AP US History Period 3
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
French and Indian War (Seven Years' War)
Nine-year war between the British and the French in North America. It resulted in the expulsion of the French from the North American mainland and helped spark the Seven Years' War in Europe...
Stamp Act Congress
A meeting of delegations from many of the colonies, the congress was formed to protest the newly passed Stamp Act It adopted a declaration of rights as well as sent letters of complaints to the king and parliament, and it showed signs of colonial unity and organized resistance.

Sugar Act
(1764) British deeply in debt part to French & Indian War. English Parliament placed a tariff on sugar, coffee, wines, and molasses. colonists avoided the tax by smuggling and by bribing tax collectors.

Quartering Act
1765 - Required the colonials to provide food, lodging, and supplies for the British troops in the colonies.

Stamp Act
1765; law that taxed printed goods, including: playing cards, documents, newspapers, etc.

Declaratory Act
Act passed in 1766 after the repeal of the stamp act; stated that Parliament had authority over the the colonies and the right to tax and pass legislation "in all cases whatsoever."

Albany Plan of Union
plan proposed by Benjamin Franklin in 1754 that aimed to unite the 13 colonies for trade, military, and other purposes; the plan was turned down by the colonies and the Crown

Townshend Acts
A tax that the British Parliament passed in 1767 that was placed on leads, glass, paint and tea

Writs of Assistance
legal document that enabled officers to search homes and warehouses for goods that might be smuggled

Coercive Acts (Intolerable Acts)
These acts were laws that punished the colonists for the Boston Tea Party.

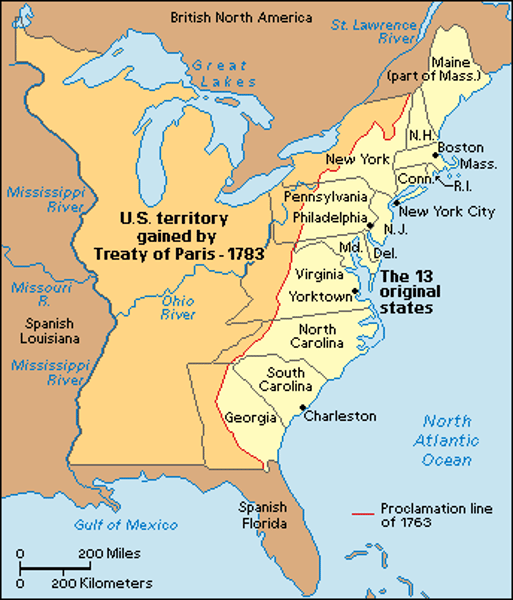
Peace of Paris (1763)
Ended French and Indian War. Britain gained all of French Canada & all territory south of Canada & east of the Mississippi River. France & Spain lost their West Indian colonies. Britain gained Spanish Florida. Spain gained French territory west of the Mississippi, including control of the port city of New Orleans.
Founding Fathers
James Madison, Thomas Jefferson and other leaders who laid the groundwork for the United States

Federalists
A term used to describe supporters of the Constitution during ratification debates in state legislatures.

Anti-Federalists
Opponents of the American Constitution at the time when the states were contemplating its adoption.

Alien and Sedition Acts
Series of four laws enacted in 1798 to reduce the political power of recent immigrants

Kentucky and Virginia Resolutions
Written anonymously by Jefferson and Madison in response to the Alien and Sedition Acts, they declared that states could nullify federal laws that the states considered unconstitutional.

National Bank
Hamilton's big idea; fiercely opposed by Jefferson and Democratic-Rep. The bank would regulate money and draw investors; showed that the constitution could be construed in many a way.

