Microbiology Chapter 4
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Prokaryote
A cell type characterized by a single circular chromosome not enclosed in a membrane, lacking histones and organelles. Binary diffusion division. Comes from the greek word prenucleus.
Eukaryote
A cell type with paired chromosomes enclosed in a nuclear membrane, containing histones and organelles. Polysaccharide cells walls, when present.
Bacteria Shape
Most bacteria are monomorphic, single shaped, but there are a few that are pleomorphic, many shaped.
Bacteria Shape Types
Bacillus (Rod-shaped)
Coccus (spherical-shaped)
Spiral
Vibrio
Spirillum
Spirochete
Star-shaped or rectangle
Vibrio
Type of spiral bacteria
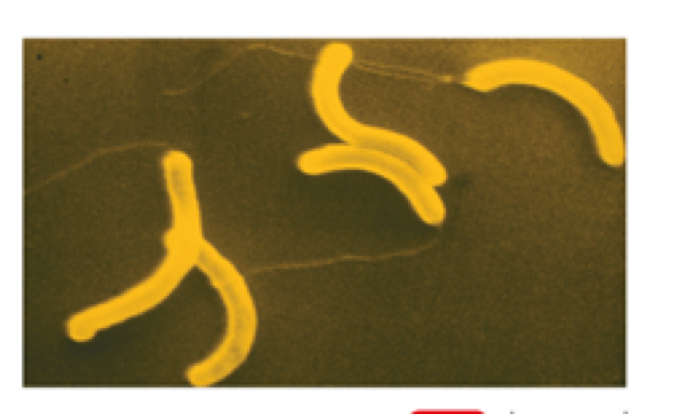
Spirillum
Type of spiral bacteria
