CMS II Final: Ortho
1/250
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
251 Terms
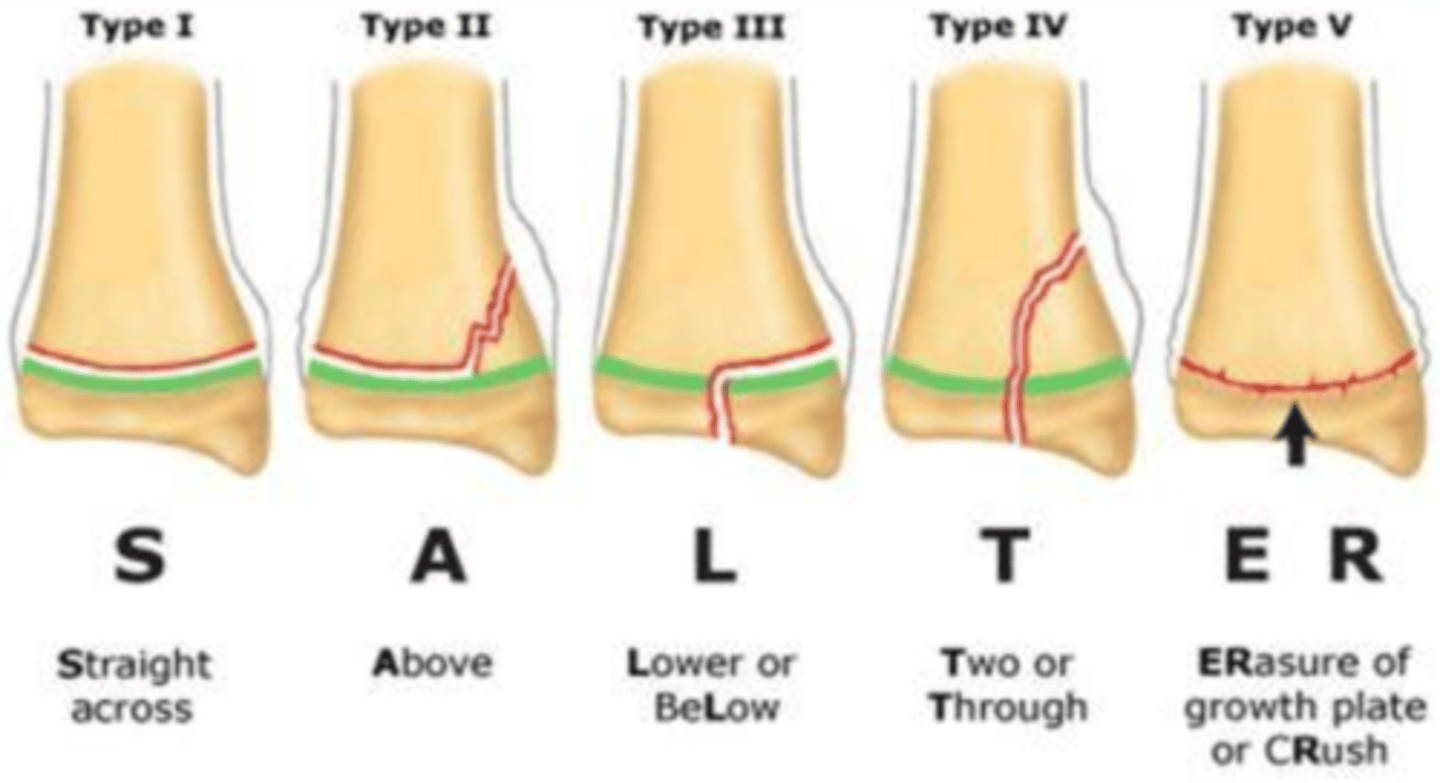
Salter-Harris Mnemonic:
SALTR
S: straight through (type I)
A: above (type II)
L: lower (type III)
T: through or transverse or together (type IV)
R: ERasure of growth plate (type V)
what are the most commonly missed fractures?
Scaphoid, Talar Neck, Radial Head, and Tibial Plateau
injury to which nerve causes foot drop?
peroneal nerve (tibial plateau fx)
injury to which nerve causes wrist drop?
radial nerve (spiral fx of humerus)
fracture of what type of bone is most commonly seen in child abuse?
long bone shaft, posterior/lateral ribs, vertebral body
what is the MC site of acute osteomyelitis?
metaphyseal end of long bone near knee joint
what is a cause of acute osteomyelitis in children <5?
recent URI
weak immune systems
what is the gold standard for dx of acute osteomyelitis?
open bx and bone aspiration***
what is the first sx of acute osteomyelitis in adults? what is the etiology?
1st sx = limitation of joint movement
MC organisms = S. aureus, pseudo, atypicals
what is the MC cause of chronic osteomyelitis? what is seen on XR?
open fx or wound of extremities
XR→ irregular sclerosis bone destruction w/ several areas of radiolucency + involucrum (dead bone surrounded by new shell of bone)
which dx is the "fallen leaf" sign indiciative of on XR?
pathologic fracture
if an XR shows bone arising from stalk or bump on bone, where do you expect this to be found?
osteochondroma → metaphysis of long bone usually around knee or proximal humerus
what would you expect to see on XR from a pt with enchondroma?
lucent in hands/fingers
matrix calcification of long bones
metaphysis of long bones
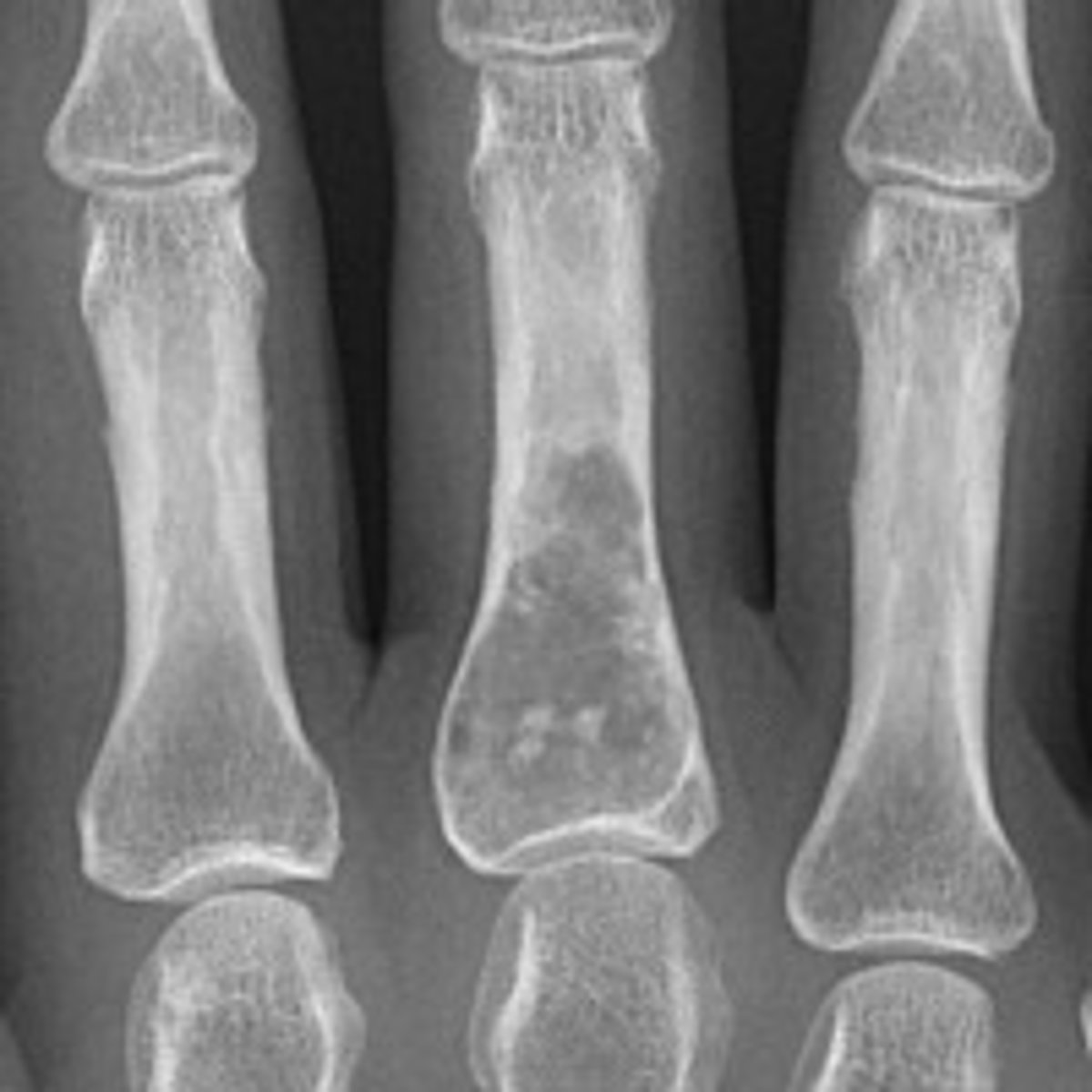
where are osteoid osteomas commonly found? which age group?
long bones and posterior segments of spine
common in ages 10-35→ typically night pain responsive to NSAIDS/ASA
is night pain from osteoid osteoma responsive to NSAIDs/ASA?
yes
what are the 3 most common primary bone tumors?
osteosarcoma
Ewing's sarcoma
chondrosarcoma
where is osteosarcoma MC found? where does it metastasize commonly?
