The Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Meiosis - Biology
1/84
Earn XP
Description and Tags
heyyyyyy guys so this is a review for bio for the cell cycle, mitosis and meiosis (meiosis 1 and meiosis 2) :)))) enjoy!!!! :) happy testing!! I wish you all the best of luck! Good luck!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
cell division
creates new cells(from 1 to 2 new cells)
asexual reproduction
creating genetically identical offspring
what are some advantages of asexual reproduction?
quick, easier, no pregnancy, less time, clone
sexual reproduction
creating genetically diverse offspring(only main advantage)
binary fission
a type of asexual reproduction
used by many bacteria
creates 2 daughter cells from 1 parent
chromatin
loosely wound DNA
chromosome
tightly wound DNA
what is the DNA in a chromosome wrapped around
histone proteins
sister chromatids
duplicated chromosomes held together at centromere (X)
interphase
G1, S, G2 except Mitosis
What is the order of the cell cycle?
G1, S, G2, M
mitosis
nuclear division that maintains chromosome number
how many chromosomes per human
46 chromosomes
what are the 4 phases of mitosis
prophase
metaphase
anaphase
telophase
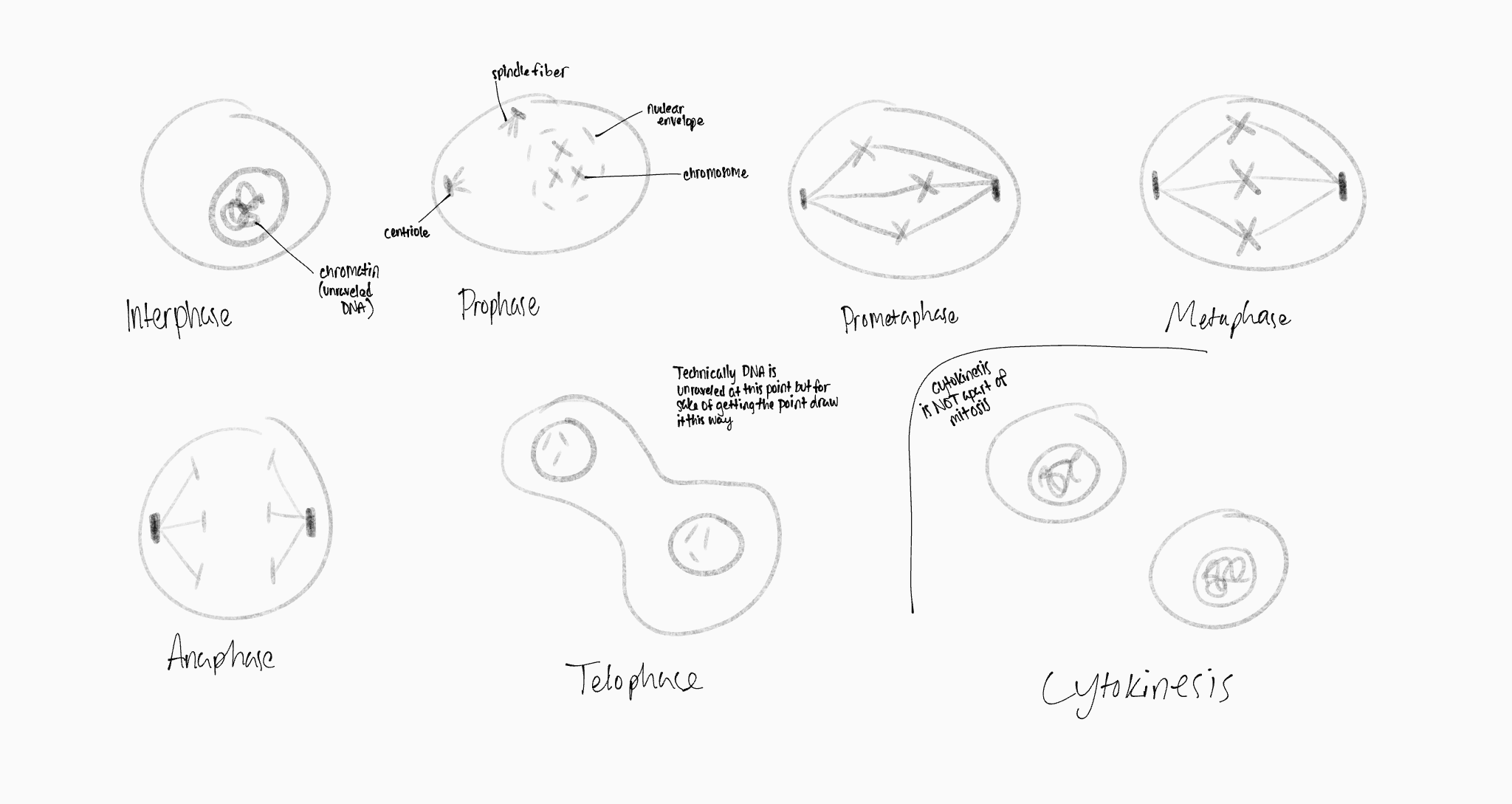
what happens in prophase
nucleolus disappears
chromatin condense into chromosomes
separation of centrosomes(centrioles)
formation of spindle fibers
what happens in prometaphase
nuclear envelope disassembles
spindle fibers (microtubules) attach to chromosomes
what happens in metaphase
chromosomes align on the metaphase plane (middle)
what happens in anaphase
chromatids separate towards opposite poles
what happens in telophase
new nuclear envelope forms
chromosomes unfold back into chromatin
nucleoli reappear
what is cytokinesis
occurs after mitosis
daughter cells divide
