VM 602 Neuro
1/327
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
328 Terms
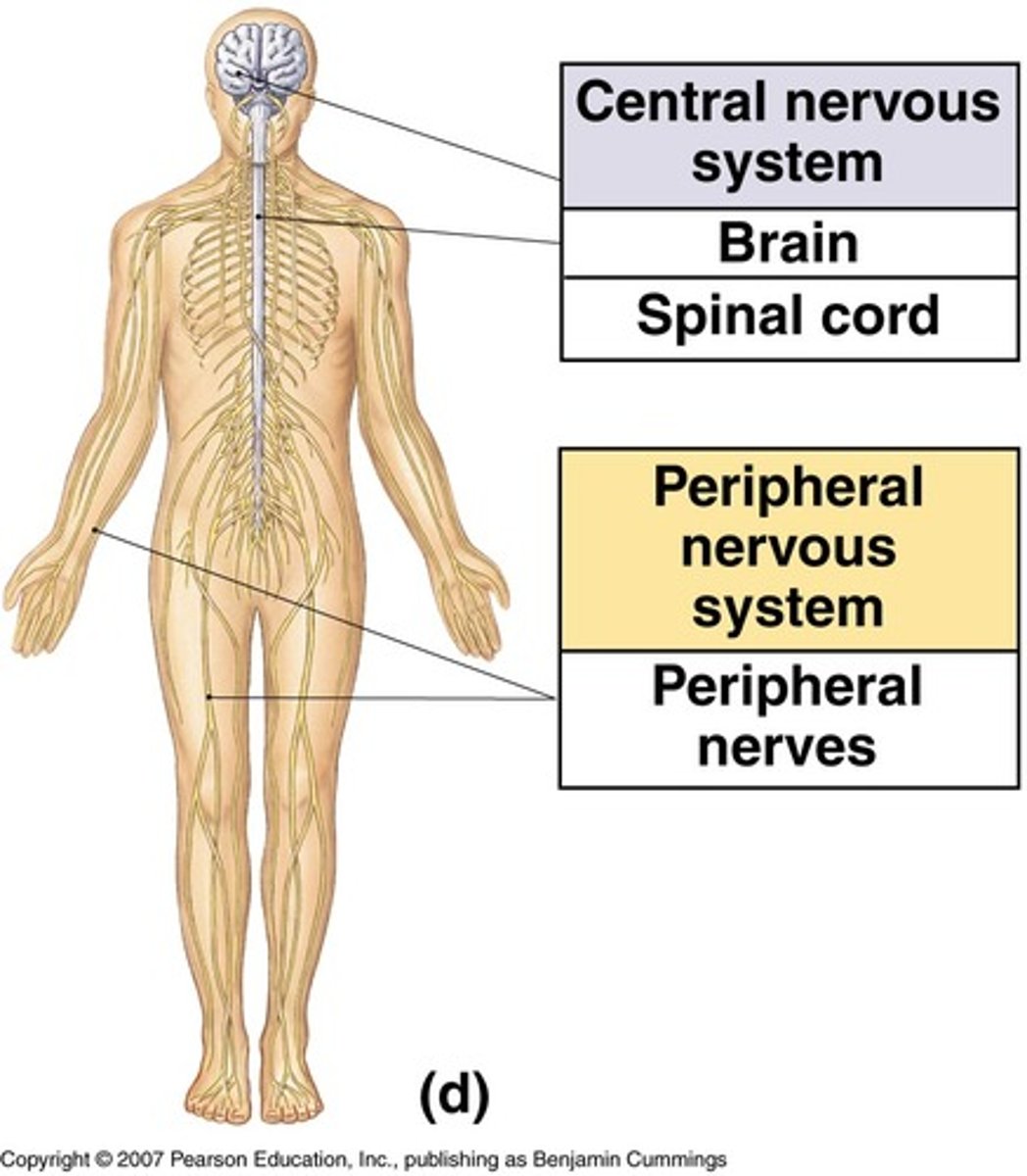
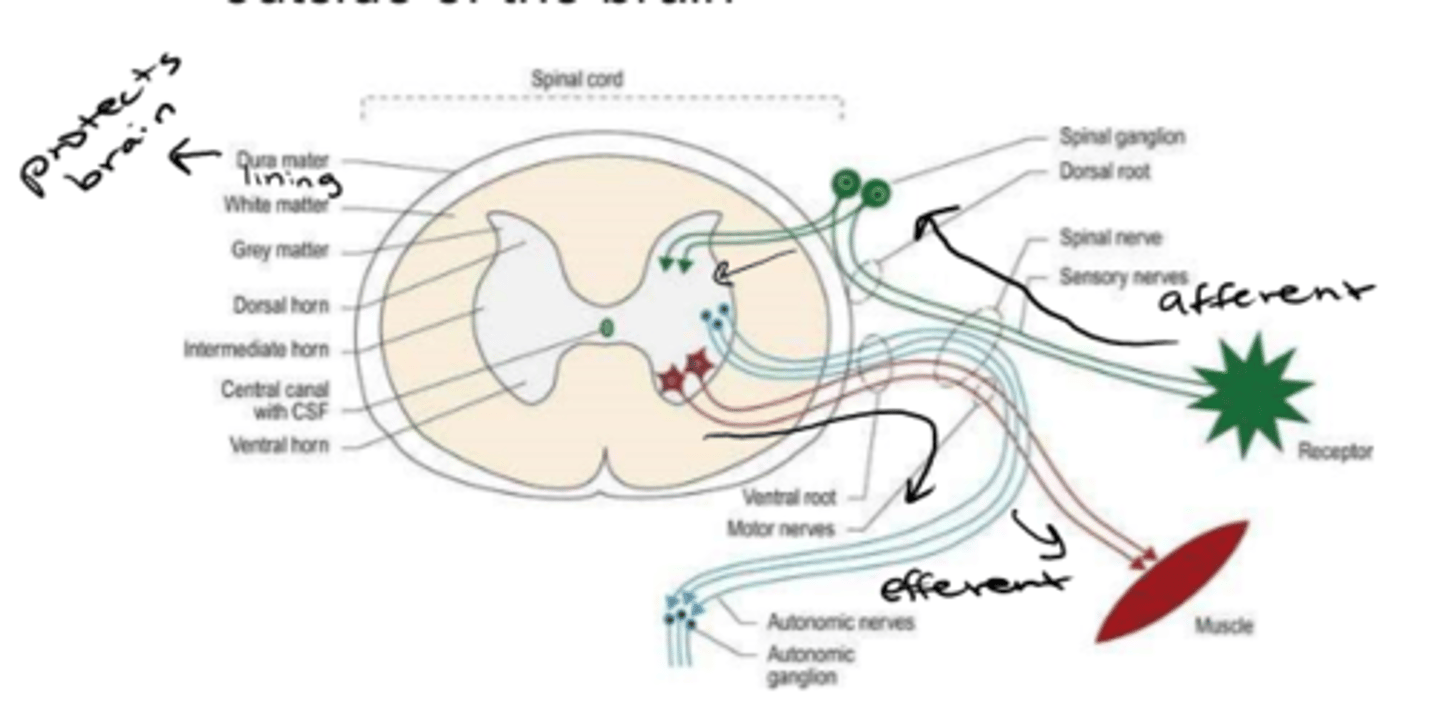
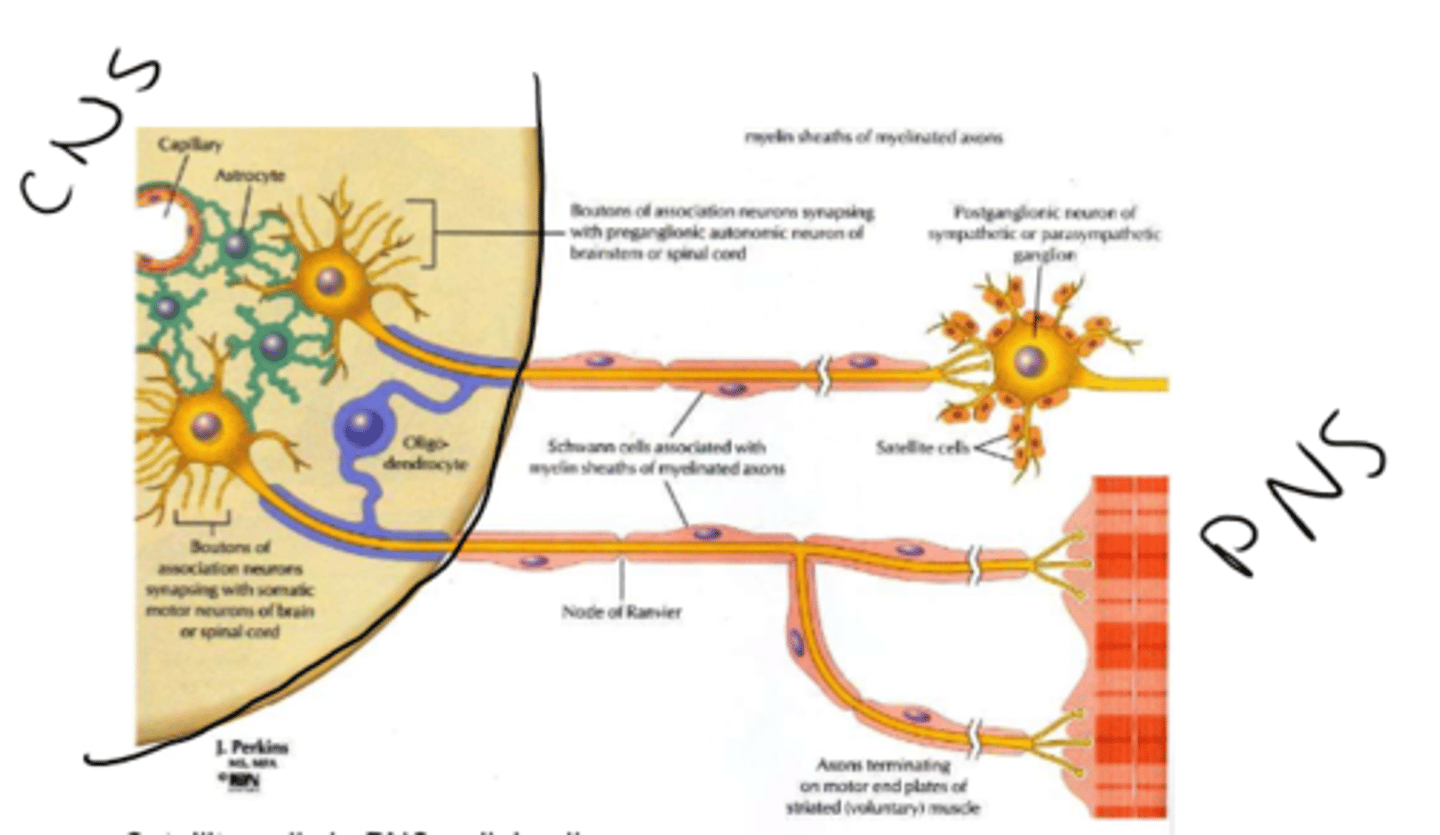
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
-conveys info to and from CNS
info from PNS toward CNS
afferent
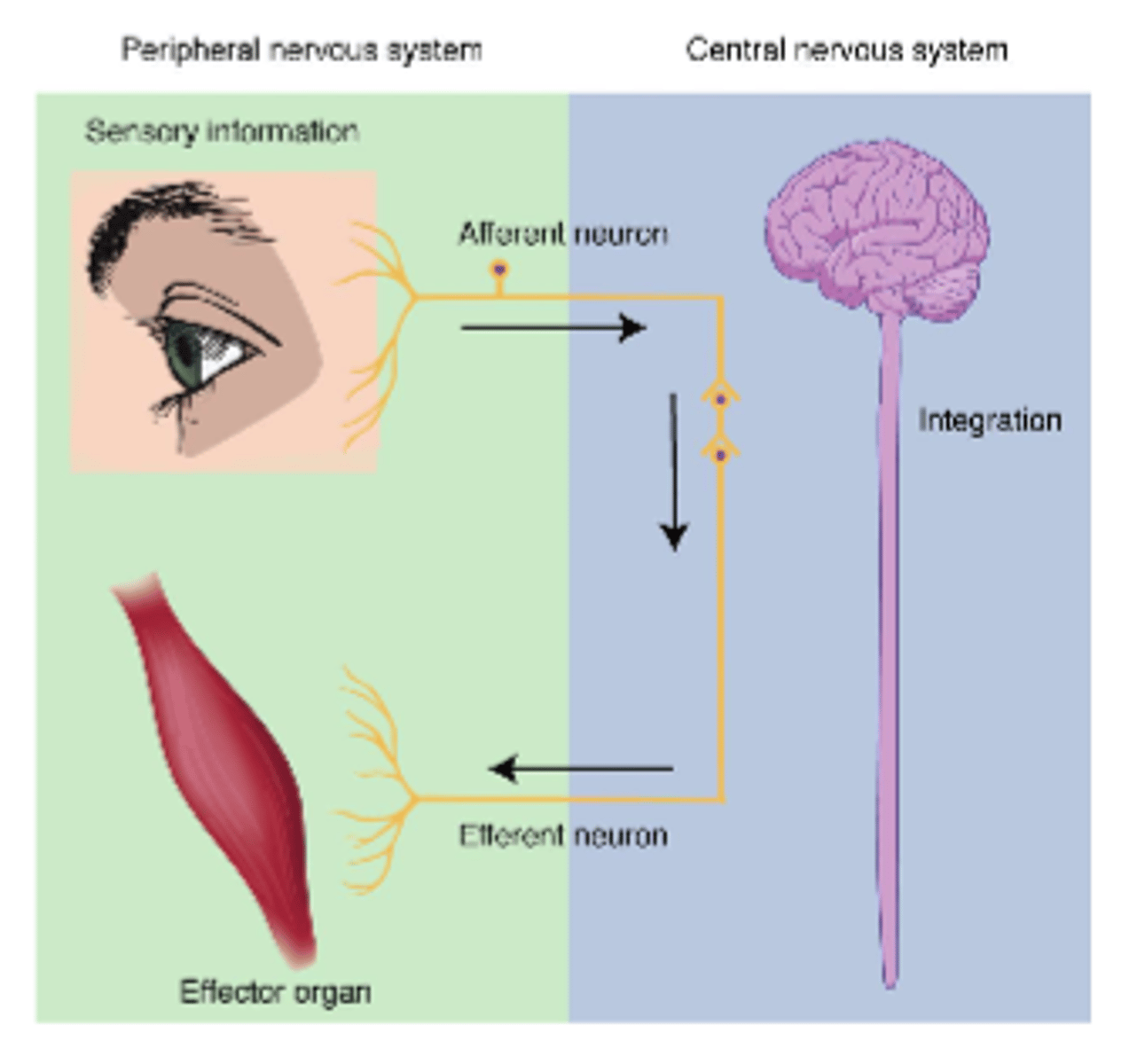
info from CNS to PNS (away from CNS)
efferent
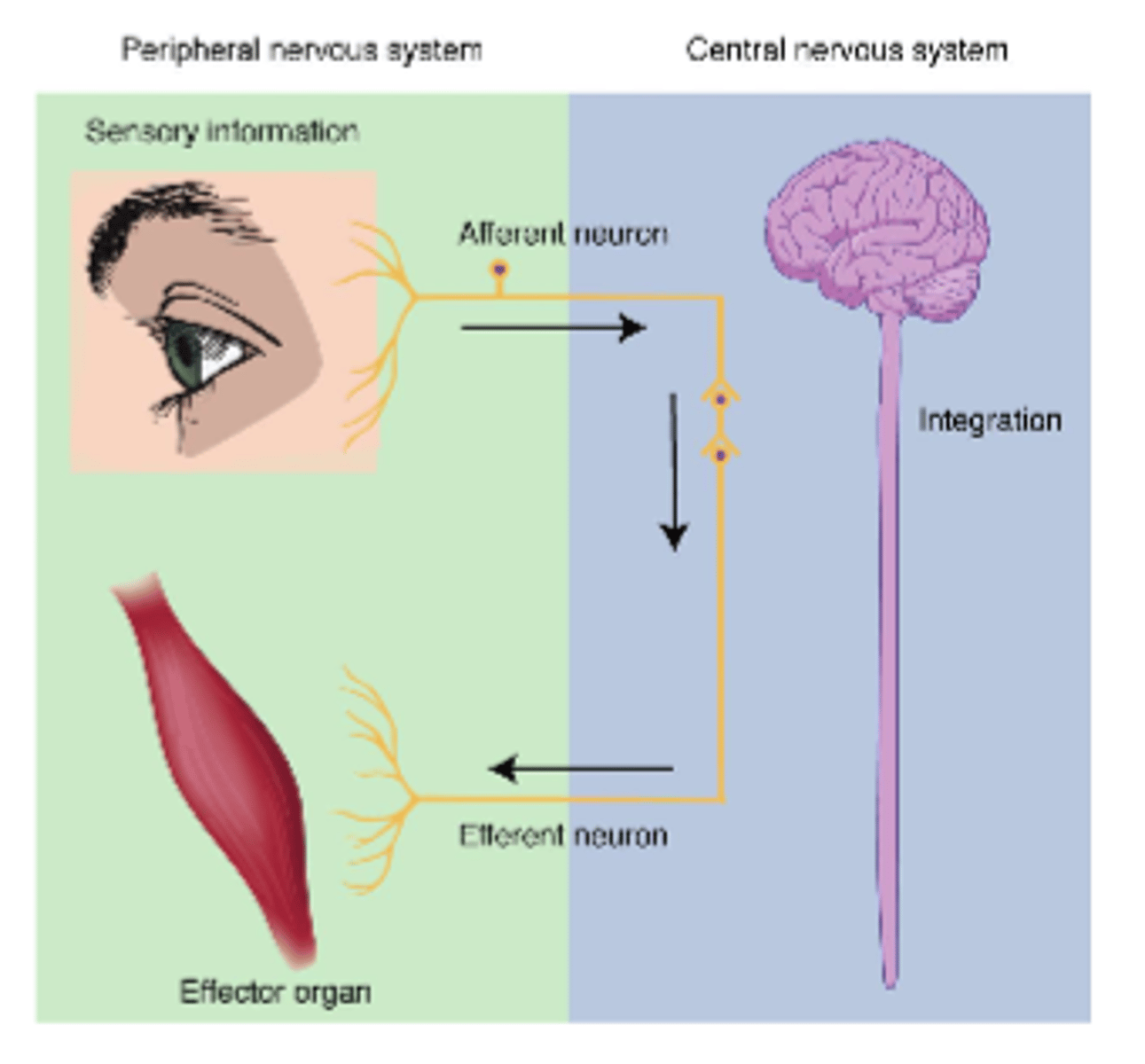
Central Nervous System (CNS)
-integrates sensory info
-generates output
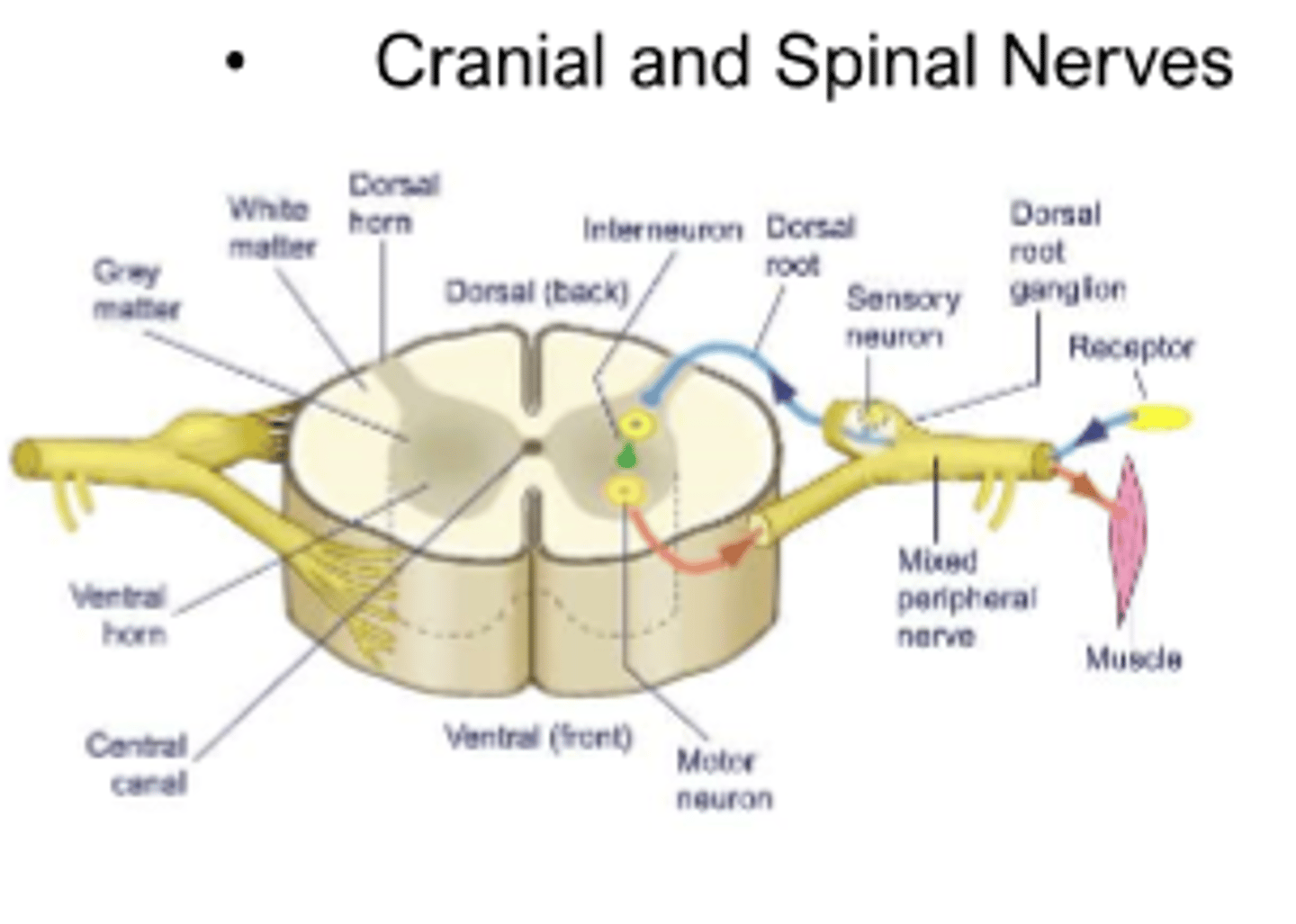
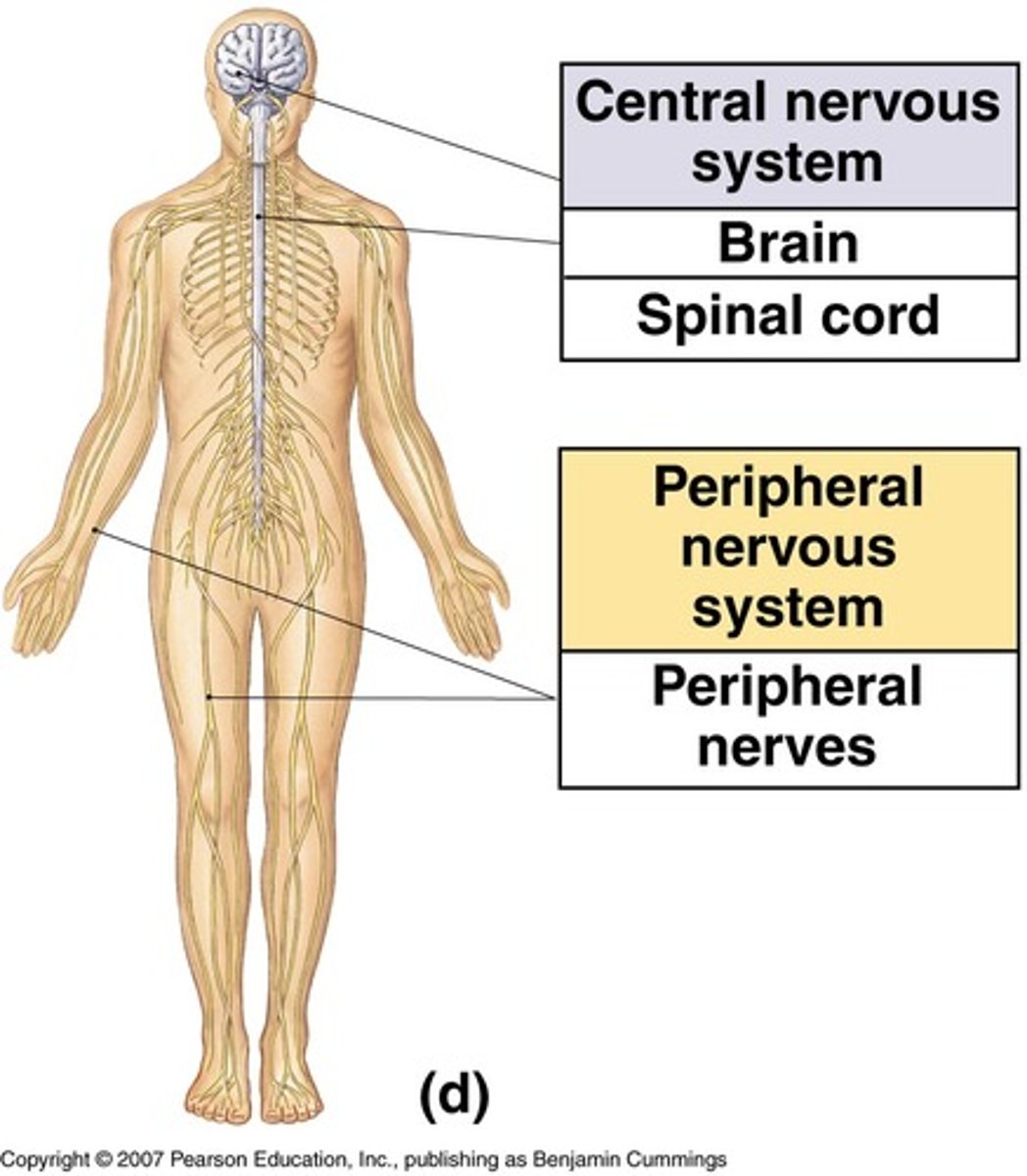
anatomical classification of PNS
cranial and spinal nerves
anatomical classification of CNS
brain and spinal cord
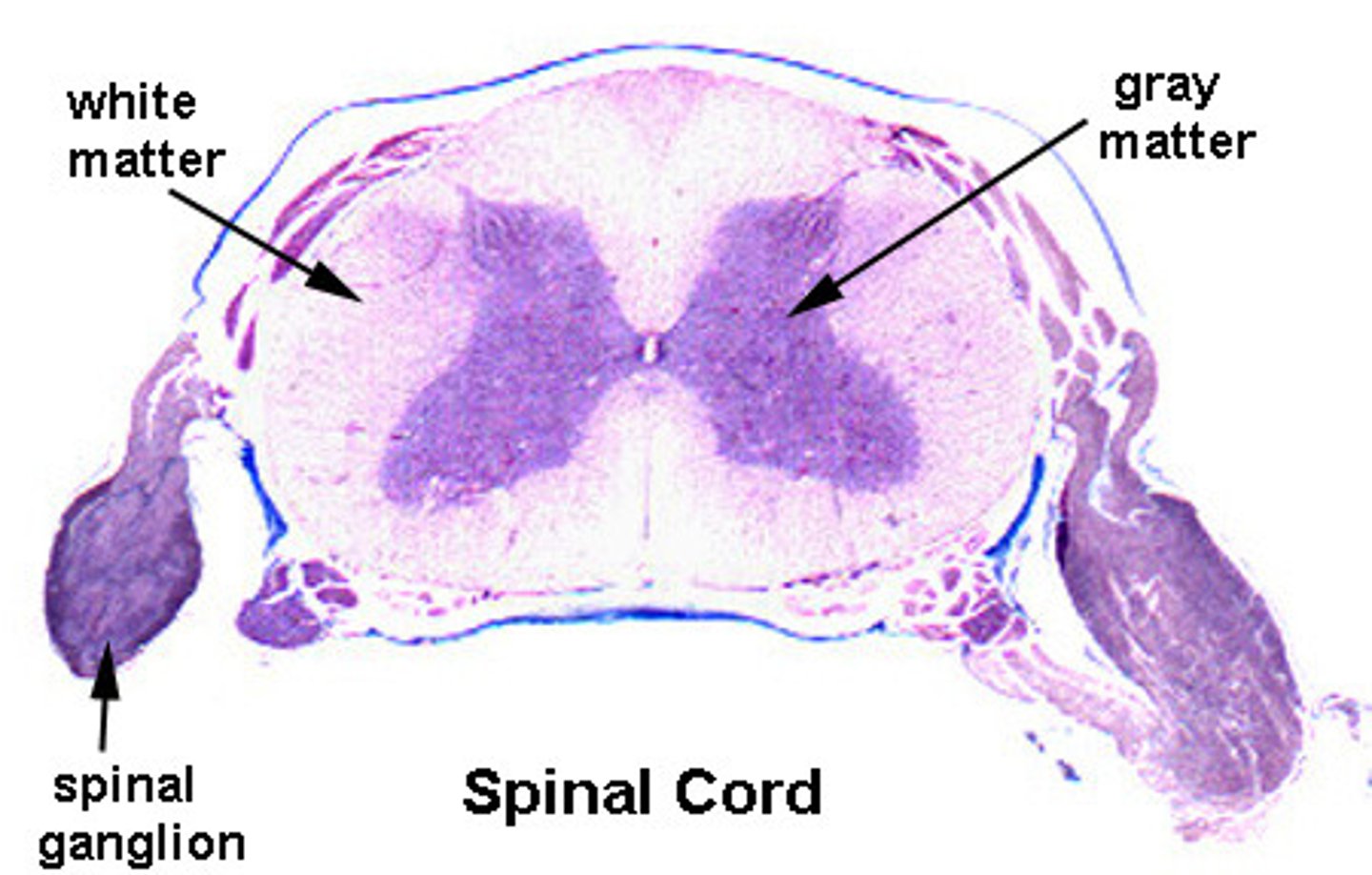
aggregations of fibers in CNS
white matter
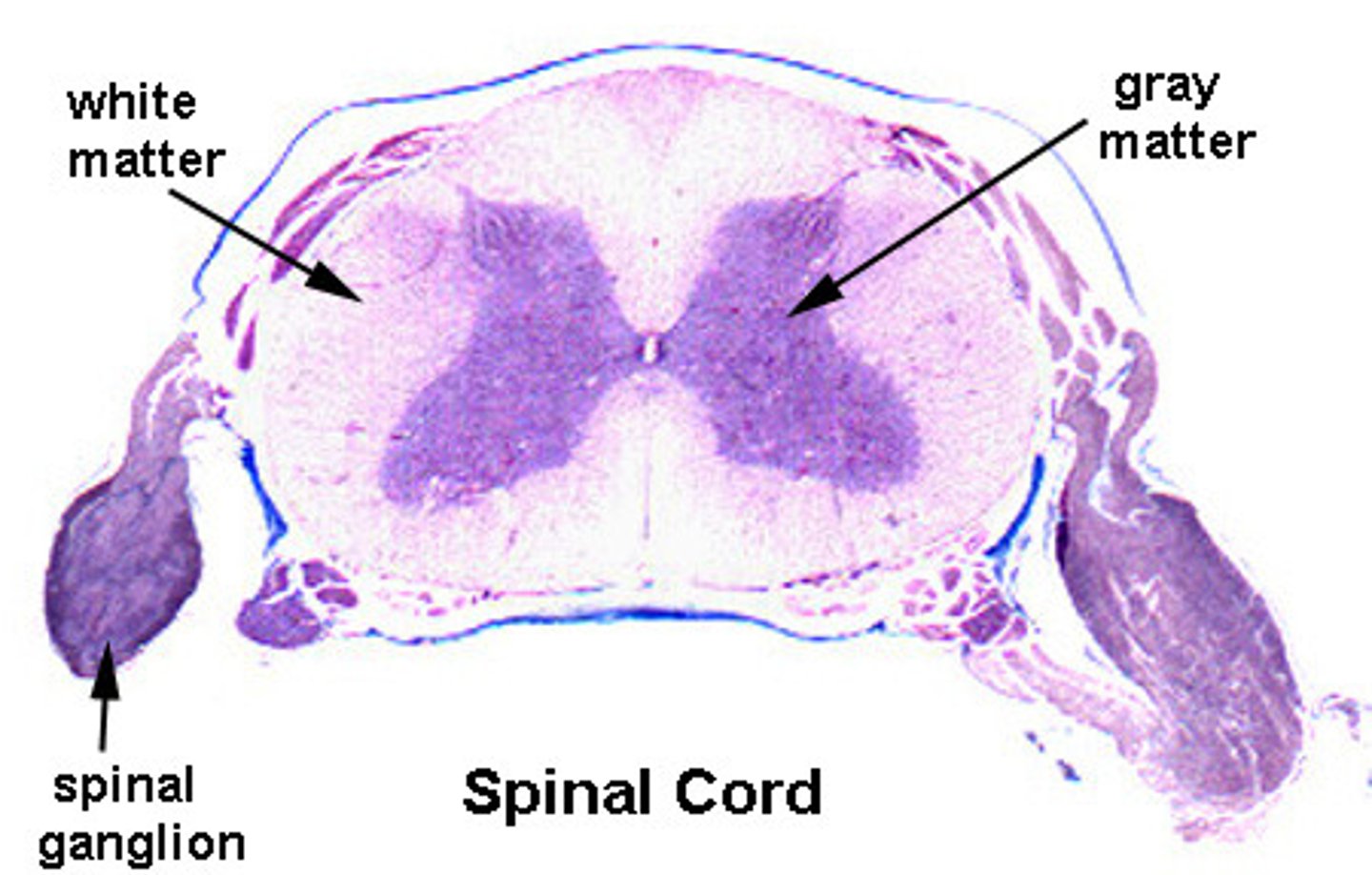
aggregations of cell bodies in the nervous system (ganglia, nucleus)
grey matter
bundle of nerve fibers which cross the midline/ connect hemispheres of the brain
commissure
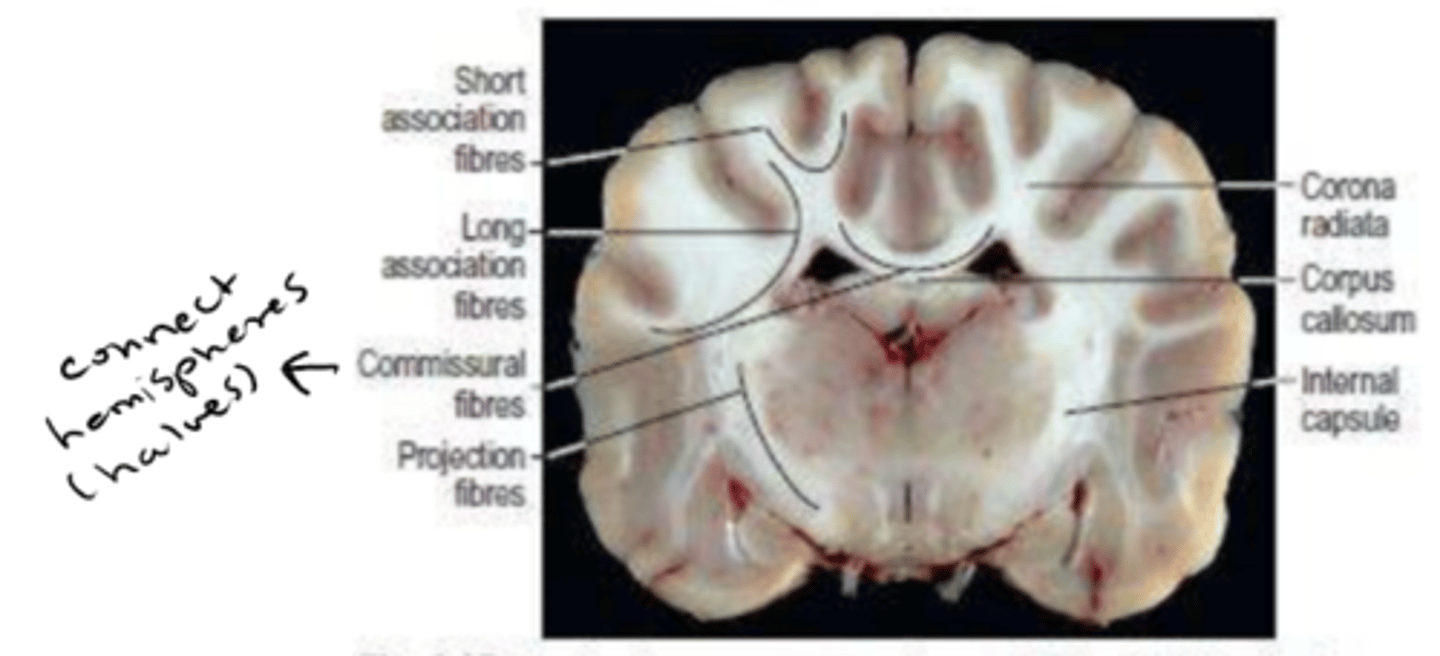
bundle of nerve fibers in CNS
tract
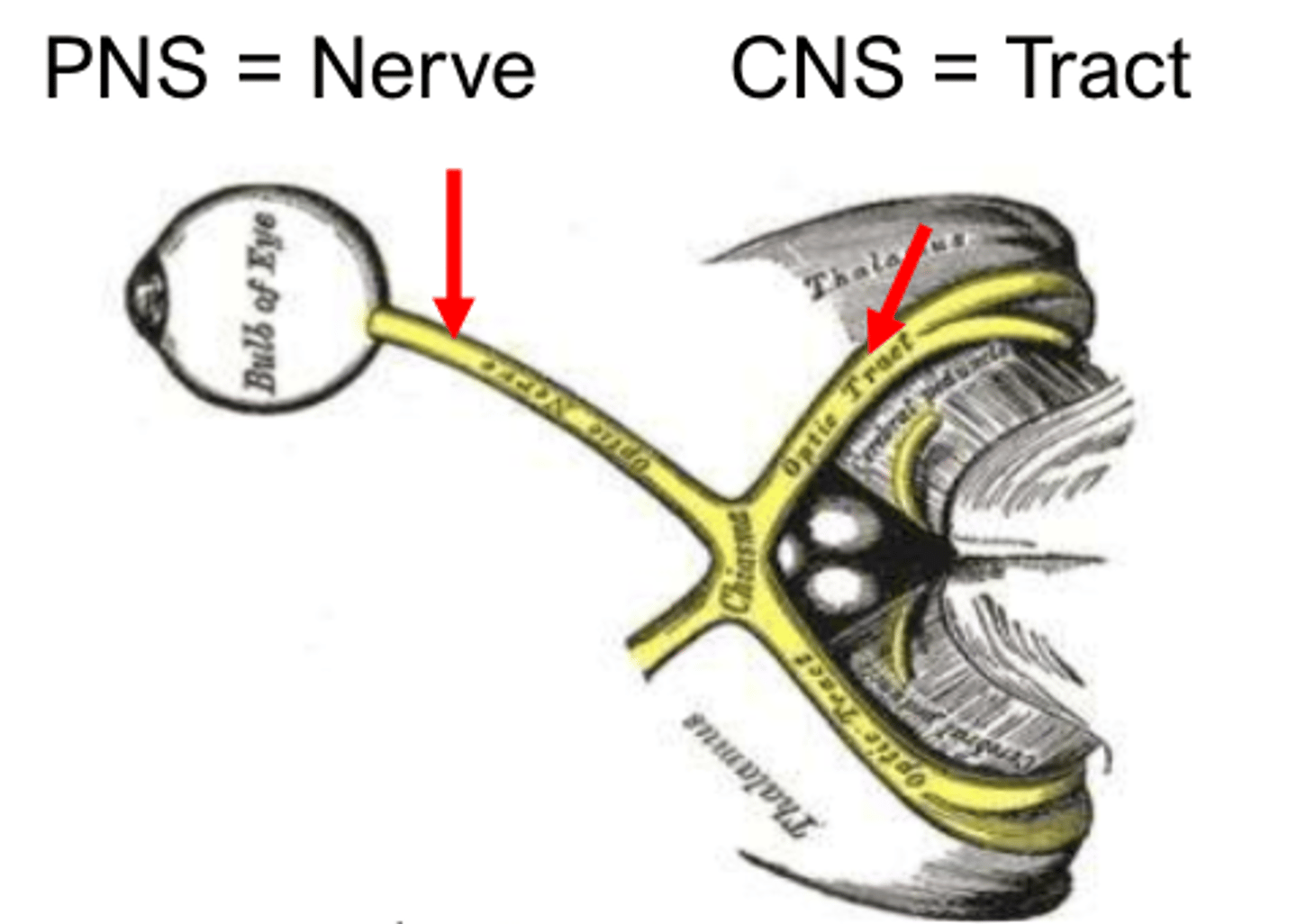
bundle of nerve cell projections (axons) in PNS
nerve
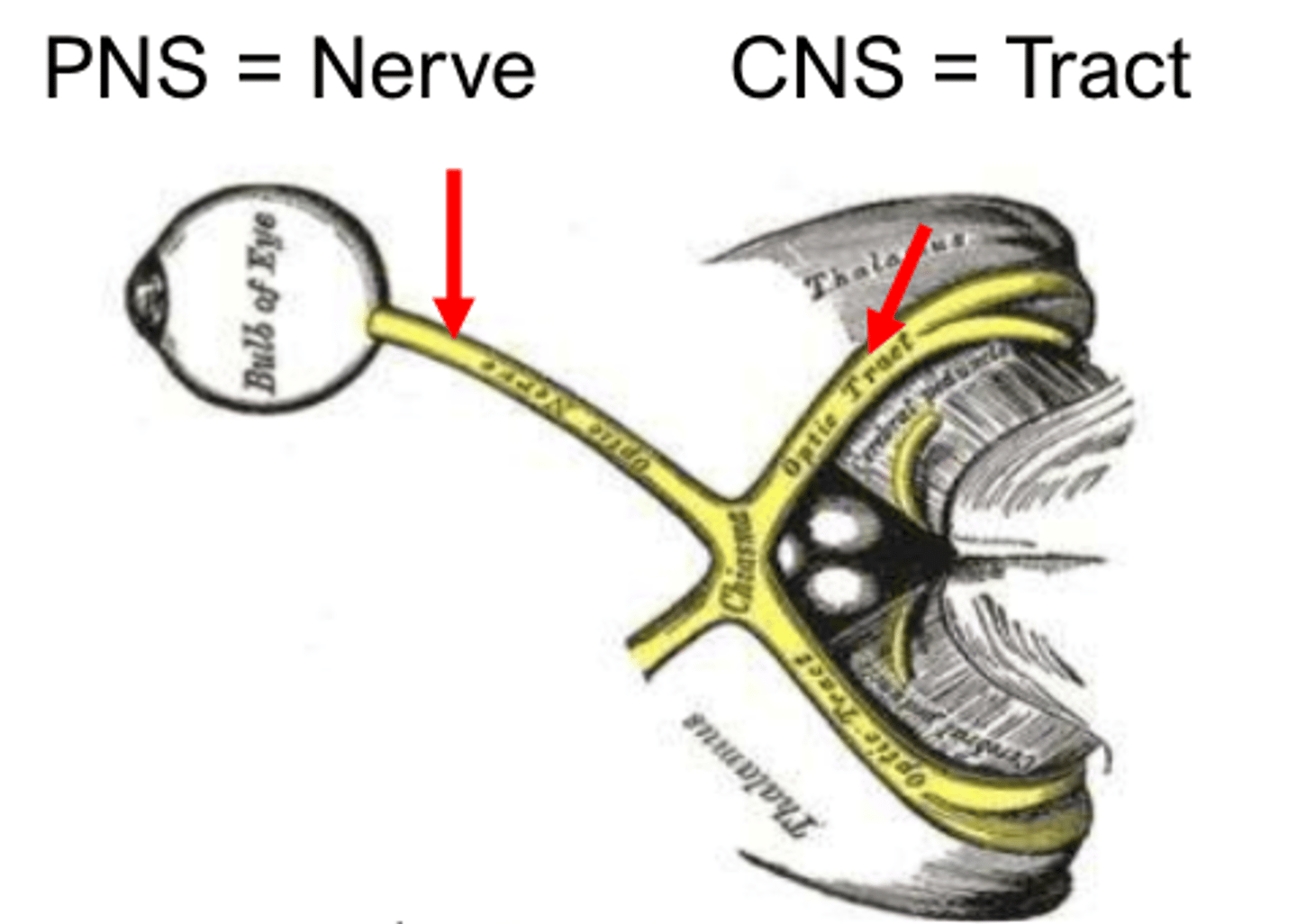
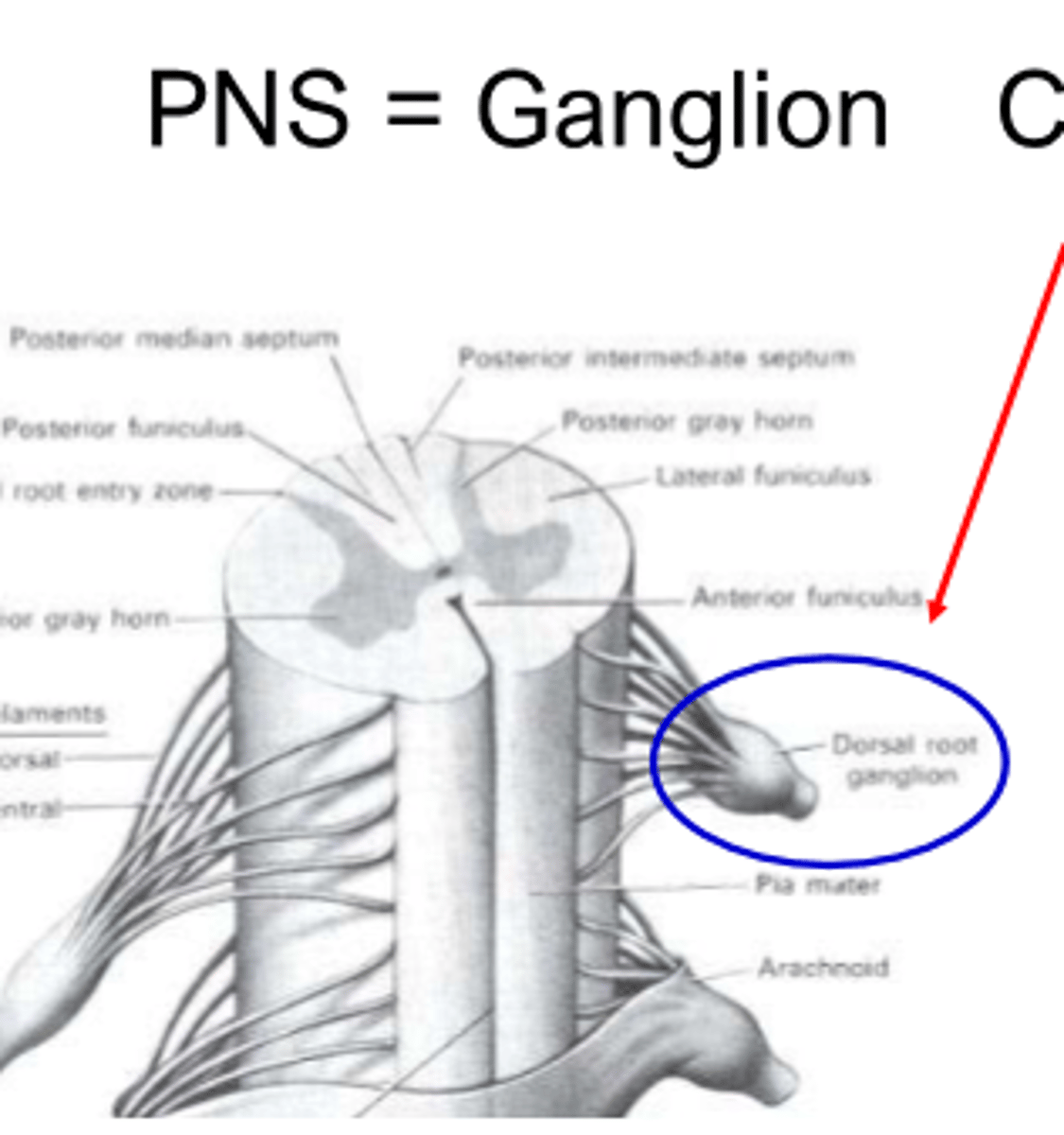