most lesions originate in metaphysis → femur, tibia, humerus
mets → lungs
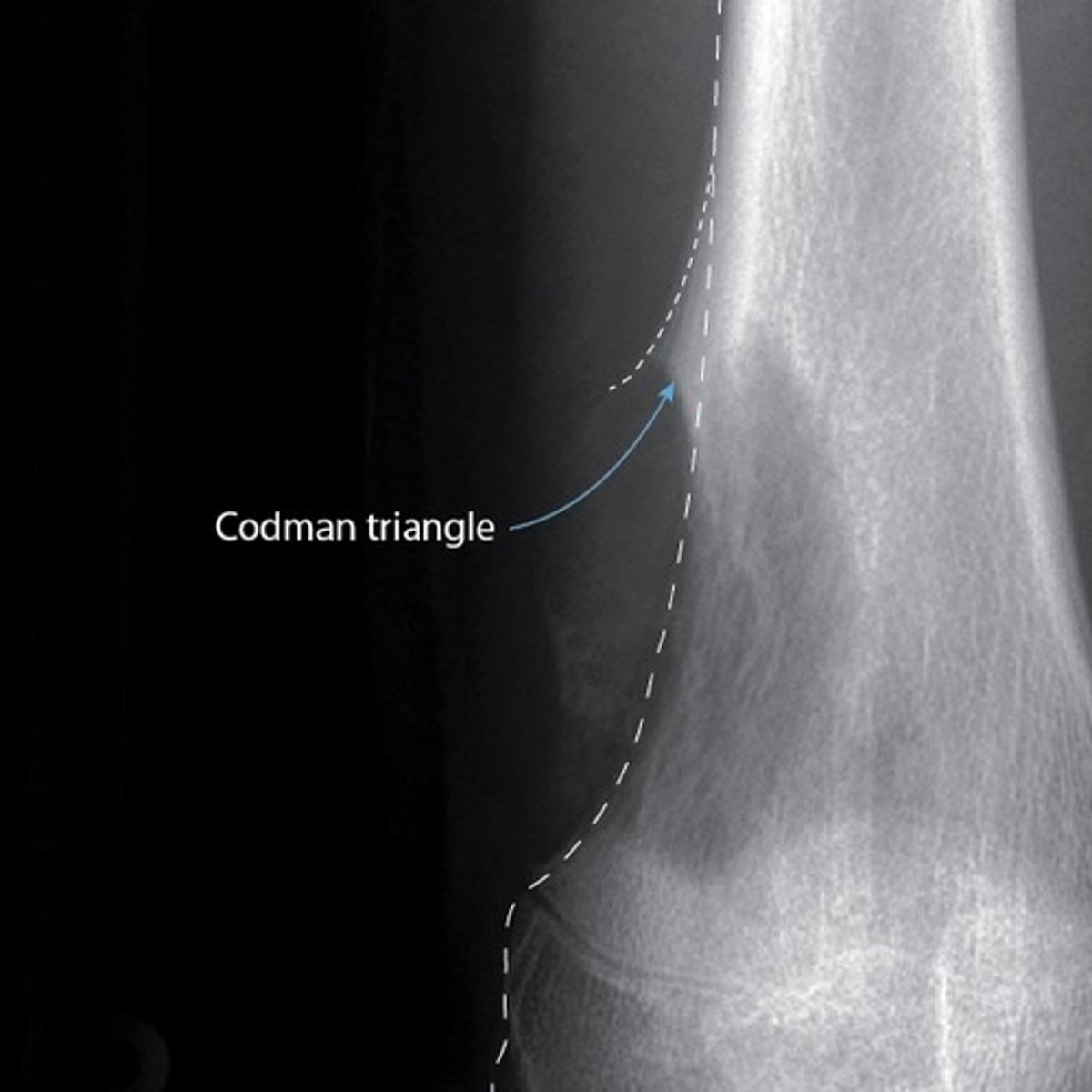
which bone tumor has a "hair on end" appearance or sunray burst appearance on XR?
osteosarcoma
also "codmans triangle" and periosteal rxn on XR
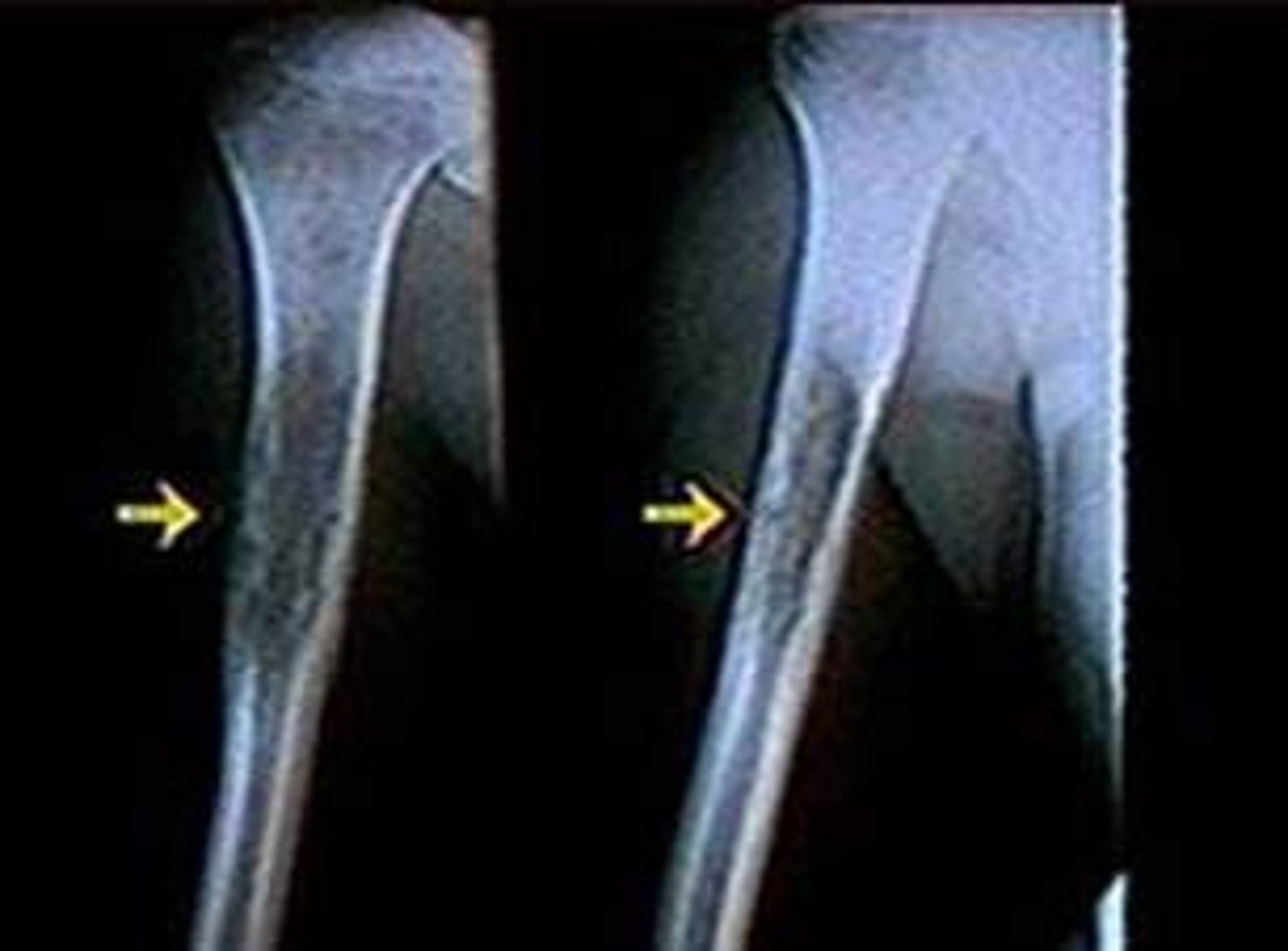
which dx is seen as a lytic lesion with periosteal reaction "onion peel" appearance on XR?
Ewing's sarcoma
what is a progressive, irreversible condition involving the loss of articular cartilage that leads to pain and deformity specifically in the weight bearing joints (LEs and spine)?
osteoarthritis → assoc. with obesity, age, trauma, or genetics
what sx are assoc. with osteoarthritis?
stiffness
pain
decreased ROM and deformity
pain is deep and poorly localized/aching
may occur w/ changes in weather
which dx shows loss of joint space, sclerosis, subchondral cysts, or osteophytes at the joint?
osteoarthritis
what is a systemic autoimmune disorder w/ acute and chronic inflammation in the synovium causing proliferative and erosive joint changes?
RA → symmetric!!!
what are sx of RA?
- ulnar drifting and subluxation
- hallux valgus
- claw deformities of foot
- centra/axial joint involvement
- neck pain/stiffness
if a pt presents with joint swelling, reduced grip strength, pain elicited by pressure, and boggy feeling of joints, what should you suspect?
RA
what does RA show on XR?
bone erosion at joint margin
what is the first line tx for RA?
NSAIDs to reduce pain and inflammation
what is systemic inflammation triggered by GI or GU infection that is common in young men?
reactive arthritis (reiter syndrome)
what is the triad assoc. with Reiter syndrome?
conjunctivitis
urethritis
oligoarticular arthritis
(can't see, can't pee, can't climb a tree)
What differentiates polyarthritis from RA?