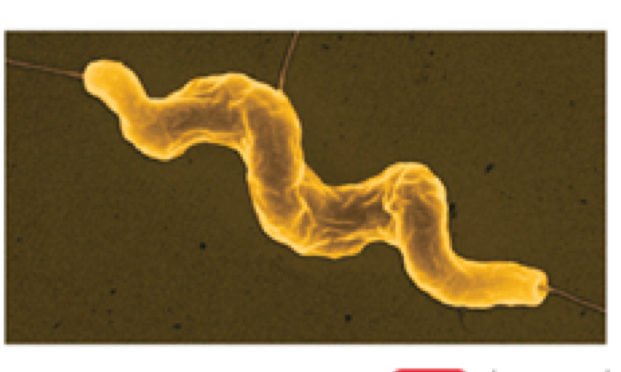
Spirochete
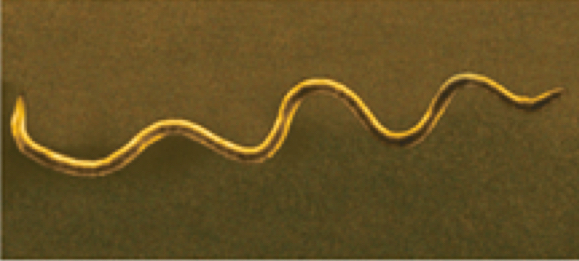
Type of spiral bacteria
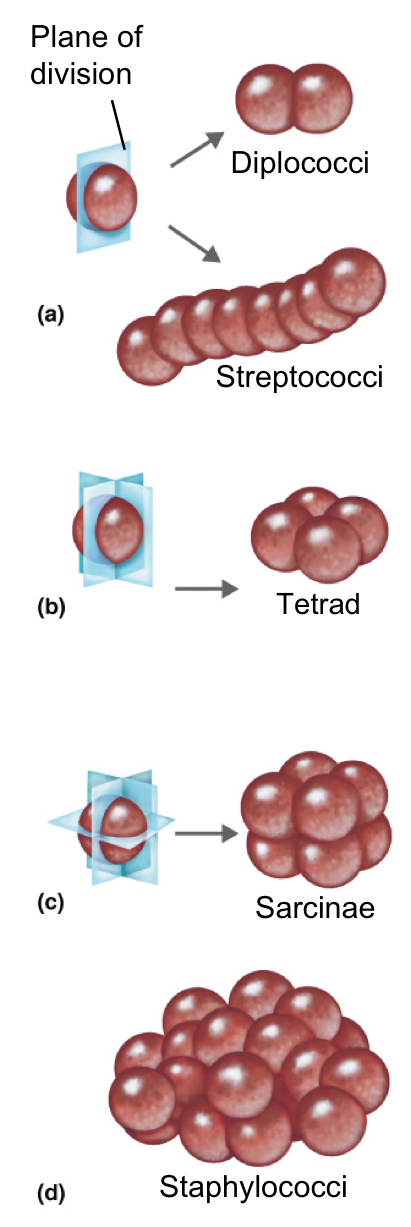
Different arrangements of bacteria
Pairs: Diplo
Clusters: Staphylo
Chains: Strepto
Groups of 4: tetrads
Groups of 8: sarcinae
Glycocalyx
A viscous and gelatinous layer external to the cell wall, made of polysaccharides and/or polypeptides, contributing to virulence (AKA Prevents death). There are two types
Capsule: neatly organized and firmly attached (common)
Slime Layer: Unorganized and loose (less common)
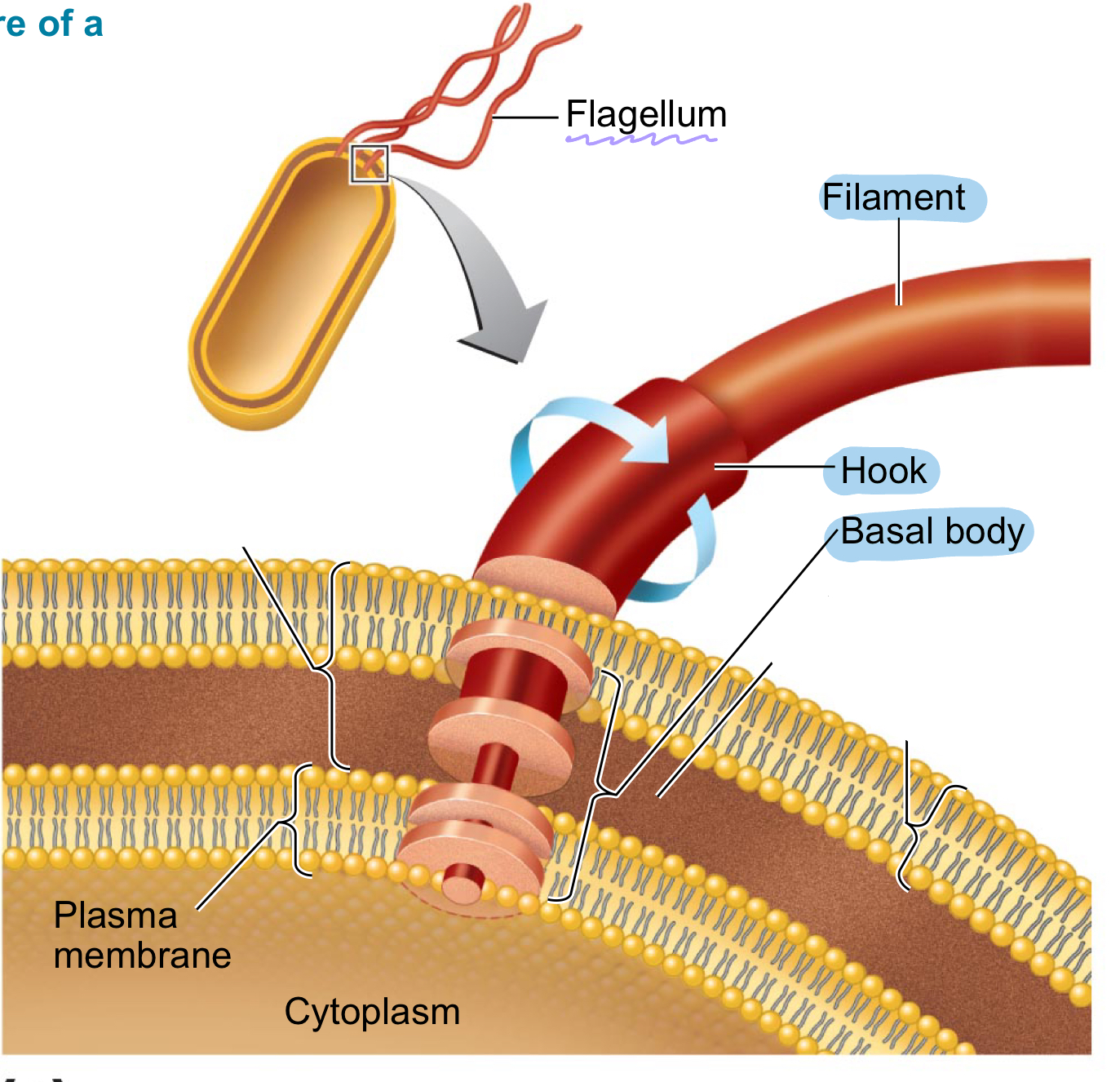
Flagella
Filamentous appendages composed of protein flagellin that propel bacteria and facilitate movement. This part allows bacteria to move toward or away from stimuli.