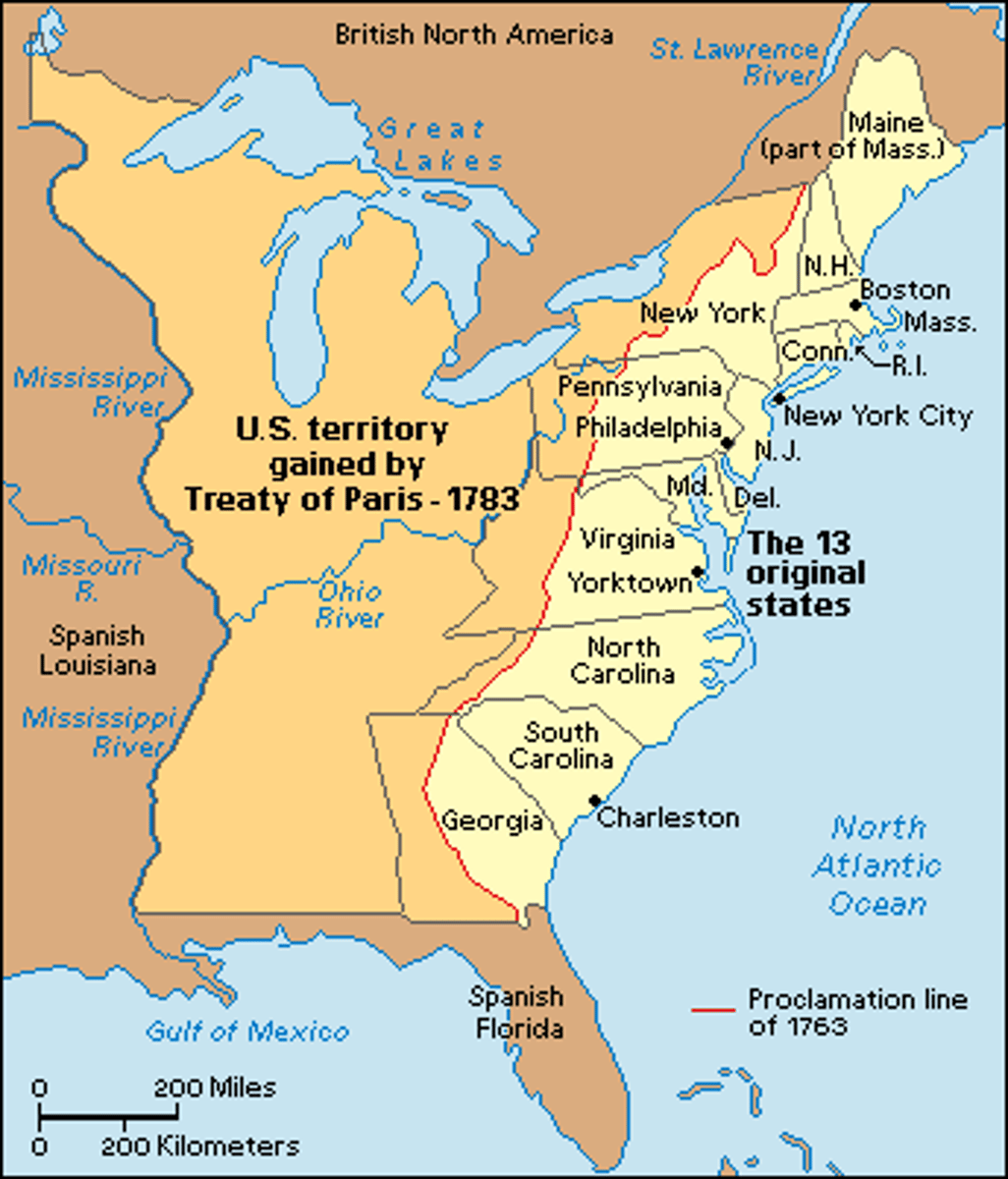
Treaty of Greenville
Gave the United States claim to most Indian lands in the Northwest Territory.
Annapolis Convention
A convention held in September 1786 to consider problems of trade and navigation, attended by five states and important because it issued the call to Congress and the states for what became the Constitutional Convention
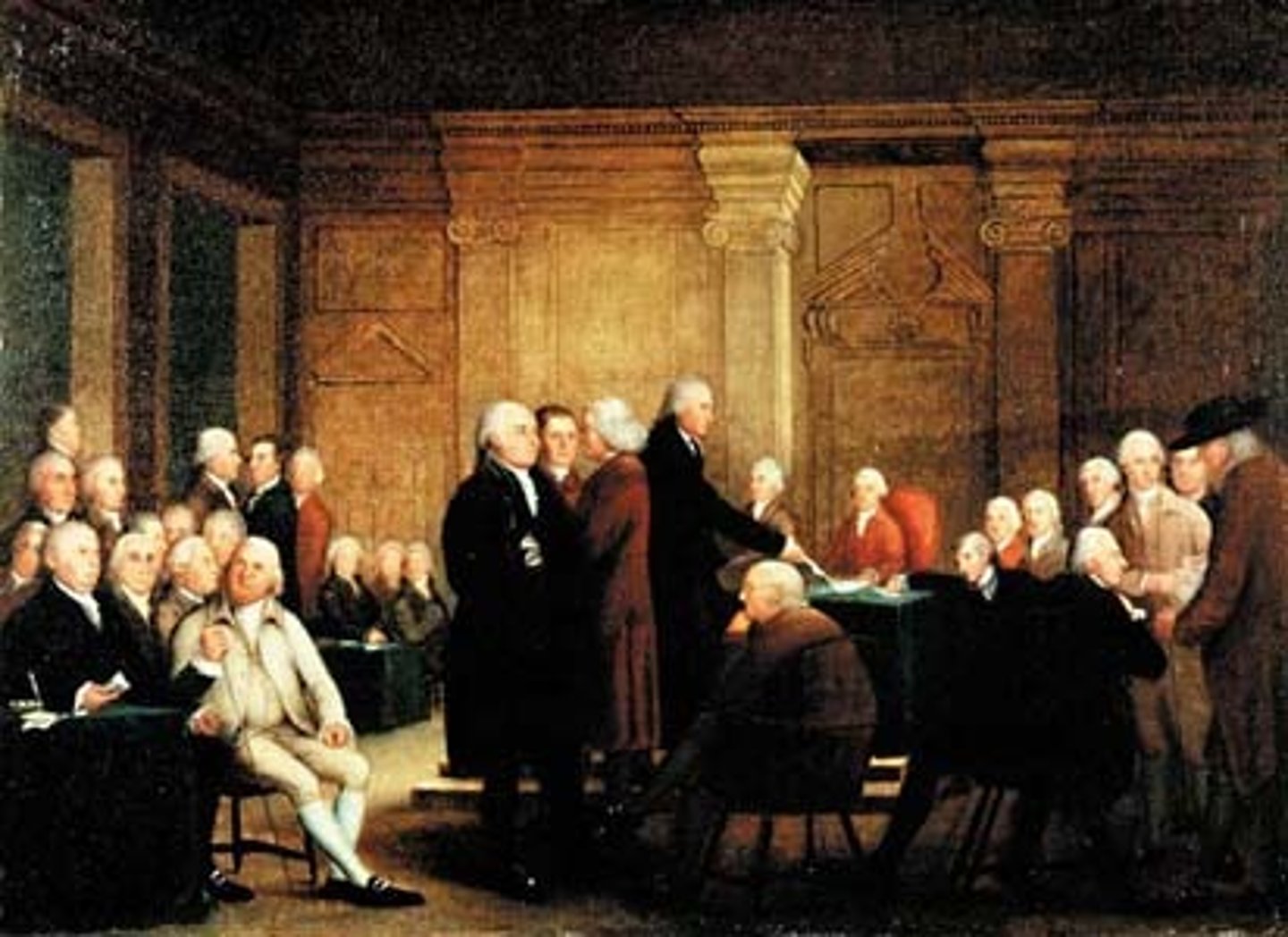

