Reproduction (Male + Female)
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Puberty
Known as “sexual maturity”, it occurs at a young stage of growth

What is the common age for cattle to hit puberty?
6-9 months
What is the common age for swine or sheep/goats to hit puberty?
4-6 months
What is the common age for horses to hit puberty?
9-12 months
When should animals not be bred?
During puberty
Why should animals not be bred during puberty?
The skeleton is not matured enough which affects the tractions
Scrotum (Male)
Muscles in the lining of the sac
What is the purpose of the scrotum?
To raise and lower the testicles, keeping them 2-3 degrees colder than the body and protect gonads from injury
Testicles (Male)
Made up of miles of microscope tubes that produce sperm cells
What does the testicle produce?
Male hormones known as testosterone that cause secondary sex characteristics and develop sex drive in the male
Epididymis (Male)
A coiled tube along the outside of testicles that stores and matures unused sperm cells
How long does it take for cells to mature in Epididymis?
Usually 2 weeks
Vas Deferens (Male)
A long, muscular tube that leads from epididymis to the urethra and carries only sperm
What happens to the vas deferens during a vasectomy?
The tubes are severed and plugged in to prevent bleeding and act as a heat detector in the animal
Bladder
Holds urine produced from the kidneys
Seminal Vesicles (Male)
Two small tubular glands that produce a bulk of seminal fluids
What do the fluids in seminal vesicles contain?
Proteins, sugars, and salts
What is the purpose of the fluids in seminal vesicles?
To transport, protect, and nourish the sperm cell
Semen (Male)
A thick, white fluid containing sperm and other seminal fluids
Prostate (Male)
A gland located at the neck of the urinary bladder that produces (some) fluids in the semen and stimulates sperm mobility
Cowper’s gland (Male)
Produces seminal fluids that cleanse and neutralize acids in the urethra
Urethra
Carries urine from the bladder to the outside
What does the urethra carry during breeding? (Male)
Semen
Sigmoid Flexure (Male)
S-curve in penis on bulls, rams, and boars that holds length inside the body
What is the highest possible length a bull’s penis can reach to?
2 and a half feet long
Retractor Muscles (Male)
Holds penis up in body until breeding
Penis (Male)
Deposits semen within the female reproductive system
Which animal should have their penis cleaned prior to breeding?
Horses
Sheath (Male)
Protects and houses the penis
What animal could develop a urine pocket in their sheath?
Boars (genetic trait)
Rectum (Female)
The final section of the large intestine that leads to the anal canal and stores feces
Vulva (Female)
External opening of the tract, consisting of vulgar lips, that keeps out large particles of dirt
How do the vulvar lips indicate heat?
Swelling and a pink-ish color
Why is it important to keep females that show heat easily?
The more feminine, the easier it is to breed and develop a stronger reproductive system
Vagina/Birth Canal (Female)
Consists of walls made of many folds to expand and lining that secretes acids mucus
Blind Sac/Diverticulum (Female)
Has no function but may act as trapping bacteria
Cervix (Female)
Made up of spiral folds that are a gateway between the vagina and the uterus and secrete a high acid mucus that kills bacteria
What is the purpose of the cervix during pregnancy?
The formation of a plug that has to expand and dilate during birth
Body of the uterus (Female)
The beginning of the uterus before it spills into two horns
Horns of the uterus (Female)
Site of fetal development
Caruncles (Female)
Buttons that attach to the fetus inside of the walls of the horn’s uterus
What is the purpose of the lining located inside the horns of the uterus?
Engorges with blood during heat and pregnancy
Which animals contain longer uterus horns?
Litter type animals (Cat, rabbits, pigs, etc.) due to the birth of multiple babies
Singleton-type animals (Horses)
Contain shorter horns due to singular baby births
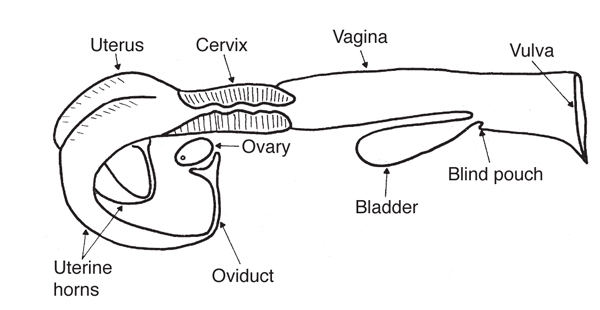
Oviducts (Female)
The primary site of fertilization that carries the ovum from the ovary to the uterus
How long are the oviducts?
Ranging from an 1/8 inch tube to almost one foot long
Infundibulum (Female)
Funnel-like tissues that catch ovum released from the ovary and guide them to the
Ovaries (Female)
Produces the ovum (eggs) and the female hormone known as estrogen