DIP joint involvement and absence of nodules
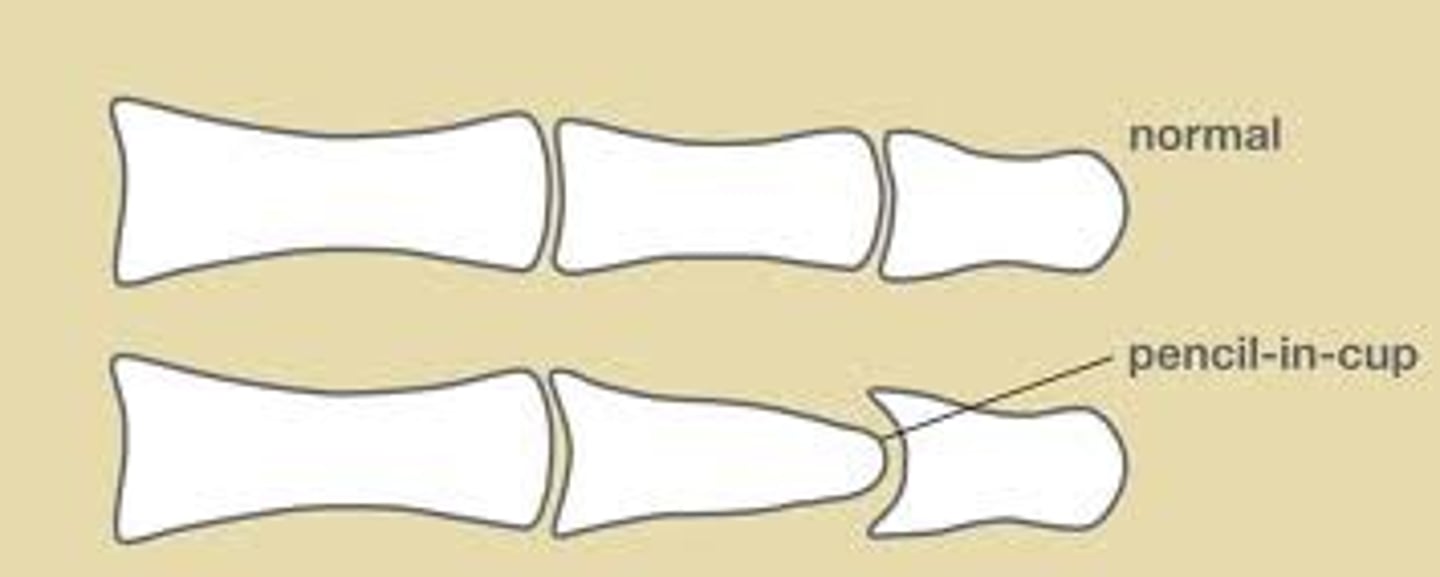
which dx shows a pencil-in-cup deformity on XR?
psoriatic arthritis → resorption of terminal phalanges and proliferative bone reaction in DIP joints
what are the 5 types of psoriatic arthritis?
DIP joint
asymmetric oligoarthritis
symmetric polyarthritis
arthritis mutilans
sacroiliitis
which dx is HLA-B27 antigen commonly found in patients?
Reiter's syndrome
what are physical signs of reiter's syndrome?
keratodermia blenorrhagicum (rash on palms/soles appears like papular psoriasis)
pt presents with skin lesions, nail changes, dactylitis, iritis. what is the appropriate treatment?
psoriatic arthritis → NSAIDs, DMARDs, TNF blocker
what dx is defined by excess monosodium urate crystals deposit in tissue causing and inflammatory process?
gout→ accumulation causes tophaceous deposits (tophi), uric acid stones, and nephropathy
what is the MC joint affected by gout?
1st MTP (podagra)
spurling or distraction special test: axial load, then laterally flexed and rotate neck ?
spurling→ radiating pain indicates nerve root compression
what special test involves upward distracting force?
distraction → relief of symptoms indicates foraminal compression of nerve root
what needs to be present for the the cervical distraction test be used?
when the pt is currently having radicular symptoms → positive = arm pain reduced (separating vertebrae)
which C-spine test has positive result of shocking sensation down the spinal cord indicating myelopathy or MS?
Lhermitte's → hyperflexion of C spine
gout or pseudogout: XR shows punctate or linear calcifications of cartilage; chondrocalcinosis
pseudogout
gout shows bony erosions and spurs
which joints are commonly affected by pseudogout?
knee, wrist chondrocalcinosis (linear calcification of cartilage)
gout or pseudogout: polarized microscopy shows weakly positive, birefringent rhomboid-shaped crystals?
pseudogout
gout is negative birefringent urate crystals
which dx is defined by low bone mass leading to microarchitectural deterioration and increased bone fragility leading to deformity, pain, loss of independence and death following hip fx?
osteoporosis
what are the different types of osteoporosis?
primary = type 1 (postmenopausal) and type 2 (senile)
secondary (long term steroid tx, hyperthyroid, hyperparathyroid, neoplastic, metabolic abnormalities)
what is the gold standard for dx of osteoporosis?
DEXA scan
pt with history of arm abrasion 2 weeks ago presents with temperature changes, pain out of proportion distal to the abrasion, burning, and throbbing. what is your dx?
CRPS
type 1 → no nerve lesion
type 2 → nerve lesion
which imaging study is best for soft tissue analysis? bone?
soft tissue = MRI
bone = CT (except stress fx)
what is the difference between arthroscopy and arthroplasty?
arthroscopy = small incisions with scope for eval/remove bone spurs, cysts, damaged lining or loose joint fragments
arthroplasty = "replacement"
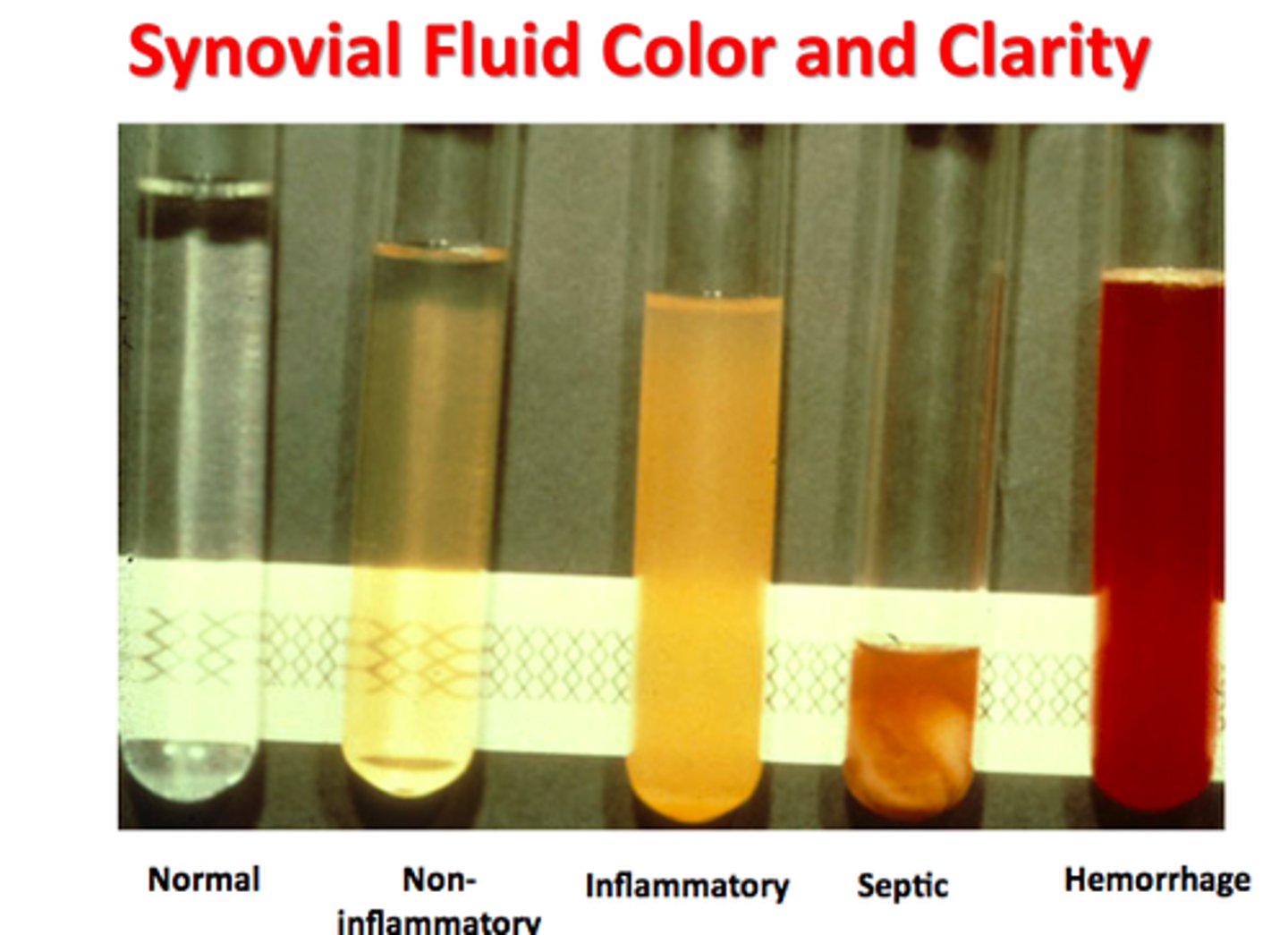
which synovial fluid analysis: clear to pale yellow/transparent with WBC<200?
normal
which synovial fluid analysis: slightly deeper yellow, transparent, WBC <2000?
osteoarthrtis
which synovial fluid analysis: darker yellow, cloudy, translucent, blurred with WBC <80,000?
inflammatory
which synovial fluid analysis: purulent, dense, opaque with WBC >50,000?
septic
which synovial fluid analysis: red, opaque?
hemarthrosis
what are the side effects of NSAIDs?