group of neurons in a cluster- PNS
ganglion
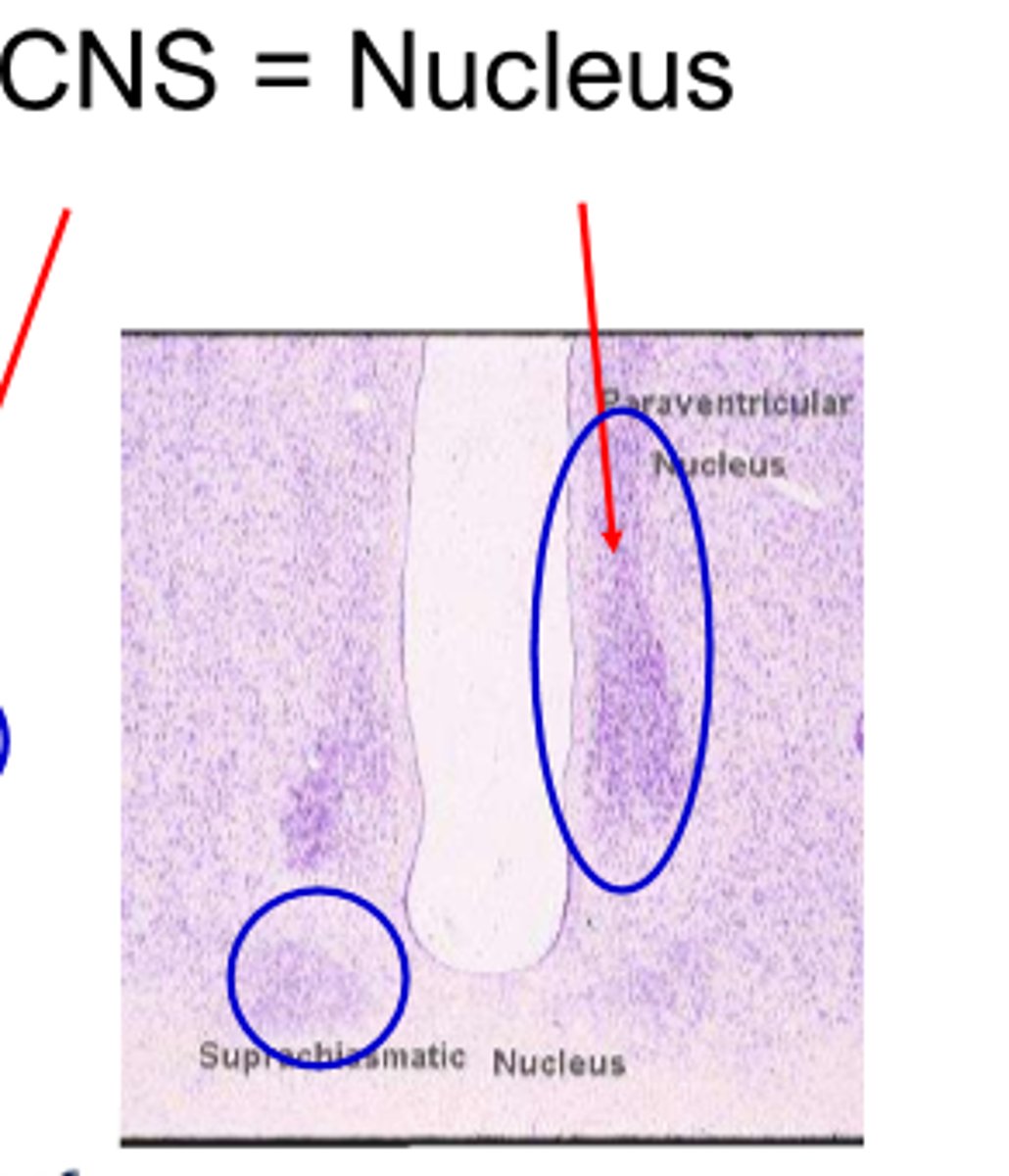
group of neurons in a cluster- CNS
nucleus
_______ is made up of nerves and ganglia outside of the brain
PNS
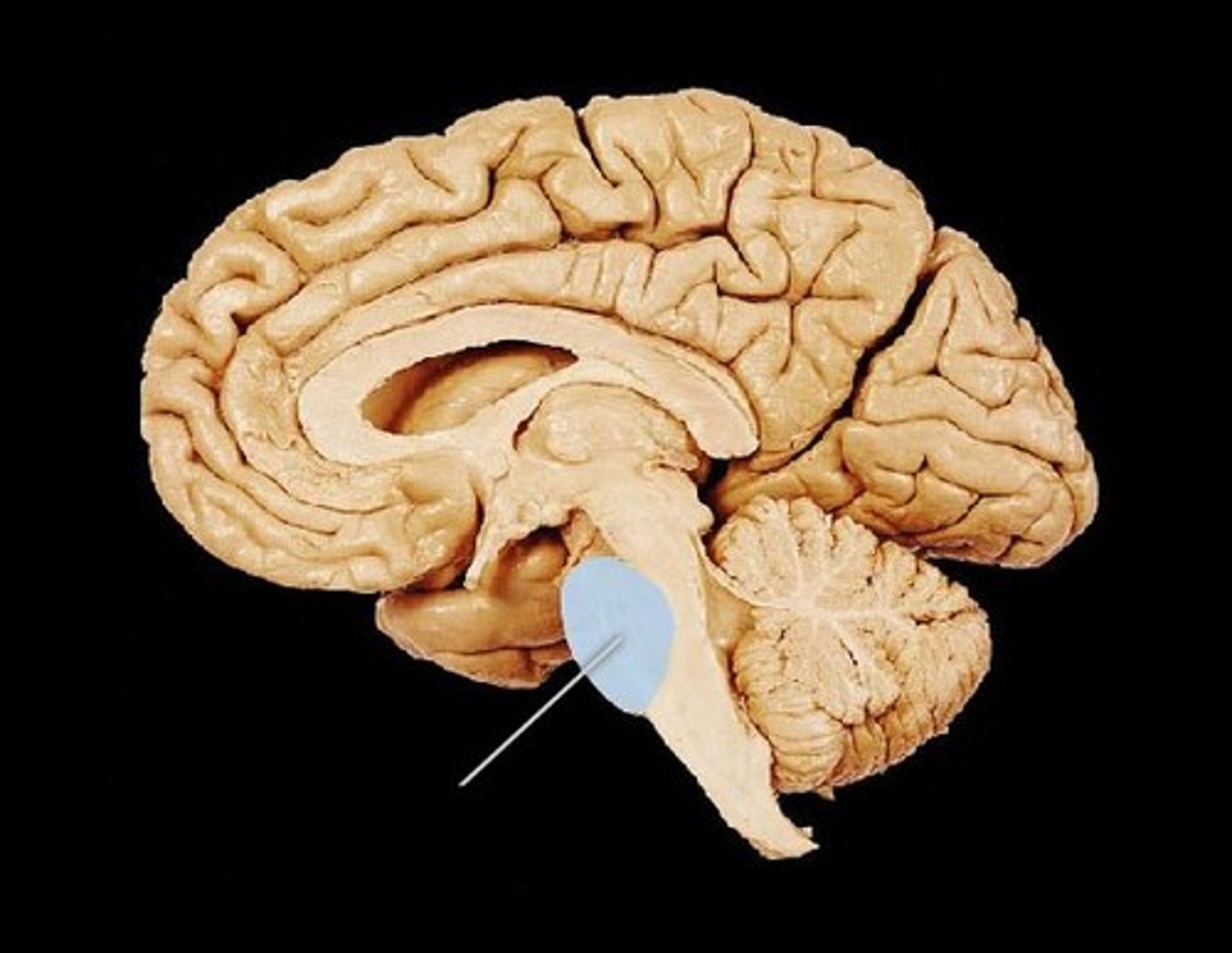
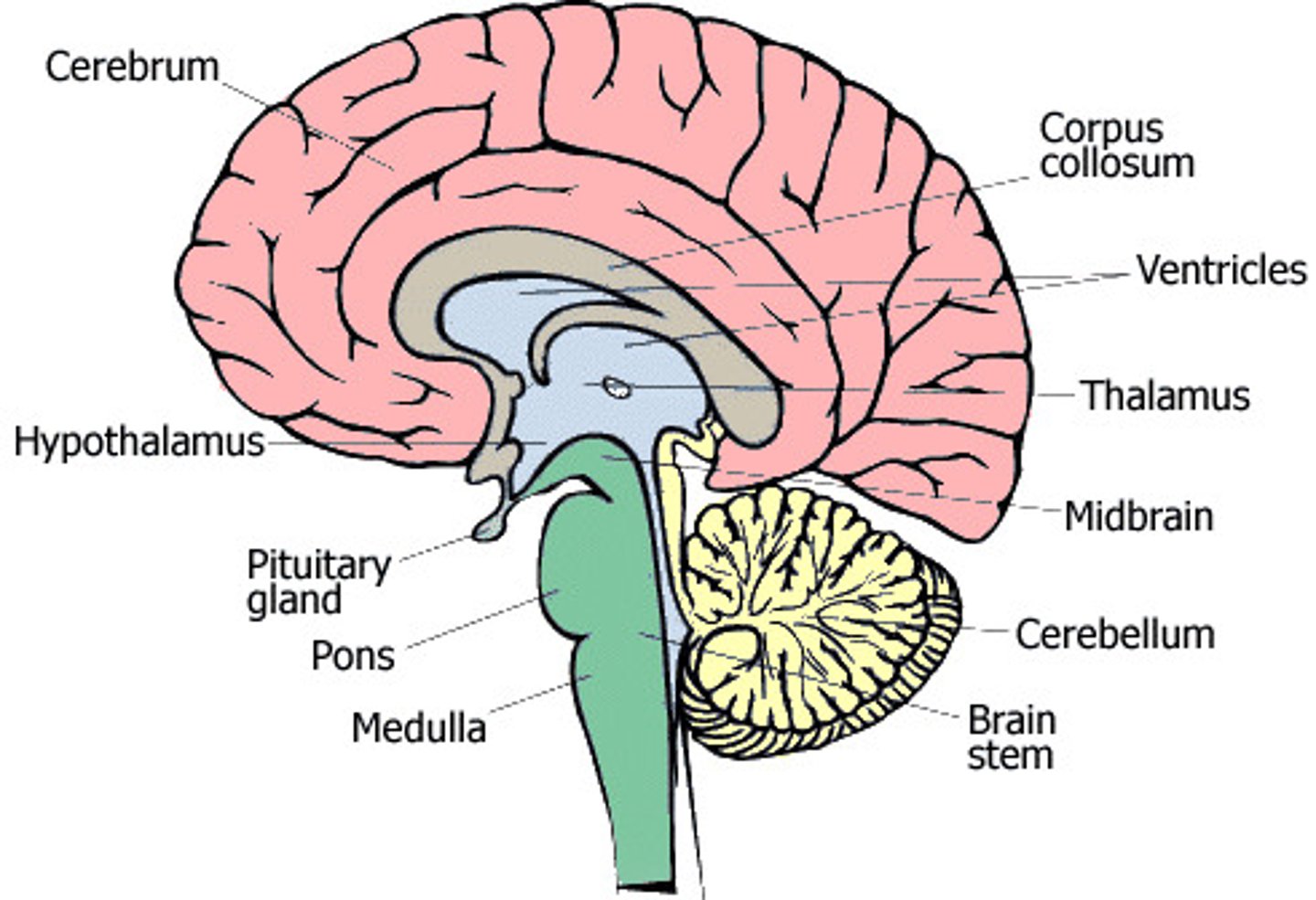
CNS mesencephalon
midbrain
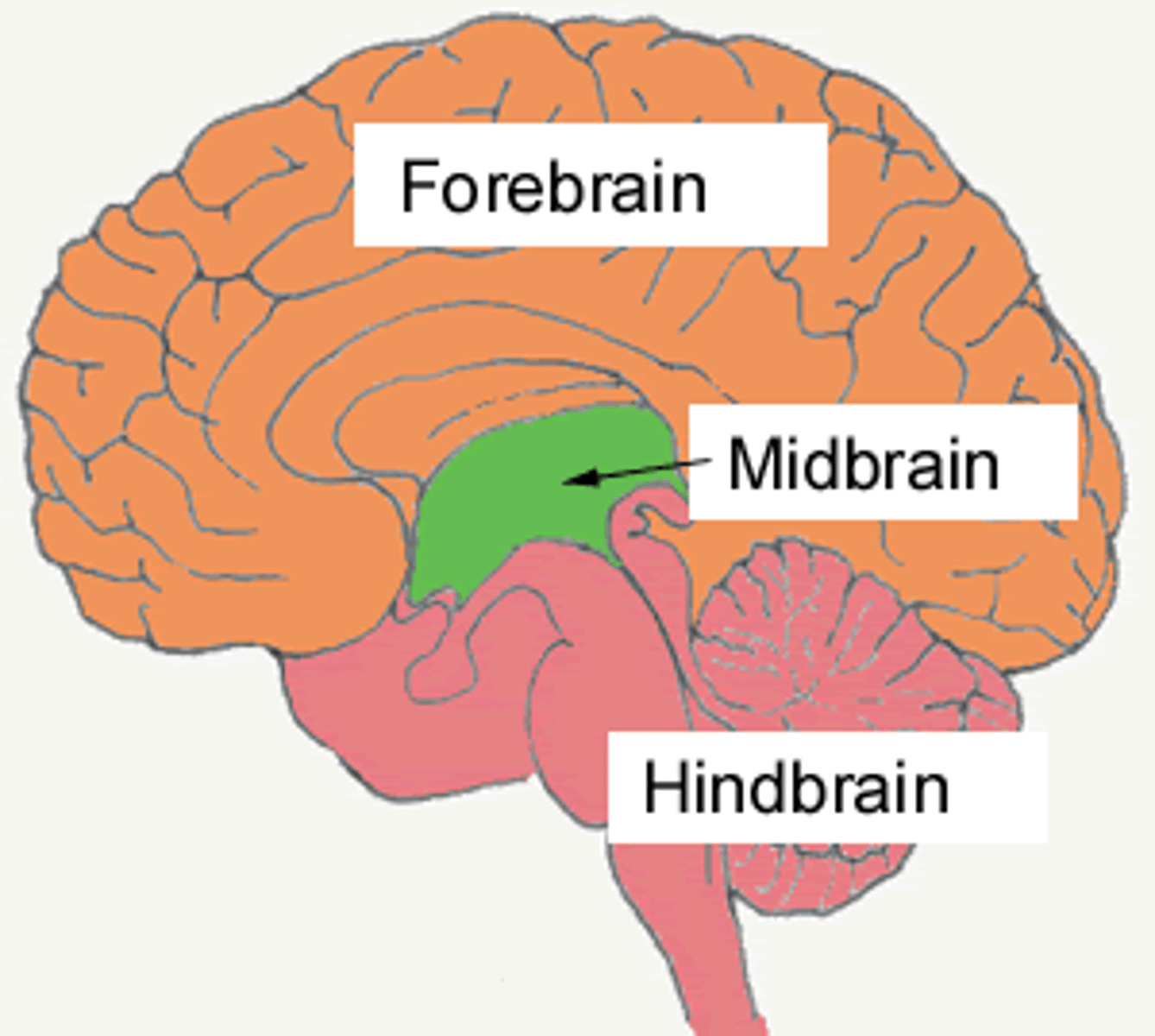
CNS metencephalon
pons
CNS myelencephalon
medulla
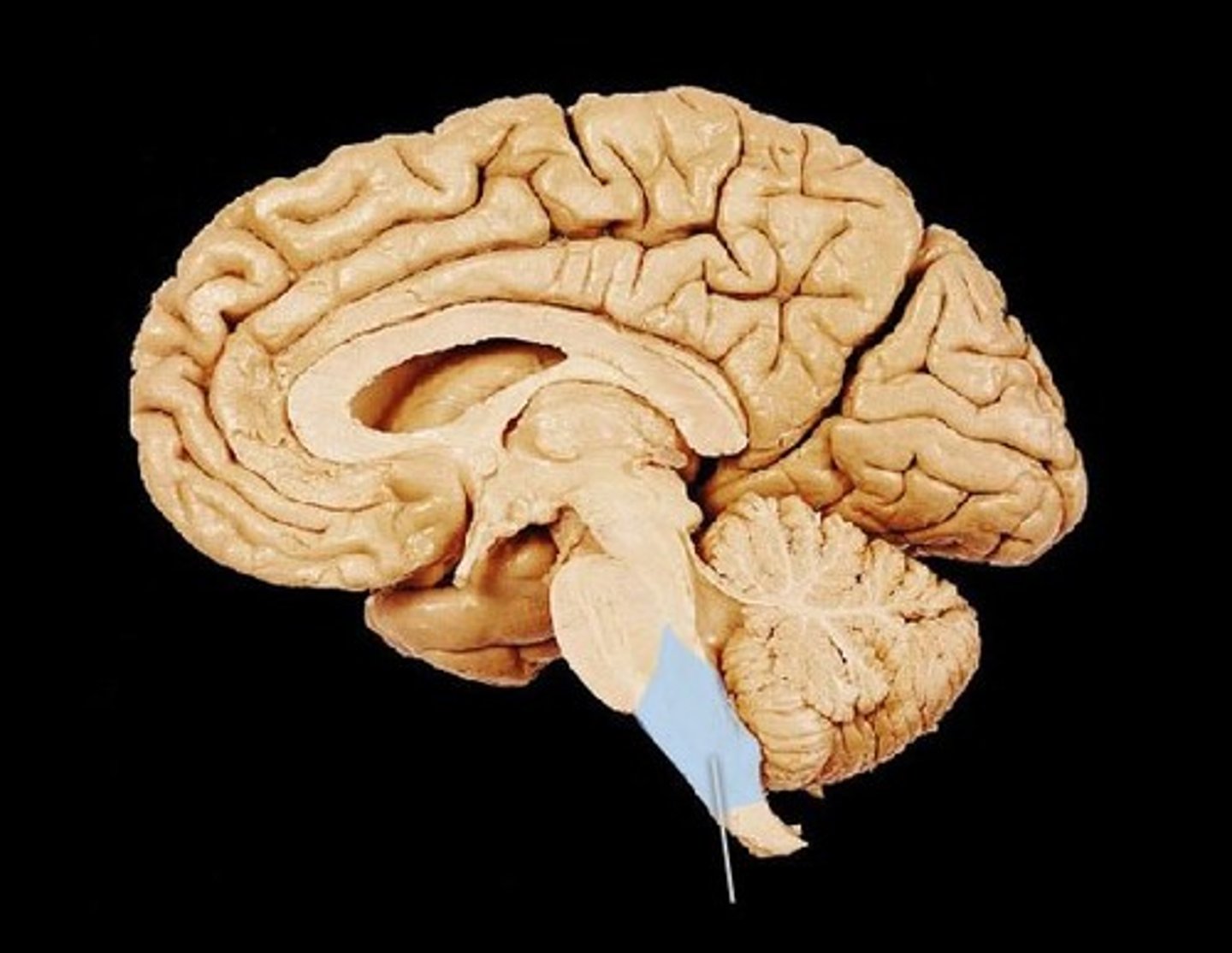
brainstem composed of
medulla, pons, midbrain
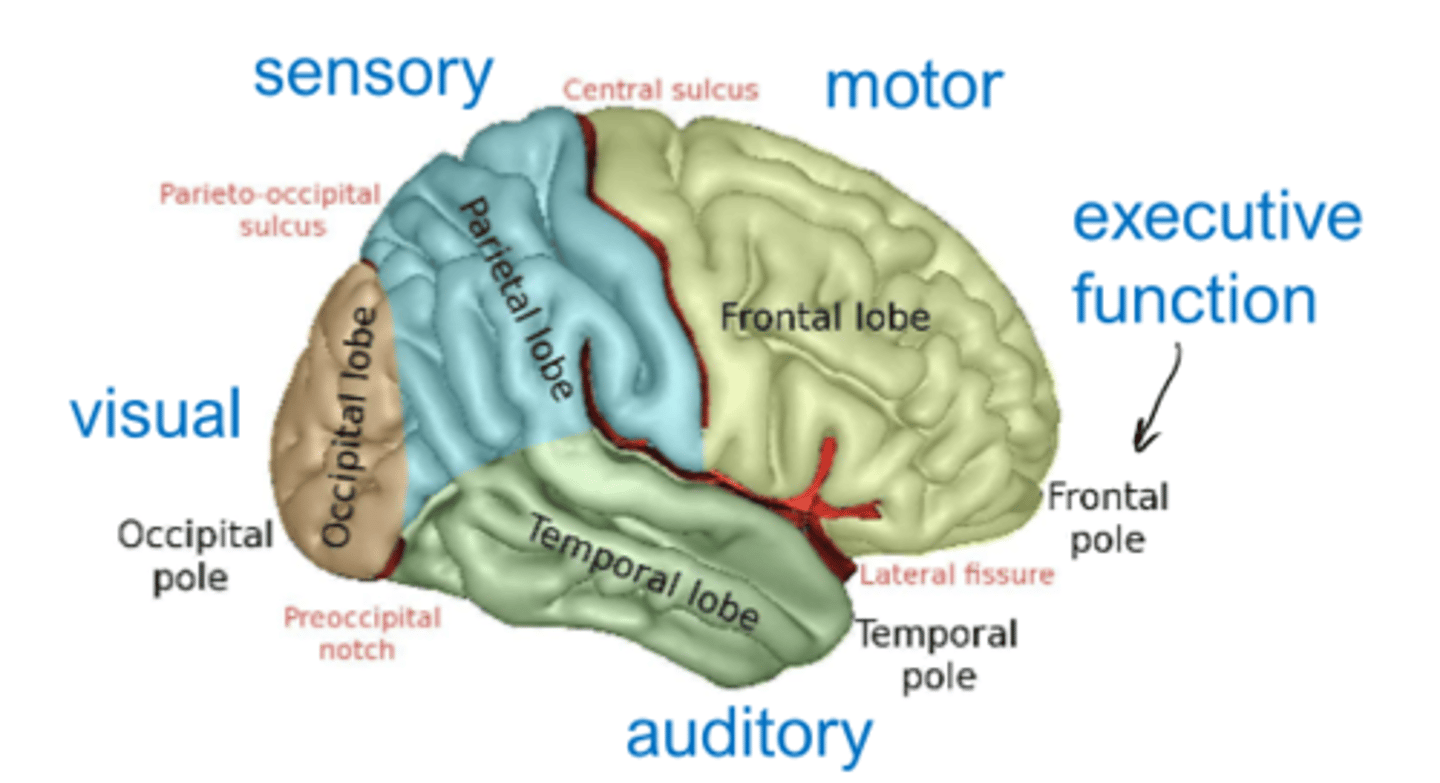
executive function part of brain
frontal pole
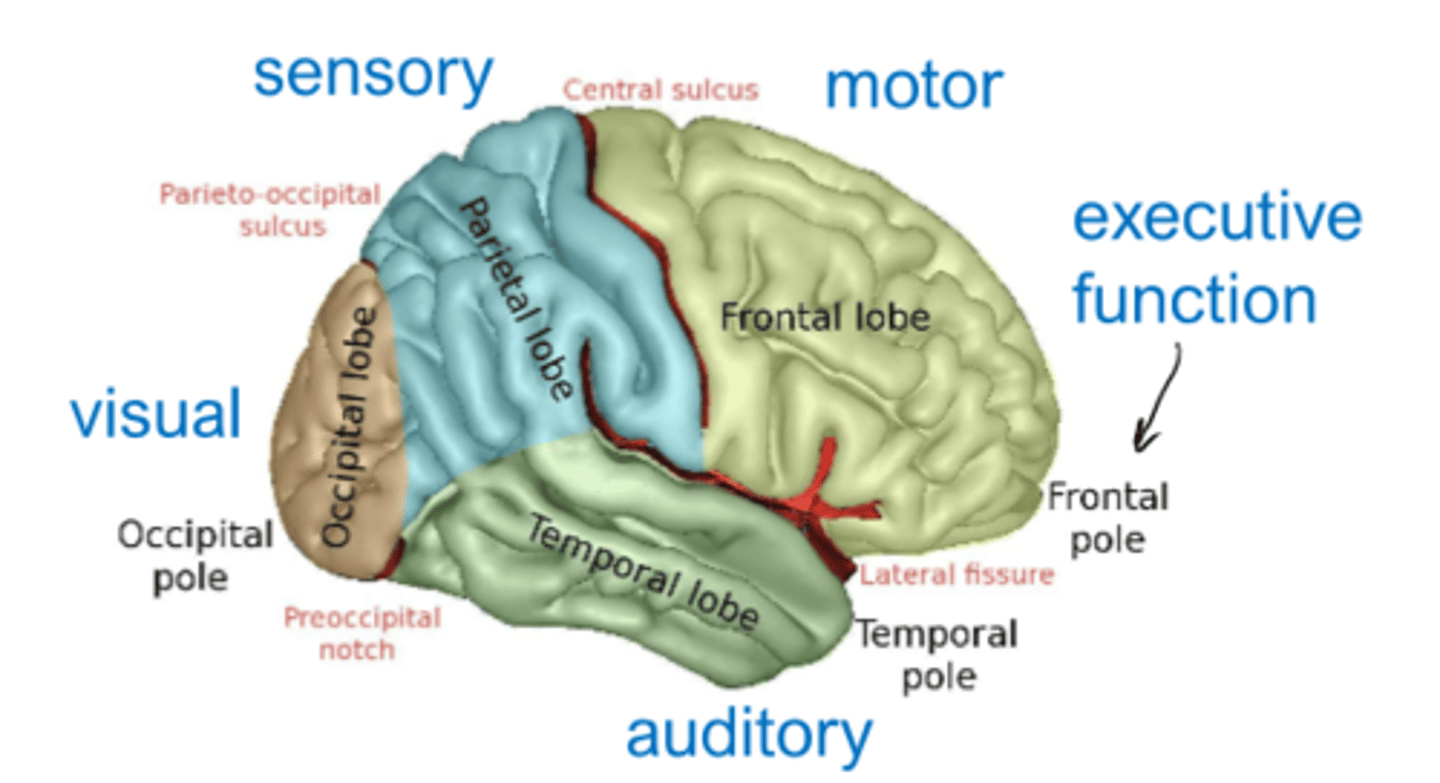
motor part of brain
frontal lobe
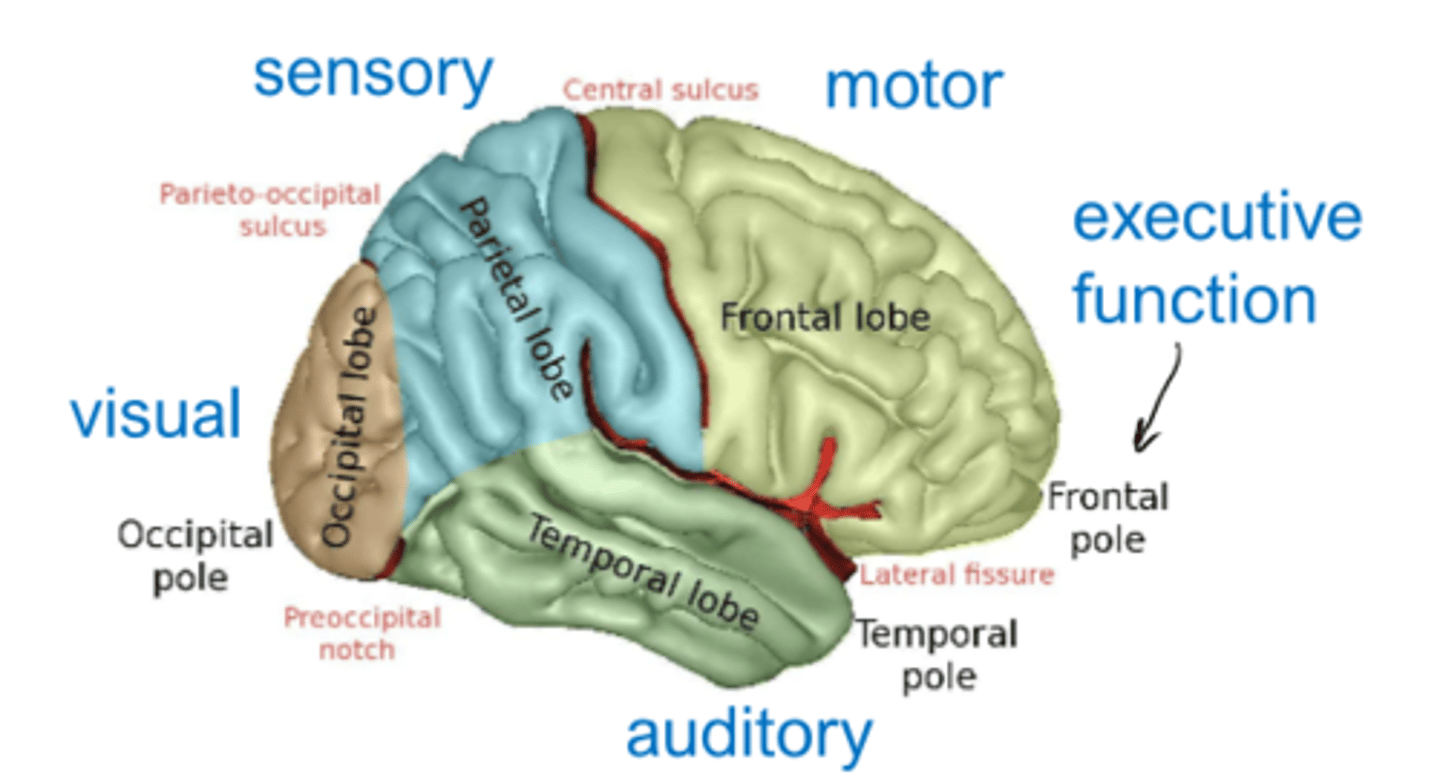
sensory part of brain
parietal lobe
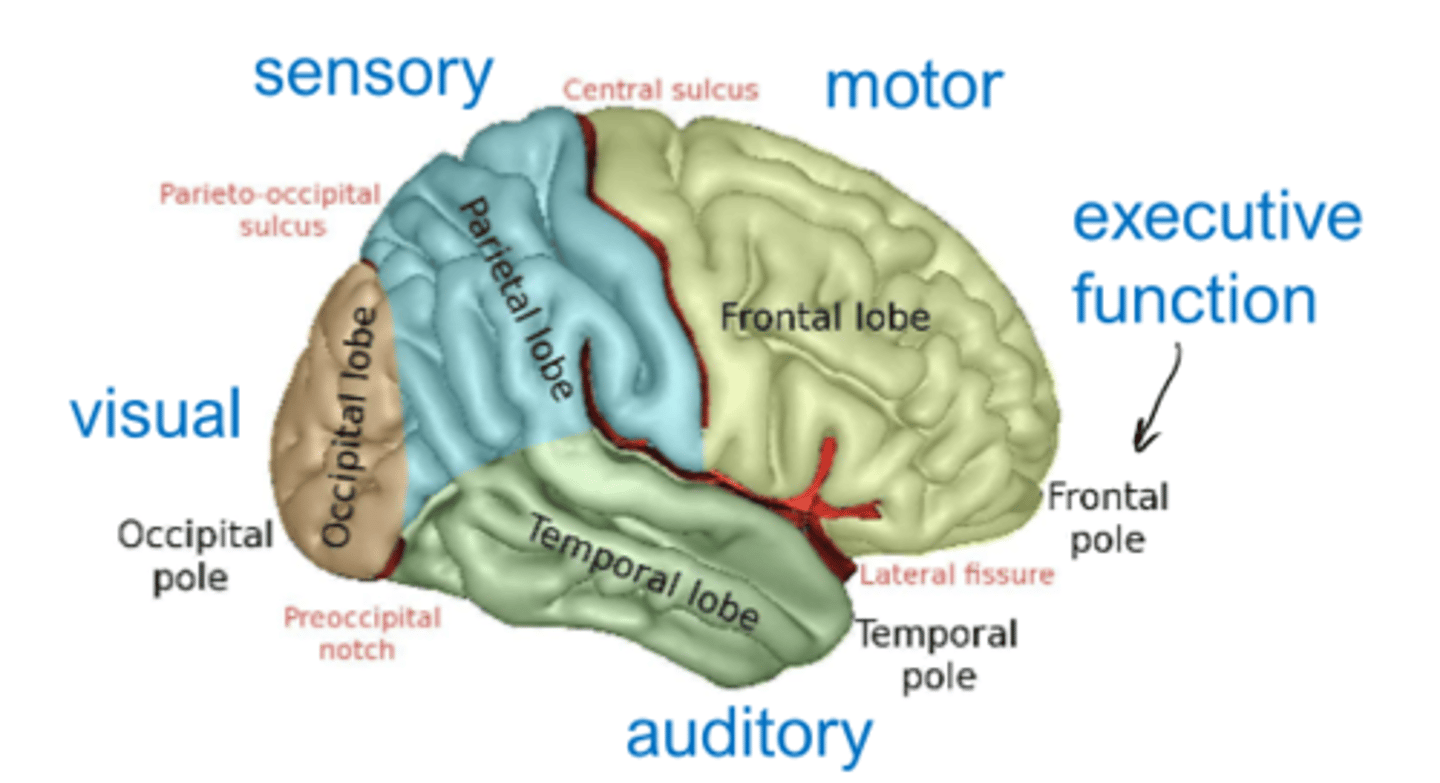
visual part of brain
occipital lobe
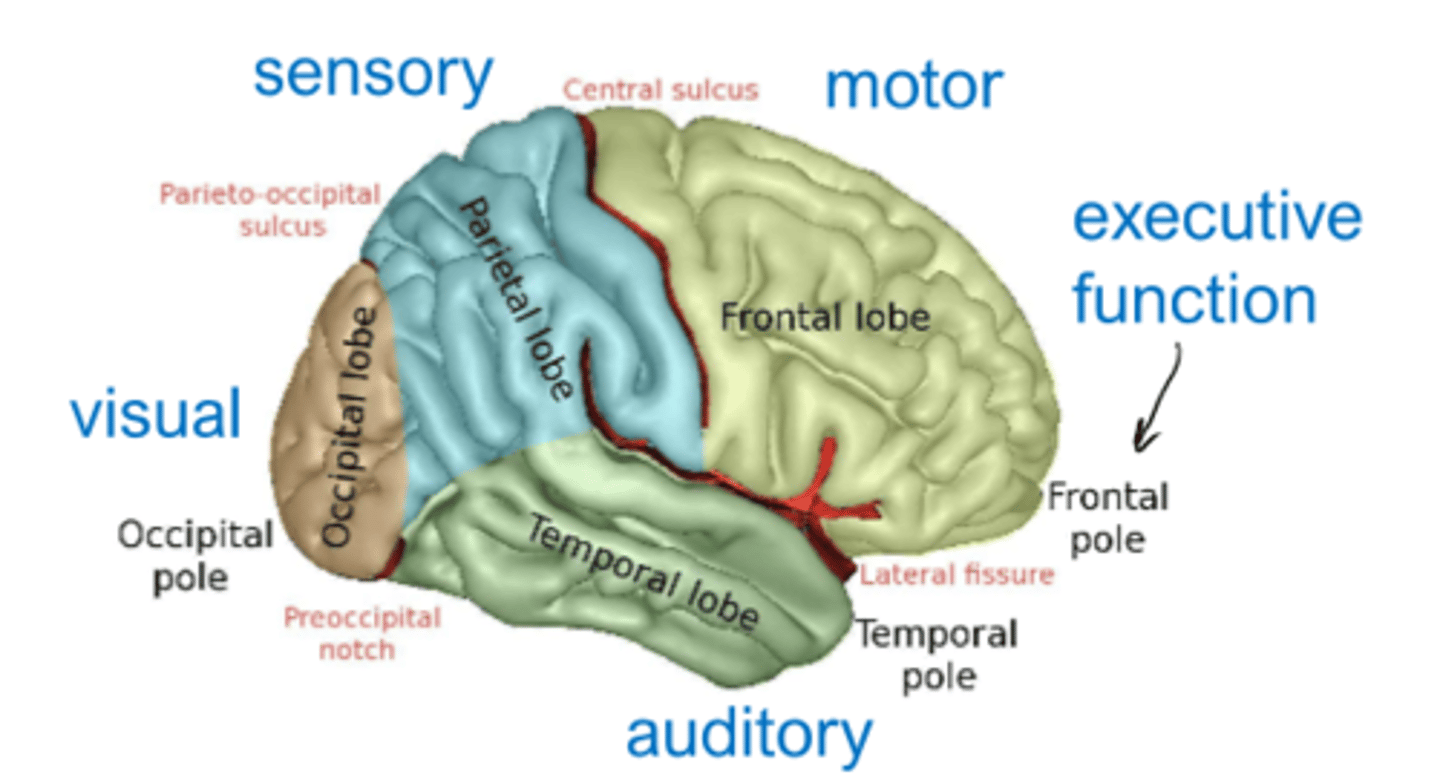
auditory part of brain
temporal lobe
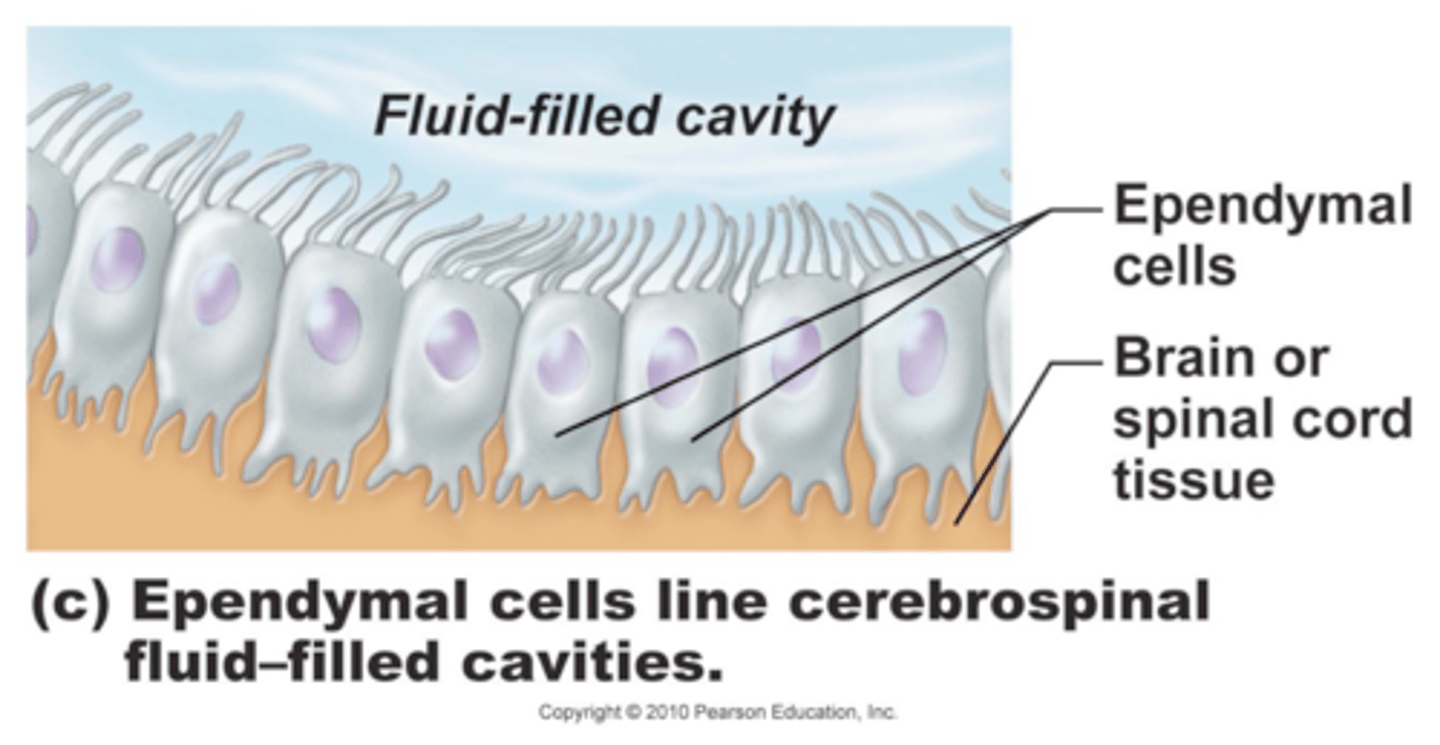
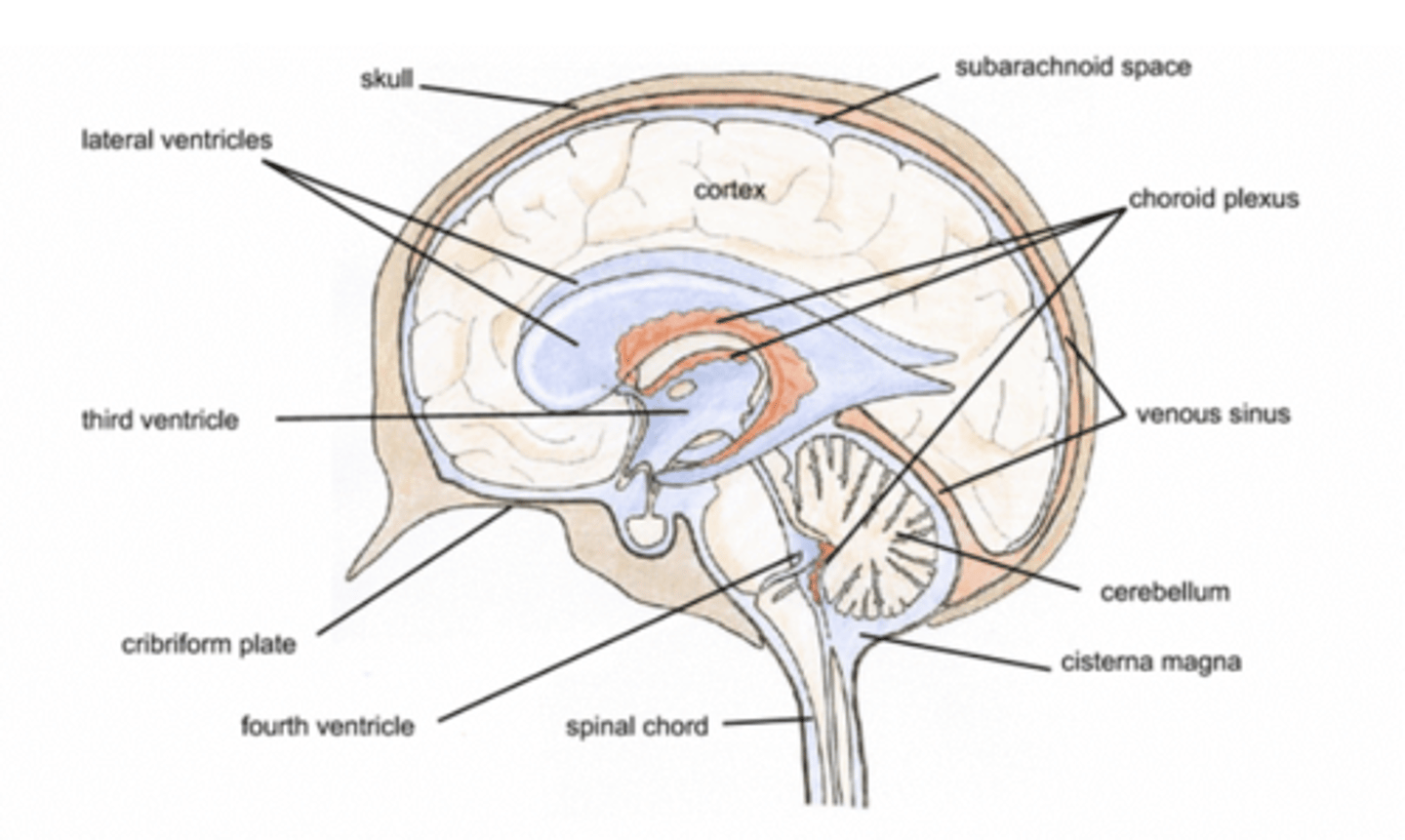
specialized epithelial cells that line the ventricles of the brain and spinal cord
ependyma
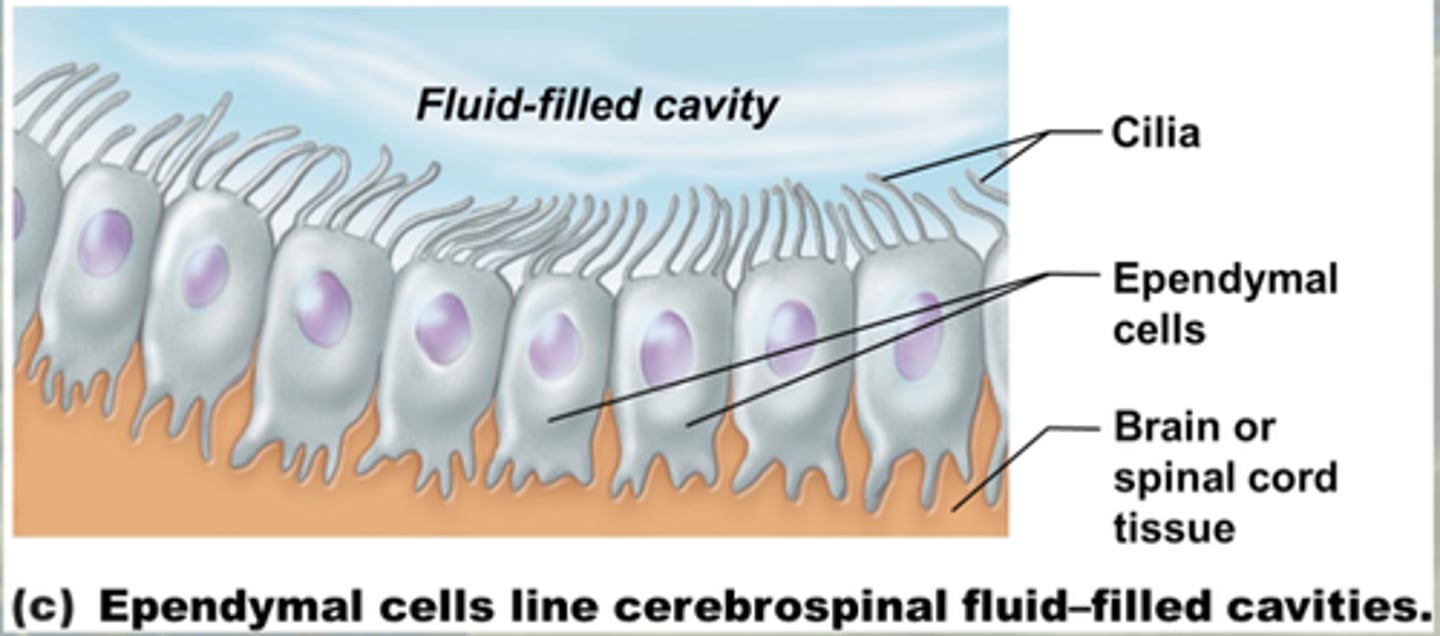
ependyma function
move CSF through ventricular system
spaces within brain and spinal cord where CSF flows
ventricular system
choroid plexus function
-secretes CSF