Constitutional Convention
Meeting in 1787 of the elected representatives of the thirteen original states to write the Constitution of the United States.
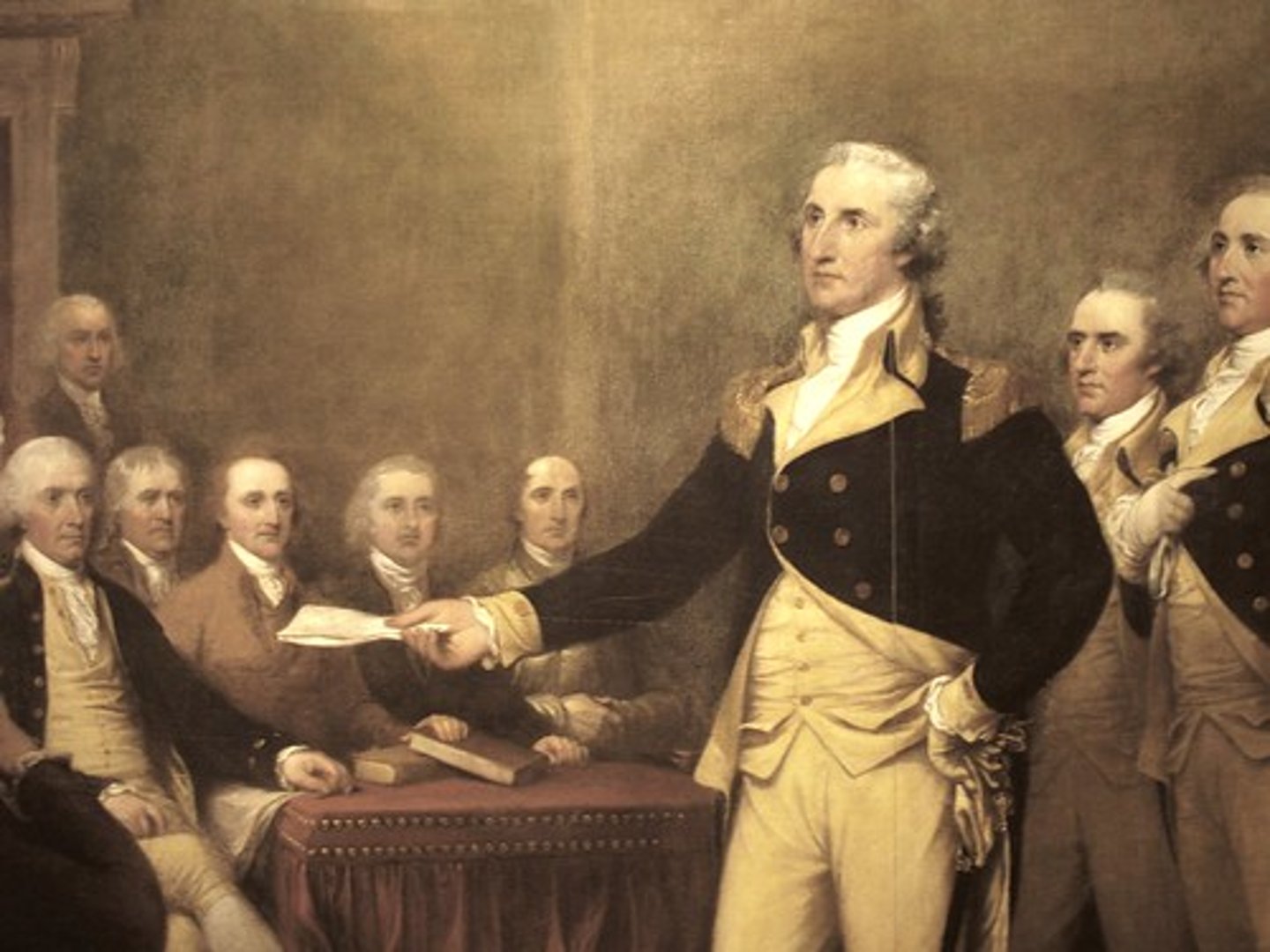

Constitutional Compromises
Created two branches of government lower house was population based representation, the upper house was equally represented.

