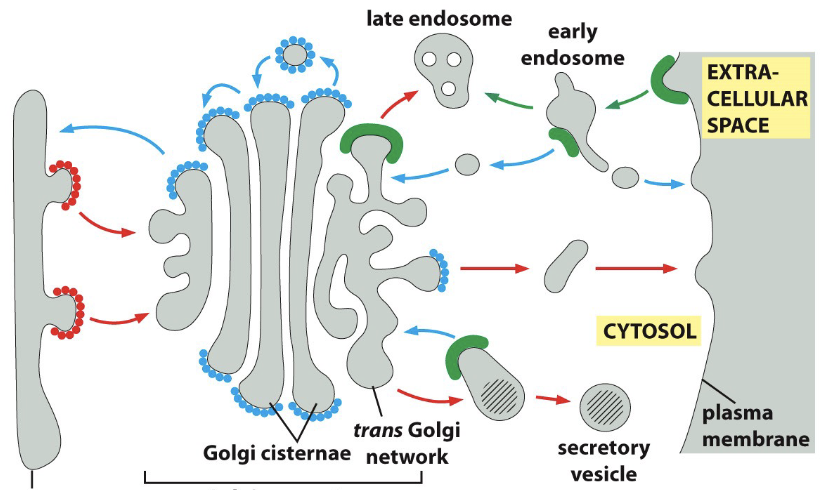
what is the red? blue? green?
COPII, COPI, clathrin
clathrin “coat” protein subuntis assemble into -
triskelions self-assemble into hexagons and pentagons, creating final - structure that encloses the - into a coated pit
triskelion, basket-like, plasma membrane
coat assembly causes local - of the membrane “bud” leading to the assembly of a -
curvature, protein coated vesicle
general steps of protein coated vesicle formation
cargo receptors in membrane of - compartment bind -
adaptor proteins bind and bridge - to -
local - of membrane
membrane-bending and fission protein proteins use - to regulate rate at which vesicles - from donor membrane and bud
donor, cargo molecule, outer coat proteins, membrane cargo receptors, curving, GTPase, pinch off
CRG stands for
coat recruitment GTPases
CRGs regulate where and when - form
donor vesicles
the region of membrane where vesicle formation initiates and the type of protein coat assembled are regulated by - and their corresponding -
CRGs, GEFs
how do CRGs work?
CRG is - into regions of donor membrane where the - is concentrated
- is loaded onto CRG by CRG-GEF
insertion of - into membrane
membrane bound CRG recruits -
inserted, CRG-GEF, GTP, CRG amphipathic helix, cargo adaptors
essentially, - starts the vesicle formation
CRG
CRGs add another level of - specificity, based on the location of the - in the donor membrane
consequently, only membrane proteins and their bound cargo in the vicinity of the - wil be - in the vesicle bud
vesicle cargo, CRG-GEF, CRG, taken-up
coat disassembly occurs when the CRG GTPase hydrolyzes - to -
GTP, GDP
v and t SNAREs have characteristic - domains, whose complementary pairs specifically interact by -
helical, wrapping around each other
v-SNAREs are typically a - chain on the -
single polypeptide helical, vesicle
t-SNAREs are composed of - proteins on the -
2 or 3 helical, target membrane
SNAREs form tight interactions that bring the two membranes very - allowing for - of vesicle and target membrane
close together, fusion
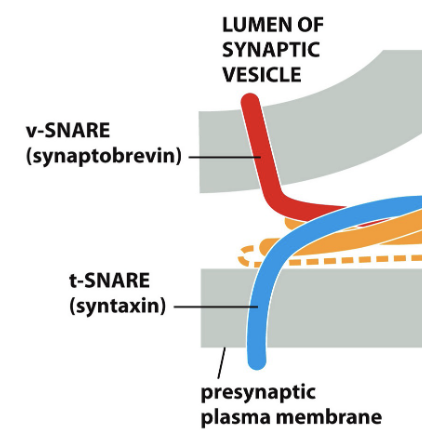
based on this photo, which membrane is the vesicle membrane and target membrane?
top is vesicle, bottom is target membrane
Rab GTPases help specify and regulate - and -
vesicle-target recognition, blocking
How do Rab GTPases work?
membrane-bound Rab GEFs activate - on both - and - membrane
cytosolic Rab is - into respective membrane via a -
on the target membrane, Rab GTP recruits -
Rab effector will recognise corresponding - on the donor vesicle
results in vesicle and target membranes being pulled - and - can interact
cytosolic Rabs, target, donor, inserted, lipid tail, Rab effector, Rab GTP, closer, SNAREs