-significant role in blood-CSF barrier
-specialized ependymal cells
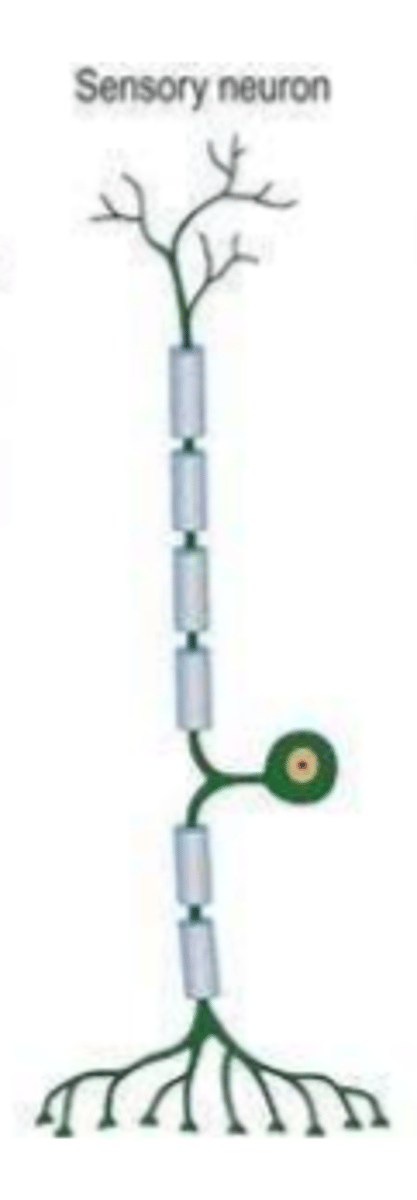
specialized neuron that detects change in external or internal environment and sends info about these changes to CNS
-from CNS to periphery
sensory neurons

neuron that controls contraction of muscle or secretion of a gland
-originate in CNS, project outside
motor neurons
neuron located entirely within the CNS
interneuron

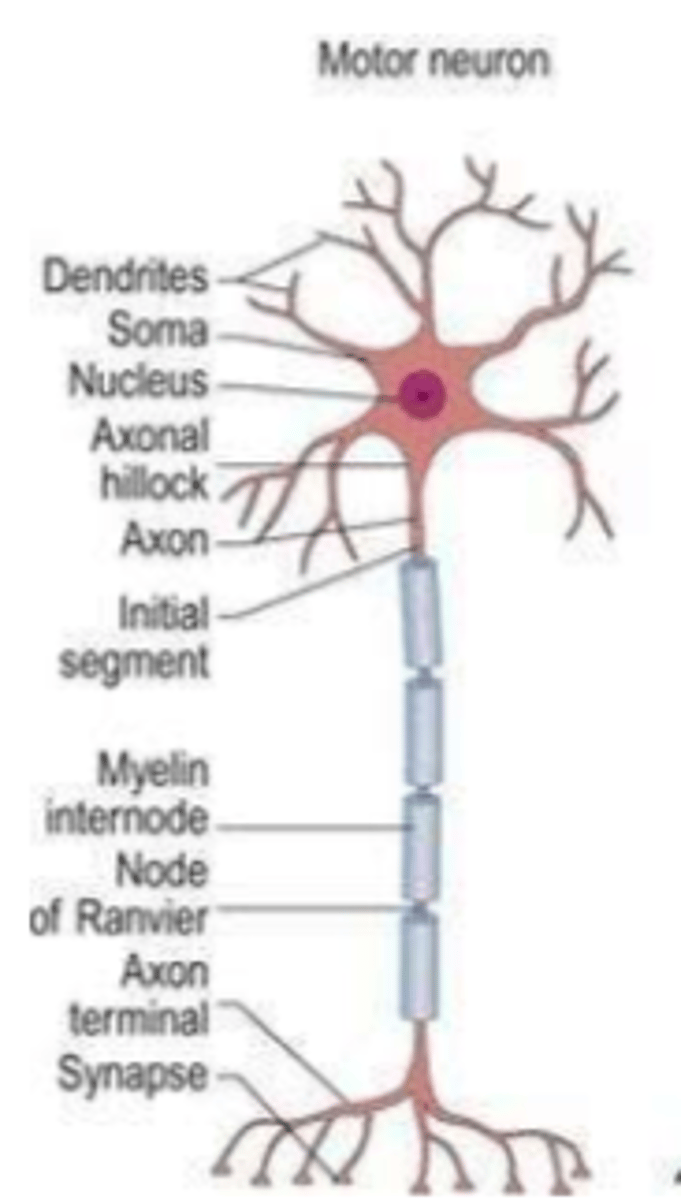
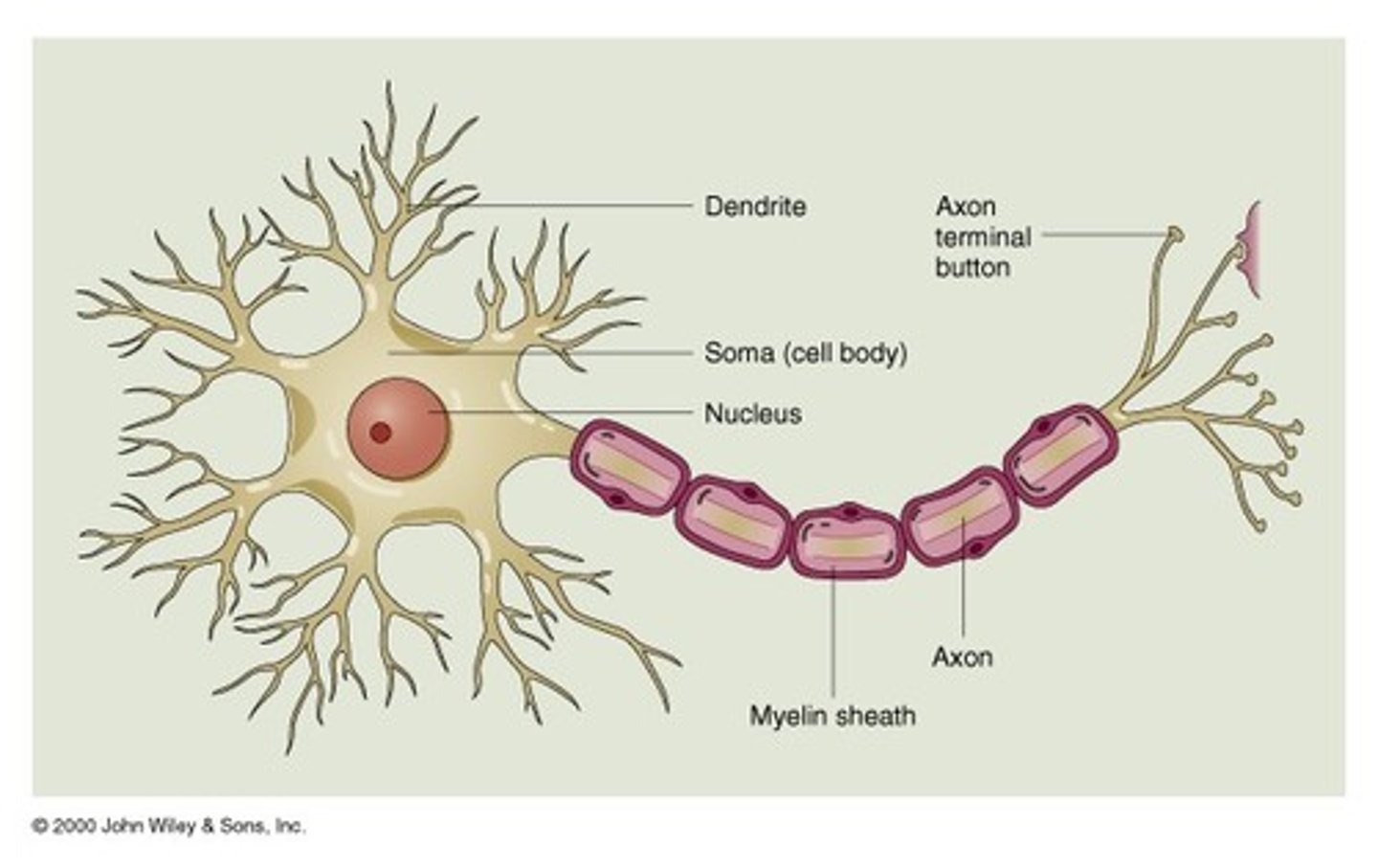
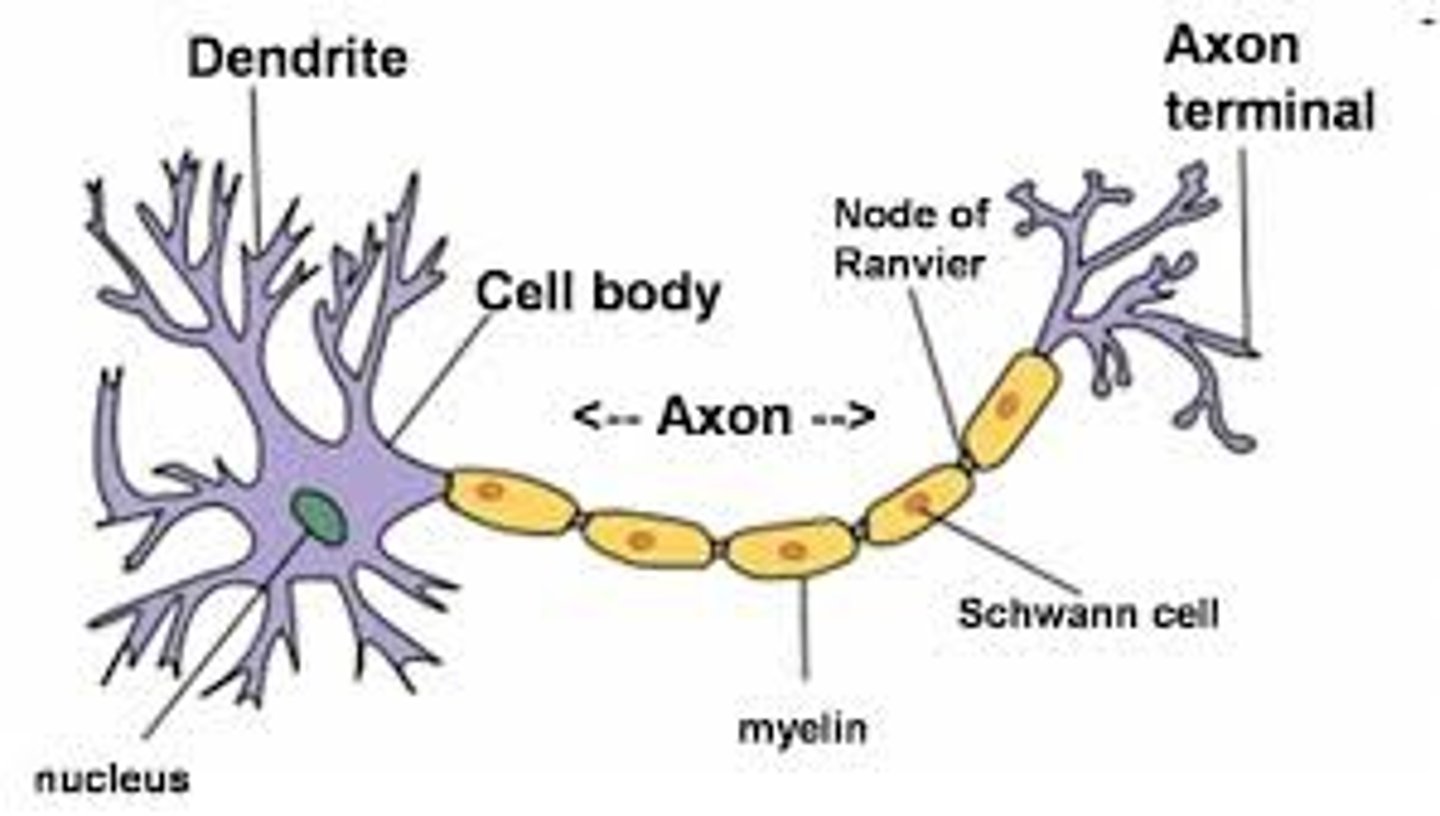
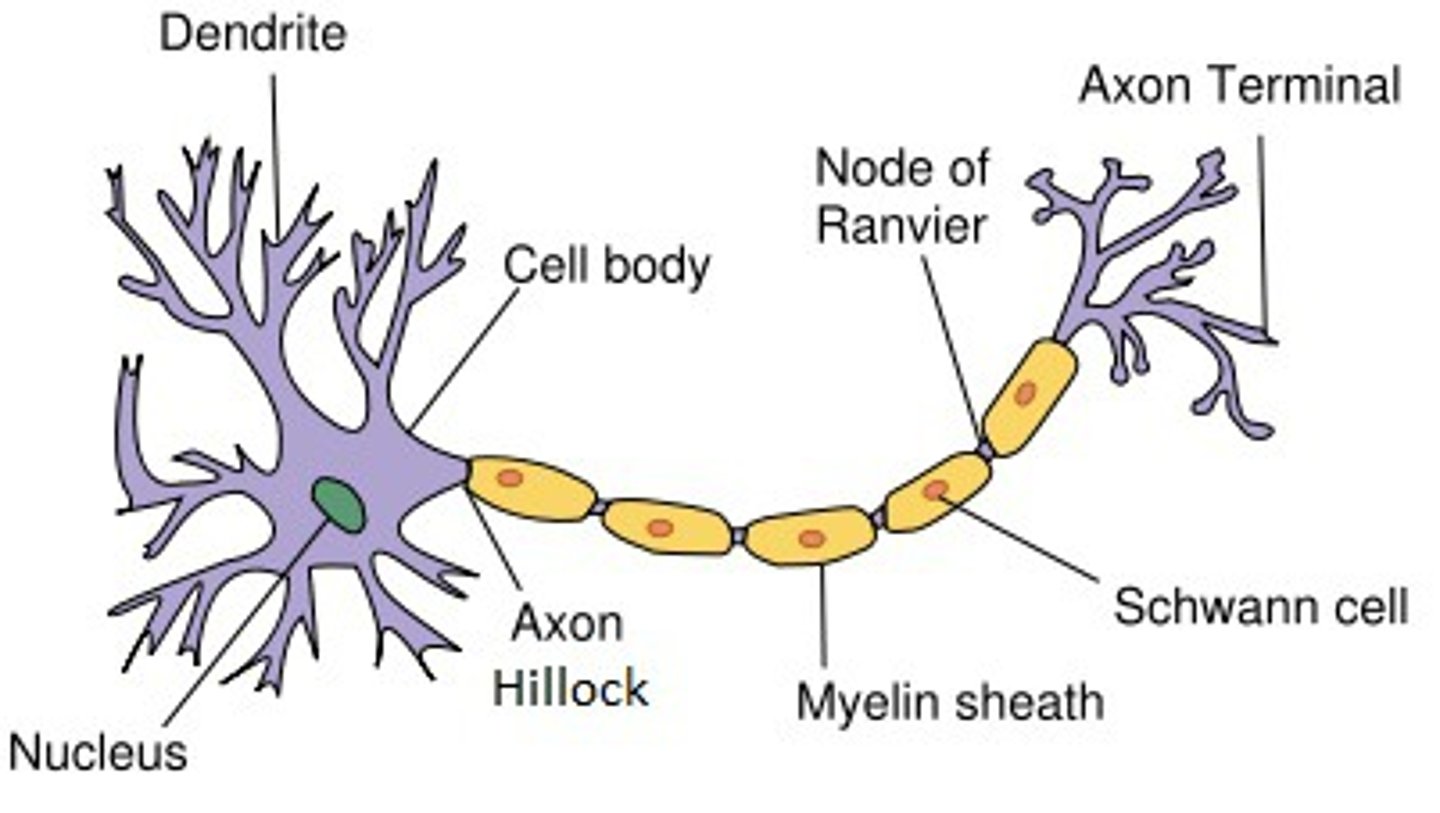
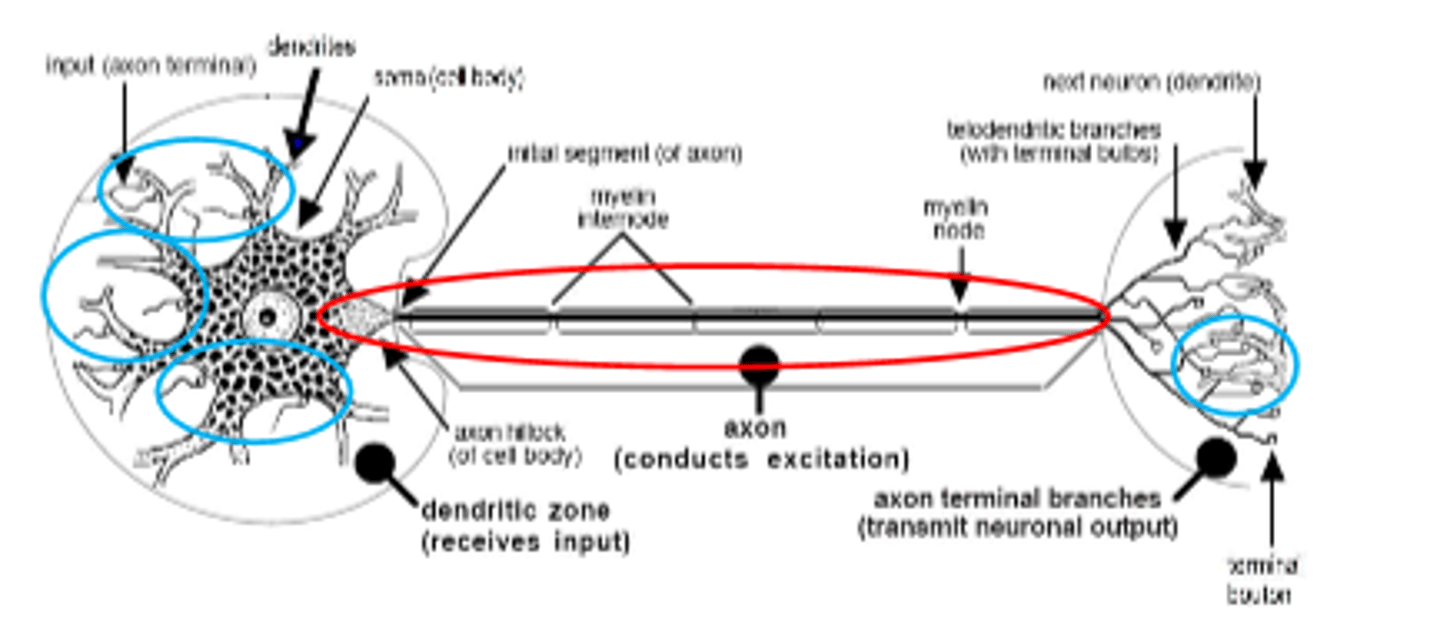
neuron structure: 4 basic parts
1. dendrites
2. cell body (soma/ perikaryon)
3. axon
4. terminal boutons
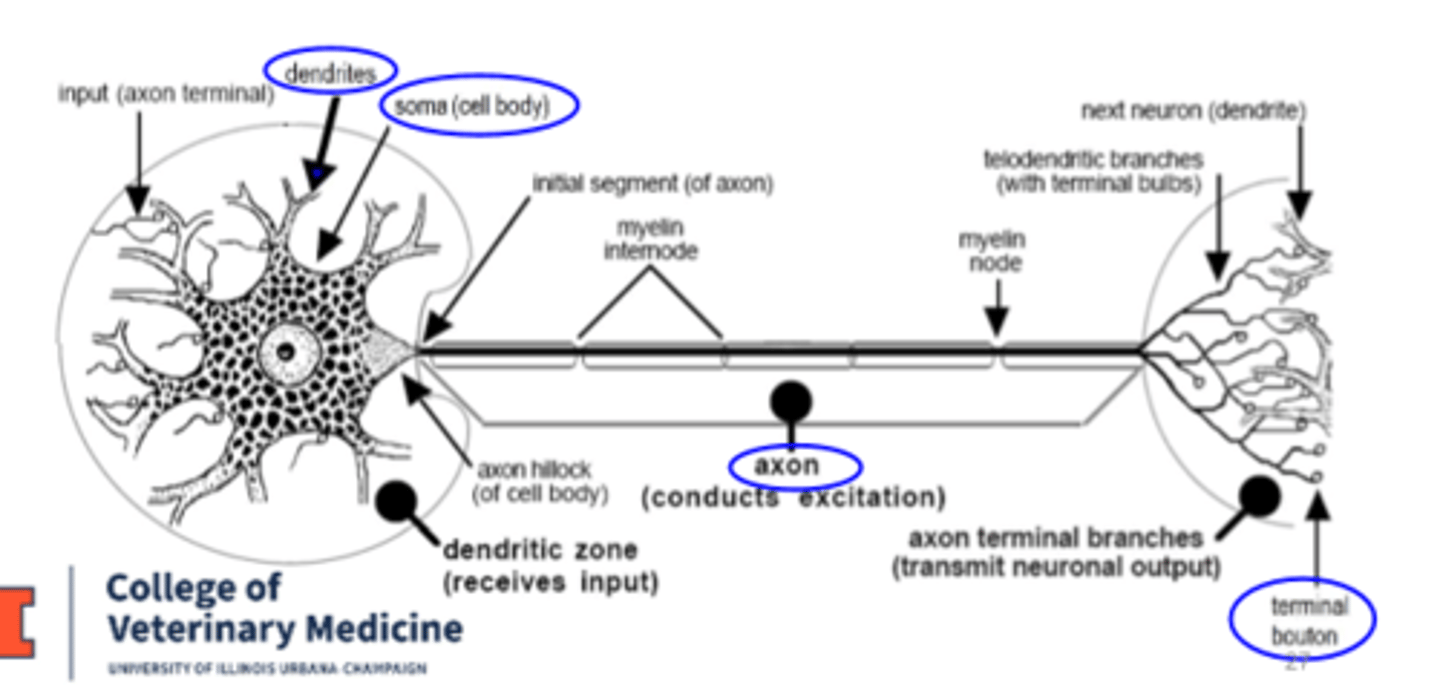
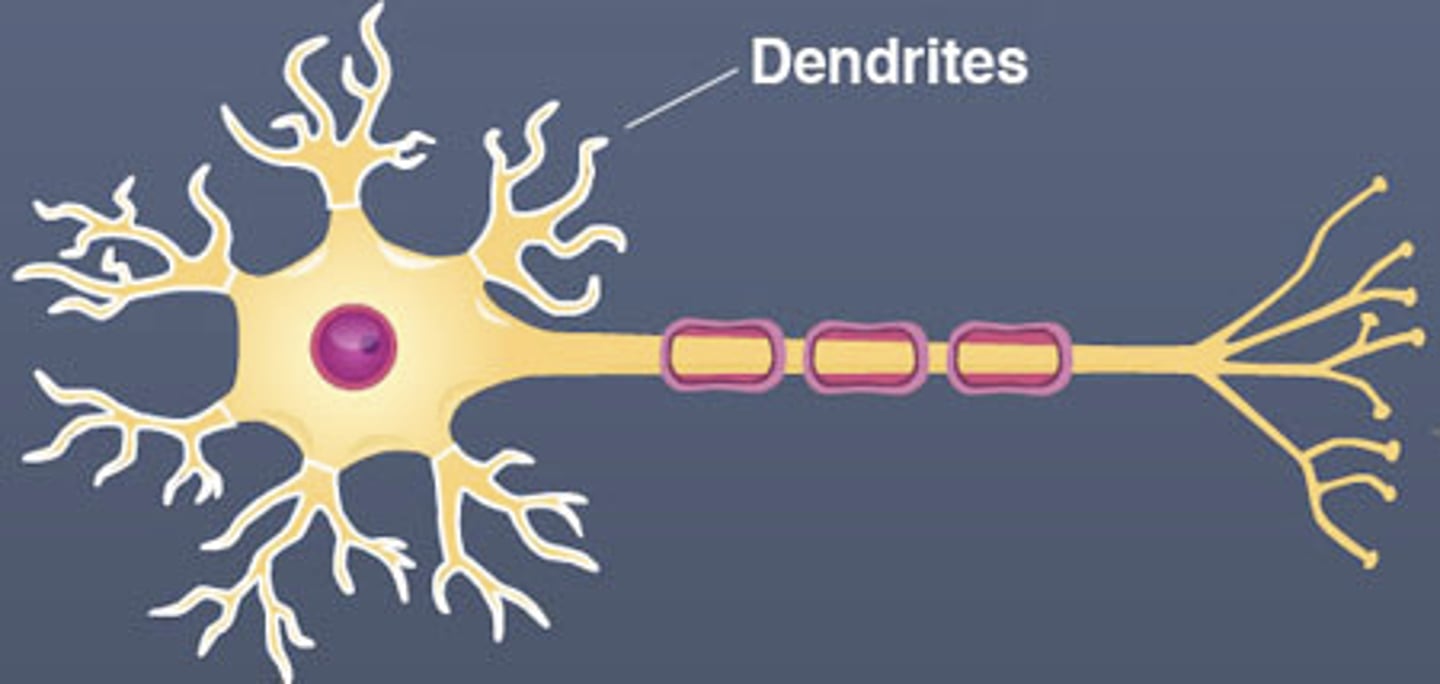
dendrites
-emanate from cell body
-receive input
-function: receives SENSORY info from other neurons/receptors
Cell Body (soma/perikaryon)
-contains nucleus
-dendrites branch from cell body
-integrate input (decides whether or not to send signal)
-function: metabolism and synthesis for cell
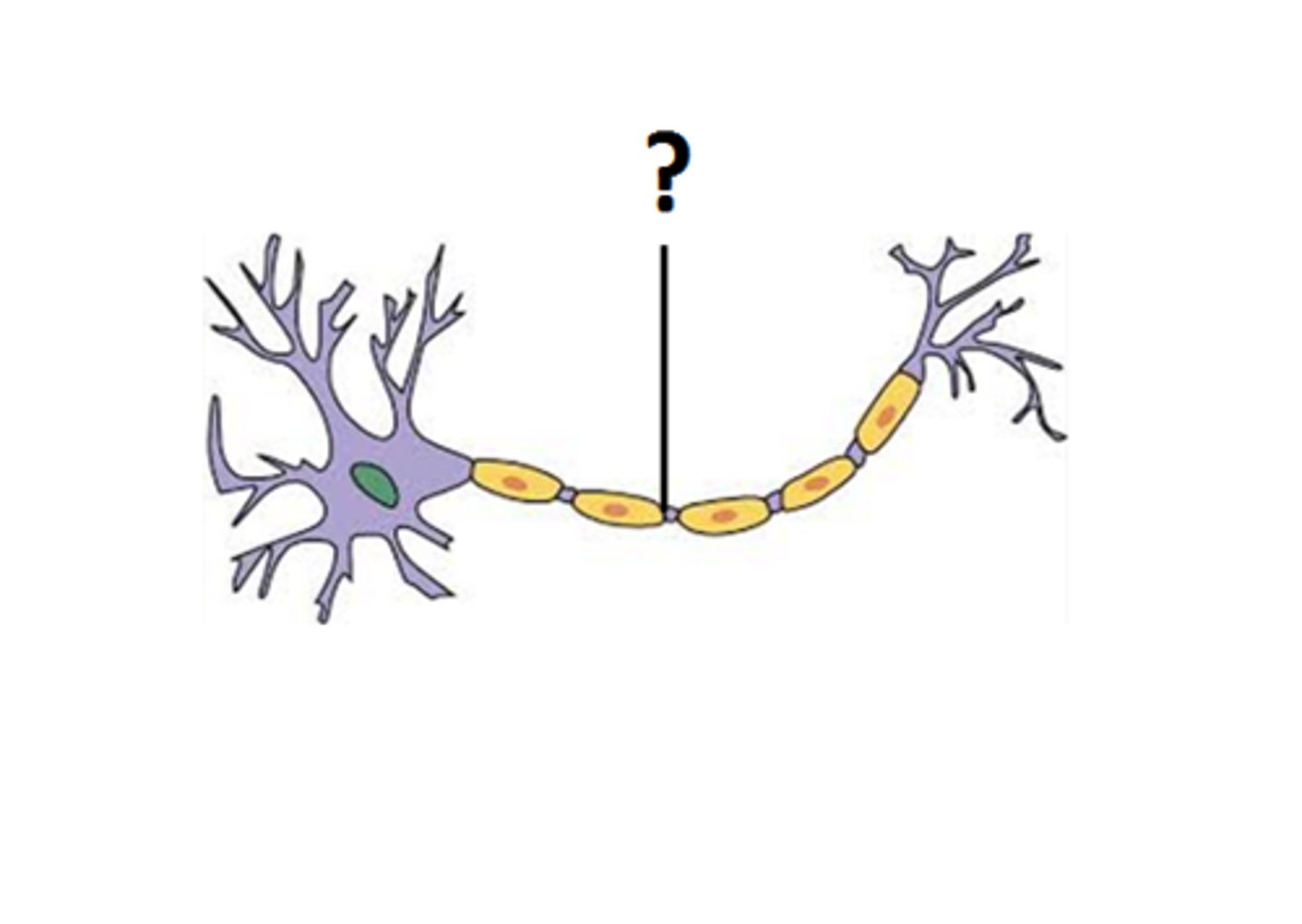
axon hillock
-interface between axon and cell body
-function: generates action potentials
-part of cell body