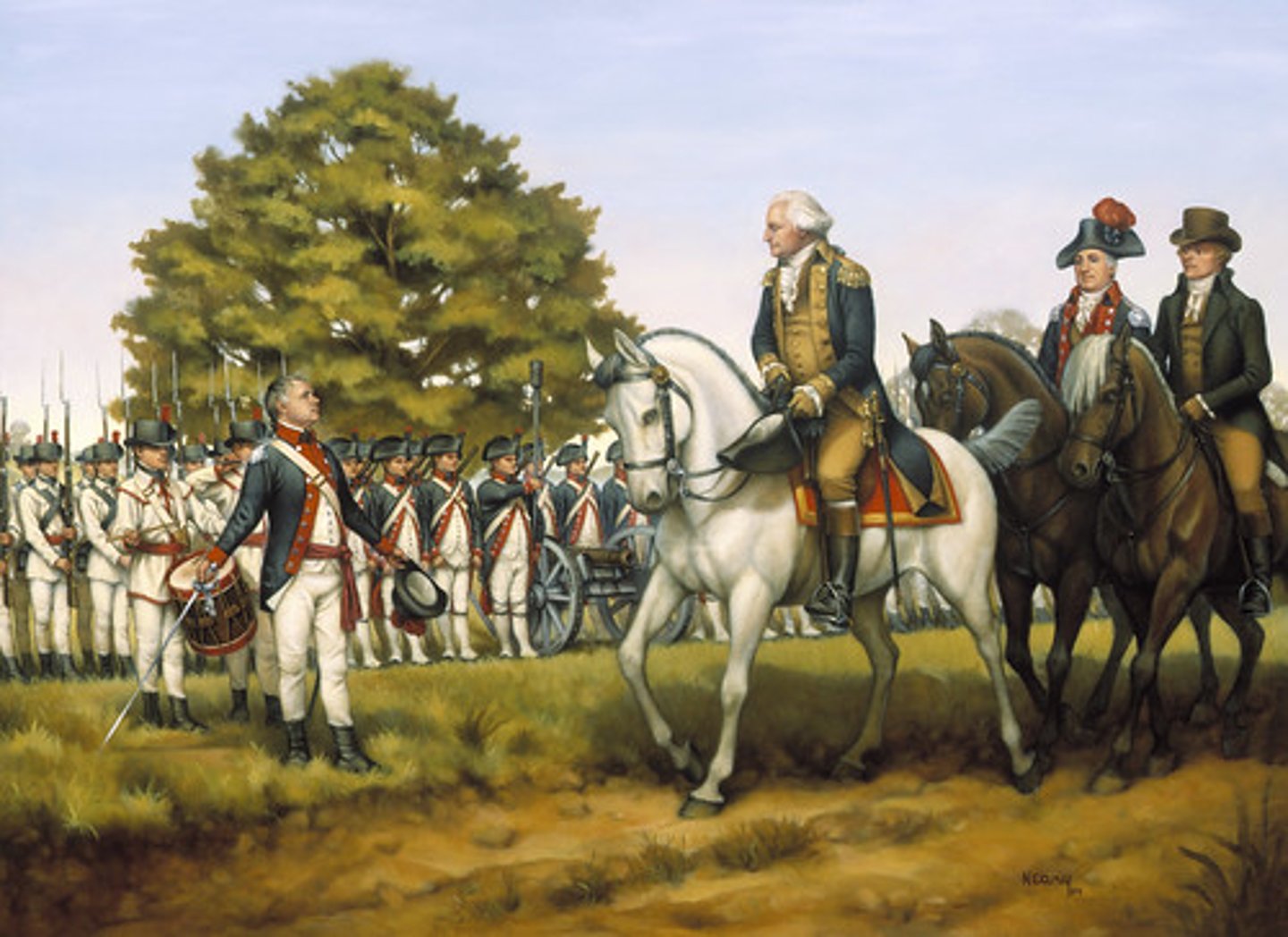
Whiskey Rebellion
In 1794, farmers in Pennsylvania rebelled against Hamilton's excise tax on whiskey, and several federal officers were killed in the riots caused by their attempts to serve arrest warrants on the offenders. In October, 1794, the army, led by Washington, put down the rebellion. The incident showed that the new government under the Constitution could react swiftly and effectively to such a problem, in contrast to the inability of the government under the Articles of Confederation to deal with Shay's Rebellion.

