Chapter 15: Special Senses
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
General senses
Senses found throughout the body; somatic and visceral
Somatic senses
Tactile, thermal pain, proprioception
Visceral senses
Detexts internal organ conditions (ex: internal pain)
Special senses
Senses founds in specialized organs and have something to do with our smell, taste, vision, balance, and hearing
Nociceptors
Receptors that respond to potentially damaging stimuli that result in pain like searing heat, excessive pressure, and inflammatory chemicals; found all over your body
Photoreceptors
Receptors that respond to light (ex: rods and cones); found in the retina of your eye
Chemoreceptors
Receptors that respond to chemicals in a soulition like molecules smelled/tasted, or changes in your blood (ex: tastebuds); found on your tongue and nasal cavity
Thermoreceptors
Receptors that respond to temperature changes
Cold receptors
Thermoreceptors that sense from 10oC-40oC, or 50oF-105oF; located in the epidermis
Warm receptors
Thermoreceptors that sense from 32oC-48oC, or 90oF-118oF; located in the dermis
Mechanoreceptors
Receptors that respond to mechanical force such as touch, pressure (including BP), vibration, and stretch
Tactile receptors
Receptors that respond to light pressure; found in the dermal papillae of hairless skin (especially the nipples, fingertips, soles of feet, and eyelids)
Baroreceptors
Receptors that activate when arterial blood pressure rises; found in the carotid sinuses, aortic arch, and in the walls of nearly every large artery of the neck and thorax
Proprioceptors
Receptors that respond to internal stimuli and advises the brain of our body movement by monitering how much the organs containing these receptors are stretched; found in skeletal muscles, tendons, joints, ligaments, and in the connective tissue coverings of bone and muscle
Meissner’s corpuscle
Detects light pressure, discriminative touch, and vibration of low frequency; located in the dermis
Pacinian corpuscle
Detects deep pressure, stretch, and vibration of high frequency; located in the dermis and hypodermis
Tactile discs
Detects light pressure; located on the basal layer of the epidermis
Ruffini corpuscles
Detects deep pressure and stretch; located deep in the dermis, hypodermis, and joint capsules
Free nerve ending
Detects changes in temperature, chemicals, pressure, and pain; locatedin most body tissues , especially connective tissue (ligaments, tendons, dermis, joint capsules), and epithelia
Root hair plexus
Detects movement of hair; located around the hair follicle in the dermis
Muscle spindle
Detects muscle stretch and length; located on skeletal muscles, particularly in the extremeties
Golgi tendon organ
Detects tendon tension and force of muscle contraction; located in the juunctions between muscles and tendons
Medulla oblongata
Detects changes in the CSF’s pH to regulate breathing rate; located in the brainstem
Hypothalamic chemoreceptors
Detects internal chemical changes and helps regular thirst, temperature, and endocrine functions
Aortic body
Detects blood O2, CO2, and pH levels; located along the aortic arch
Carotid body
Detects blood O2, CO2, and pH levels; located at the bifurcation of the carotid arteries
Fibrous layer
The outermost coat of the eyb=ebal composed of dense avascular connective tissue; has 2 different regions
Sclera
The white, tendon-like region of the eye; protects and shapes the eyeball, and also provides a sturdy anchoring site for the extrinsic eye muscles
Cornea
The transparent region that bulges anteriorly from its junction with the sclera; forms a window that lets light enter the eye
Vascular layer
The middle coat of the eyeball; has 3 regions
Iris
The colored part of the eye; acts as a reflexively activated diaphragm to vary pupil size
Choroid
The blood-vessel rich, dark brown membrane of the eye; nourishes alleye layers, helps absorb light, and contains a posterior opening where the optic nerve leaves the eye
Ciliary body