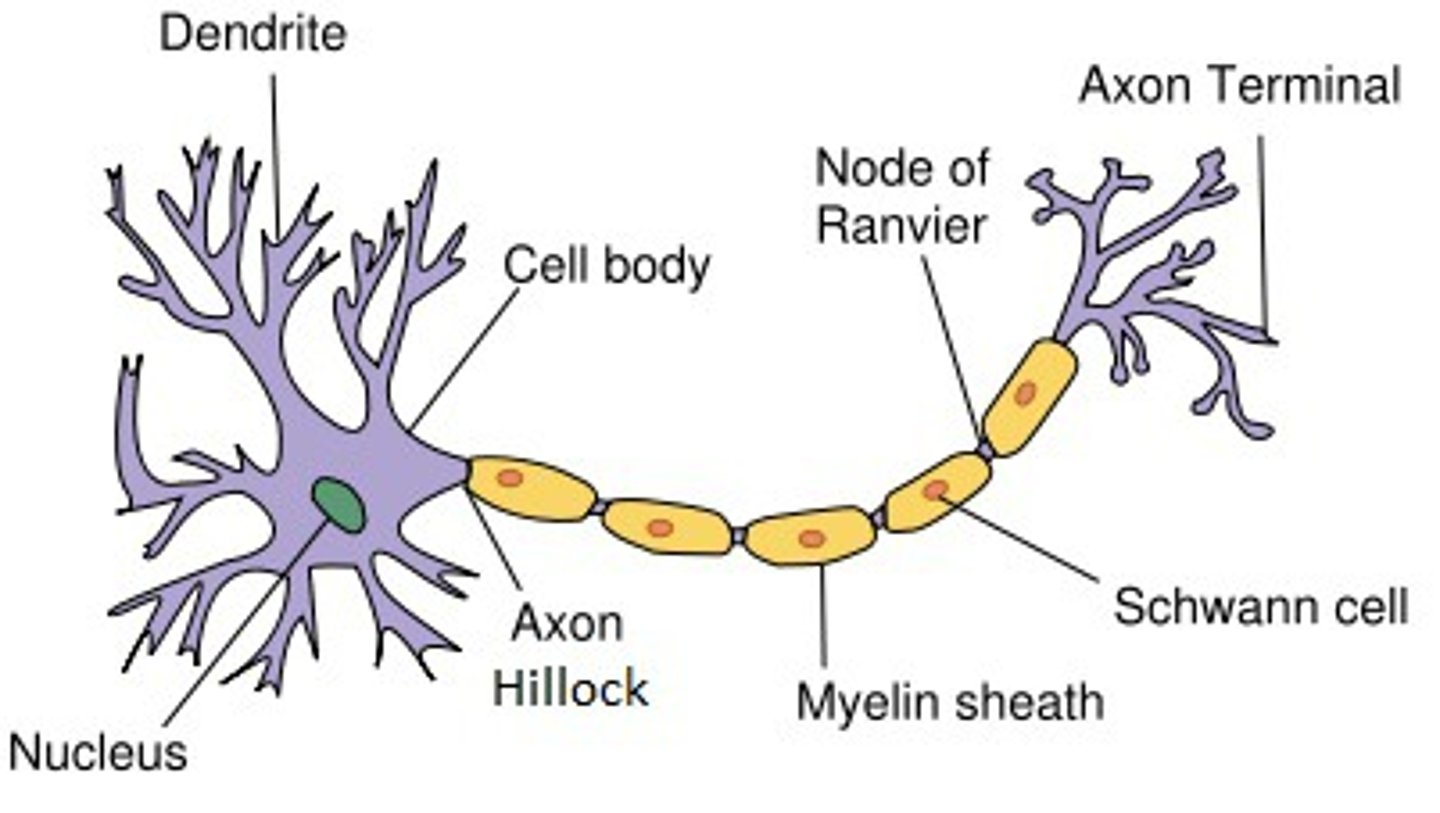
axon
-conducts signal (action potential) from cell body to terminal boutons
-can be myelinated (impulses fast) or non-myelinated (slow)
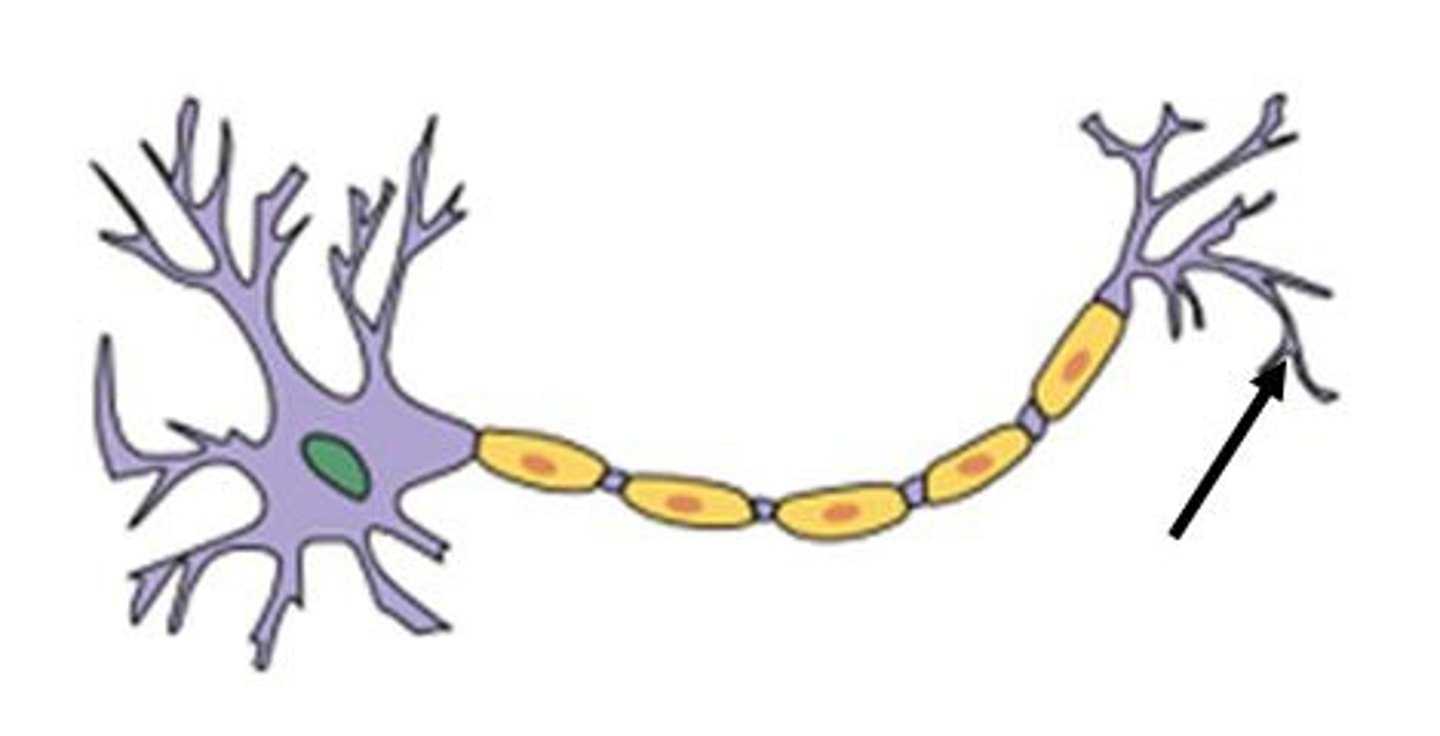
terminal bouton
-specialized process for communication
-releases neurotransmitters when activated by action potential
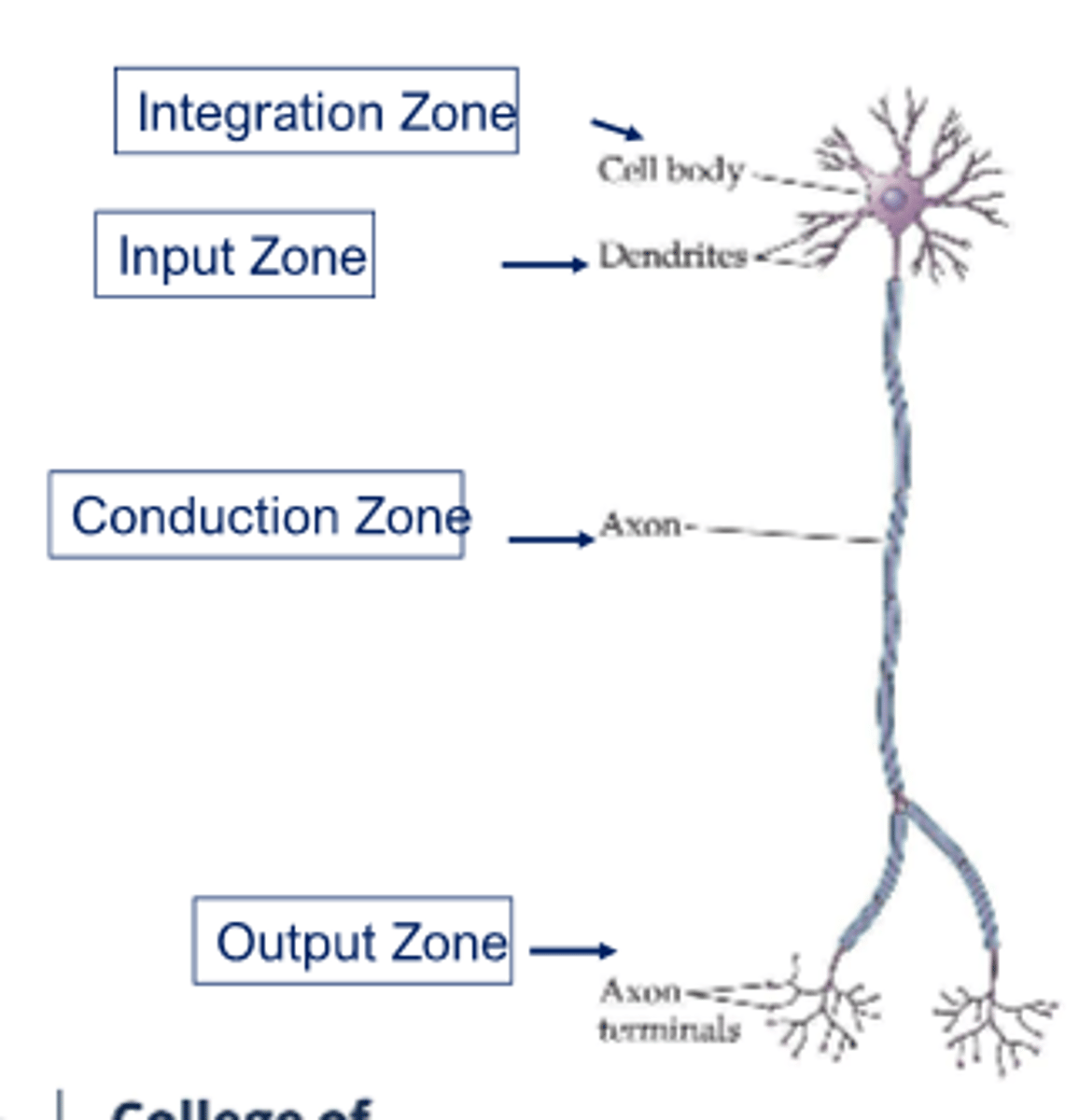
Structures of Neuron: Function (Neuronal Zones)
Integration zone -> cell body
input zone -> dendrites
conduction zone -> axon
output zone -> axon terminals
single cell
info travels in ONE DIRECTION
neuron
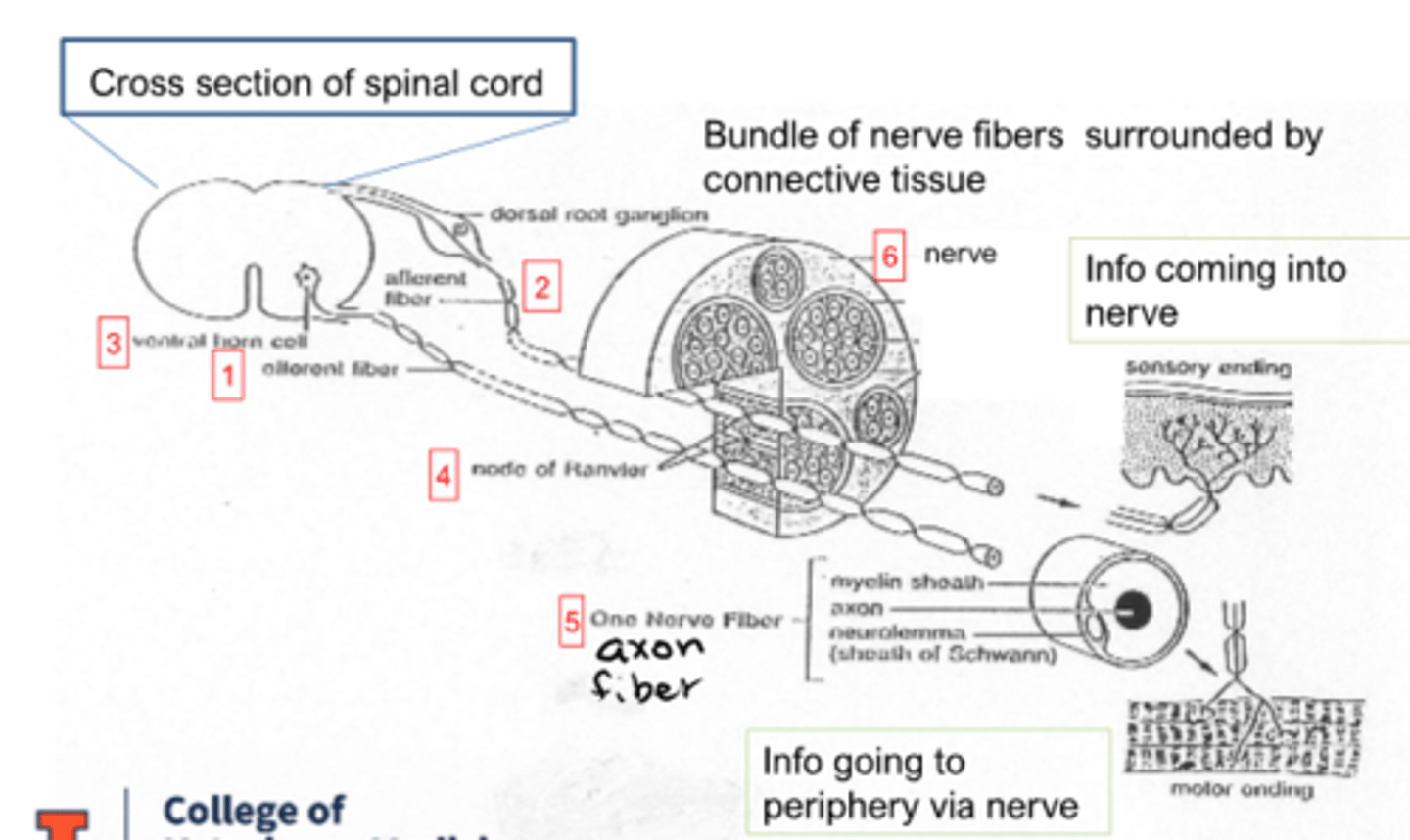
axon of neuron
nerve fiber
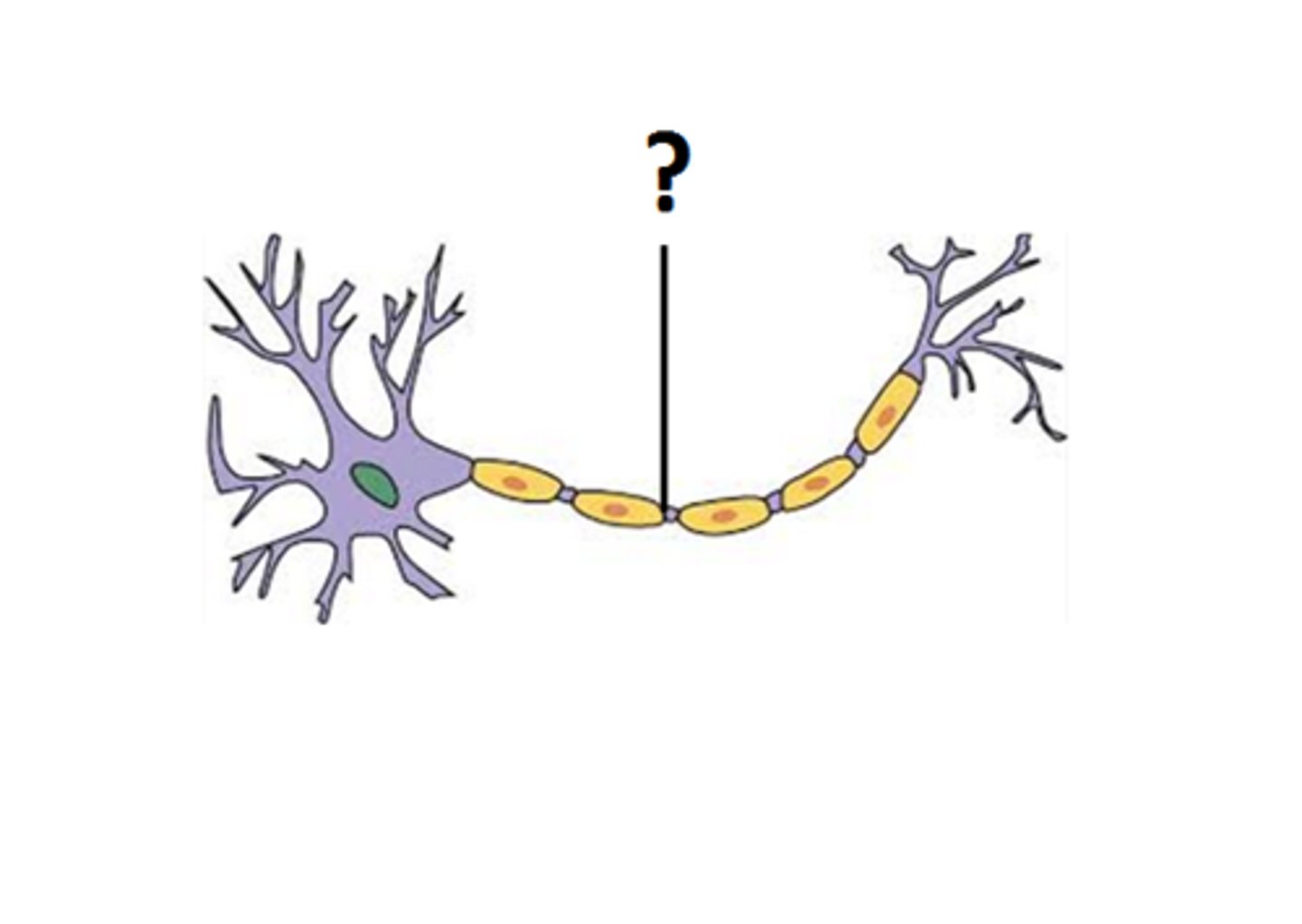
-groups of fibers travelling together
-info can go EITHER DIRECTION
Nerve (PNS)
Tract (CNS)
Review slide
Review
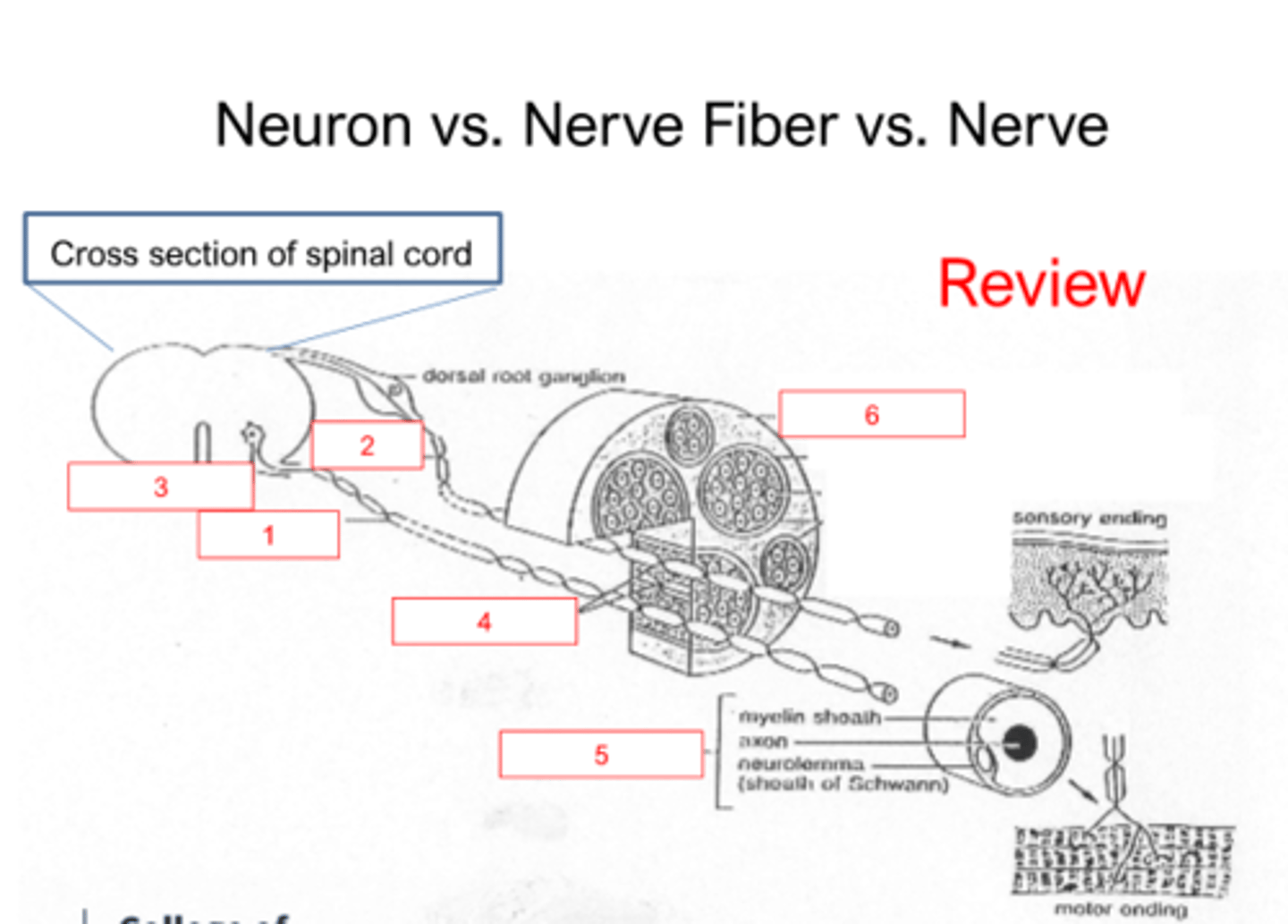
Answers to review slide
Answers
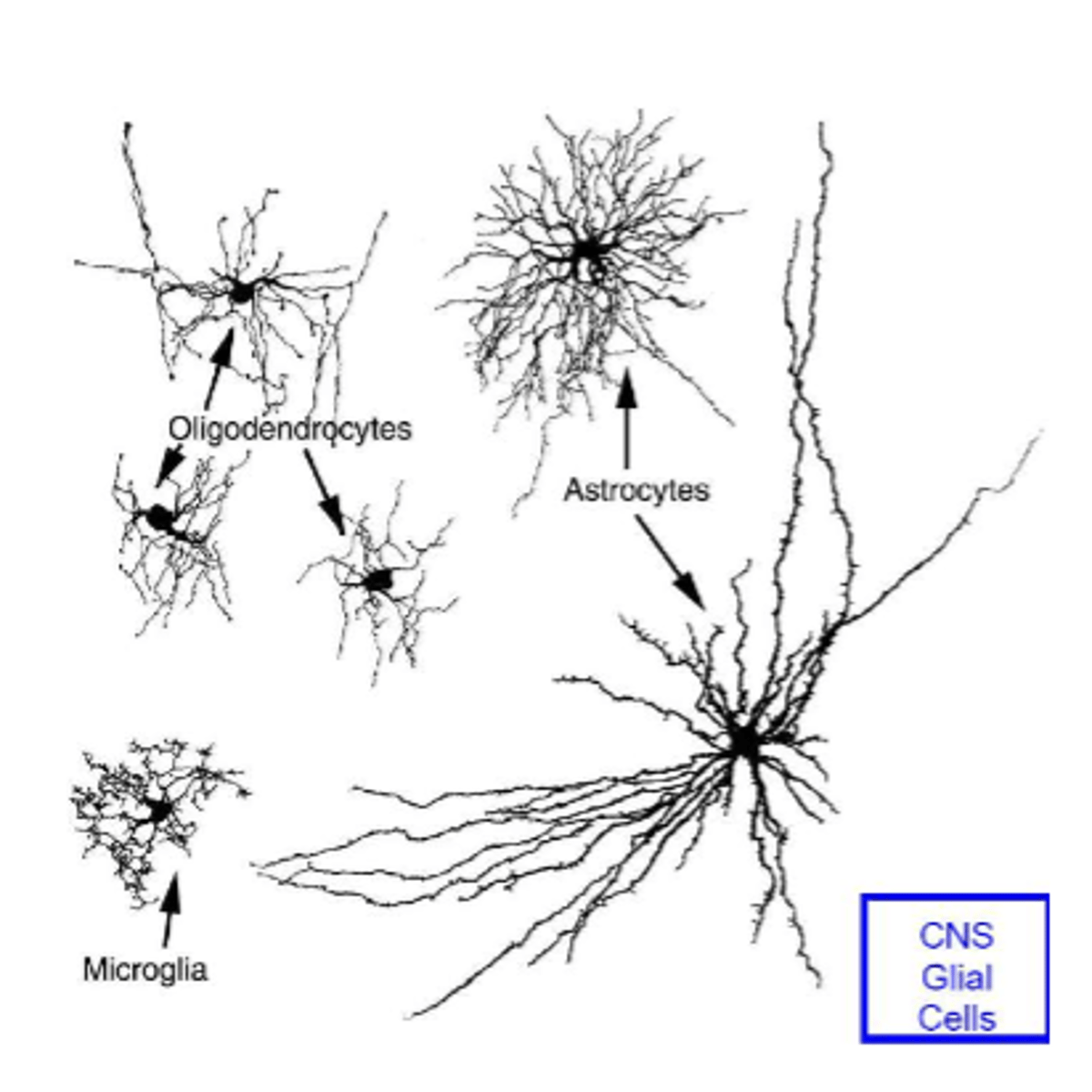
supporting cells in the nervous system are called
neuroglia ("nerve glue")
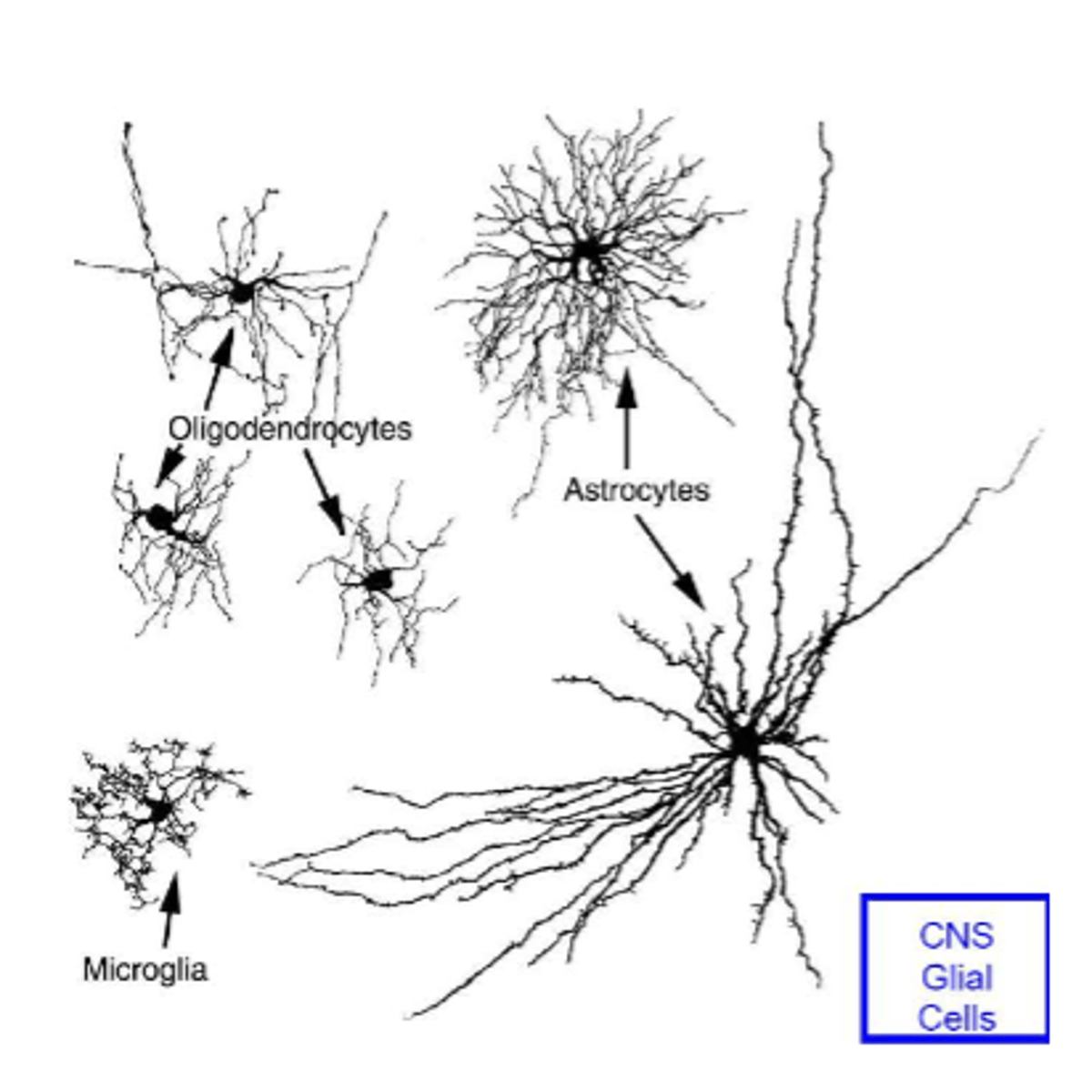
neuroglia
-provide structural support
-form the myelin sheaths of axons and act as insulators and aid conduction velocity (fast conduction)
-control supply of nutrients across blood brain barrier
-maintenance: support and clear dead neurons