#1: GI ulcer/bleeds
#2: kidney problems (bc renally eliminated)
which COX pathway mainly mediates inflammatory response?
COX-2→ less likely to cause GI ulcer/bleed
COX ___ inhibitors are associated with increasing risk of stroke/MI
COX-2
what are the risks for developing DVT?
Virchow's triad:
stasis
hypercoagulable states
endothelial injury
21 year old female pt presents with left leg swelling and pain/tenderness as well as a fever of 99.6. Med list includes OCP. What should you perform during PE?
DVT → Homan's sign
and order a doppler
which type of contraction produces a muscle contraction w/o moving the joint angle; length of muscle doesn't change?
isometric contraction

which type of contraction: manual/mechanical resistance applied as muscle moves through ROM, length of muscle changes. may be concentric (shorten) or eccentric (lengthen)
isotonic contraction

which type of contraction: muscle shortens and contracts, which occurs at a constant rate of speed?
isokinetic contraction
which type of anesthesia is utilized for major joint/spine sx, decreases need for opioids and has risks of resp. depression, postop n/v, prolonged sedation/recovery?
general anesthesia
which type of anesthesia is used in procedures involving LEs, decreases postop sedation in elderly, and has a complication of epidural hematoma w/ anticoag?
epidural/spinal anesthesia
which type of anesthesia is used for procedures of UE/LE and involves blocking nerve pain?
peripheral nerve block
may do brachial, sacral plexus, popliteal, intra-scalene, femoral or ankle block
which type of anesthesia is used for short procedures of the forearm, wrist, and hand?
IV regional anesthesia
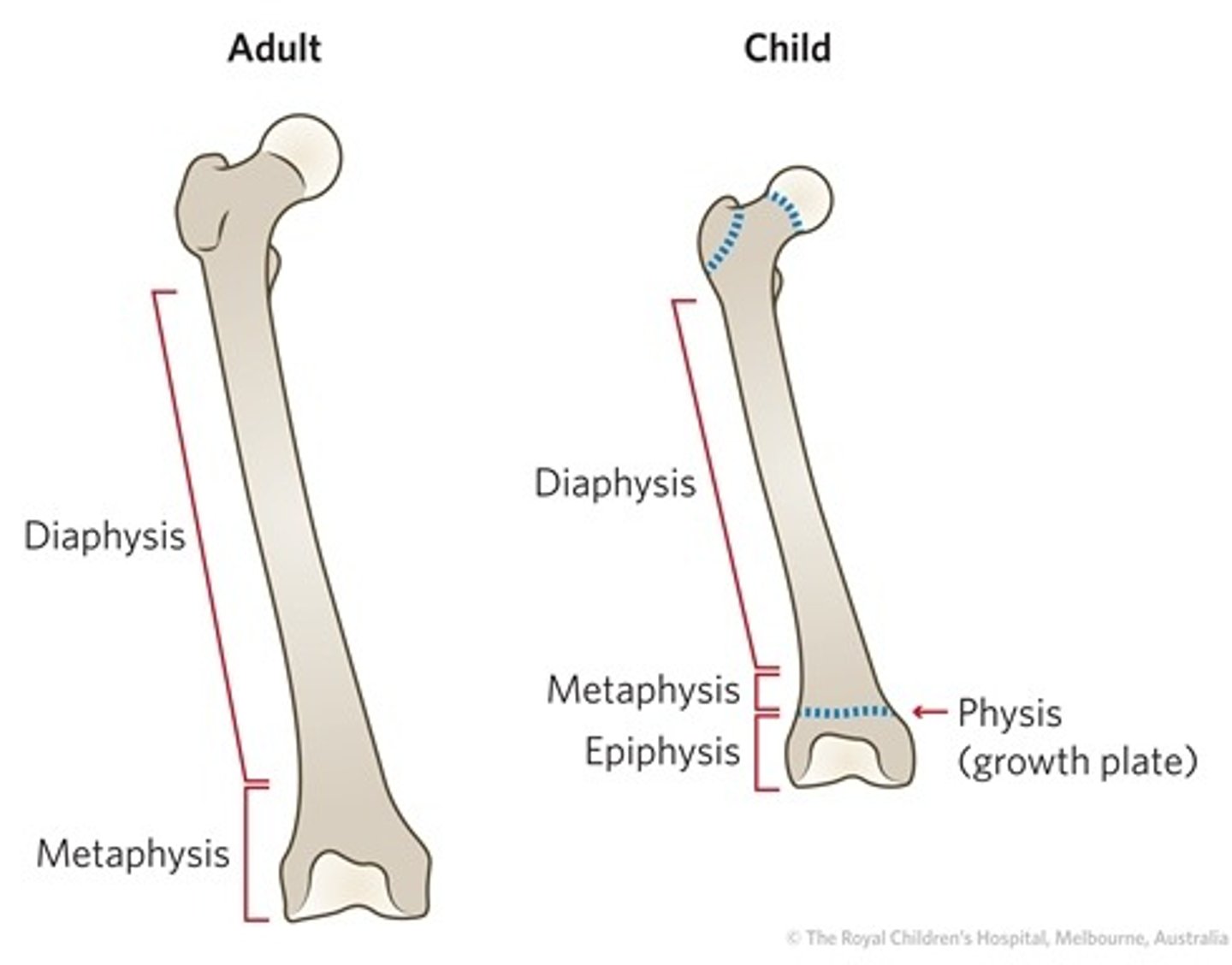
what are the different parts of the bone?
epiphysis, metaphysis, diaphysis, physis (growth plate)
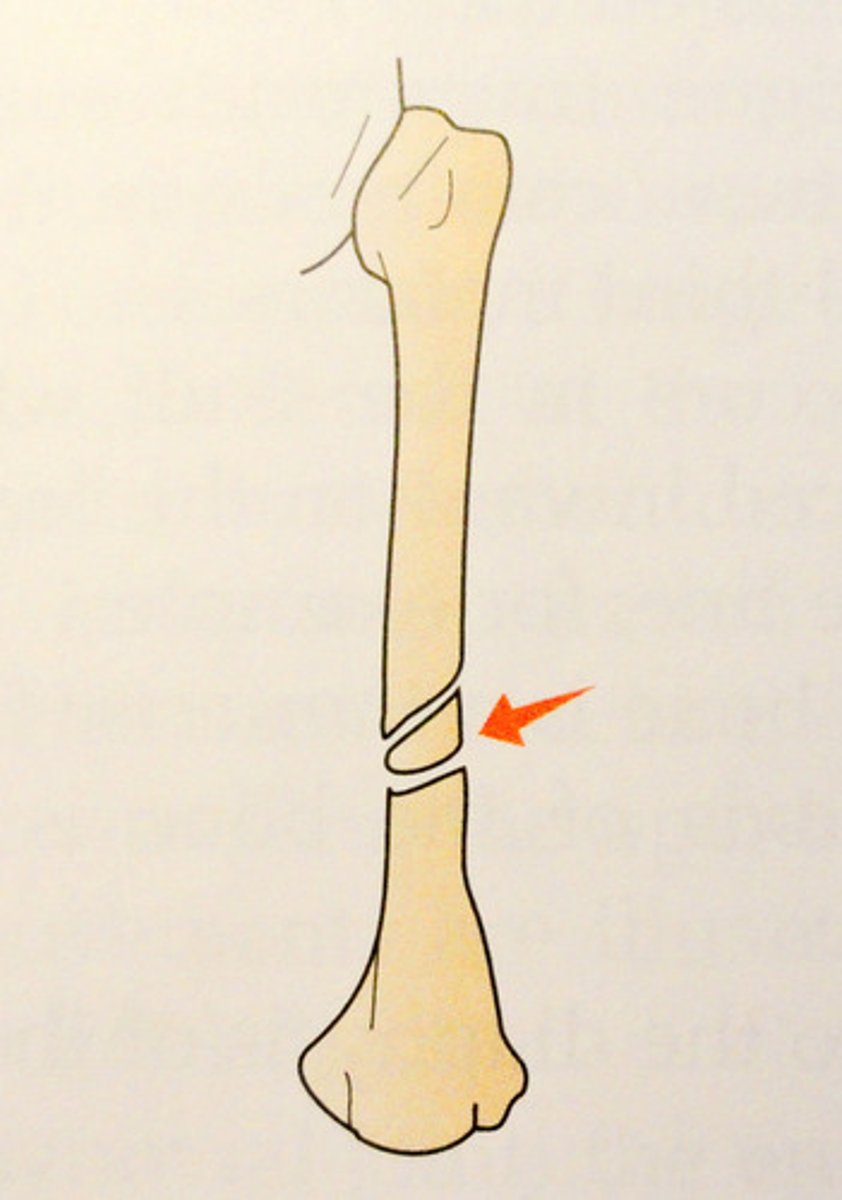
what is an oblique fracture?