Flagella three parts
Filament: outermost region
Hook: attached to the filament
Basal body: consists of rod and pairs of rings; anchors flagellum to the cell wall and membrane
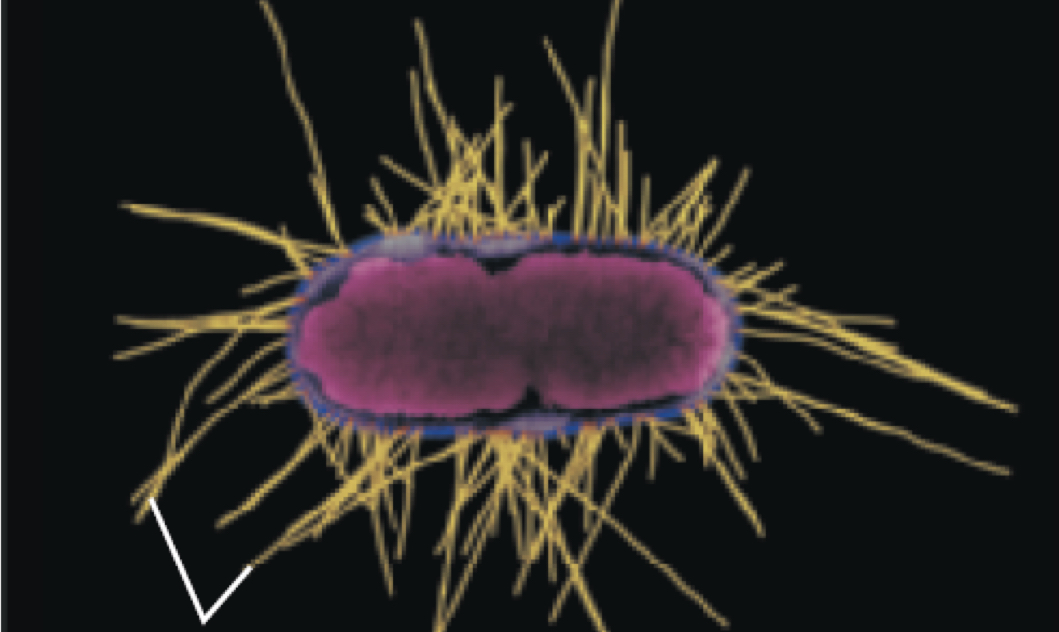
Fimbriae
Hairlike appendages on bacteria that assist in attachment to surfaces.
Pili
Appendages involved in bacterial motility and DNA transfer through conjugation phili.
Cell Wall
A protective layer that prevents osmotic lysis (cell explosion), primarily made of peptidoglycan in bacteria. This also contributes to the pathogenicity of bacteria. (ability to causes disease)
Cell wall contains Peptidoglycan
A polymer of repeating disaccharides in rows, NAG then NAM. Rows are linked by polypeptides.
Gram positive cell walls
If the cell walls are thick peptidoglycan and have teichoic acids they will show up as this. There are two rings of basal body of flagella and they produced exotoxins. (high susceptibility to penicillin & lysozyme).
Gram negative cell walls
If the cell walls are thin peptidoglycan, have and outer membrane and a periplasmic space they will show up as this. There are 4 rings of basal body flagella and they produce endotoxins and exotoxins. (Low susceptibility to penicillin)
Teichoic Acids
Lipoteichoic acid link cell wall to plasma membrane, wall teichoic acid links the peptidoglycan. These can carry a charge and basiclaly serve as the finger print of the bacteria (antigenic specificity)
Gram-Negative cell walls (Part 2)
Made of polysaccharides, lipoproteins and phospholipids. Protects bacteria from phagocytes, complement and antibiotics.