how do neuroglia differ from neurons?
1. neuroglia have NO ACTION POTENTIALS
2. neuroglia are able to DIVIDE
3. neuroglia do NOT FORM SYNAPSES
astrocytes functions
1. recycle neurotransmitters
2. secrete neurotropic factors (stimulate growth and maintenance)
3. maintain homeostatic balance in extracellular space
4. gatekeepers to CNS (line the blood brain barrier)
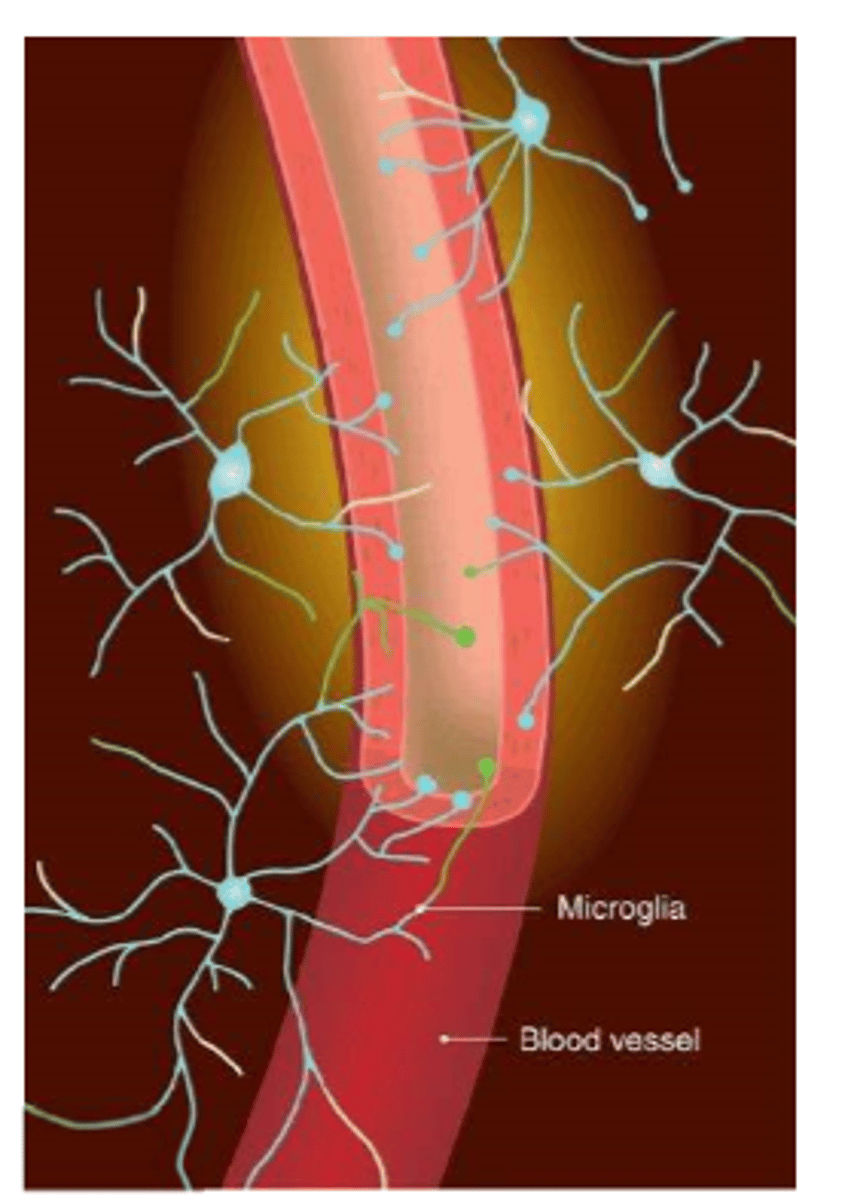
-smallest glial cells
-represent intrinsic immune cells of CNS
microglia
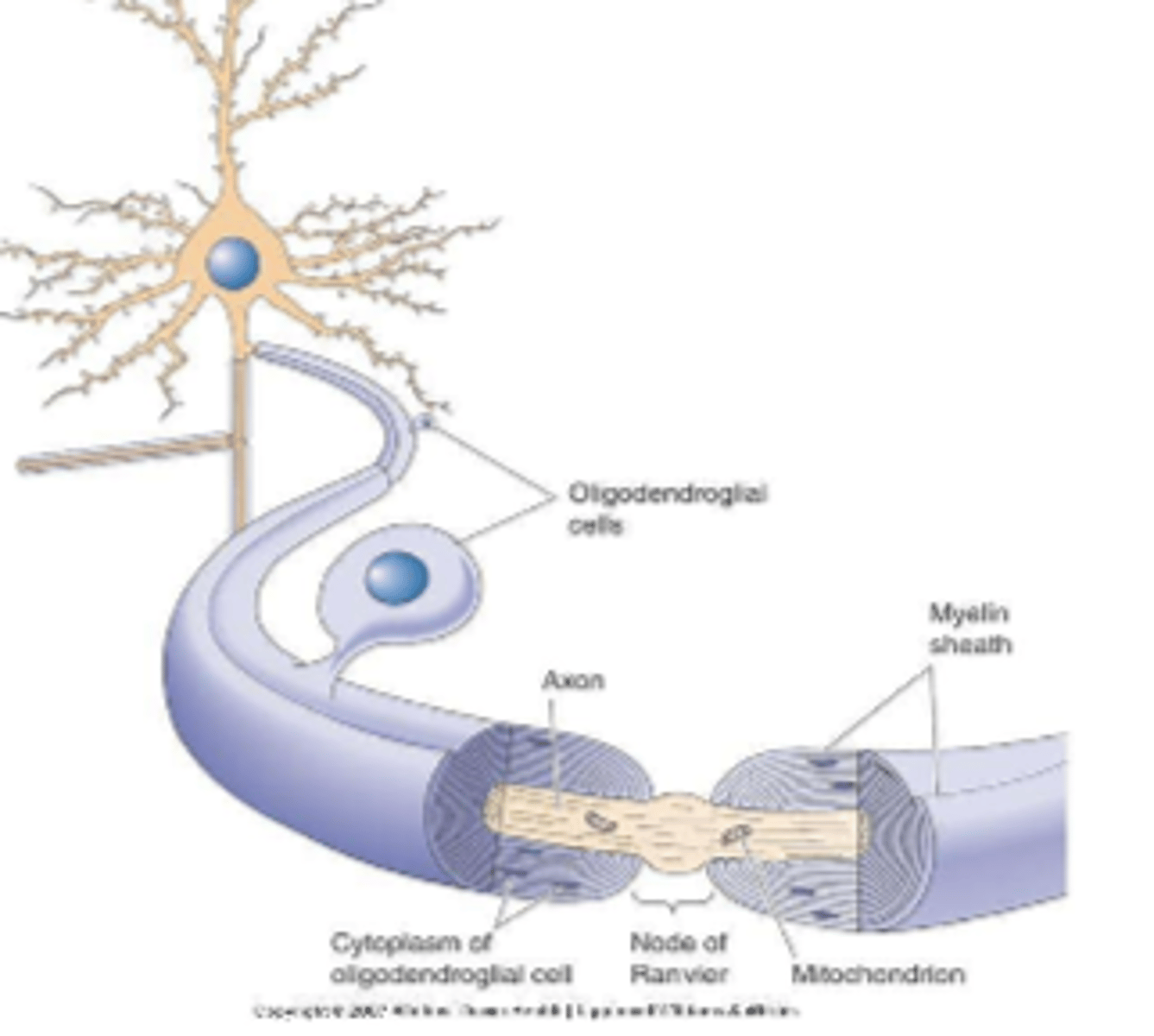
Oligodendrocytes functions
1. forms myelin sheaths in CNS
(around brain and spinal cord axons)
2. provide support to axons
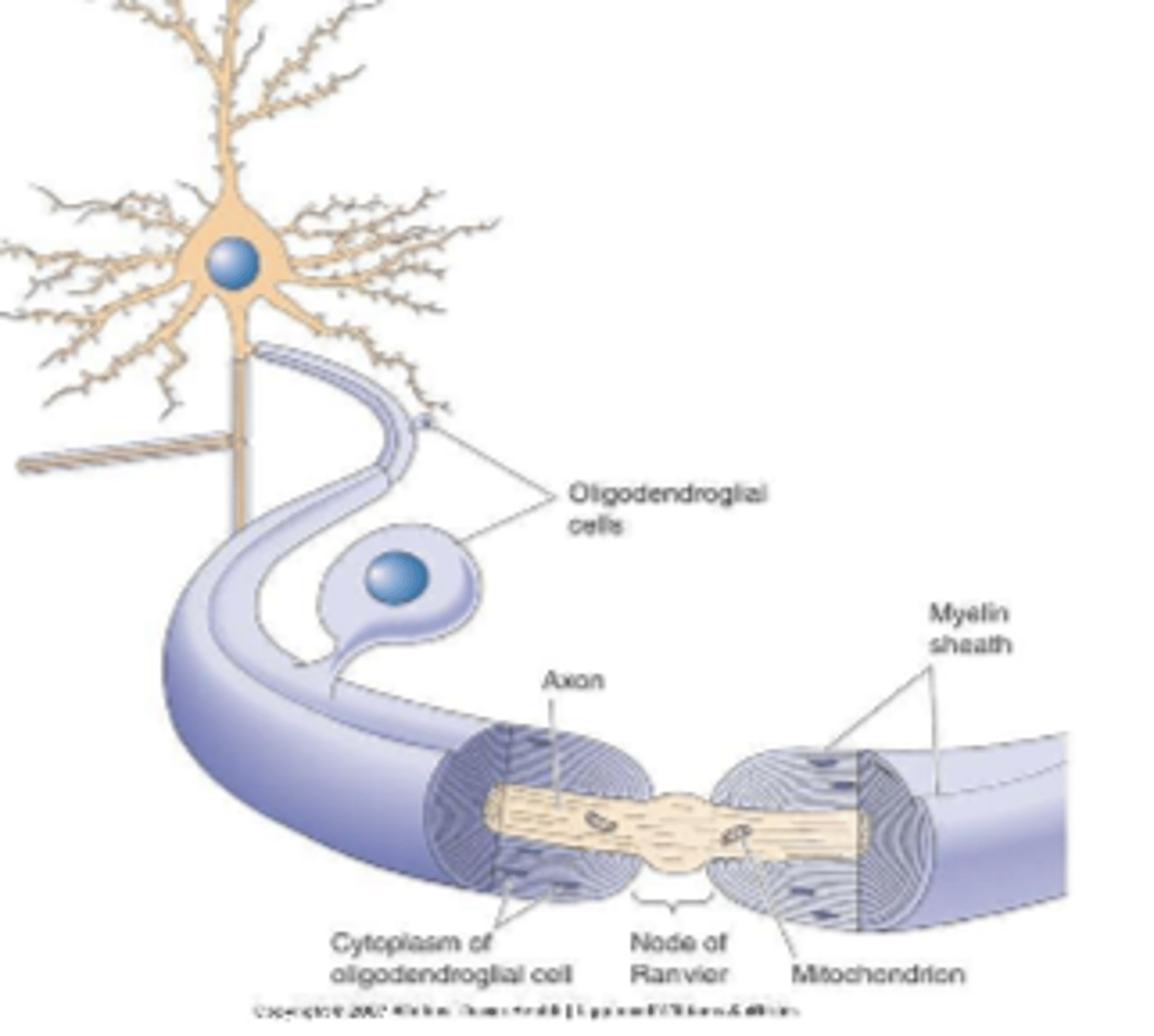
myelin is not continuous cover, there are bare spots called
nodes of Ranvier
__________ are primary glia cells of the PNS
Schwann cells
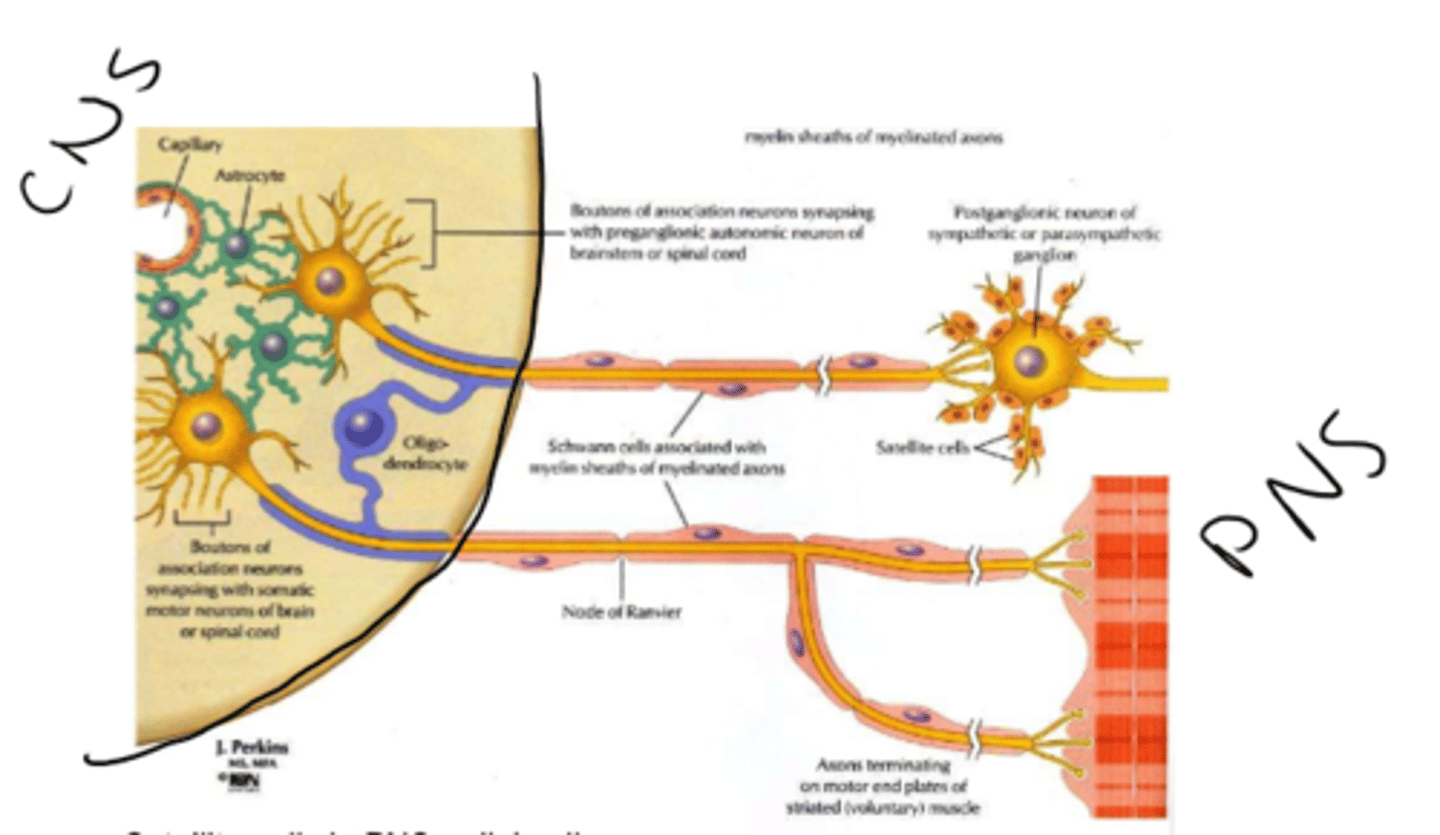
Schwann cells
-one cell wraps around one axon
-membrane composed primarily of lipids (insulator that speeds transmission rate of action potentials)
difference in electrical charge inside and outside a cell which is at rest
resting membrane potential
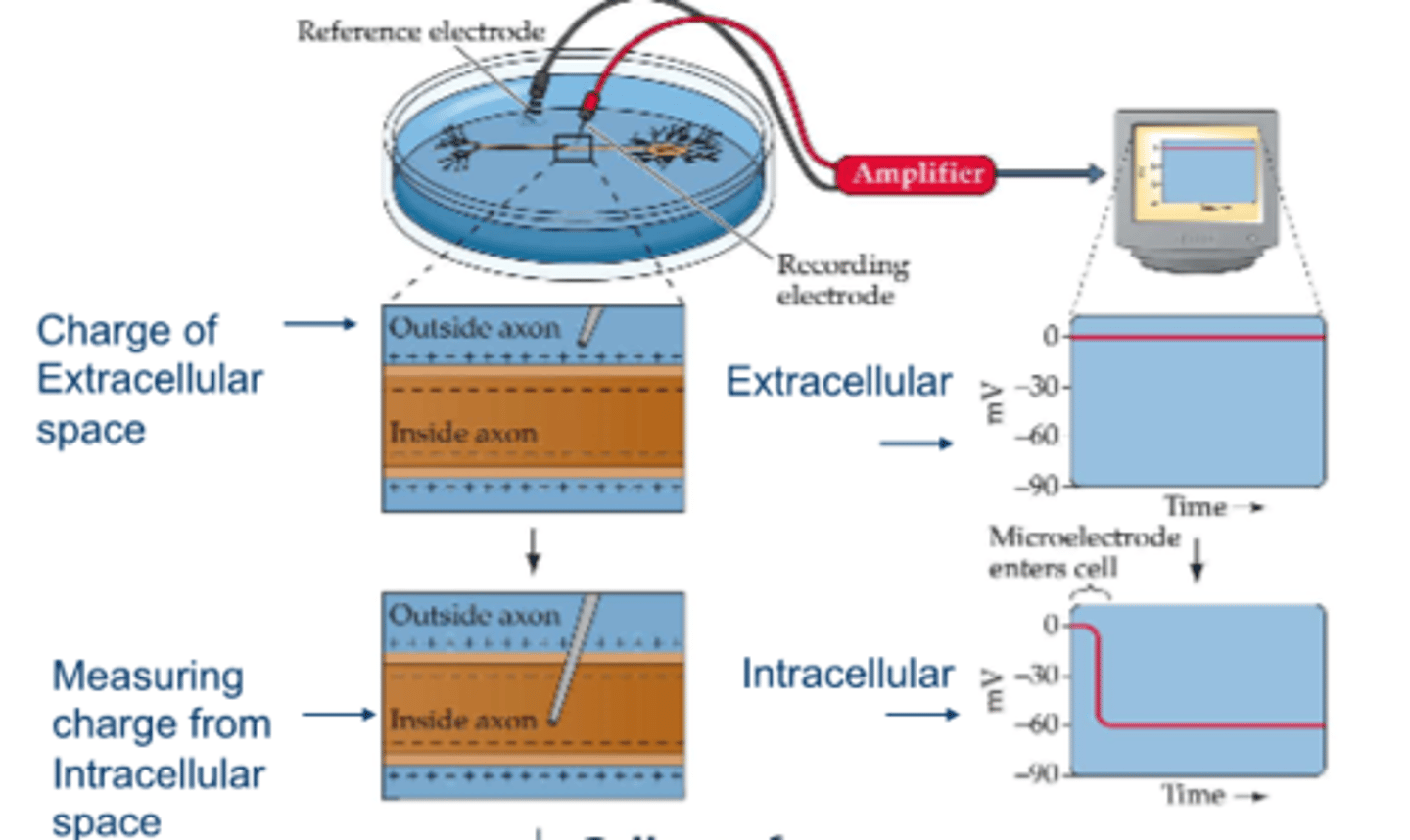
most neurons have a resting membrane potential of
-65 to -70 mVolts
how is the negative charge maintained?
