3. Schizophrenia Treatment
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
How do typical antipsychotics treat schizophrenia & what are their pros & cons?
Mechanism: Antagonist at multiple receptors (ACh, dopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine)
Example: Chlorpromazine
Advantages: Symptomatic relief in >70% of patients
Disadvantages:
Extrapyramidal symptoms: tremor, bradykinesia, rigidity, akathisia (motor restlessness), dystonia (spasms of neck & face)
Tardive dyskinesia: involuntary facial/body movements, can impair feeding/breathing
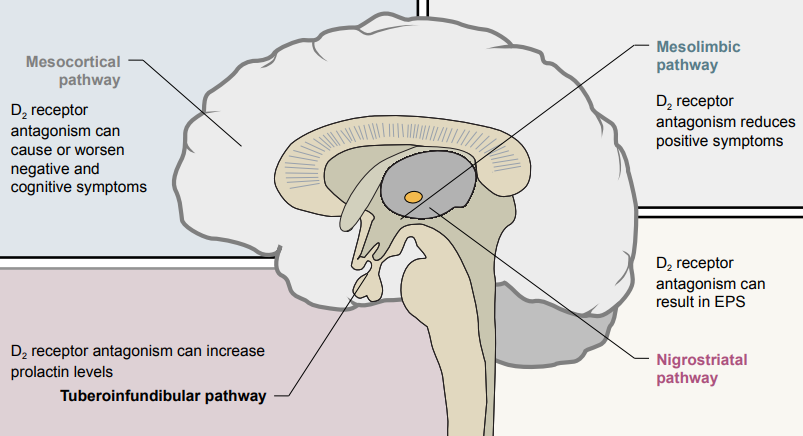
How does D₂ receptor antagonism in each dopamine pathway relate to schizophrenia symptoms or side effects?
Mesocortical pathway: ↓ Dopamine = negative symptoms; D₂ antagonism can worsen or cause these
Mesolimbic pathway: ↑ Dopamine = positive symptoms; D₂ antagonism reduces these
Nigrostriatal pathway: D₂ antagonism = extrapyramidal side effects (motor symptoms)
Tuberoinfundibular pathway: D₂ antagonism = ↑ prolactin = ↓ sex drive & endocrine effects
What are the key features of atypical antipsychotics, particularly clozapine?
Used in treatment-resistant schizophrenia (~20%)
Clozapine action: high affinity for D₁ & D₄ > D₂; partial 5HT₁A agonist; 5HT₂A antagonist
Advantages: treats positive & negative symptoms, ↓ EPS risk, ↓ suicide risk
What are the disadvantages of clozapine?
Expensive (~£1,800/year vs £100 for typical antipsychotics)
Weight gain
Risk of agranulocytosis (Severe ↓ in white blood cells):
Fever ≥40°C
Rapid pulse & breathing
Prone to infections (bacteria/fungi)
Sore throat, swollen gums, painful ulcers
What are the features & advantages of cariprazine (third-gen antipsychotic)?
Partial agonist at D3/D2 receptors (prefers D3)
D3 receptors → mainly in ventral striatum, thalamus, hippocampus, cortex
Targets areas for reward, emotion, motivation
Advantages:
Treats positive & negative symptoms
Fewer motor side effects
Possible cognitive improvement (in trials)
Less weight gain & metabolic issues (in trials)
What do NICE recommend for schizophrenia treatment?
Consider atypical antipsychotics as 1st-line treatment
Check diagnosis, adherence & other causes before switching
If no response to ≥2 antipsychotics (incl. 1 atypical) → offer clozapine
Which of the following is a clinical sign of schizophrenia?
A. Akathisia
B. Tremor
C. Bradykinesia
D. Social withdrawal
D. Social withdrawal
Explanation: Social withdrawal is a negative symptom of schizophrenia. Akathisia, tremor, and bradykinesia are side effects of antipsychotic medications.
Which of the following brain areas is affected in schizophrenia?
A. Cerebellum
B. Substantia nigra
C. Parietal cortices
D. Spinal cord
C. Parietal cortices
Explanation: The parietal cortices are affected in schizophrenia. The cerebellum, substantia nigra, and spinal cord are not typically involved.
Which of the following theories is considered an underlying cause of schizophrenia?
A. AMPA receptor hypothesis
B. GABA hypothesis
C. Single-Carbon hypothesis
D. Benzodiazepine theory
C. Single-Carbon hypothesis
Explanation: The Single-Carbon hypothesis is linked to schizophrenia. There is no GABA hypothesis or benzodiazepine theory for schizophrenia.
Non-genetic causes of schizophrenia-like symptoms can include:
A. Amino acids such as glycine
B. Dopamine receptor antagonists
C. Ketamine or phencyclidine
D. High levels of highly unsaturated fatty acids
C. Ketamine or phencyclidine
Explanation: Ketamine or phencyclidine can cause schizophrenia-like symptoms, such as hallucinations and paranoia. Amino acids like glycine, dopamine receptor antagonists, and high levels of unsaturated fatty acids are not causes.
Clozapine is:
A. A dopamine and 5HT receptor agonist
B. A cause of Parkinson’s disease
C. An inhibitor of D2 or D4 receptors
D. An inhibitor of D1, D4, and 5HT2A receptors
D. An inhibitor of D1, D4, and 5HT2A receptors
Explanation: Clozapine is an inhibitor of D1, D4, and 5HT2A receptors. It is not a dopamine receptor agonist, nor does it cause Parkinson's disease. It can cause motor dysfunction similar to Parkinson's, but this is not the same as Parkinson's disease.