Porins
Proteins form channels through membranes, mainly found in gram-negative but can be found in gram positive.
Gram-Stain Process
Crystal violet-iodine crystals form inside cell.
Alcohol added (either derphdrayte peptidoglycan (positive) or dissolves the outer membrane and leave holes in the peptidoglycan
CV-I will either get washed out (negative) or stay (positive).
Then safranin is added to stain cells red.
Atypical Cell Walls
Acid-fast cell walls, like gram positive cell walls. Waxy lipid bound to peptidoglycan. There are multiple types including mycoplasmas and archaea.
Mycoplasmas
This type of atypical cells walls: Lack cell walls, sterols in plasma membrane.
Archaea
This type of atypical cell wall is either wall-less or walls of pseudomurein, which lacks the d-amino acid.
Damages cells walls
Lysozyme: hydrolyzes bonds in peptidoglycan.
Penicillin: Inhibits peptide bridges in peptidoglycan.
Transport Proteins
Peripheral proteins on the membrane surface, Integral and transmembrane proteins penetrate the membrane.
Plasma Membrane
A phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins that regulates selective permeability and ATP production.
Fluid Mosaic Model
The membrane is a thick fluid, where proteins move freely for various functions. Phospholipids rotate and move laterally and can be self sealing.
Plasma membrane function
It is selectively permeability, collectively contains enzymes for ATP Productions and some membranes have photosynthetic pigments on folding called chromatophores
Ways of Transportation
Passive processes: Simple diffusion, Facilitated diffusion, Osmosis.
Active Processes: require transport protein
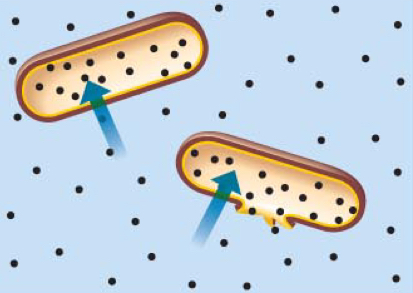
Hypotonic Solution
Solute concentration lower outside then inside
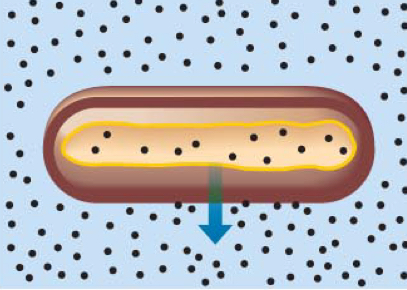
Hypertonic Solution
Solute concentration higher outside then inside.
Cytoplasm
The substance within the plasma membrane, consisting of water, proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and ions.
Nucleoid
The region in prokaryotic cells containing DNA, including the bacterial chromosome and plasmids. Not a membrane bound structure.
Ribosomes
Sites of protein synthesis, composed of protein and rRNA, with a size of 70S in prokaryotes.
Inclusions
Storage structures within prokaryotic cells for various substances like phosphate and energy reserves.
Endospores
Dormant, resistant cells produced by certain bacteria (e.g., Bacillus, Clostridium) when nutrients are scarce.