more negatively charged anions in intercellular space
-ion channels are membrane proteins that allow the passage of certain ions depending on size and charge
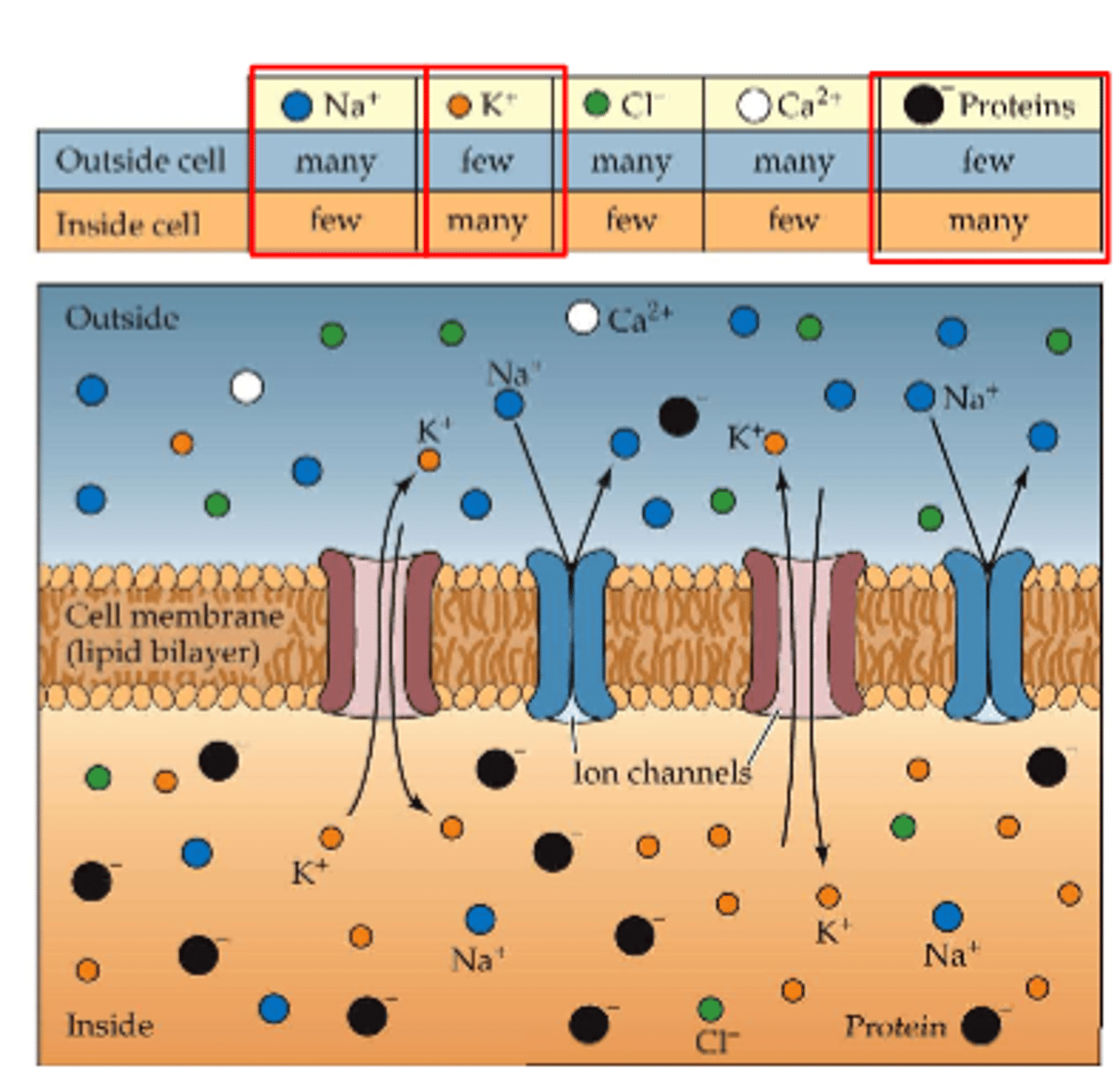
3 factors that maintain the negative charge of the resting potential
1. selectively permeable membrane
-large protein anions (negative) that can't pass through cell membrane to get outside of cell
2. ions moving toward equilibrium potential
-resting passive K+ channels allow K+ cations to pass through membrane into intracellular space
-concentration gradient pushes K+ out of cell
-balance (equilibrium) of forces reached (at -65mV)
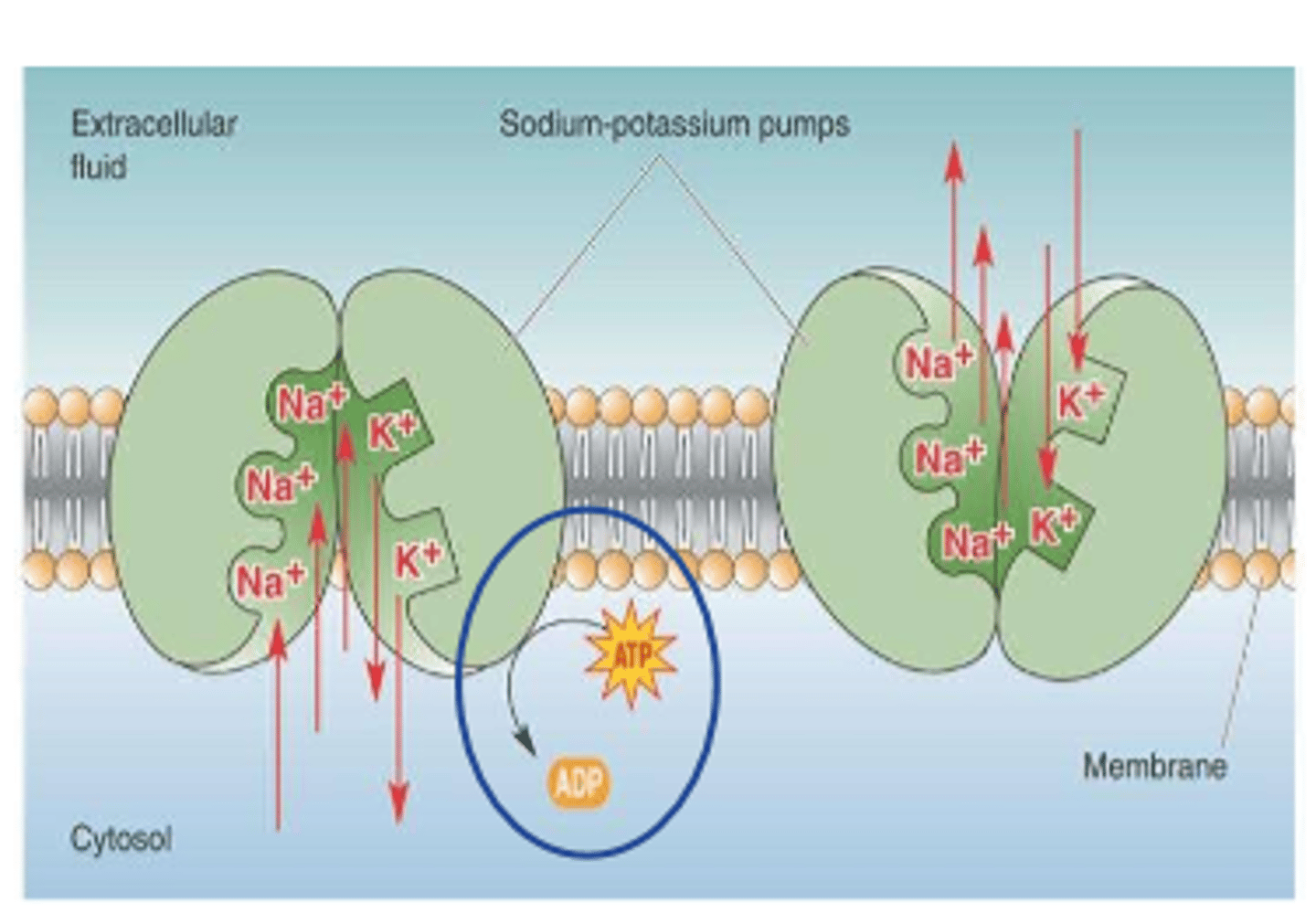
3. Na/K pump (active)
-Na+ cations pumped out of cell against electrostatic and concentration gradients (leak into cell)
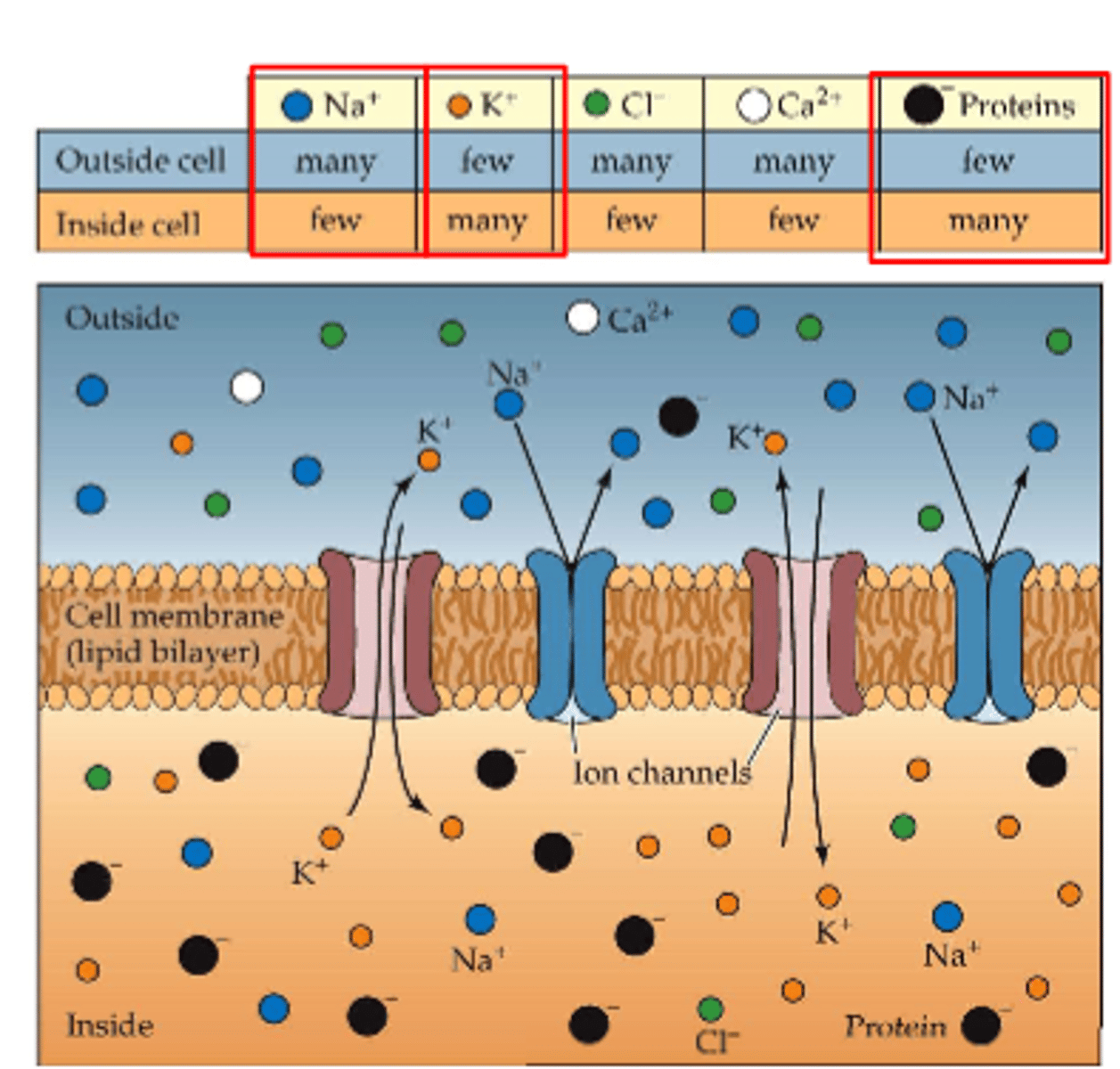
Na+ cations are actively moved to extracellular space by
Na+/K+ pump
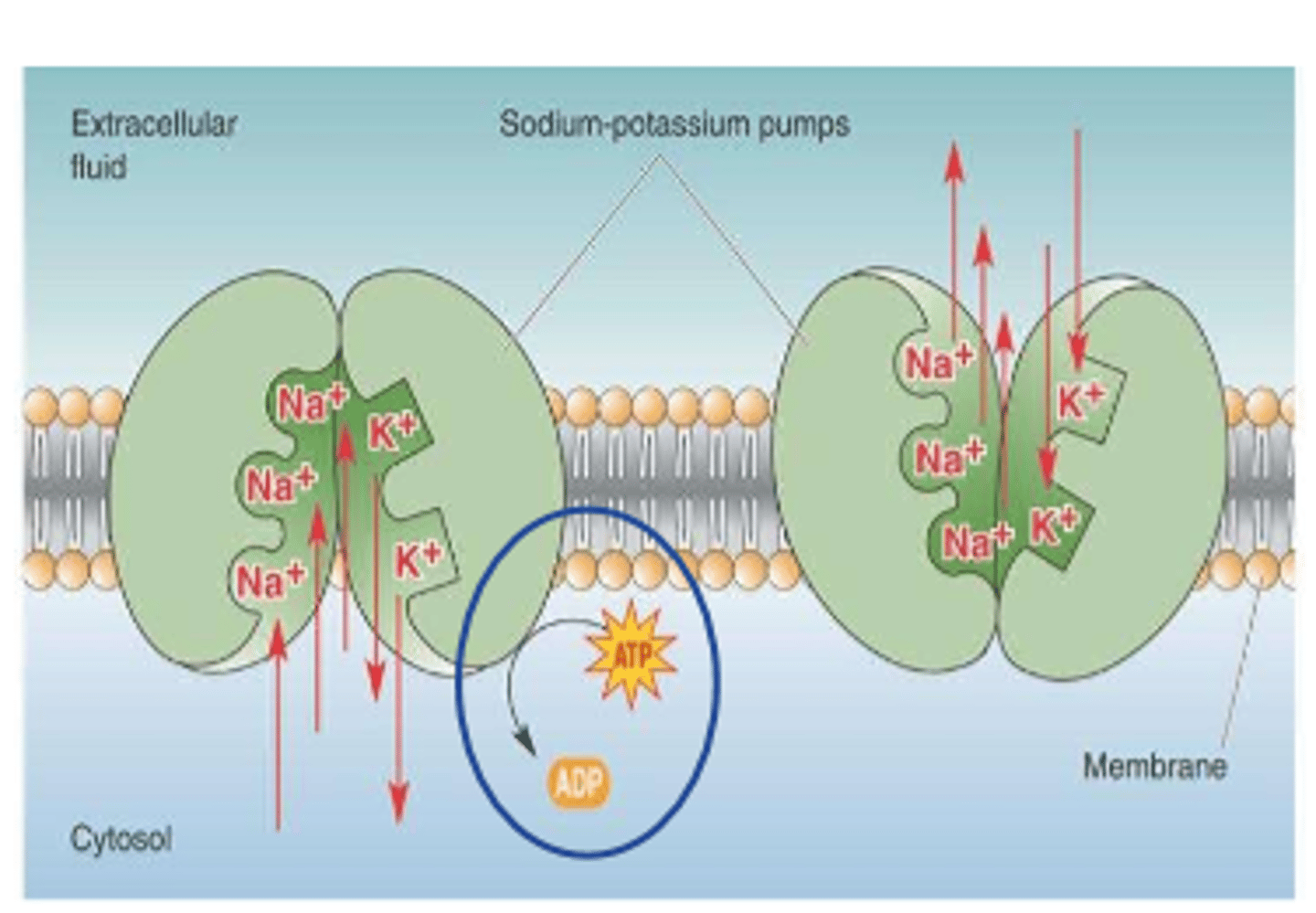
Na+ has ___________ gradient and ____________ gradient forces
concentration, electrostatic
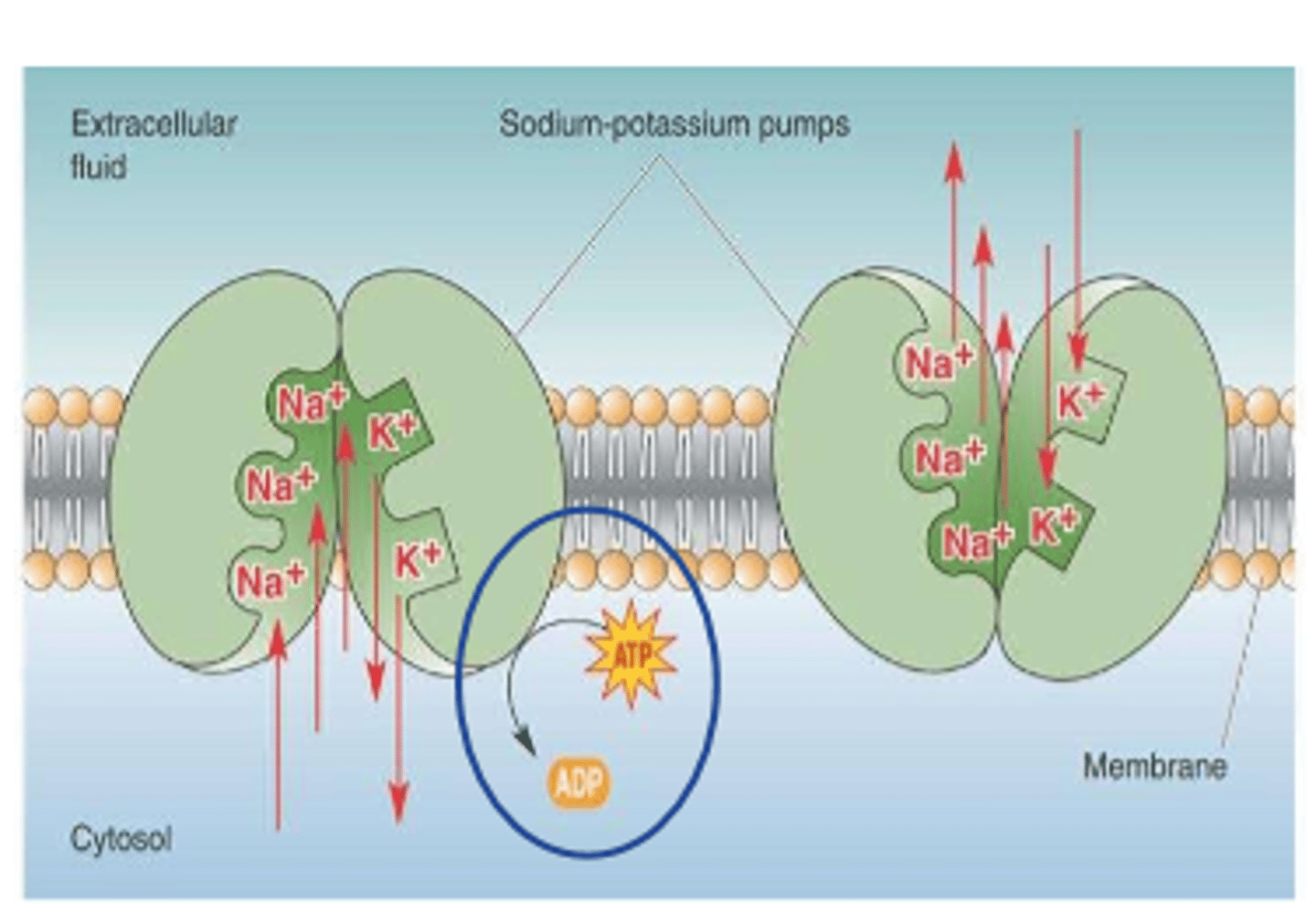
Na+ drives to _________ the cell
enter
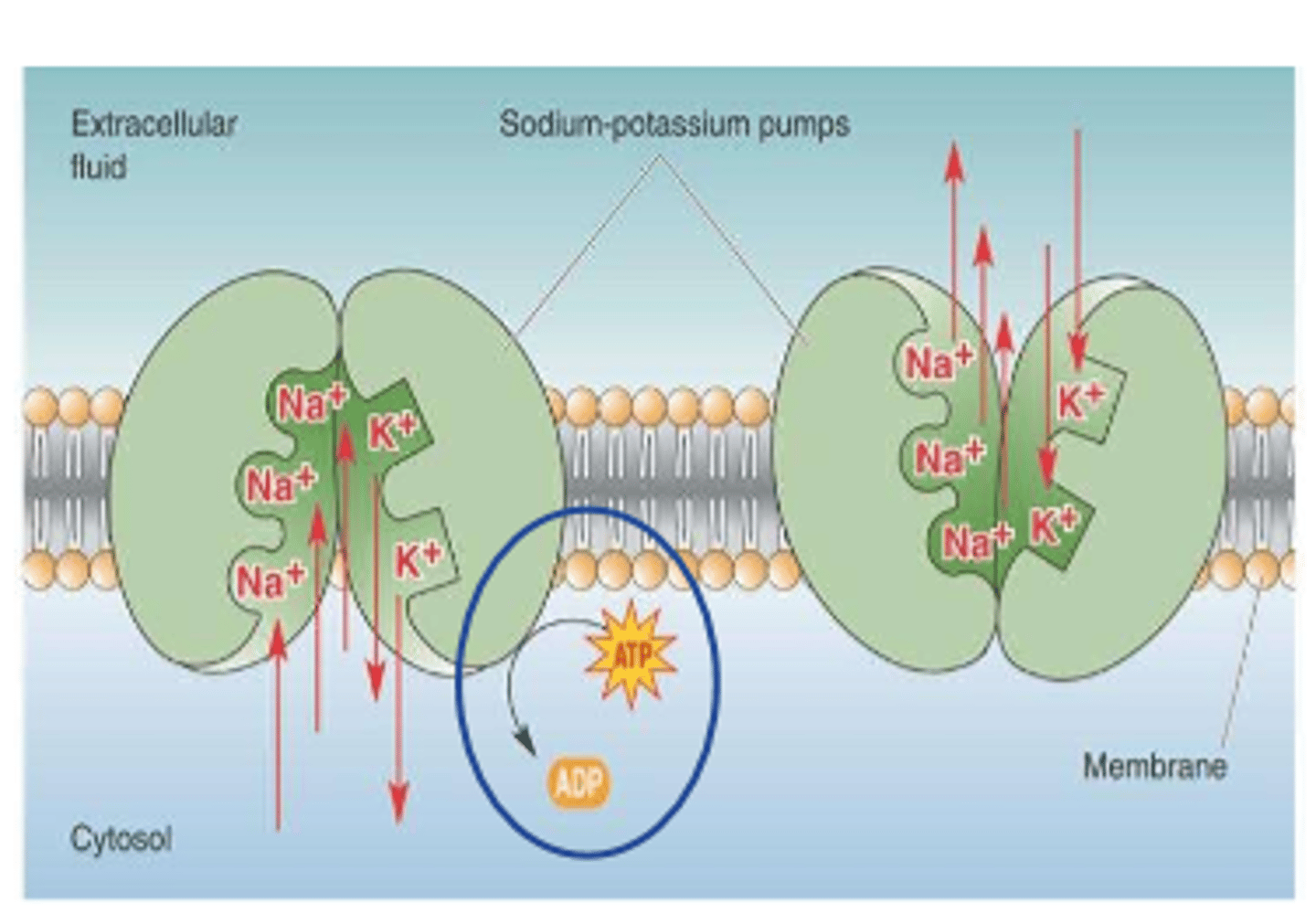
___________ reduces Na+ concentration in cell
active pump
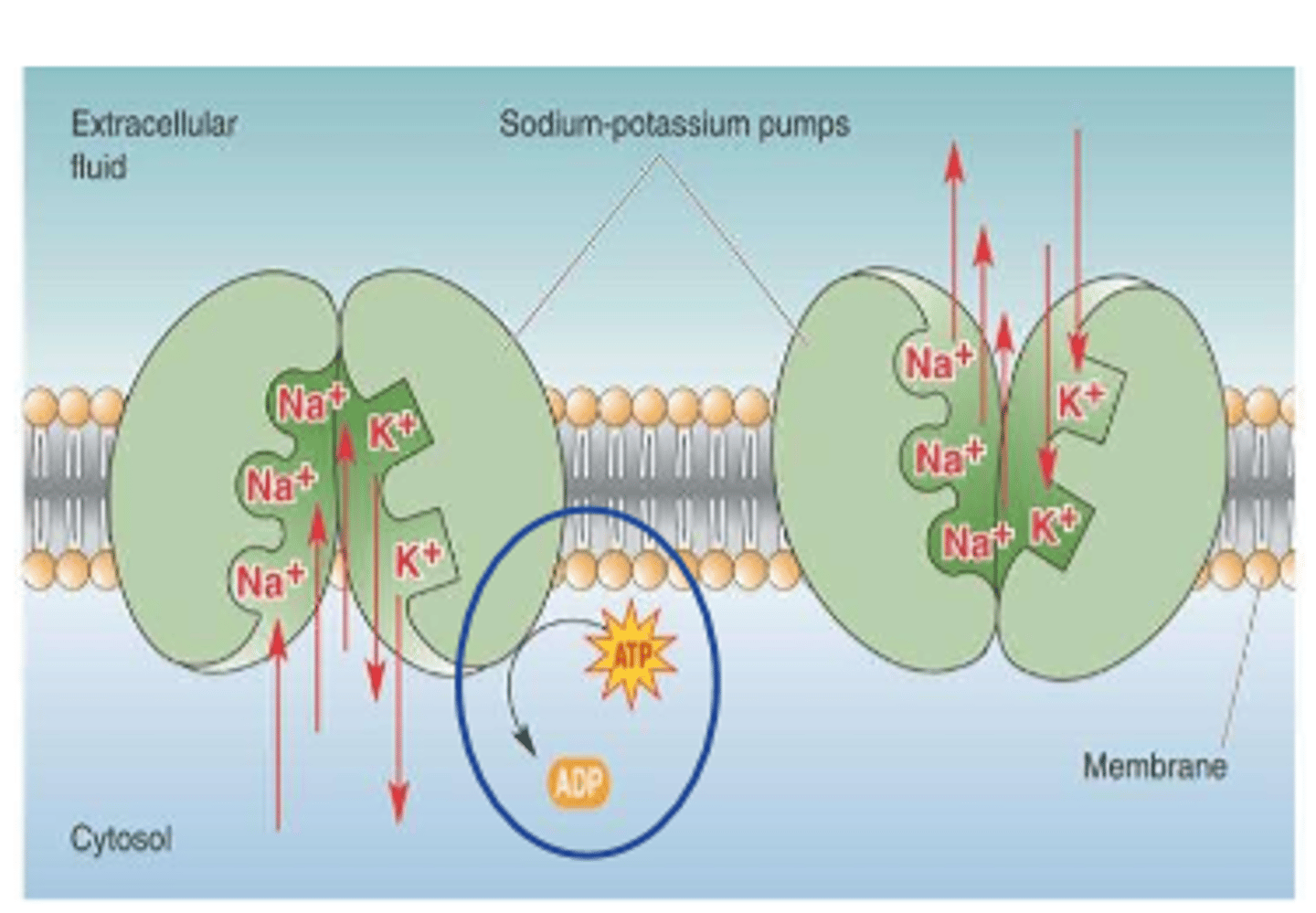
exchange ______ Na+ for ______ K+ coming in
3 Na+
2 K+
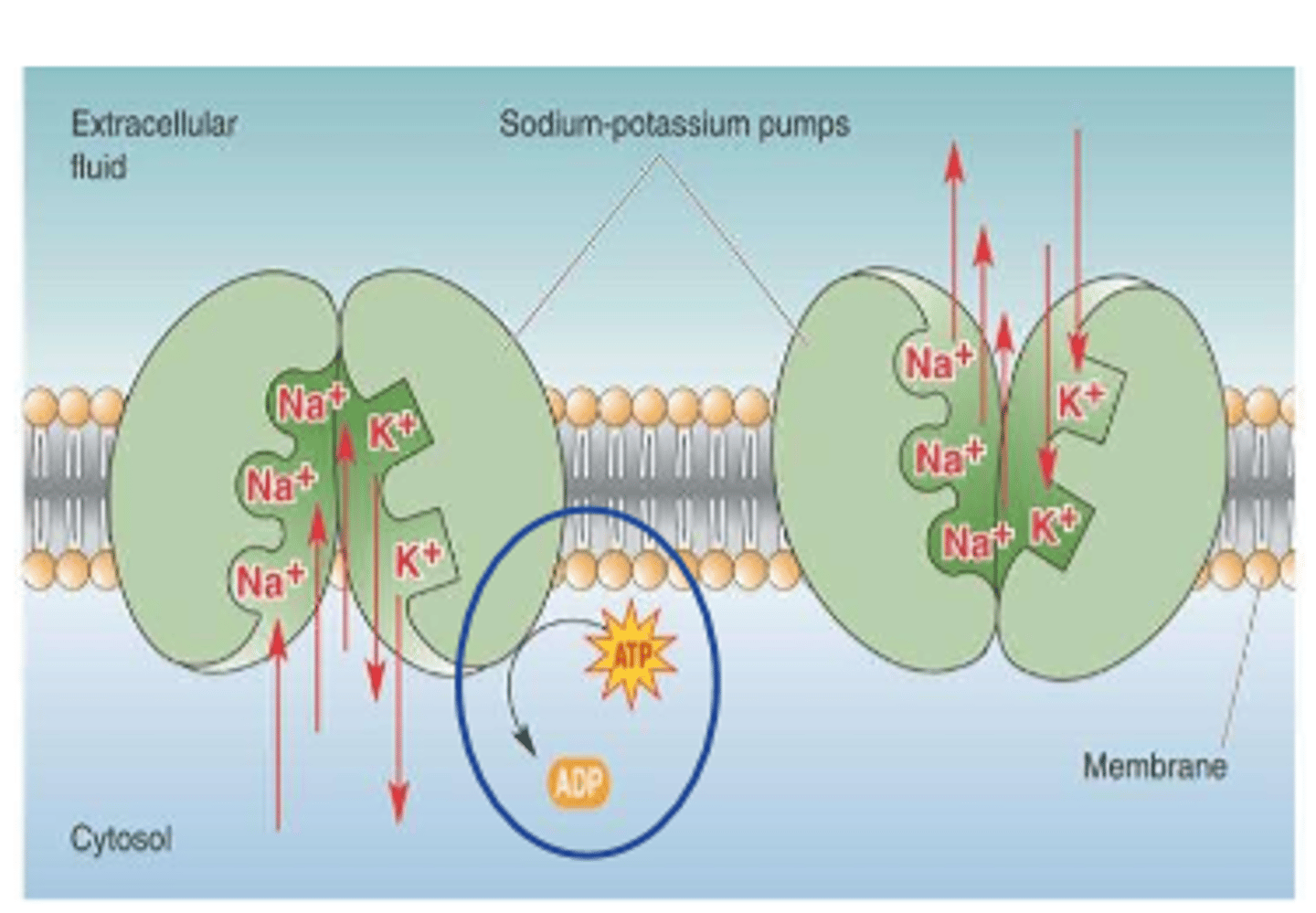
Na+/K+ pump is a _________ dependent process
ATP
ATP generation requires _________ and _______ but neurons do not store them
glucose
oxygen
anything that alters _______ or ________ will alter Na+/K+ pump effectiveness and produce neurological defects
glucose or oxygen
why is resting membrane potential important?