Neutrality
A refusal to take part in a war between other nations

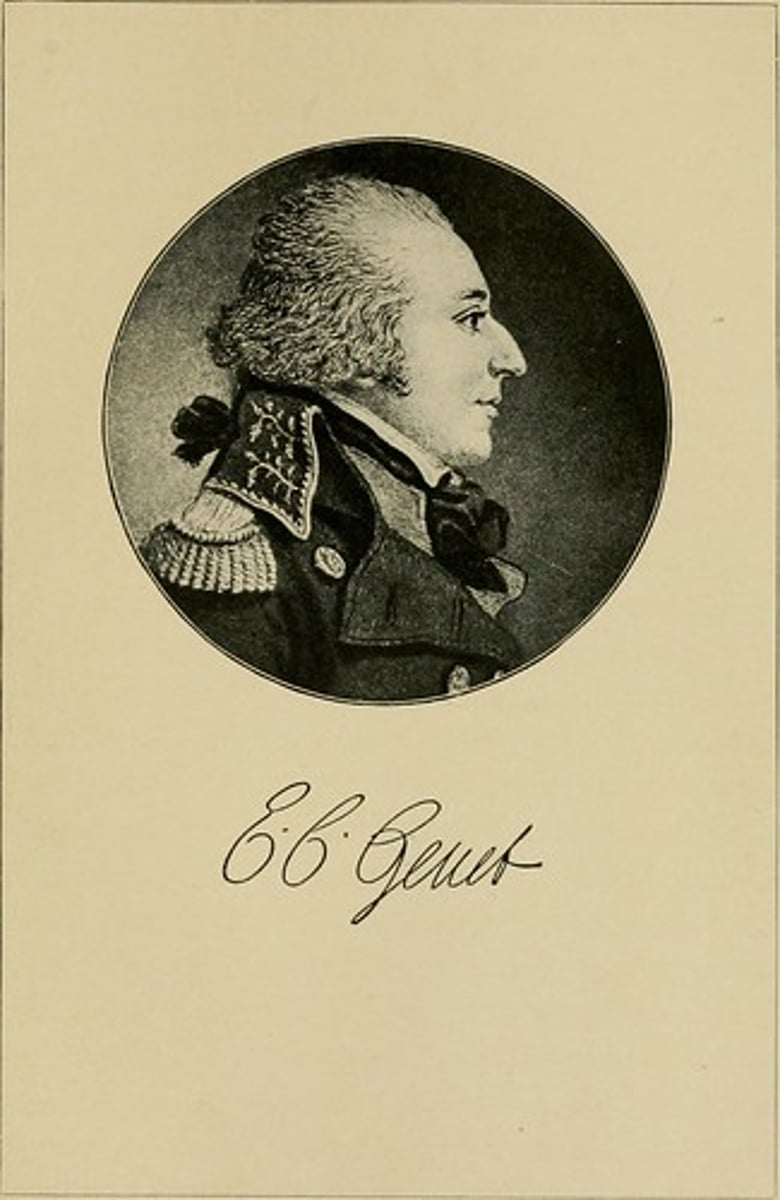
"Citizen" Genet
Sent to the United States of America to gather support for the French regime in their war against Britain. France had a change in leadership and made a home in America.

Articles of Confederation
1st Constitution of the U.S. 1781-1788 (weaknesses-no executive, no judicial, no power to tax, no power to regulate trade)

Jay's Treaty
On November 19, 1794 representatives of the United States and Great Britain signed this which sought to settle outstanding issues between the two countries that had been left unresolved since American independence. The treaty proved unpopular with the American public but did accomplish the goal of maintaining peace between the two nations and preserving U.S. neutrality.
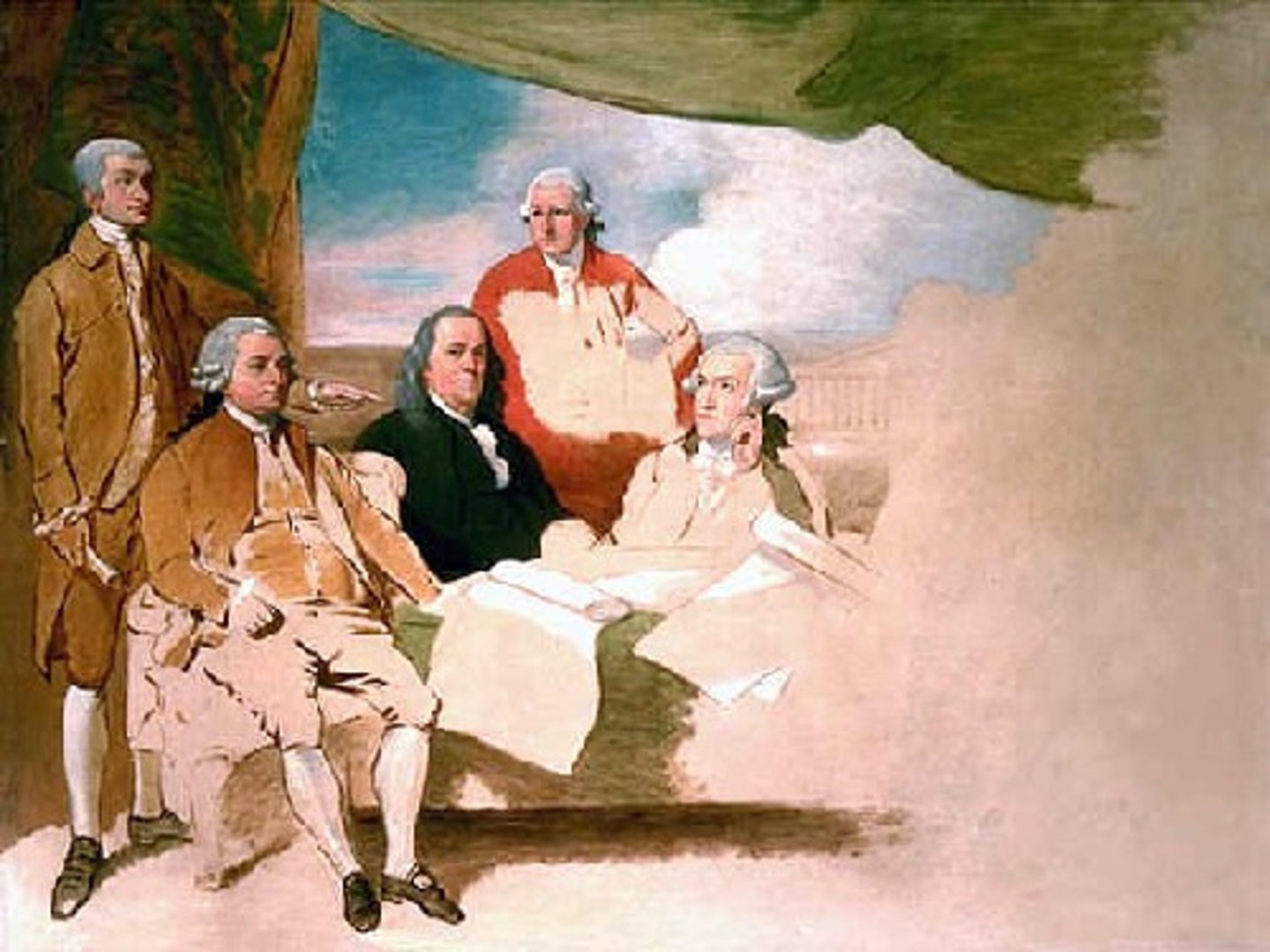