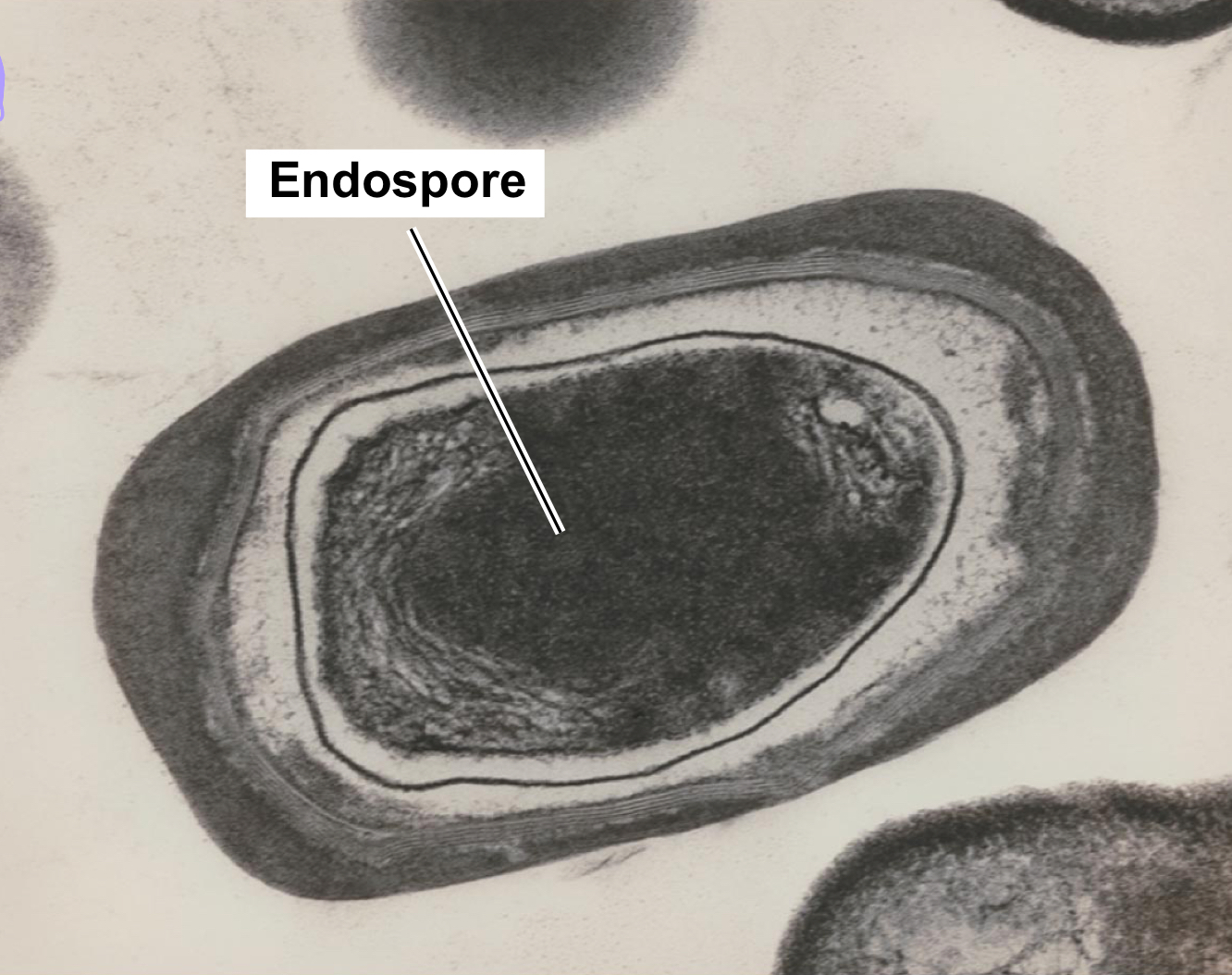
Sporulation & Germination
Sporulation: Endospore formation
Germination: Endospore returns to vegetative state
Flagella and Cilia (eukaryotic)
Consist of microtubules made of protein tubulin. Projections in eukaryotic cells for locomotion or moving substances, with a 9+2 microtubule arrangement.
Cell Wall (Eukaryotic Cells)
Found in plants, algae and fungi. Will be made of carbohydrates, Cellulose, chitin, mannan.
Glycocalyx
Carbohydrates bond to proteins and lipids in the plasma membrane, found in animal cells.
Nucleus
The membrane-bound organelle in eukaryotic cells that contains DNA and is involved in cell division. Double membrane strucutre that contains the DNA. Histone proteins in the to form chromatin.
Plasma Membrane Eukaryotic cells
Both have phospholipid bilayer and intergral/perpheral proteins. They are both selective permeability. The difference is this type have sterols and carbohydrates. Another difference is Endocytosis and phagocytosis.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
An organelle with rough ER for protein synthesis and smooth ER for synthesizing membranes and hormones.
Golgi Complex
An organelle that modifies and transports proteins via vesicles.
Lysosomes
Organelles containing digestive enzymes for breaking down waste materials.
Vacuoles
Storage organelles in eukaryotic cells that help maintain cell shape.
Mitochondria
Organelles responsible for ATP production, featuring a double membrane with cristae and matrix.
Chloroplasts
Organelles in plant cells that conduct photosynthesis, containing thylakoids with chlorophyll.
Peroxisomes
Organelles that oxidize fatty acids and detoxify harmful substances.
Centrosomes
Structures in eukaryotic cells that contain protein fibers and centrioles, essential for forming the mitotic spindle.