this electrical potential is stored energy required for neural communication -> action potential
_____________ is the basic mechanism for transmission of info in the nervous system and muscles
action potential
an action potential is caused by __________ of a membrane past a certain ___________ followed by ____________
depolarization
threshold
repolarization
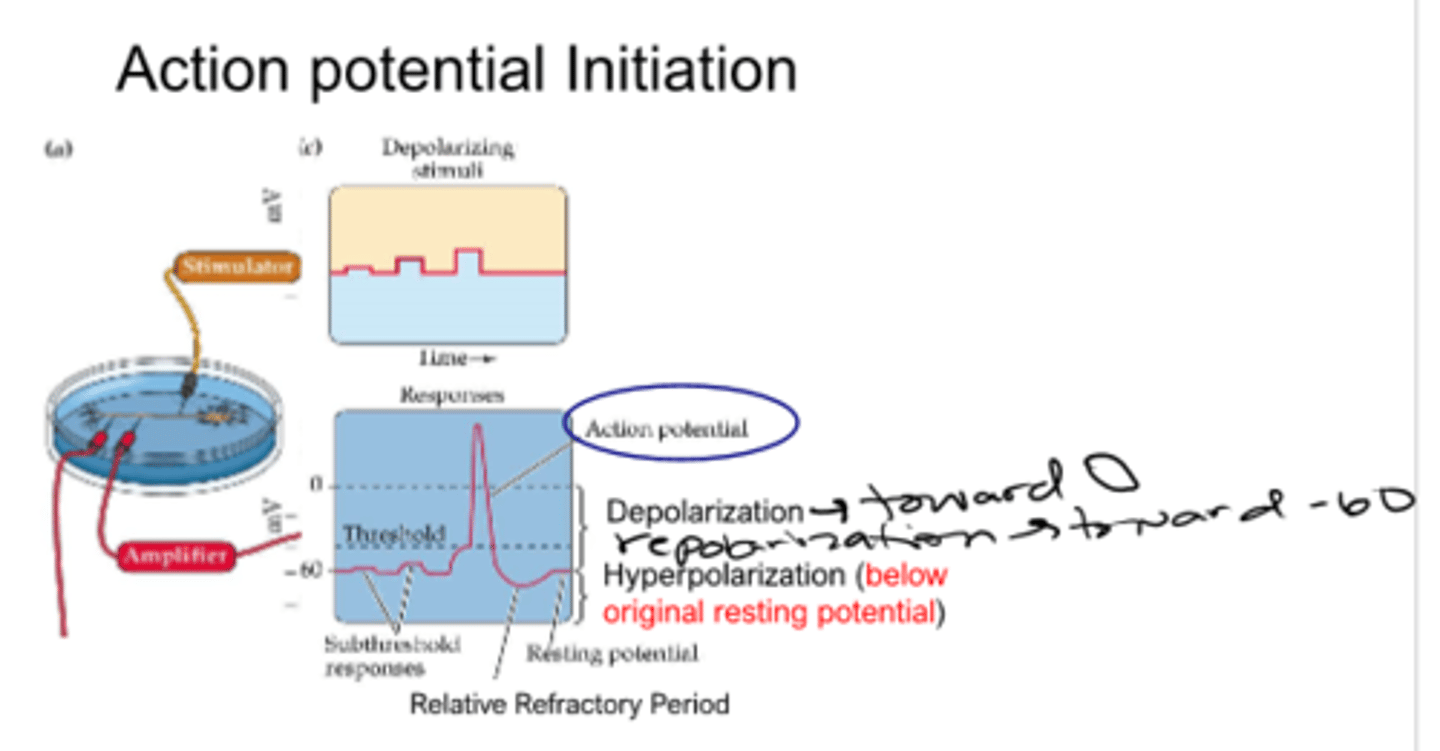
an action potential is an __________________ response: only occurs if cell is depolarized past a threshold
"all-or-none"
propagation of action potential is a ______________ reaction
chain
AP at one site of axon causes ____________ adjacent to current AP, brings adjacent sites to _______________
depolarization
threshold
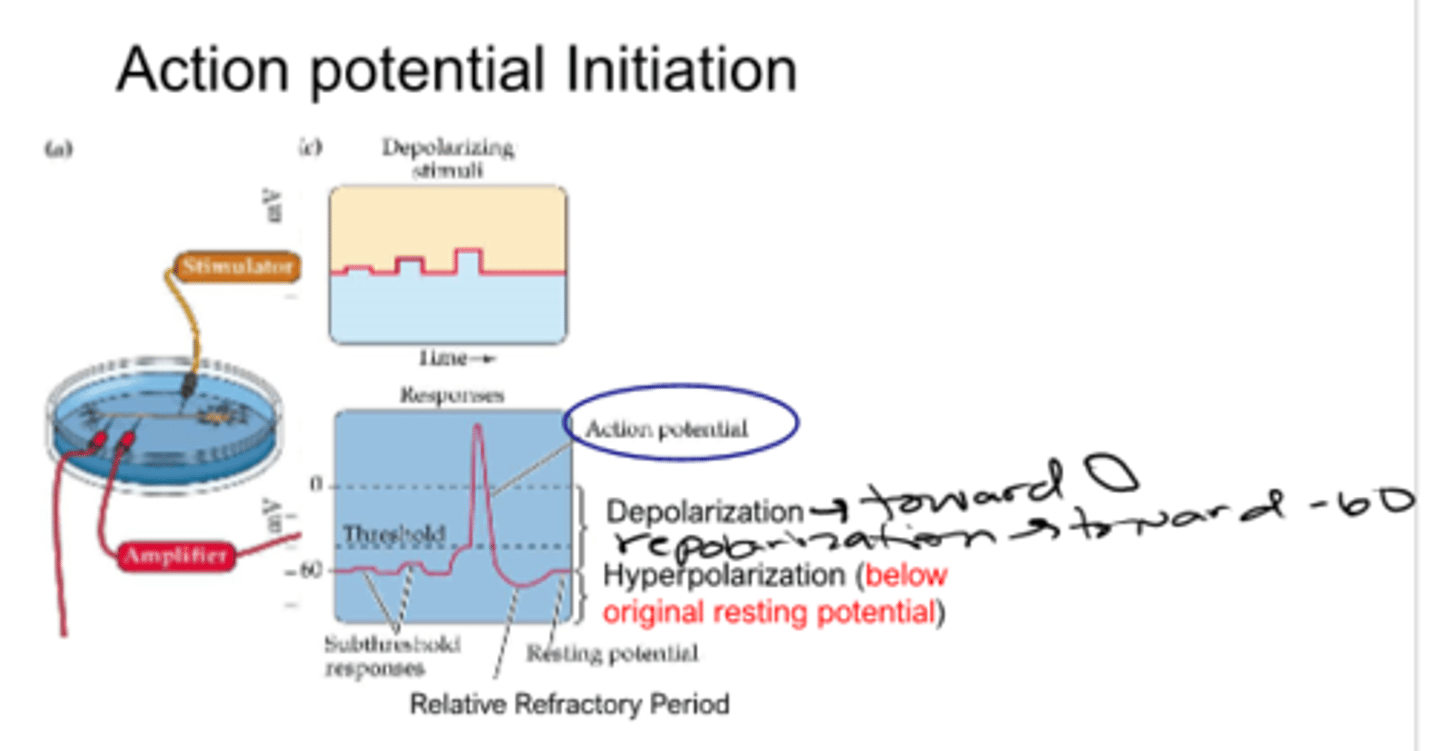
membrane potential becomes less negative (does not need to be positive)
-less negative when compared to resting membrane potential
depolarization
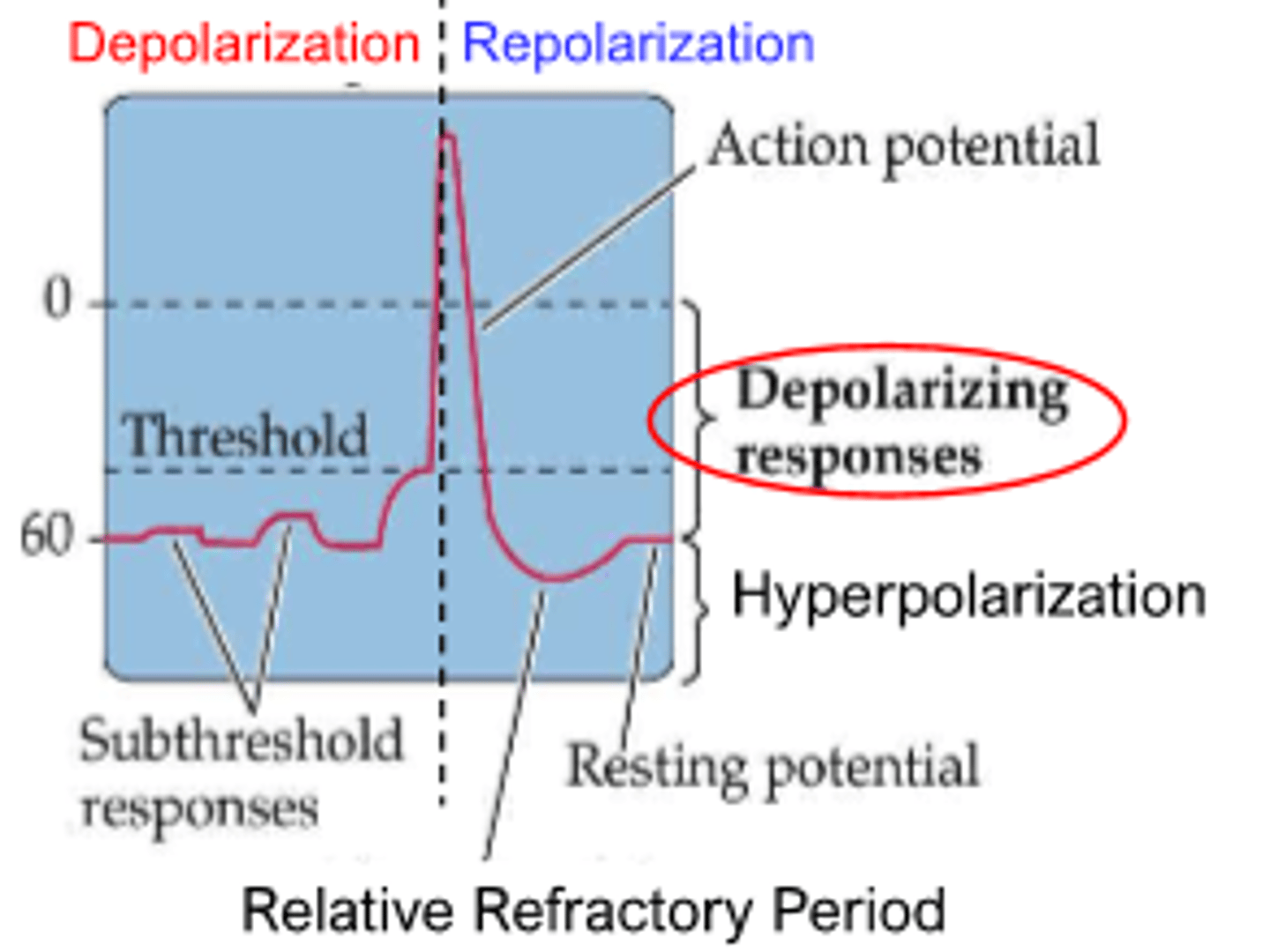
membrane potential (charge of cell) at which an action potential is inevitable
threshold
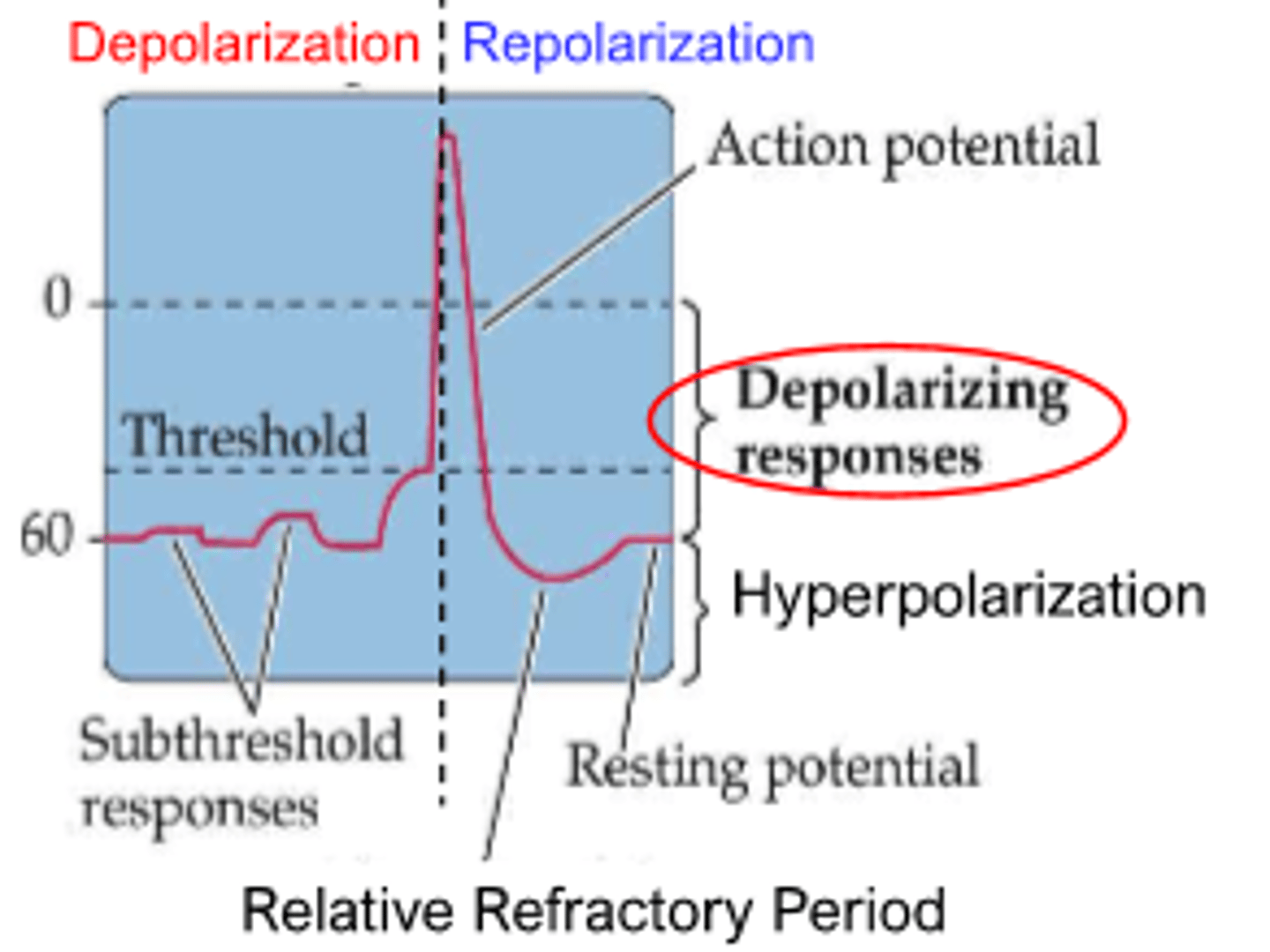
what happens when membrane potential becomes less negative
-cell can overshoot and be positive relative to outside
action potential occurs
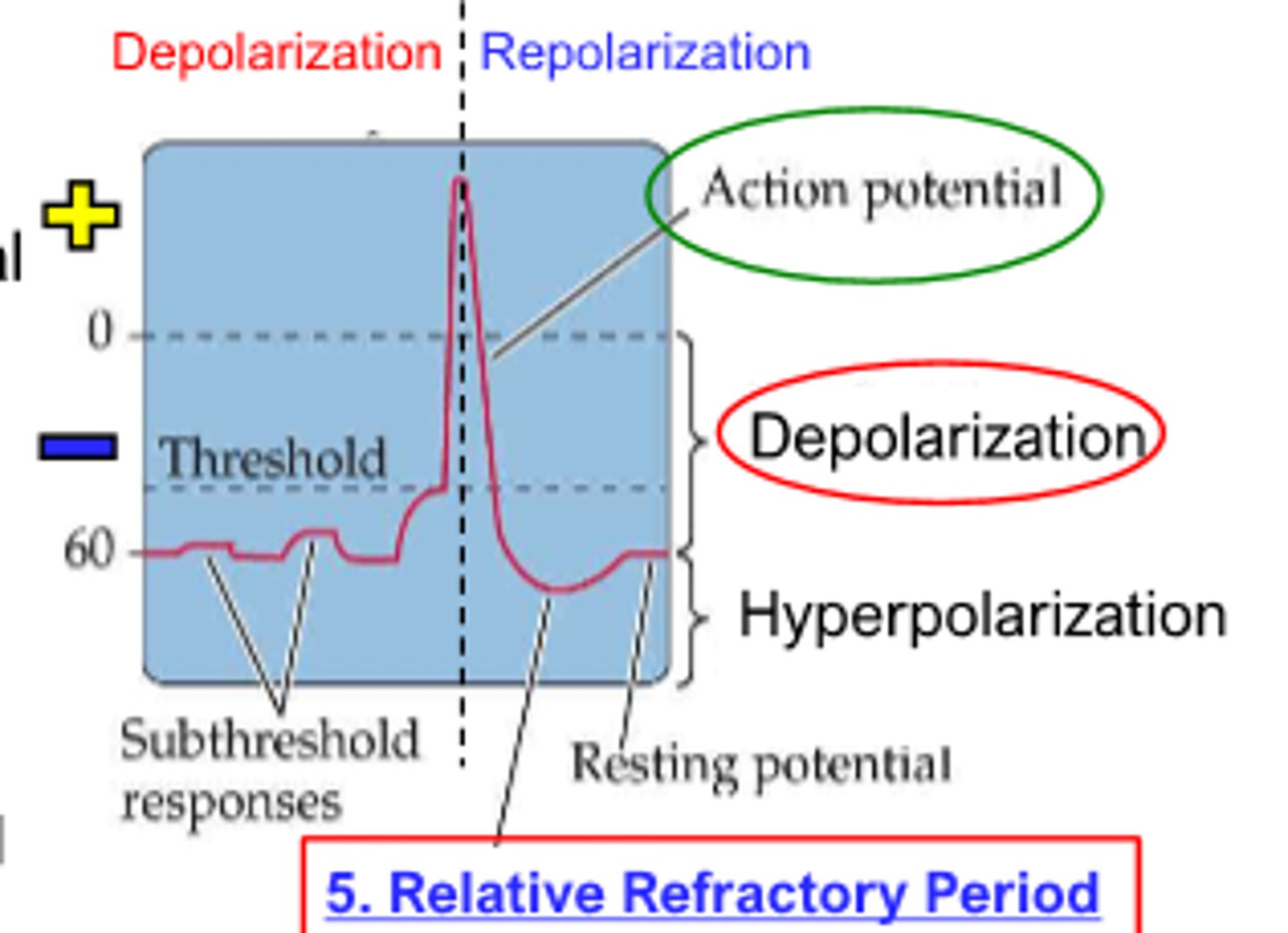
membrane potential heads to original resting spot
repolarization
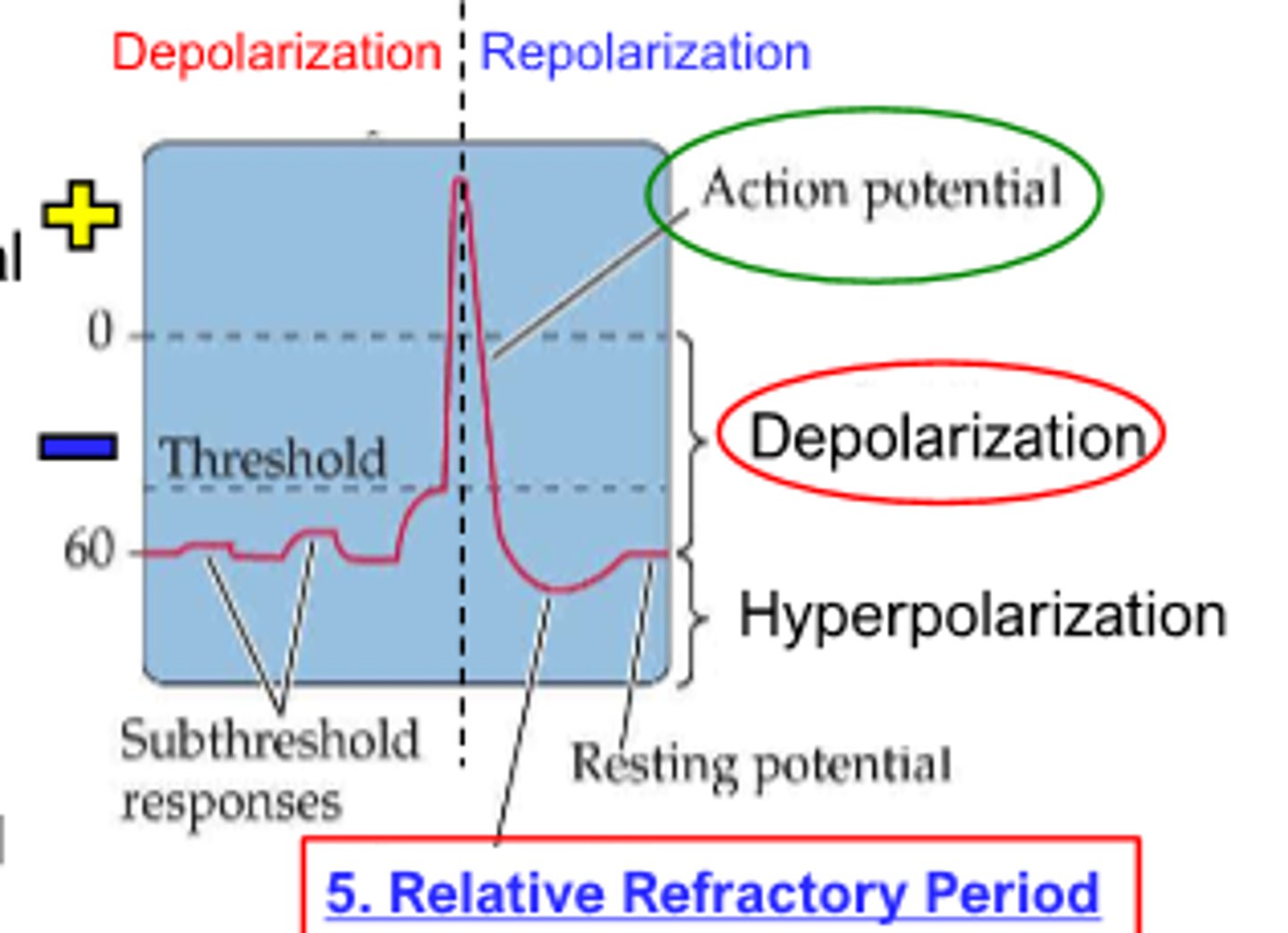
period where cell overshoots generally becoming more negative to resting potential
relative refractory period
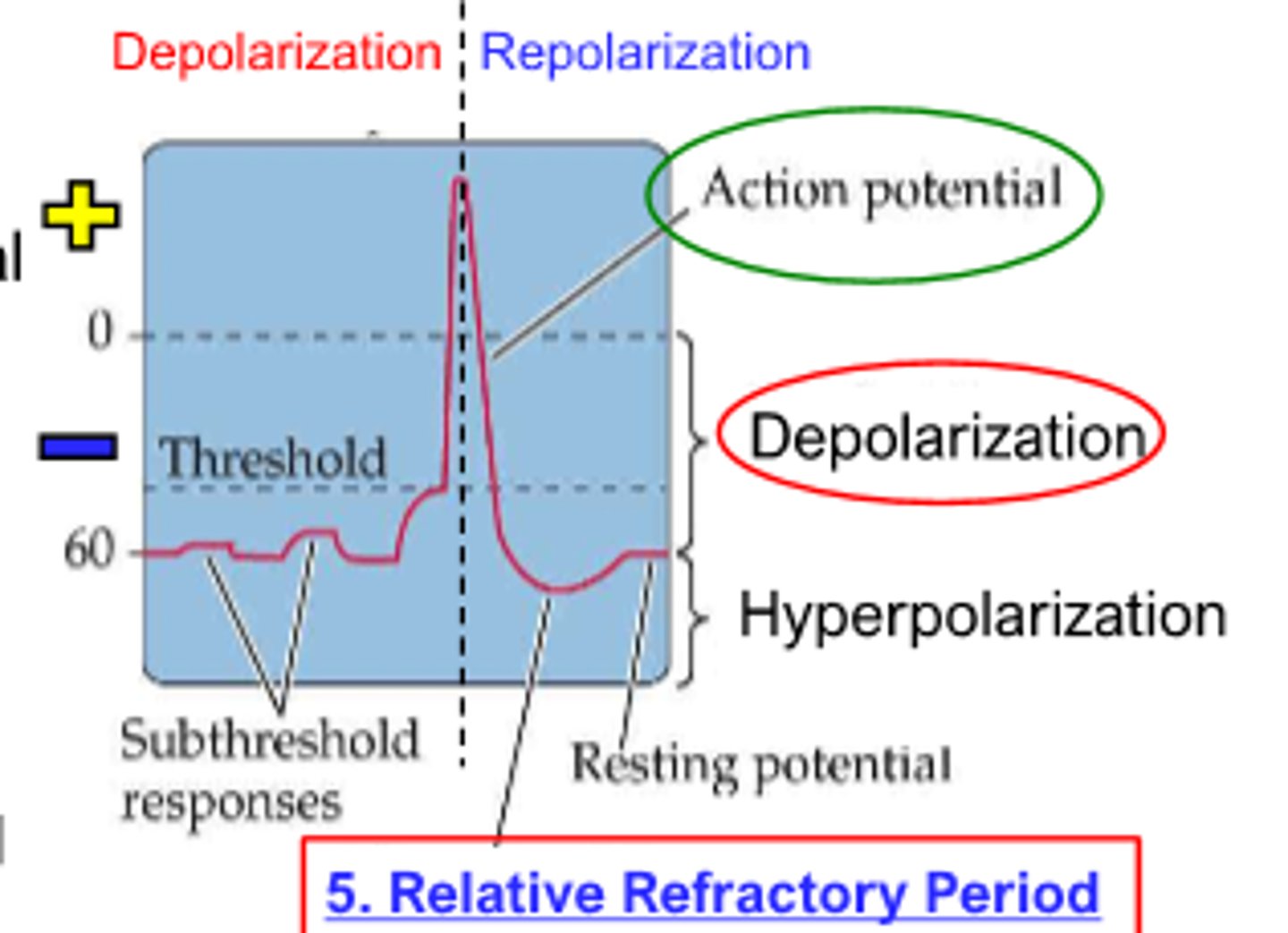
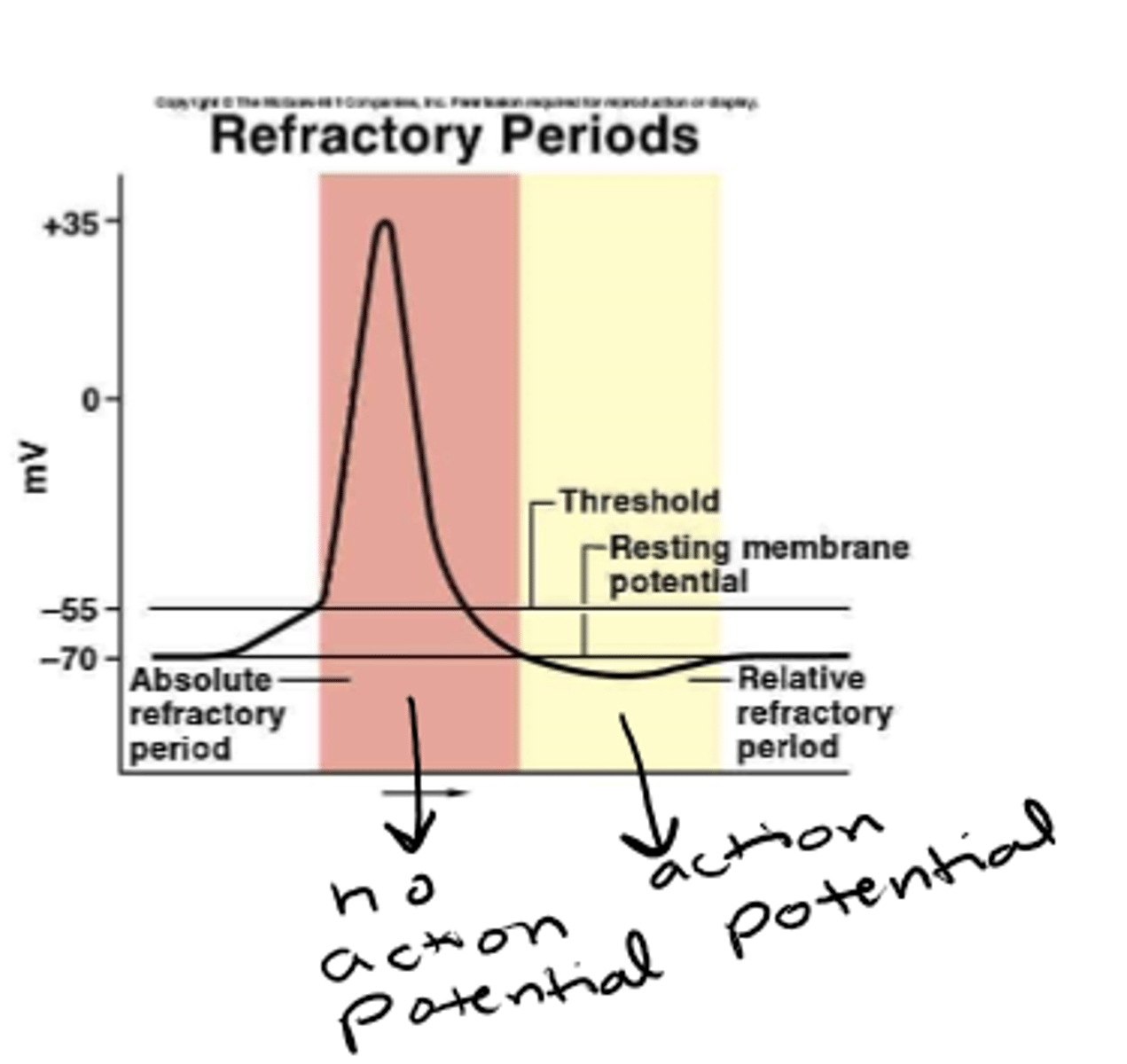
during refractory period, neurons have __________ capacity to produce an action potential
diminished
period where no amount of stimulation can induce an action potential (immediately after action potential)
absolute refractory
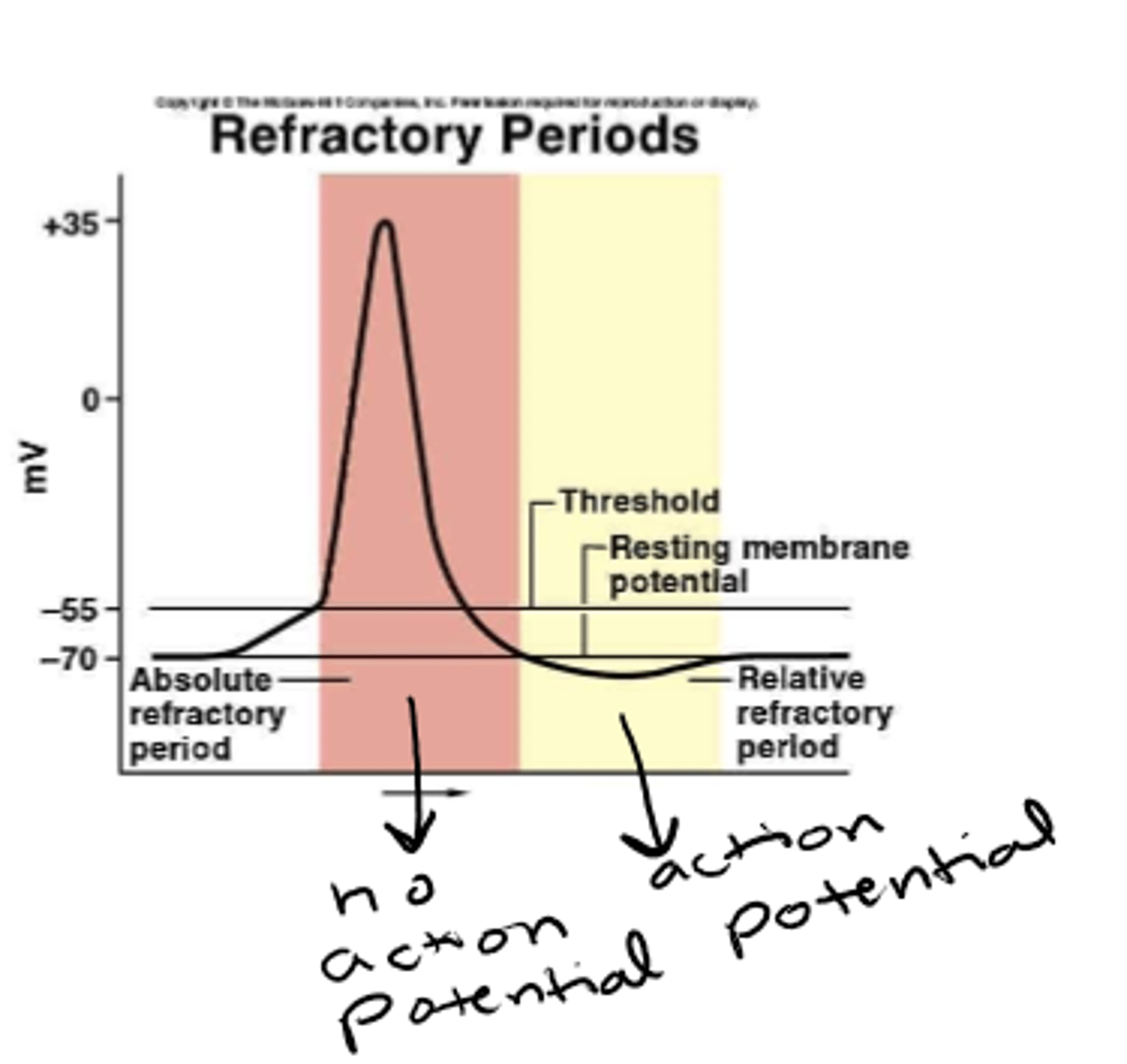
period where a very strong stimulation can induce another action potential (not immediately after action potential, but prior to return to resting potential)
relative refractory
neurons encode intensity using this mechanism
"rate coding"
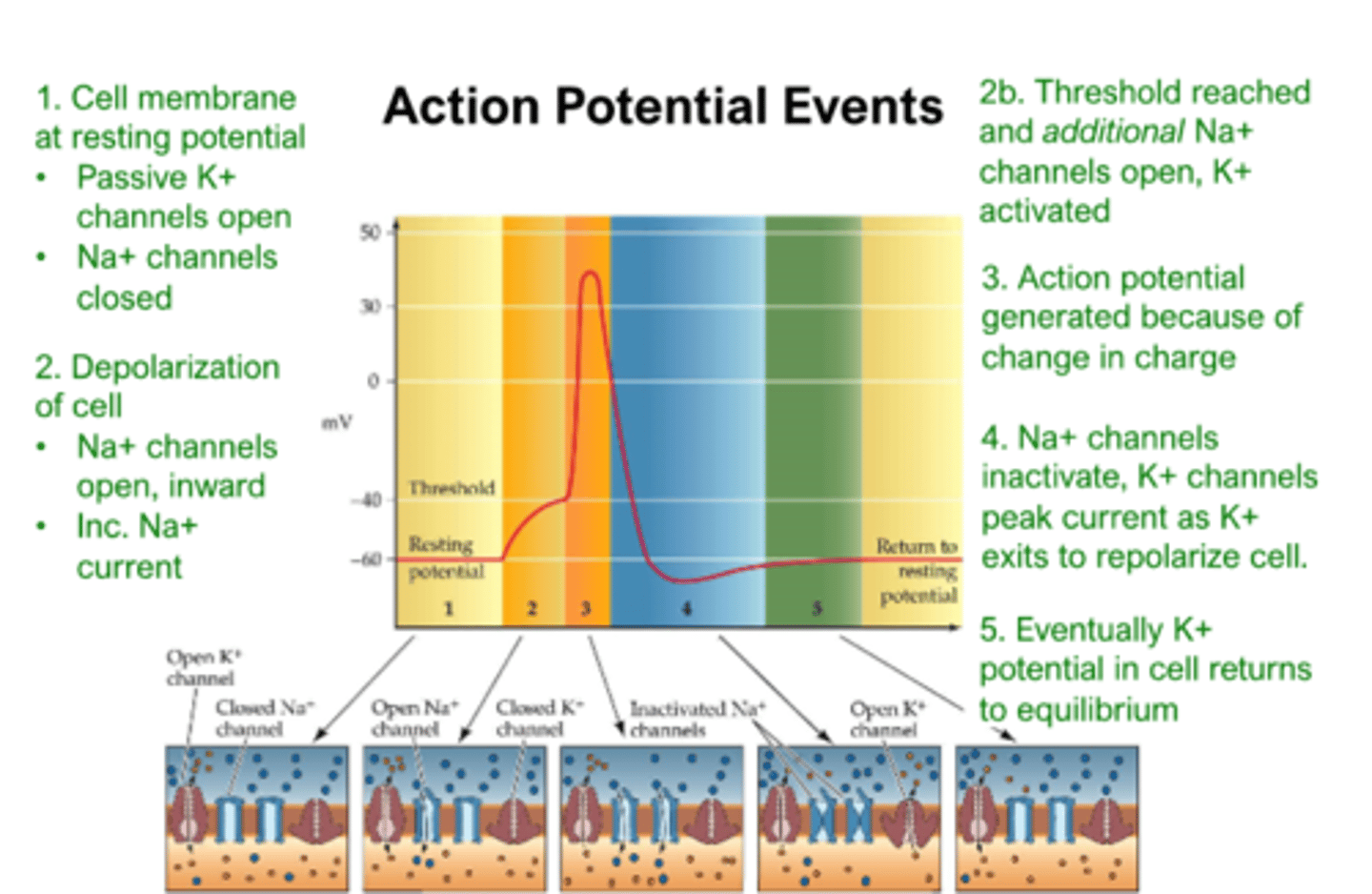
how does ion movement underlie changes in cell membrane potential?
1. depolarization
-stimulus results in slight positive charge, which allows some voltage-gated Na+ channels to open, leading to depolarization
2. if threshold reached, additional voltage-gated Na+ channels open, causing rapid change in charge
3. action potential is generated
-intracellular region becomes positively charged due to large influx of Na+ ions