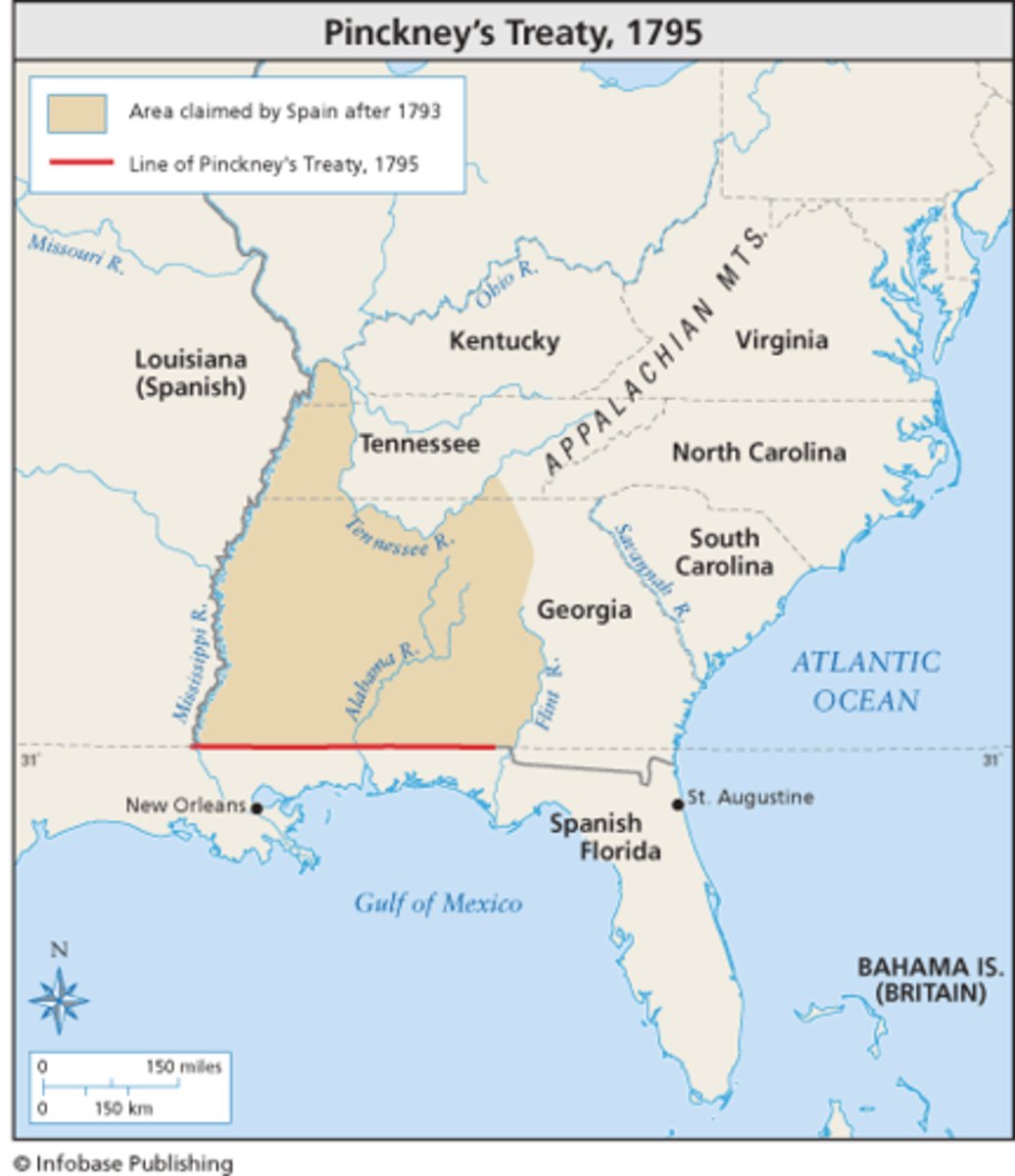
Pinckney's Treaty
signed in San Lorenzo de El Escorial on October 27, 1795 and established intentions of friendship between the United States and Spain.
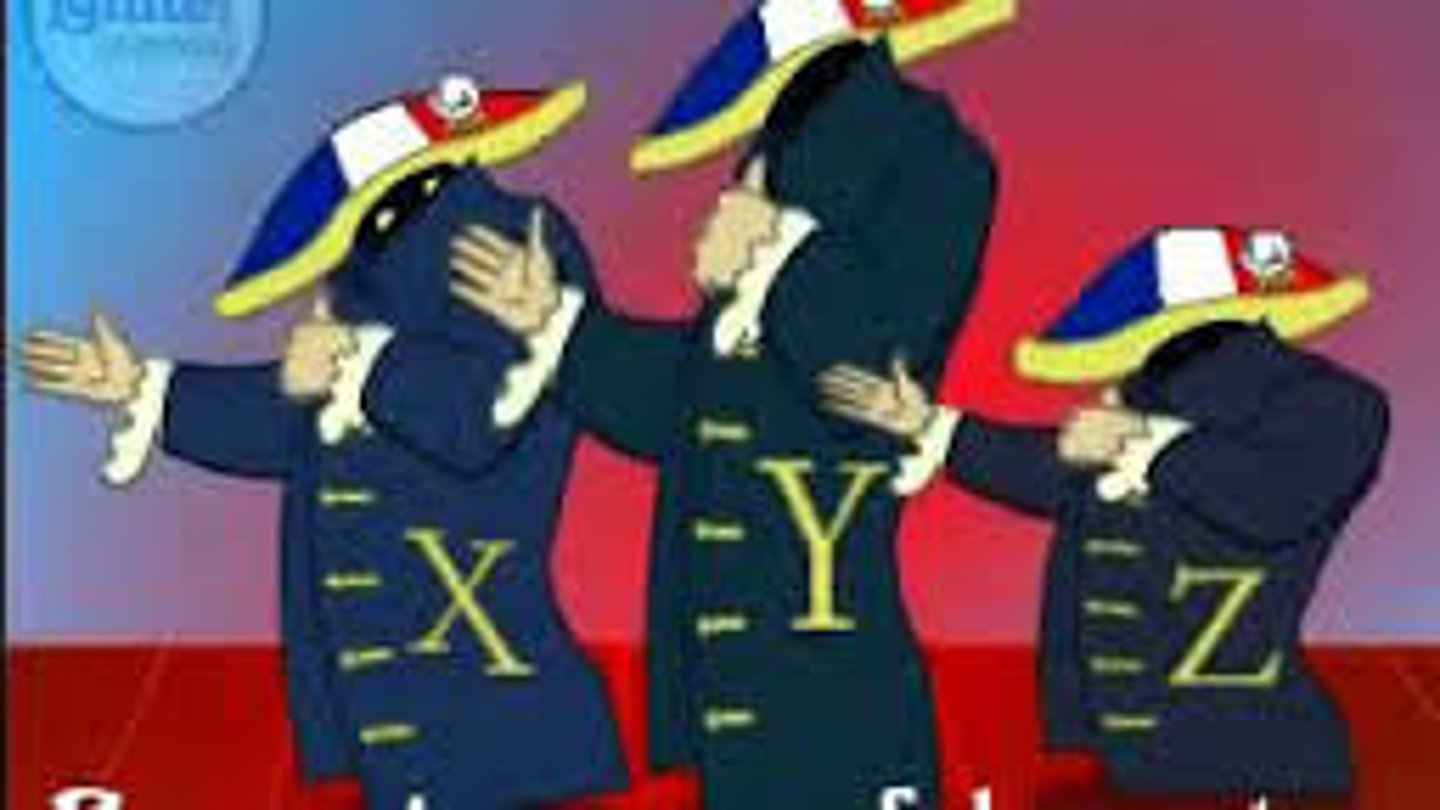
XYZ Affair
A 1797 incident in which French officials demanded a bribe from U.S. diplomats