2 new cells form from 1 original cell
how do plant cells do cell division
form a new cell wall from cell plate
how is a cell plate formed
vesicles line up
how do animal cells do cell division
they pinch and turn into 2 cells from 1 cell
how do animal cells pinch
cleavage furrow with is a contracting ring making 2 new cells from 1
what is cancer
uncontrolled cell division
what is a mass of cells called
tumor
what do most cells need to divide
growth factor (proteins and signals tell them to divide)
why are checkpoints important
to make sure cells are good and correct so that there are no issues, no bad cells replicating
what happens if a cell fails a checkpoint
G0 —> try to fix cell—> can’t fix them destroy cell
apoptosis
programmed cell death
why is apoptosis good
it prevents cancer and only affects the 1 cell (not like all cells getting damaged)
necrosis
cell dies due to trauma, etc., not programmed, causes damage to other cells
what do cancer cells do at checkpoints
ignore them
what are the stages of cancer and what do they mean
1- small mass
2- spread in the same area
3+4- spread to other parts of the body
what is it called when cells spread to other parts of the body
metastasize
ploidy
number of sets of chromosomes
haploid
1 set of chromosomes
diploid
2 sets of chromosomes
humans are diploid or haploid
diploid we have 46 chromosomes in 2 sets 1 set from mom and 1 from dad (23 from each)
what is the 23 set of our chromosomes
XY
for every single type of chromosome we have we have how many sets
2
mitosis drawing
Meiosis definition
nuclear division that halves chromosome number
What is the result of meiosis 1 and meiosis 2
meiosis 1 - starts from 1 diploid cell and results in 2 haploid cells
meiosis 2 - starts from 2 haploid cells and results in 4 diploid cells
haploid shorthand
1n
diploid shorthand