4. Na+ channels now inactivated by gate terminates the AP and voltage-gated K+ channels open. The positive charges inside the cell force K+ cations out. Excess K+ channels open leads to a hyperpolarization (more negative cell membrane charge relative to resting state). Relative refractory state.
5. Cell membrane repolarizes and returns to resting potential. K+ charge reaches equilibrium with electrostatic and concentration gradients. cell membrane ready for another AP.
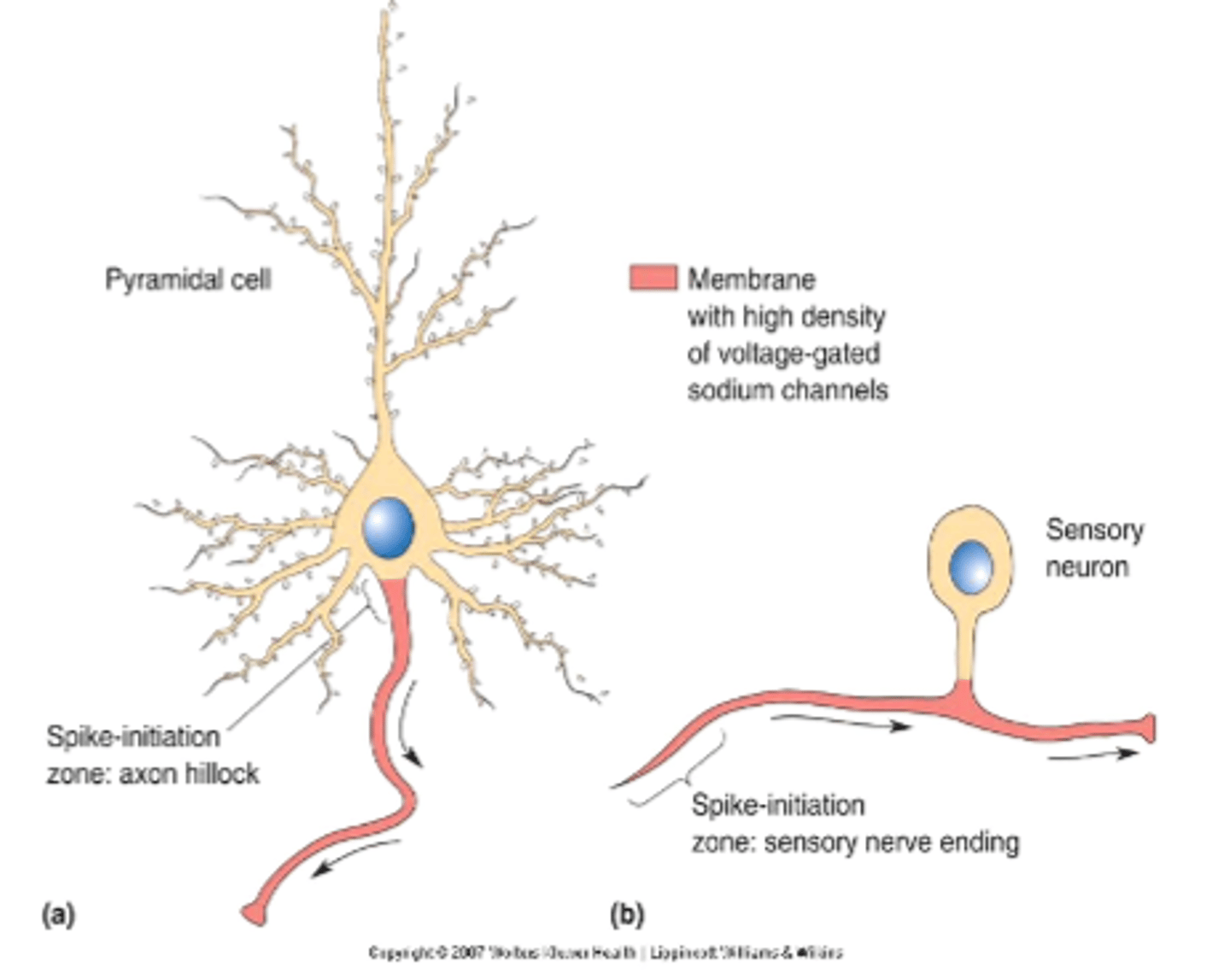
where is depolarization initiated?
spike-initiation zone
-> sensory nerve endings or axon hillock
change in membrane potential occurs in ___________ down the axon
one direction
-due to blockade behind it, it can't go backwards
-in absolute refractory period behind
membrane depolarizes in region __________ to action potential
adjacent
myelin sheath influences ________ of action potential conduction
speed
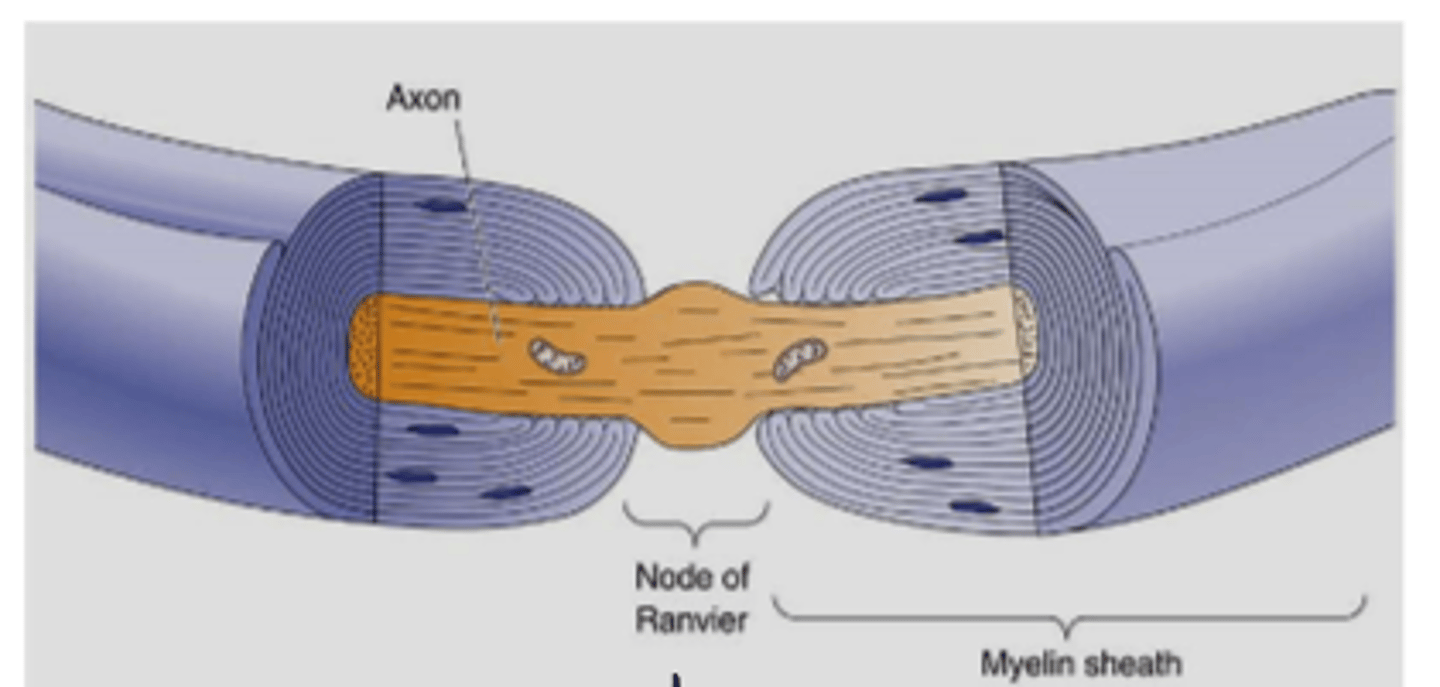
lipid insulator of neuronal axons
myelin
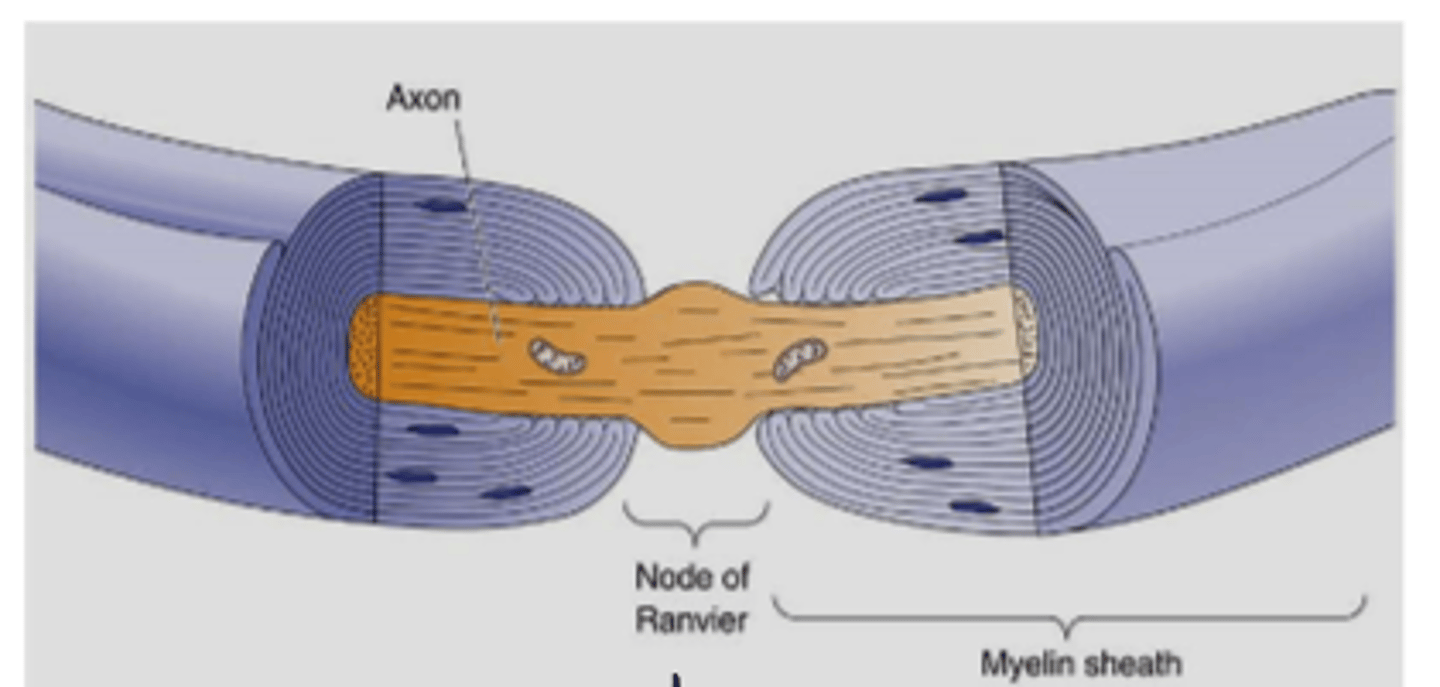
myelinated cells in PNS
Schwann cells
myelinated cells in CNS
oligodendrocytes
why can't an entire neuron be covered in myelin?
no place for current flow across membrane and no action potential
separation in myelin sheath
nodes of Ranvier
what are concentrated at the nodes of Ranvier?
voltage gated Na+ channels
nerve impulse jumps from node of Ranvier to node of Ranvier. this is called:
saltatory conduction
myelination causes nerve impulses to occur about _______ times faster than unmyelinated
50
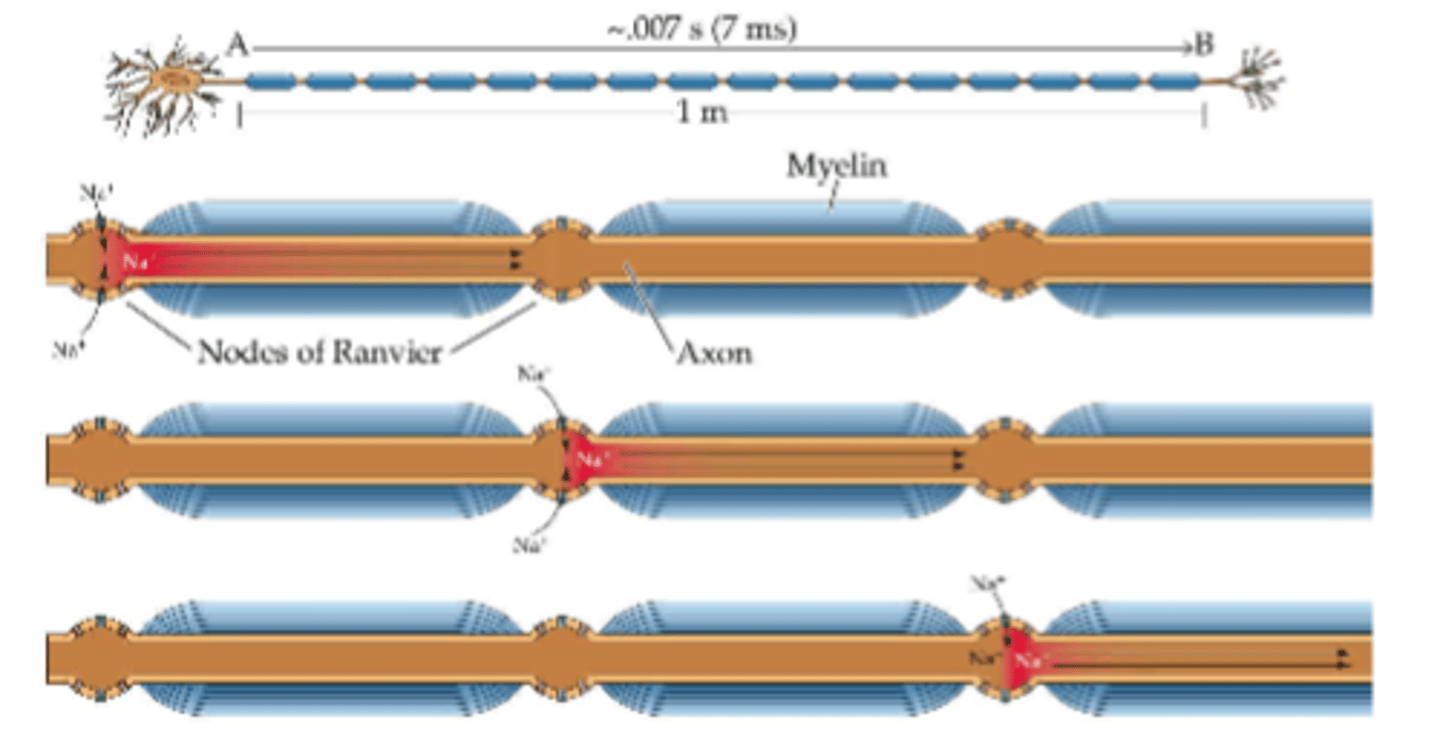
__________ cells limit the locations where ion exchange can occur
Schwann
-specializations for communication
-site where info is transmitted from one cell to the next
-electrical or chemical
synapse
where does neurotransmission occur?
dendrites: spine
axons: boutons
one of the 3 components of a synapse that is the source of information
-signal can be chemical or electrical
-releases neurotransmitter
presynaptic neuron or nerve terminal
one of the 3 components of a synapse that is the target
-a dendrite, cell body, or target cell receiving the synaptic input
postsynaptic neuron
link between presynaptic and postsynaptic neuron in electrical signals
gap junction
link between presynaptic and postsynaptic neuron in chemical synapses
synaptic cleft
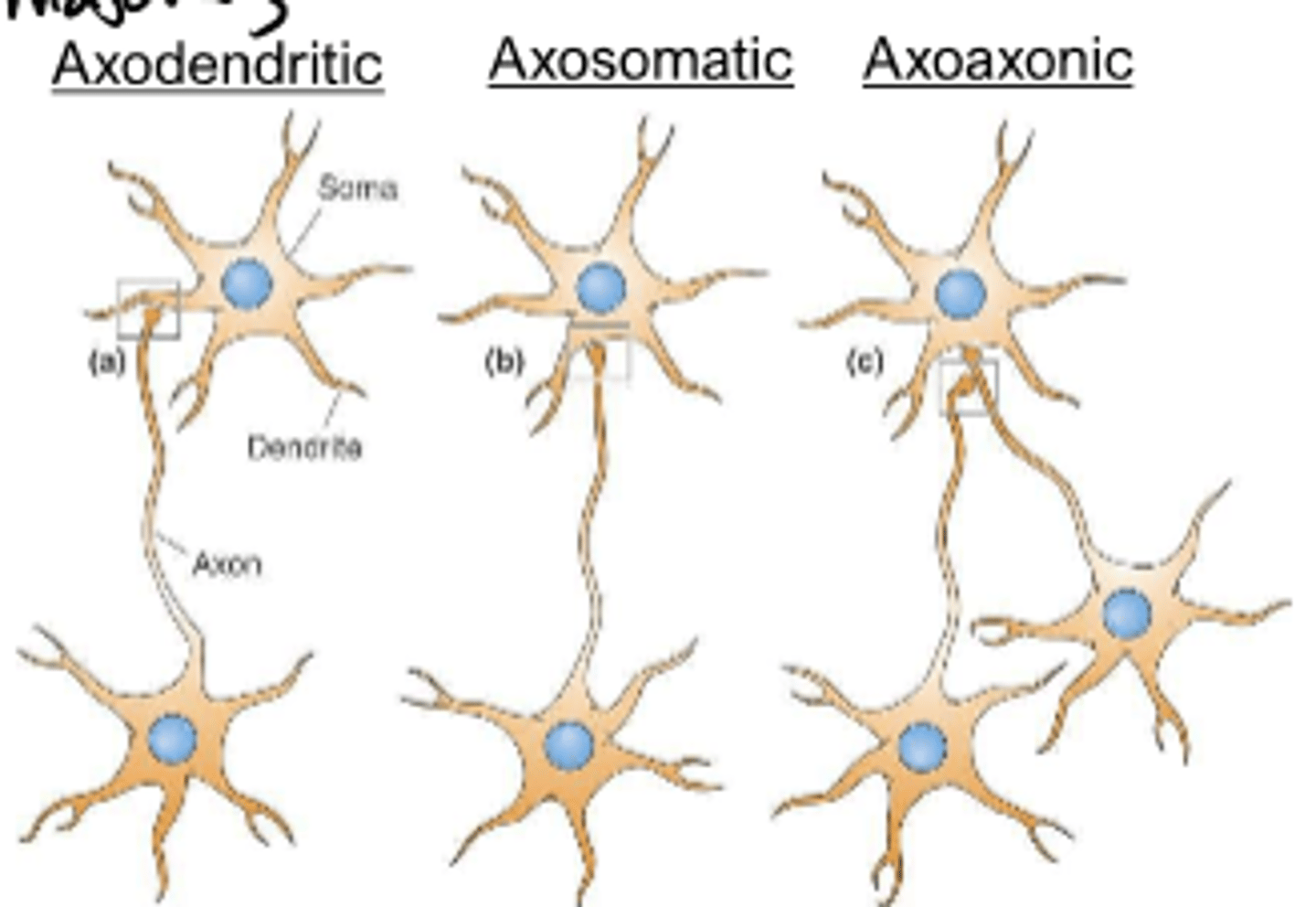
synaptic contact can occur on the dendrites, cell body, or terminal
-what are the 3 names?
axodendritic (majority)
axosomatic
axoaxonic
very fast transmission of synapse
-gap junction: proteins in membrane that form pores between 2 cells
-cells are "_________ coupled"
-flow of ions from cytoplasm to cytoplasm
electrical
(electrically)