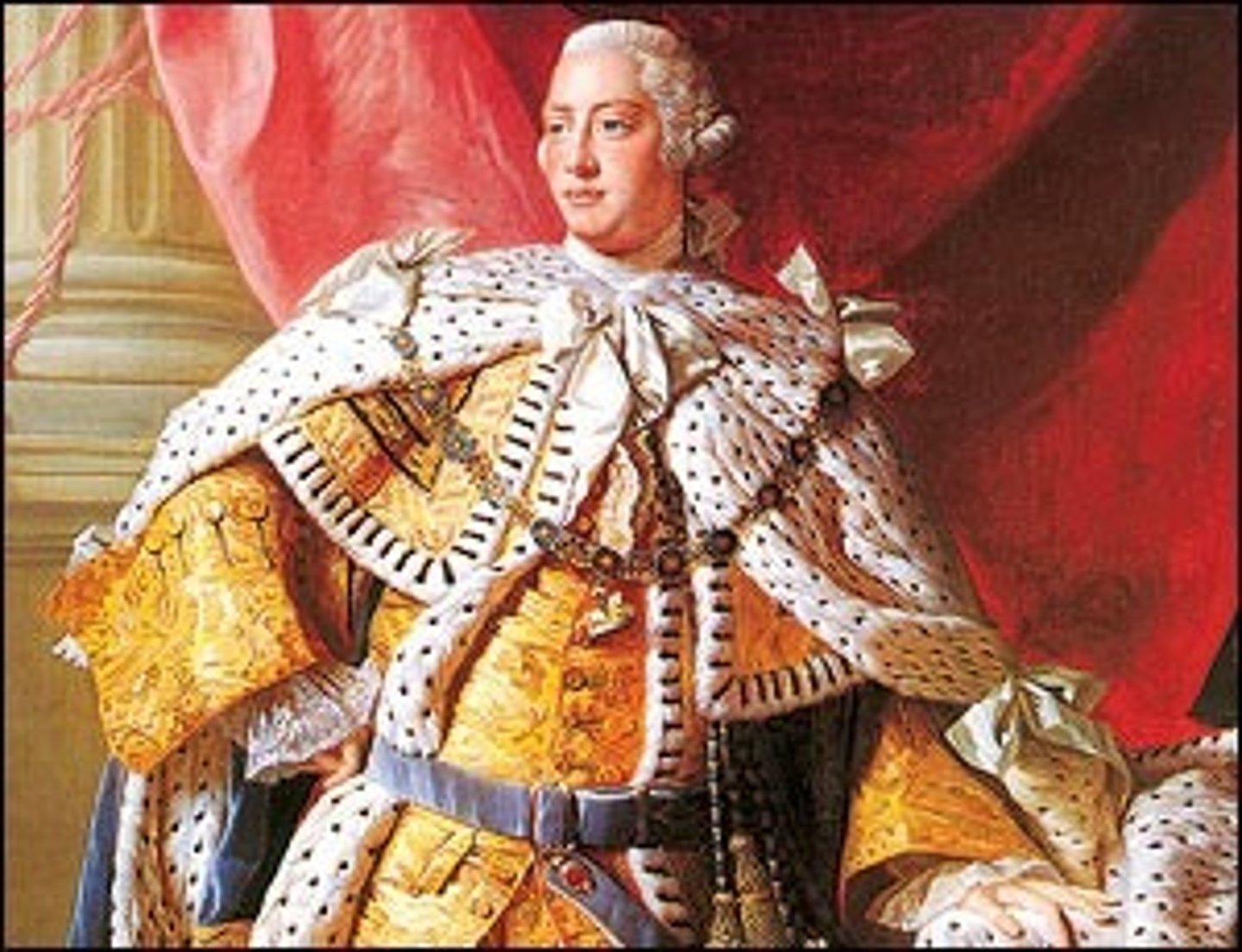
King George III
King of England during the American Revolution