occurs at an angle other than a right angle to the axis of the bone
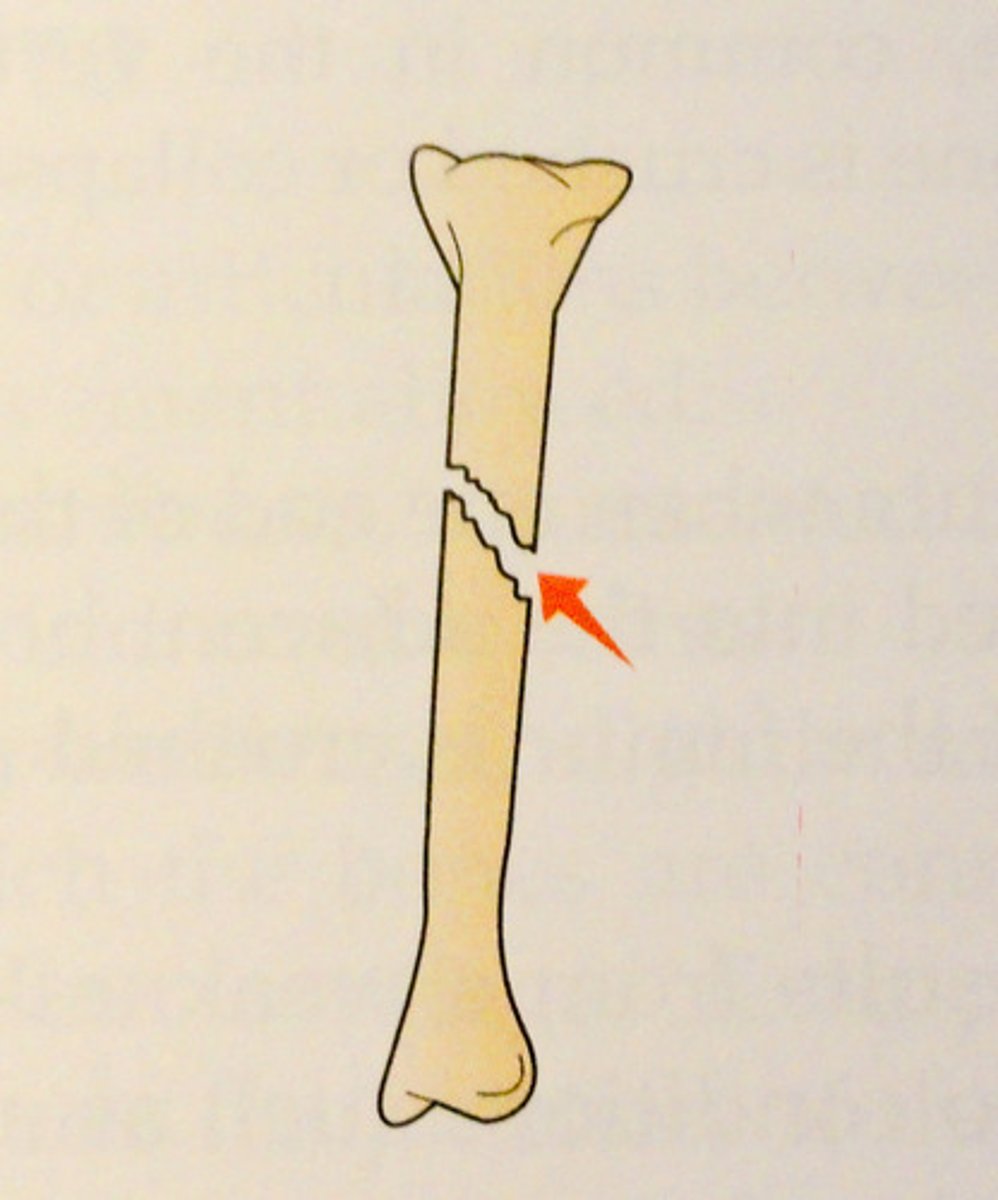
what is a transverse fracture?
When the bone is fractured at a right angle to the long axis.
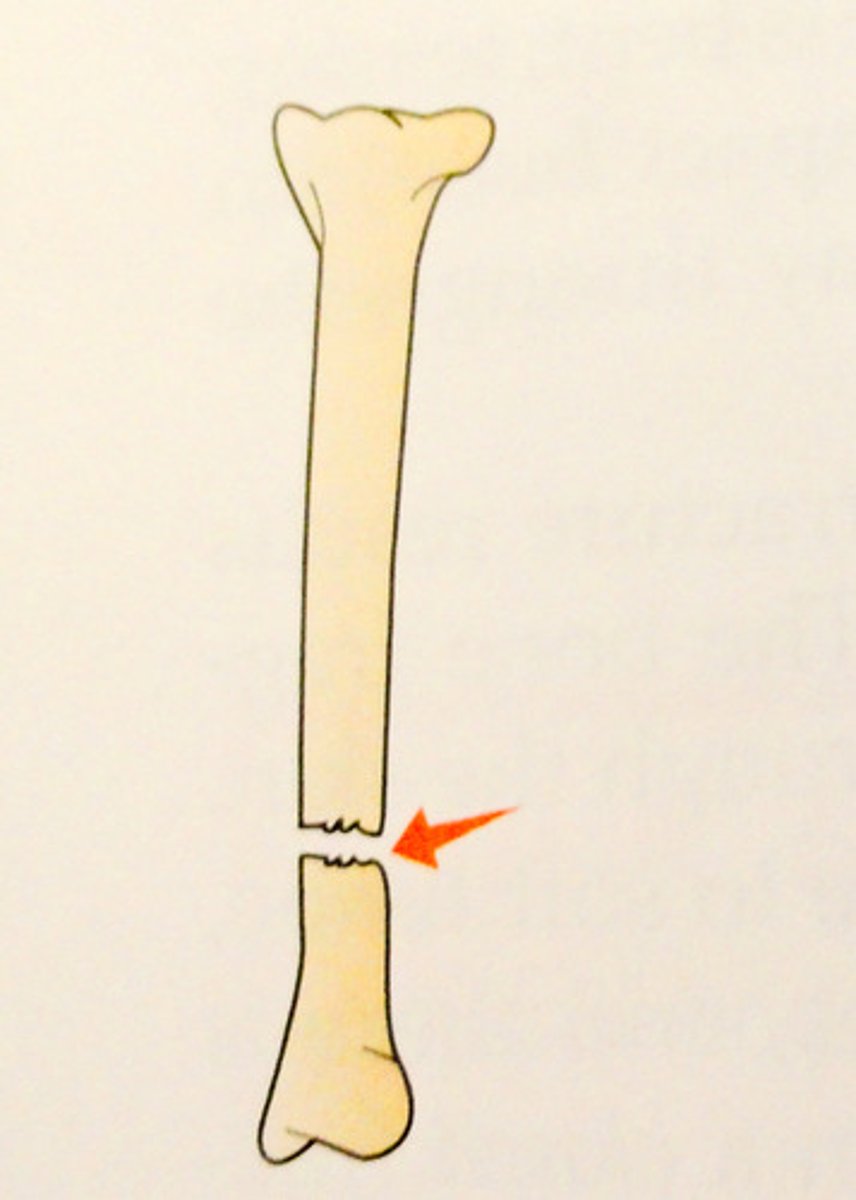
what is an comminuted fracture?
Where the bone is completely shattered
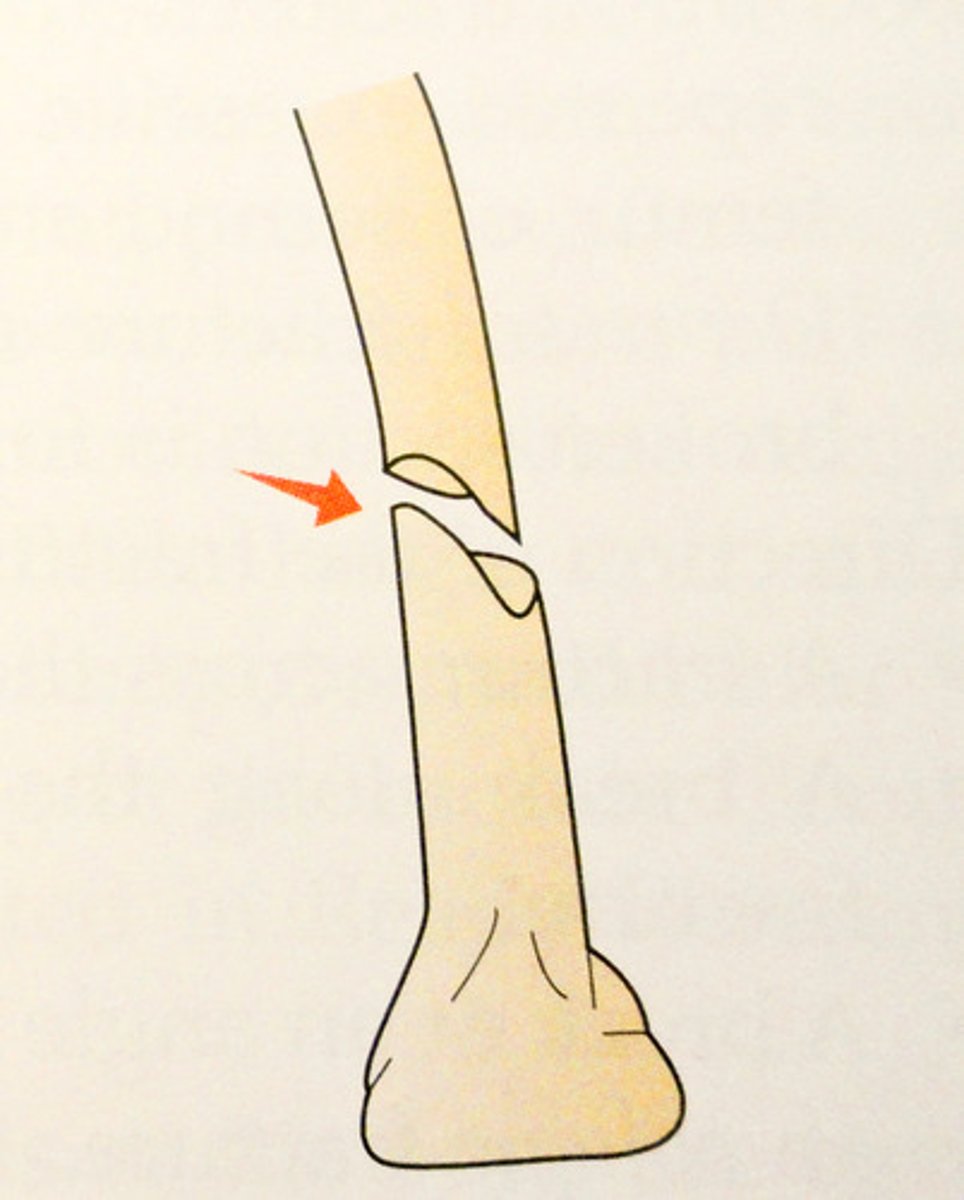
what is a spiral fracture?