2n
what kind of cells come from meiosis
gametes (sperm and eggs)
what kind of cells are the first cells in meiosis
germ cells
what are germ cells
they are in ovaries and testes and are supposed to make sperm and egg
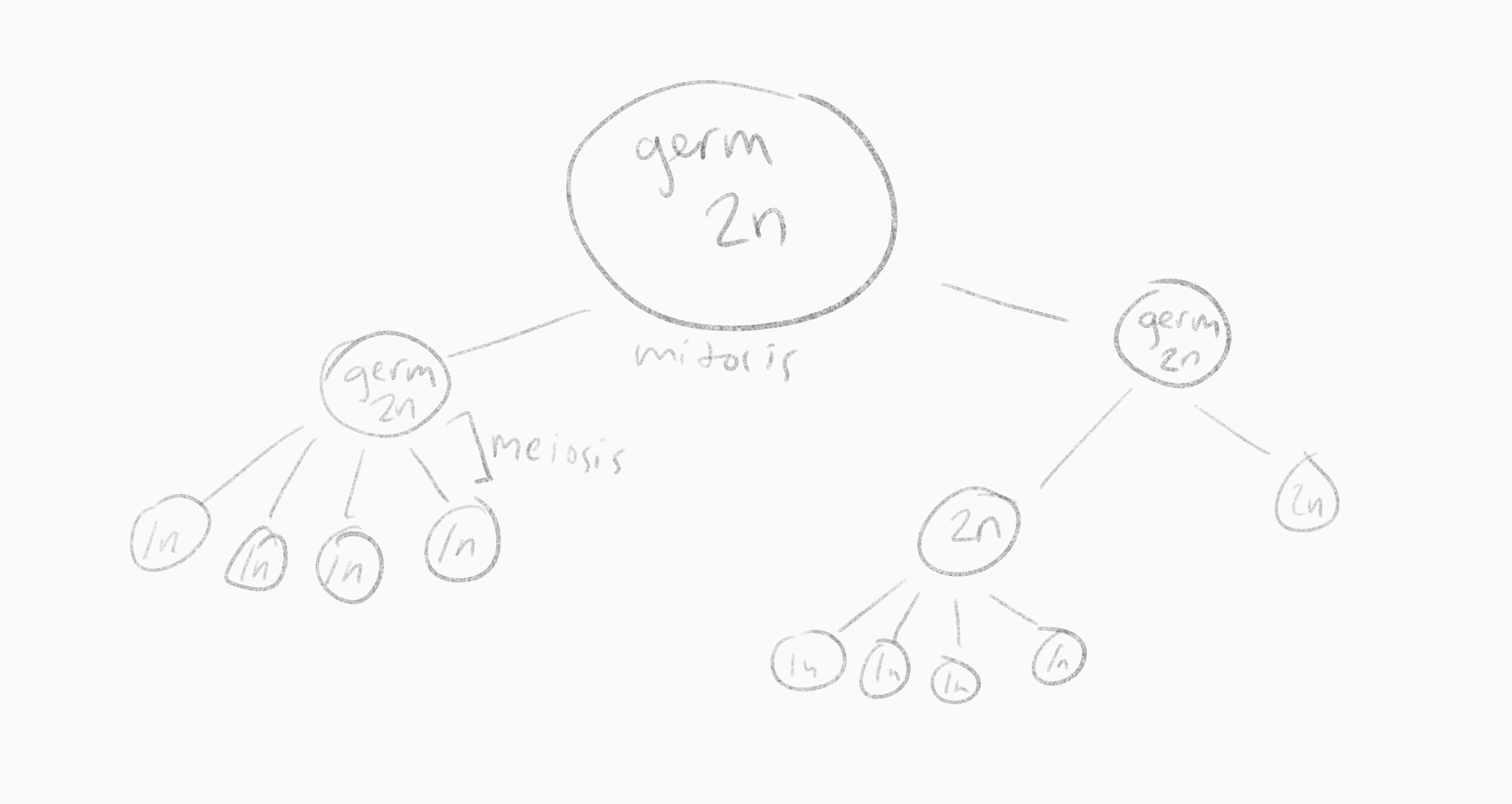
why don't germ cells just immediately split into four cells
we would run out of germ cells
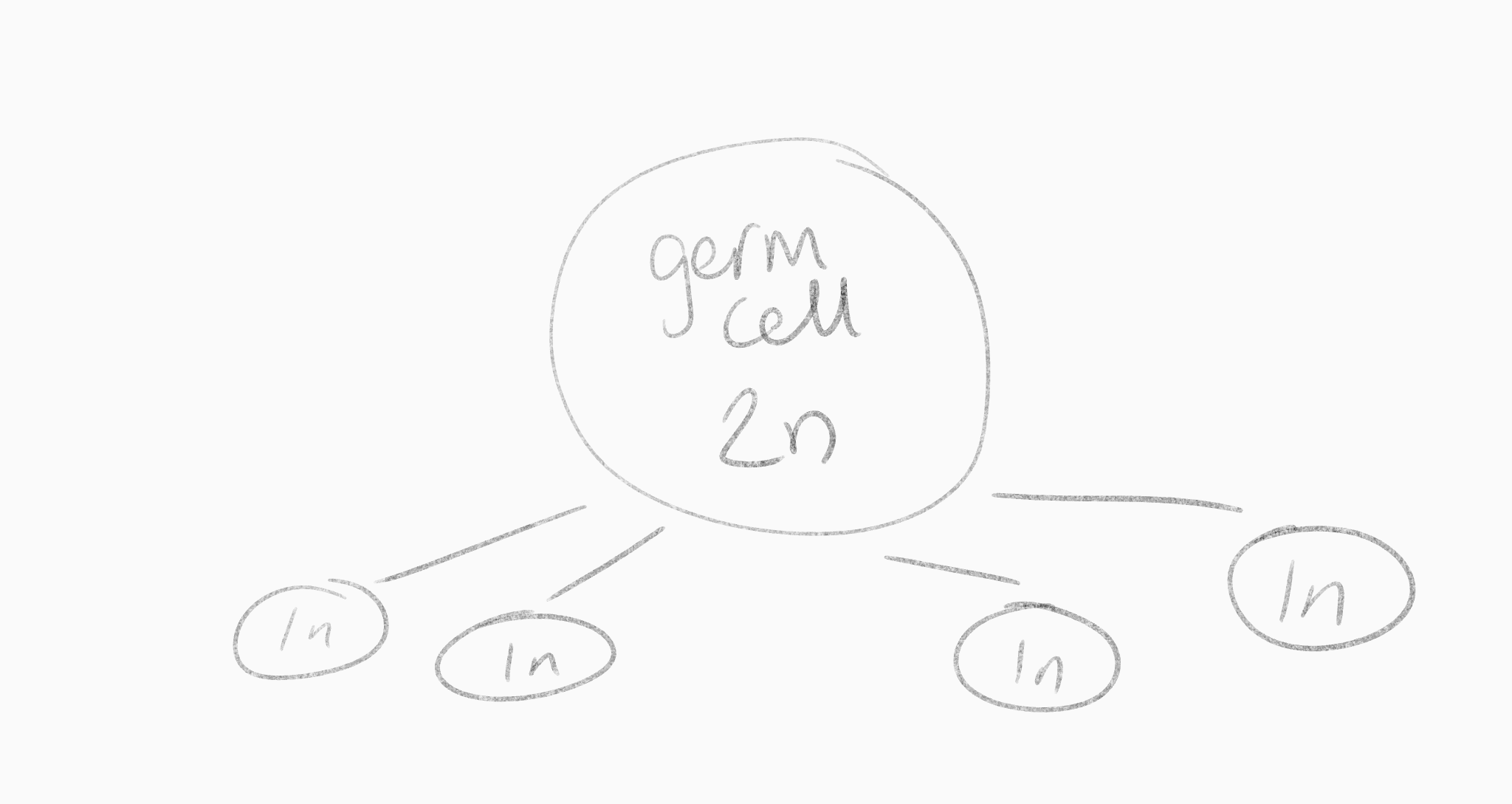
What do the cells do instead to preserve a germ cell
they perform mitosis
what are the 3 ways meiosis increases genetic diversity
crossing over, independent assortment, random fertilization
what is independent assortment
how they line up all ways are equally likely because it is random
when does independent assortment occur
metaphase 1
what does the diploid shorthand (2^n) mean/determine
n = sets of chromosomes (for example humans have 23)
so 2^n helps determine the number of different combinations or orders of chromosomes
(humans 2²3 = 8,000,000)
what is crossing over/ genetic recombination
when the 2 chromosomes cross over each other and swap some genes
when does crossing over occur
during Prophase 1
when crossing over what has to match for them to be able to cross over
their number (a 1 to a 1, 2 to a 2, etc)
the area that swaps on a chromosome is called
chiasma
what is random fertalization
sperm and egg are random, random sperm fertilizes random egg
what is nondisjunction
when chromosomes don’t separate correctly
how can nondisjunction occur in meiosis 1
this can happen because of the failure of a pair of homologous chromosomes to separate during meiosis 1 (an entire tetrad moves to one side)
how can nondisjunction occur in meiosis 2
the failure of sister chromatids to separate during meiosis 2
what is affected if the mistake occurs in meiosis 1
it will affect all four gametes (sperm or egg)