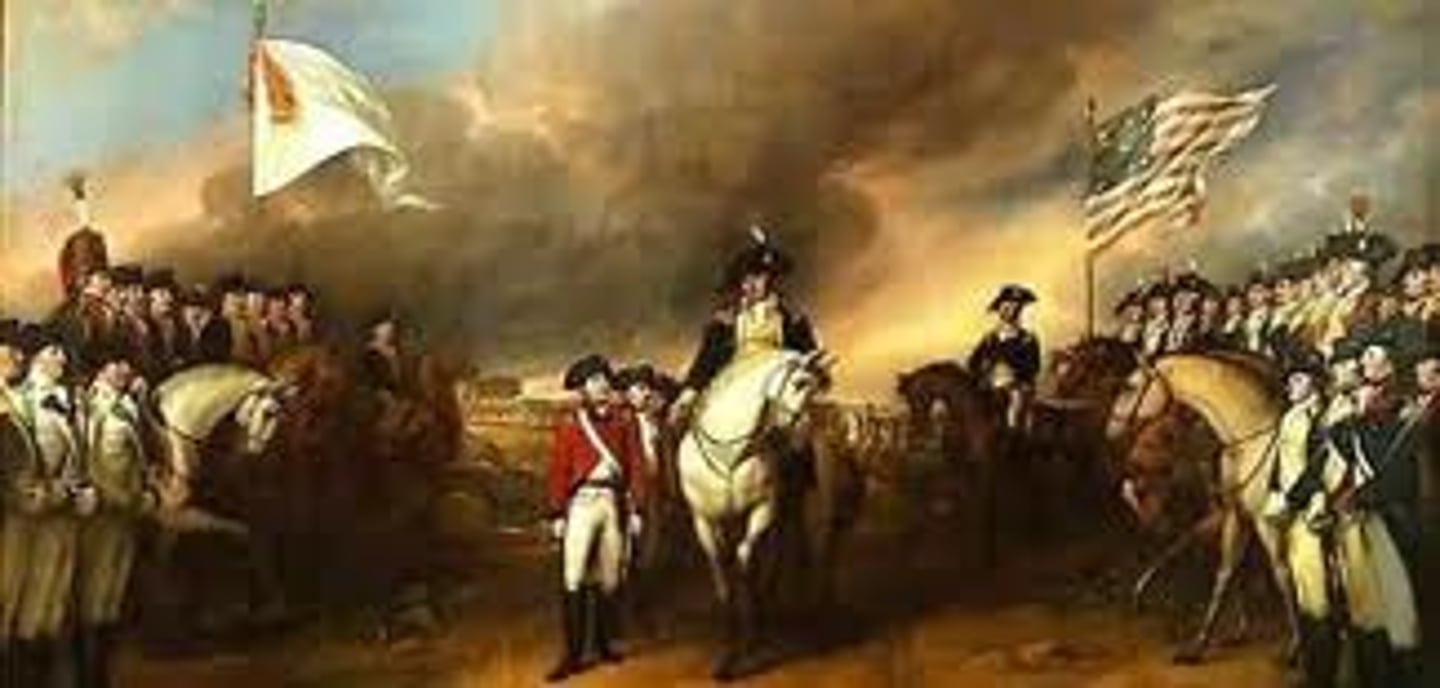
Yorktown
1781; last battle of the revolution; Benedict Arnold, Cornwallis and Washington; colonists won because British were surrounded and they surrendered