ragged break occurs when excessive twisting forces are applied to a bone
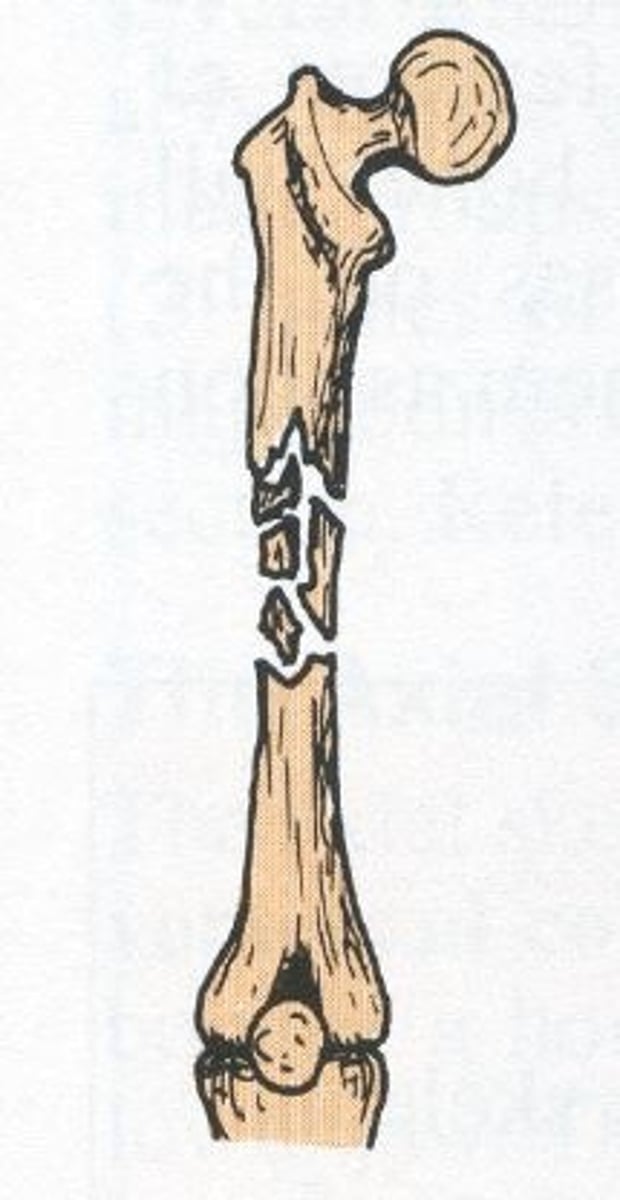
what is a segmental fracture?
Comminuted fracture where fractured pieces are in segments
what XR views are used to evaluate the odontoid?
open-mouth
Fuchs view
what is a cause of neurogenic pain assoc. with cervical nerve roots or roots w or w/o numbness, weakness, or loss of reflexes?
cervical herniated disk
what are risk factors for cervical herniated disk?
cig smoking
frequent heavy lifting
diving
what imaging study confirms the dx of herniated disk?
MRI
what are s/sx of cervical spondylosis (degenerative disease in cervical spine)?
- chronic neck pain that worsens w upright activity
- decreased ROM of C spine
- HA that originates in neck
- irritability, fatigue, sleep probs, work intolerance
- radicular pain in UEs
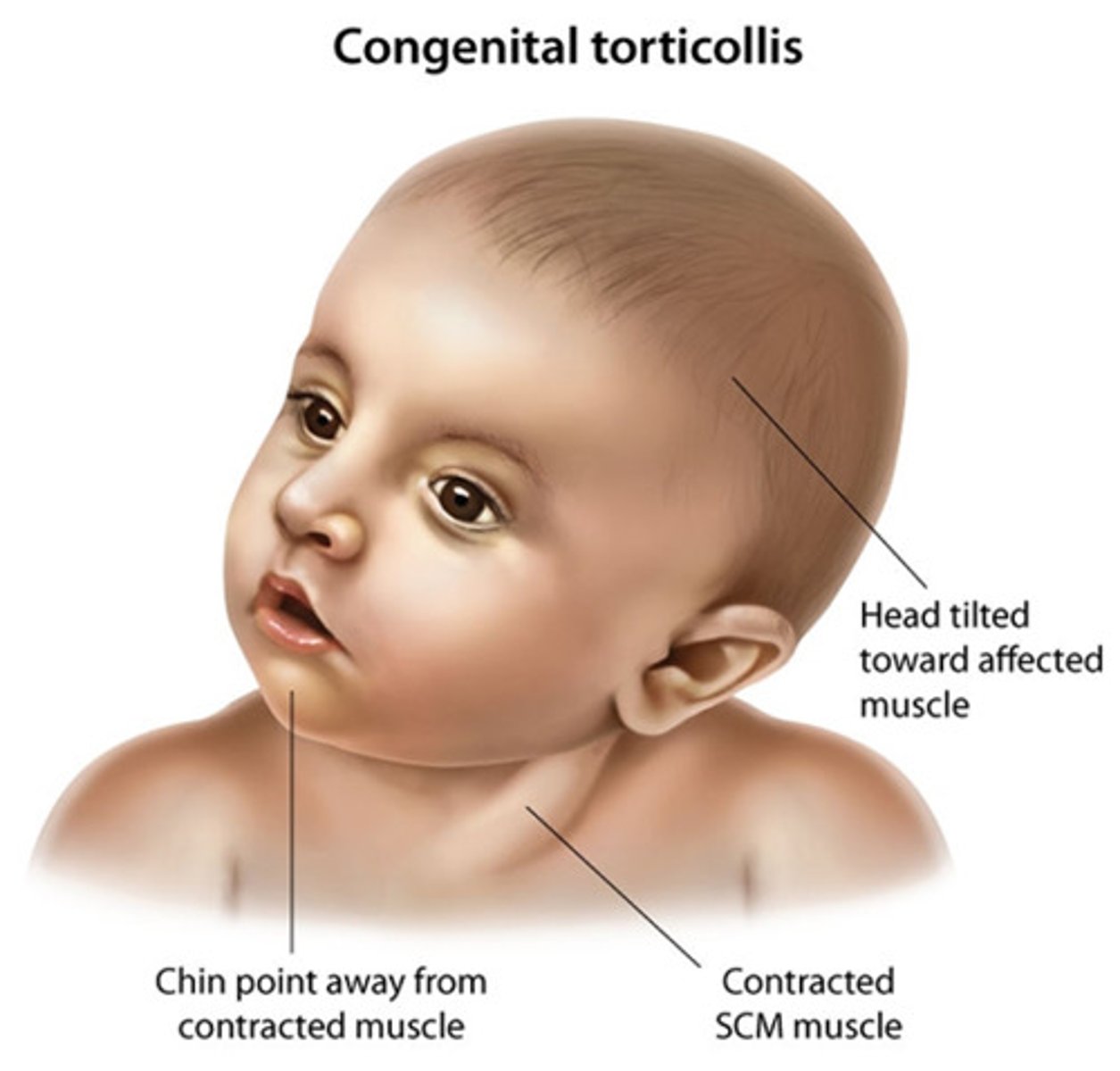
what is the typical presentation of torticollis?
head tilted toward the affected side/rotate toward the unaffected side, SCM lump (contracture that causes pain and dizziness), cranial/facial asymmetry
cervical sprain vs. cervical strain
cervical sprain = whiplash (hyperextension followed by flexion); ligamentous injury
cervical strain = muscle injury of neck
what are the MC s/sx of cervical sprain/stain?
MC = non-radicular, non-focal neck pain noted anywhere on the base of the skull
other:
SCM/trap pain, HA, irritability, fatigue, sleep disturbances, difficulty concentrating
what imaging is indicated for cervical sprain/strain?
plain films → make sure all 7 vertebrae are seen
MRI not indicated
what is the most important XR view for multiple-injured pt involving cervical fx?
cross-table lateral view of C-spine to include C1-T1 = standard trauma view of C spine!!
which XR view is required to visualize the cervicothoracic junction?