The thickened ring of tissue that encircles the lens; has 3 parts
Ciliary muscle
Makes up most of the ciliary body; consists of interlacing smooth muscle bundles that control the lens shape
Ciliary process
The posterior surface of the ciliary body; secretes the fluid that fills the cavity of the anterior part of the eyeball
Ciliary zonule (suspensory ligament)
Halo of fine fibers circling around the lens; helps hold it in its upright position
Retina
The innermost, delicate layer of the eyeball; contains millions of photoreceptors that convert light to energy, other neurons involved in processing responses to light, and glia
Pigmented layer of the retina
The single-cell-thick lining of the retina; absorbs light and prevents it from scattering into the eye, participates in photoreceptor renewal, and stores vitamin A
Neural layer of the retina
The transparent layer of the retina composed of photoreceptors, bipolar cells, and ganglion cells
Lens
The transparent, flexible structure enclosed in a capsule posterior to the iris; changes shape to precisely focus light on the retina
Pupil
The round central opening of the eye; allows for light to enter
Ora serrata
The junction where the retina extends anteriorly to the posterior margin of the ciliary body
Bipolar cell
A cell/neuron found in the neural layer of the retina; transmits visual info from photorecptors to the ganglionic cells
Ganglionic cell
A cell/neuron found in the neural layer of the retina;
Anterior margin
the anterior portion/edge of the retina; filled with aqueous humor
Anterior chamber
The space between the cornea and the iris
Posterior chamber
The space between the iris and the lens
Aqueous humor
The clear fluid similar in composition to blood plasma; helps support the eyeball internally by maintaining a constant intraocular pressure of about 16 mmHg supplies nutrients & oxygen, and carries away metabolic waste
Posterior margin
The posterior portion/edge of the retina; filled with vitreous humor
Vitreous humor
The clear gel in the posterior margin that binds tremendous amounts ofwater; transmits light, supports the posterior surface of the lens, and contributes to intraocular pressure
Rods
The dim-light and peripheral vision receptors; numerous, light-sensitive, and does not provide sharp images or color vision
Cones
The bright light vision receptors; provides high resolution color vision
Macula lutea
The oval region lateral to the blind spot of each eye; allows light to pass almost directly;
Fovea centralis
The pit in the center of the macula lutea; area of sharpest central vision
External eye muscles
Lateral, medial, superior, and inferior rectus
Superior & inferior oblique
Conjuctiva
The transparent mucous membrane that lines the eyelids and folds back over the anterior surface of the eyeball
Lacrimal apparatus
Consists of the lacrimal gland and the ducts that drain lacrimal secretions into the nasal cavities
Refraction
The bending of light rays to focus them on the retina and create an imafge
Accomodation
The changing of lens shape to focus for near (or far) vision;
flat lens = far vision
round lens = close vision
Constriction
The narrowing of the pupil to control the amount of light entering the eye
Convergence
Binocular vision
What happens after light hits the photoreceptors in the retina?
It causes the pigment called retinal to change shape, activating the photopigment which ultimately triggers phototransduction (light → electrical signal)
List the four steps of formation of image on Retina in order
refraction
accomodation
constriction
convergence of eyeballs
What is labeled “A”?
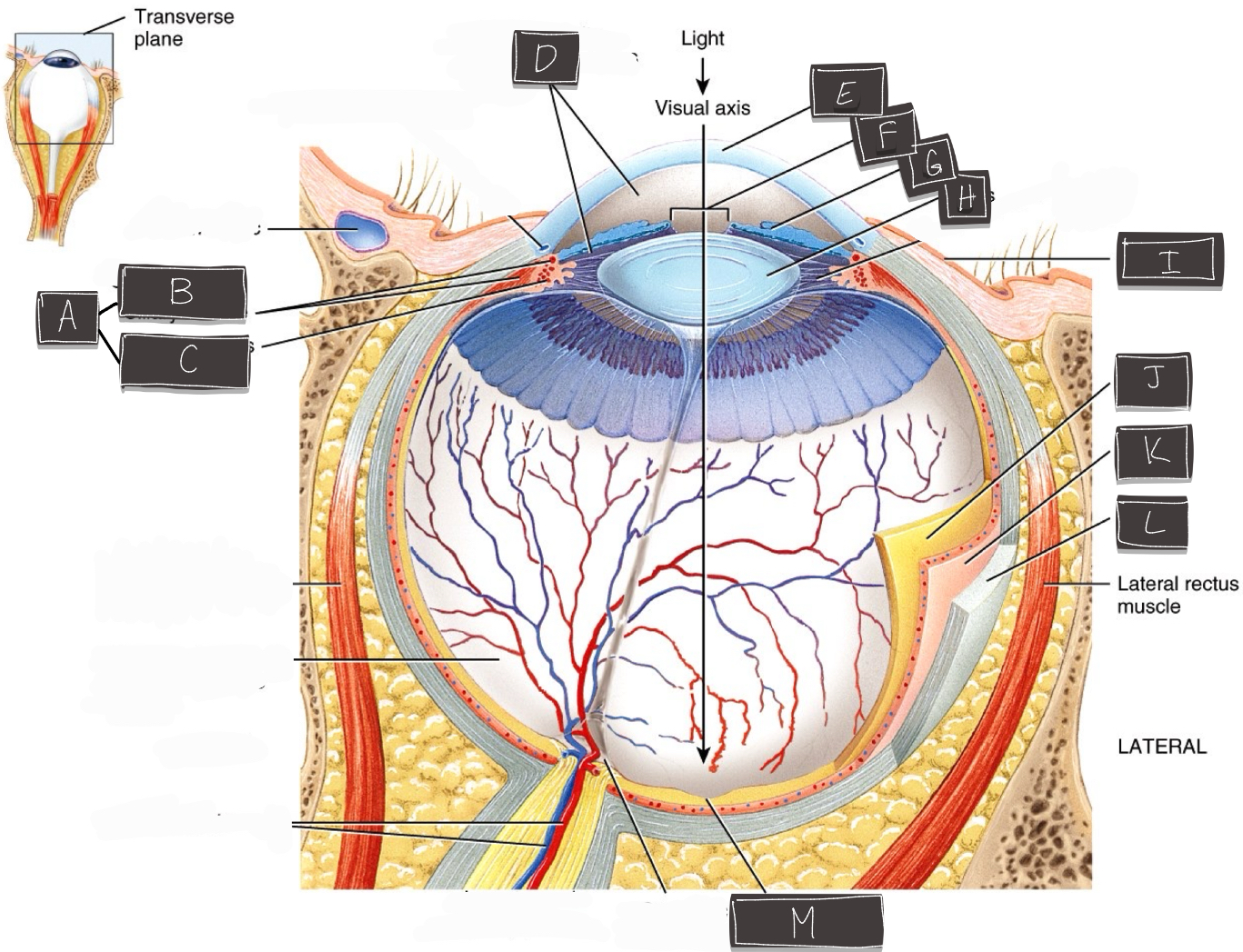
Ciliary body
What is labeled “B”?

Ciliary muscle
What is labeled “C”?

Ciliary process
What is labeled “D”?

Anterior cavity
What is labeled “E”?

Cornea
What is labeled “F”?

Pupil
What is labeled “G”?

Iris
What is labeled “H”?

Lens
What is labeled “I”?

Conjuctiva
What is labeled “J”?

Retina
What is labeled “K”?

Choroid
What is labeled “L”?

Sclera
What is labeled “M”?

Fovea centralis