what is affected if the mistake occurs in meiosis 2
only 2 gametes will be affected
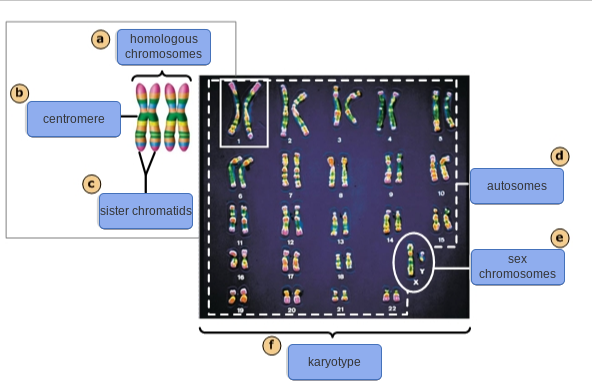
what is a karyotype
a picture of someones chromosomes
what are a males sex chromosomes
XY
what are a females sex chromosomes
XX
whta is it called when there is an extra copy of chromosomes 21
down syndrome (trisomy 21)
what is the biggest risk factor for having a child with trisomy 21
a woman’s age
why is a woman’s age a big risk factor
nondisjunction increases as you age
what is the effect of an abnormal number of sex chromosomes
not usually any effects
doesn’t usually affect survival (could)
health issues sometimes come with what chromosomes
XXY
usually normal with what chromosomes
XXX
mutation
a change in DNA
gametes are produced by
meiosis
what is the first cell of a new human called and what is the process that the cell does to create more cells to become multicelluar?
zygote and the process is mitosis
difference between mitosis and meiosis
mitosis creates all the hair, skin, nails, etc.
meiosis creates gametes (from sperm and egg cells), crossing over occurs
In humans, the haploid number of chromosomes is 23. Independent assortment has the possibility of producing __________ different gametes.
2²³
karyotype
order of meiosis I
prophase I
metaphase I
anaphase I
telophase I
cytokinesis
order of meiosis II
prophase II
metaphase II
anaphase II
telophase II
cytokinesis
difference between benign and malignant tumors
malignant tumors metastasize, spread
benign tumors do not spread
difference between meiosis 1 and meiosis 2
meiosis 1 - homologous pairs separate (happens in anaphase 1)
meiosis 2 - sister chromatids separate (happens in anaphase 2)
What is to be on the test
multiple choice, short answer, and drawing (prolly drawing cell cycle??, mitosis, meiosis 1, meiosis 2??)