Swimmer's view
what is the priority in cervical trauma treatment?
spinal immobilization → clear the spine!!
then immediate IV steroids!
imaging does not take precedence over life-saving dx and therapeutic procedures
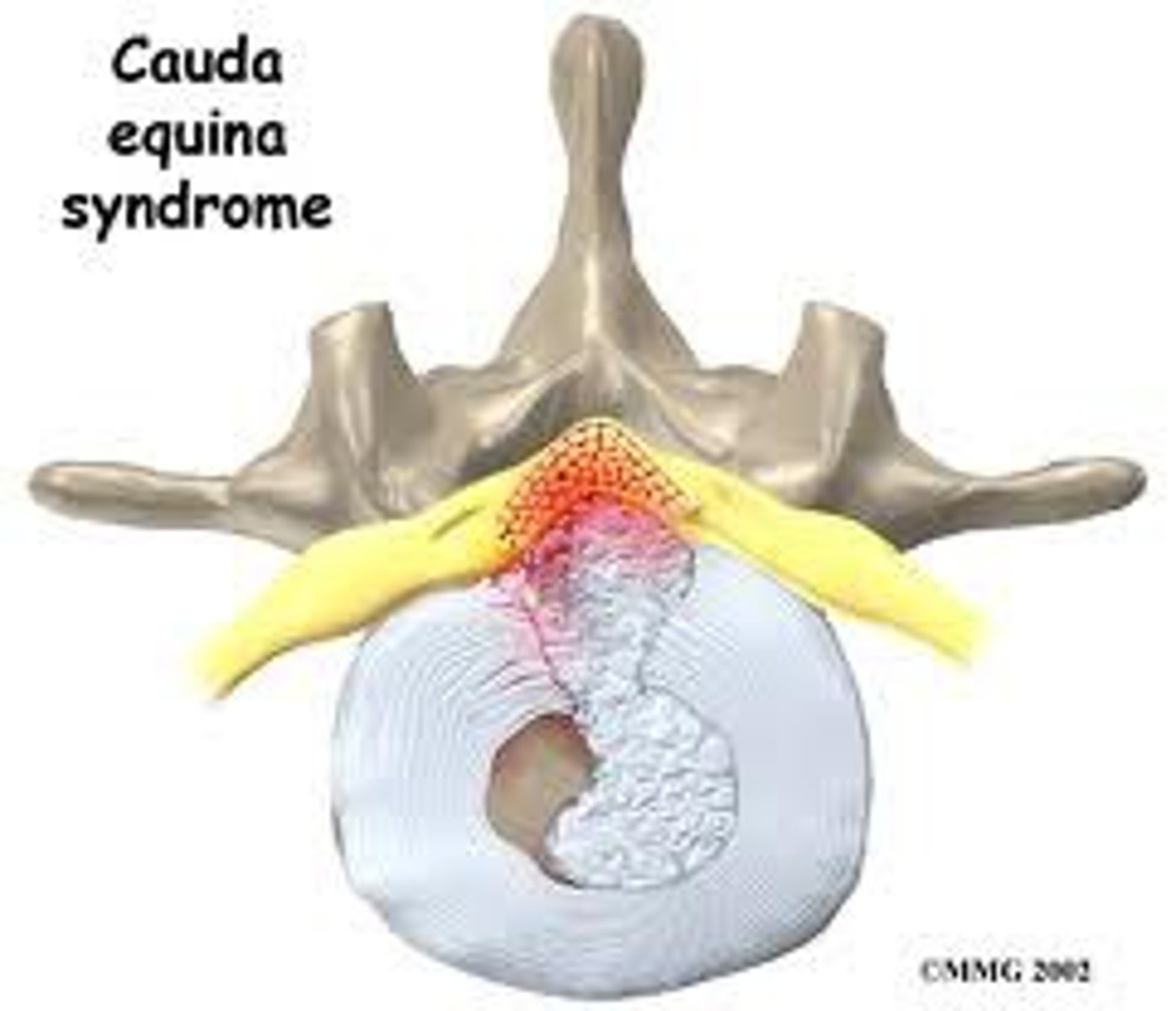
what are the s/sx of cauda equina syndrome?
urinary retention/incontinence, bowel incontinence, sensory/motor deficits, saddle anesthesia, perineal numbness, gait disturbance, lower back pain
emergency!
what is the cause of cauda equina syndrome?
causes → disc herniation, epidural abscess, epidural hematoma, trauma
cauda equina (L2-S4) syndrome= compression of roots distal to conus medullaris causing paralysis w/o spasticity
what would you expect to see on PE in a pt w/ cauda equina syndrome?
- inability to rise from a chair
- gait disturbances
- poor anal sphincter tone and/or perineal numbness
what may an XR show in a pt with Scheuermann's kyphosis?
anterior longitudinal ligament thickened, vertebral wedging, schmorl's nodes, and changes in vertebral end plates (flat and irregular)
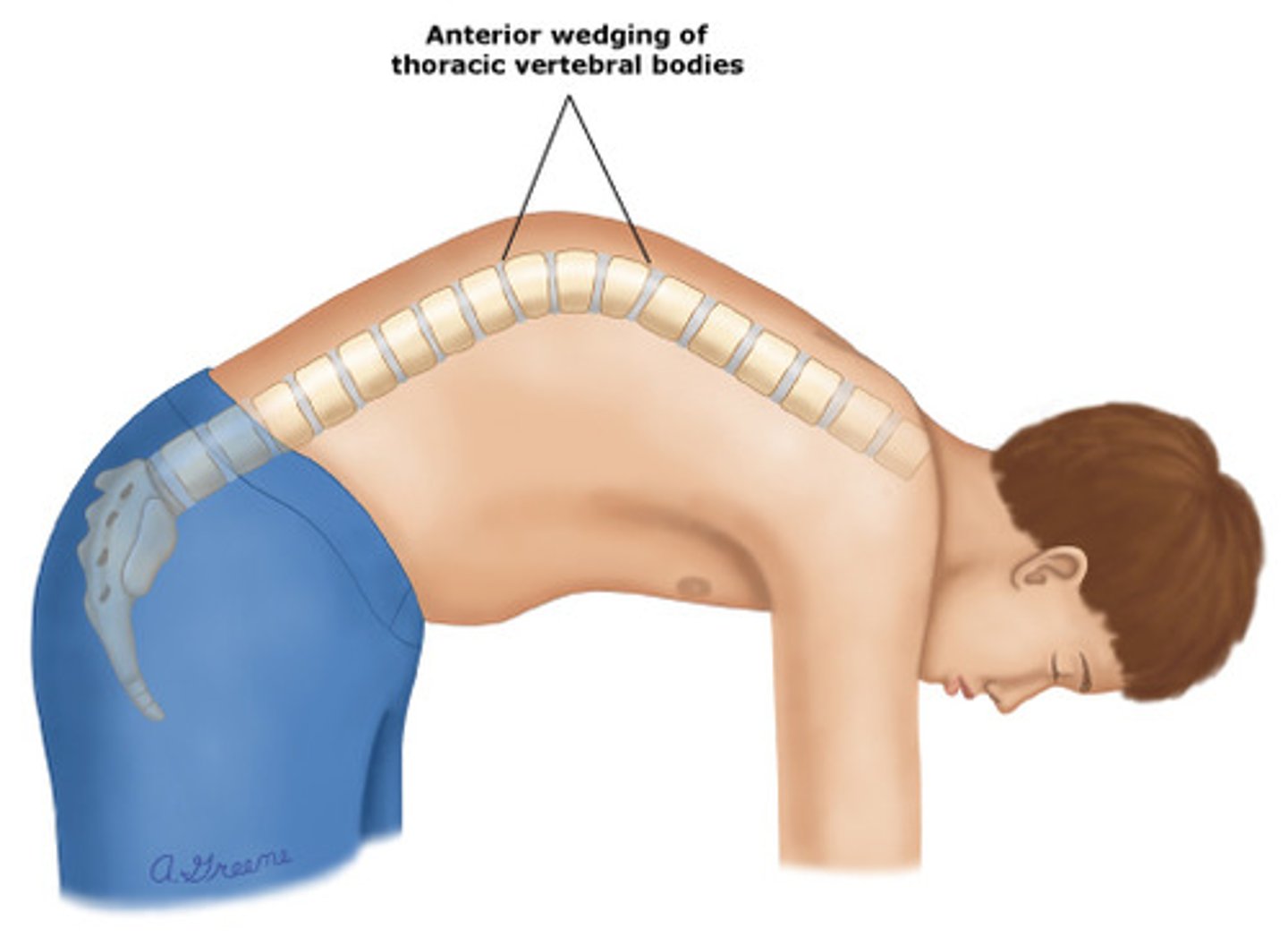
what are s/sx of Scheuermann's kyphosis?
poor posture
tight hamstrings
pain
what are s/sx of scoliosis?
lateral curvature >10 degrees
rib hump
what is the MC curve in idiopathic scoliosis?
right thoracic
what exacerbates sx associated with lumbar herniated disc?
cough, sneezing, and valsalva
sx = back/leg pain
which sx of lumbar herniated disc is assoc. with involvement of the nerve root?
paresthesia
what is a defect of the pars interarticularis of the spine that is common in children involved in activities with hyperextension of the spine (gymnastics)
spondylolysis
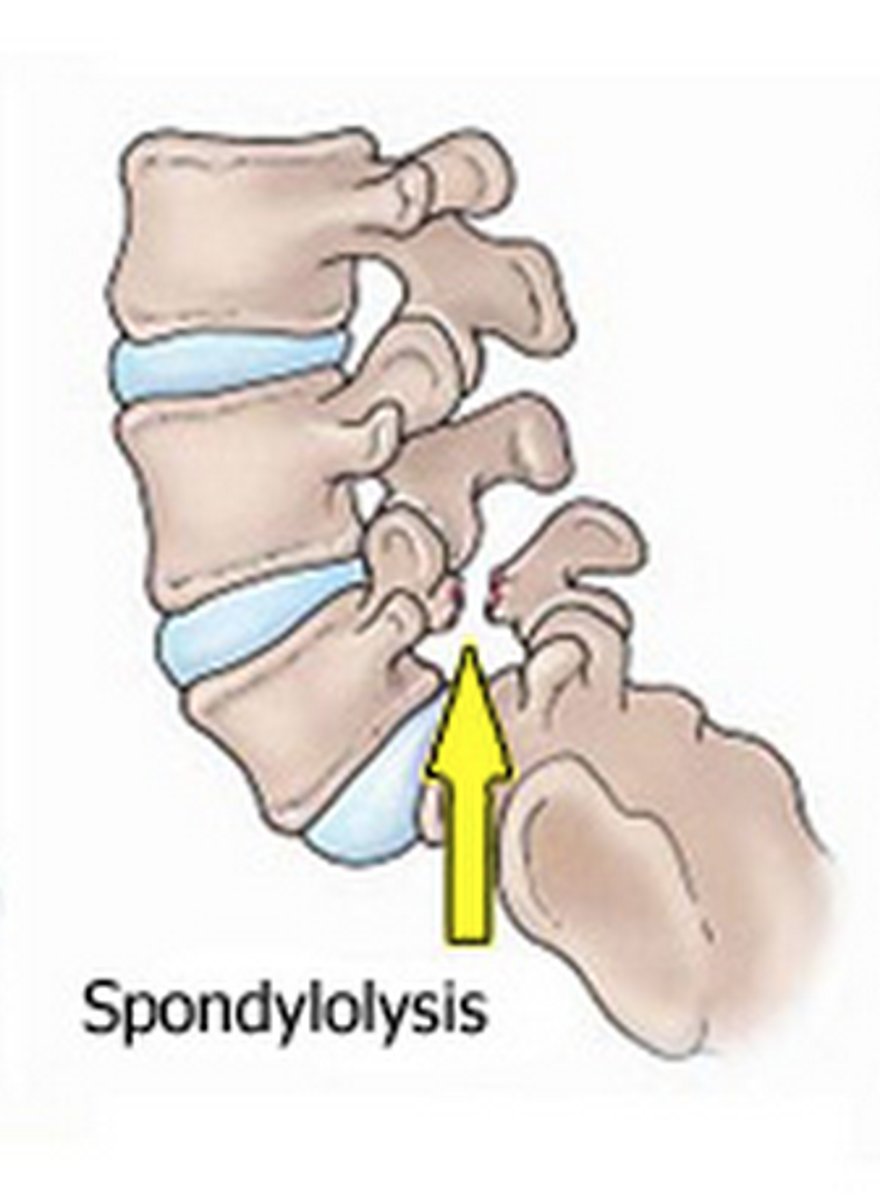
what is defined as degenerative disease of a vertebra/disc?
spondylosis (stenosis)
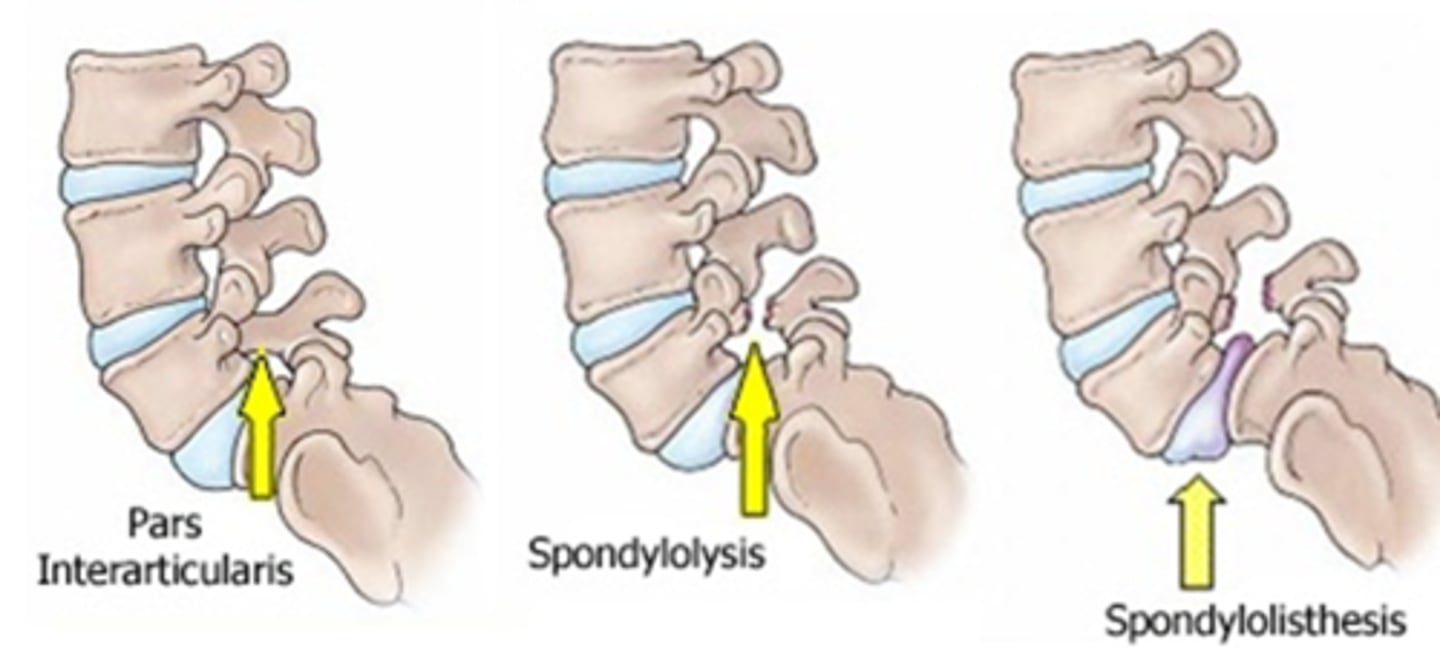
what is defined as slipping of the vertebra?
spondylolisthesis
degenerative is MC
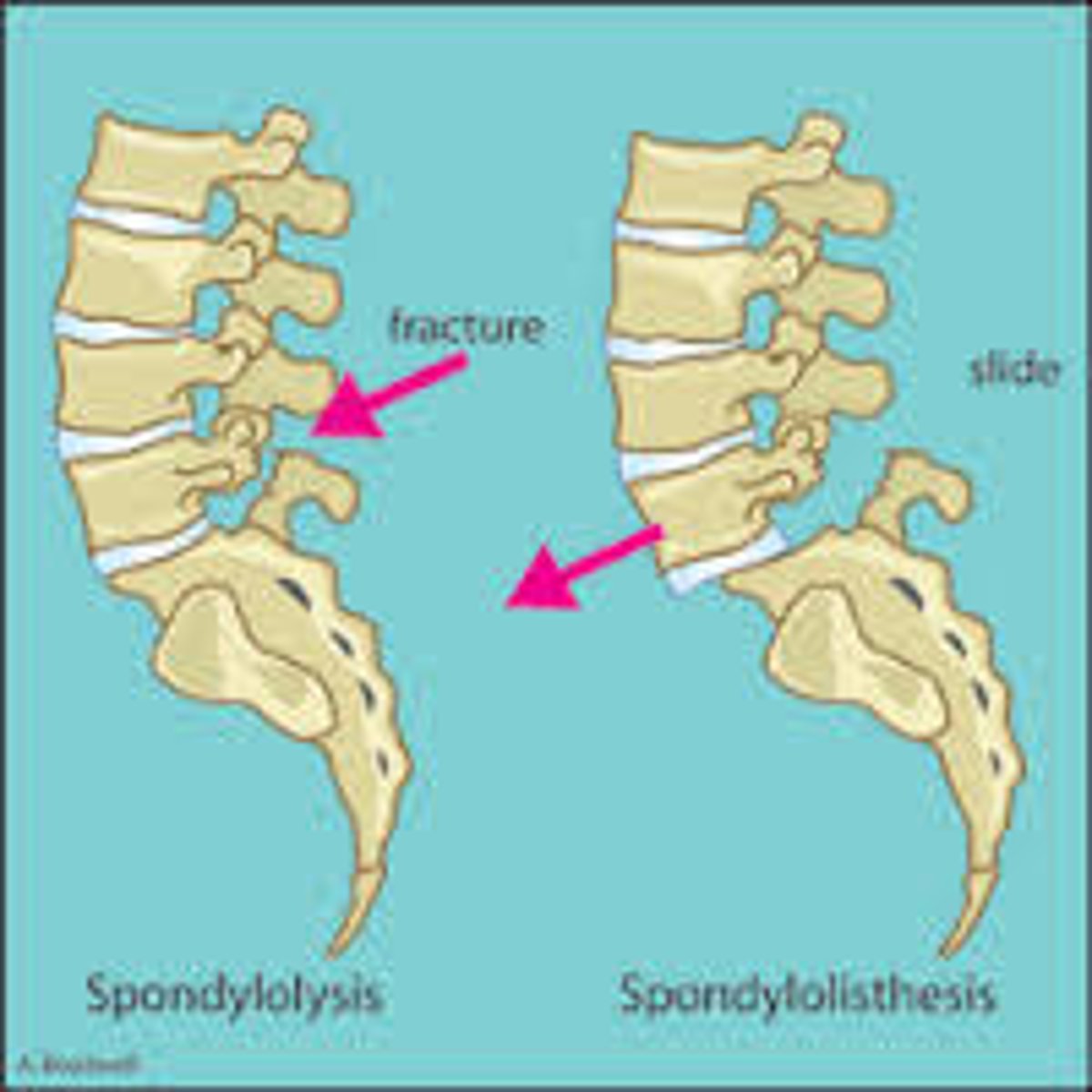
bilateral spondylolysis = ?
spondylolisthesis
what is a complication of fx of the femur?
avascular necrosis
posterior or anterior dislocation: flexion, internal rotation and aDduction; caused by knee hitting dash
posterior (MC!)