lecture 2: chemical equilibria
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
reversible reaction
reactants and products are of similar stability
goes from products to reactants and vice versa
reverse reaction
read from right to left
forward reaction
read from left to right
state of chemical equilibrium
both forward and reverse reactions occur until the concentration of reactants and products undergo no further change
reaction has reached chemical equilibrium
all substances present are being made and unmade at the same rate, so their concentrations are constant at equilibrium, even if they’re not equal
equilibrium constant K; much smaller than 0.001
only reactants are present at equilibrium; essentially no reaction occurs
equilibrium constant K; between 0.001 and 1
more reactants than products are present at equilibrium (reverse reaction is faster)
equilibrium constant K; between 1 and 1000
more products than reactants are present at equilibrium (forward reaction is faster)
equilibrium constant K; much larger than 1000
only products are present at equilibrium; reaction goes essentially to completion (irreversible reaction)
le chateliers principle (LCP)
when a stress is applied to a system at equilibrium, the equilibrium shifts to relieve the stress to restore an equilibrium
acid
proton donor
must contain a H in its formula
H2SO4, HCl, H2PO4, HNO3
base
proton acceptor
must contain a lone pair of electrons to bind to the H+ ion
NH3, CO32-, OH-
strong acid /base
dissociates completely
weak acid/base
does not dissociate completely
strong acid examples
HCl, HBr, HNO3, H3PO3-, H2SO4
weak acid examples
CH3COOH, C6H5COOH, HNO2, H3PO4
strong base examples
NaOH, KOH, CaO, Mg(OH)2
weak base examples
NH3, C5H5N
pH
the scale we use to measure how acidic or basic a solution is
pH = - log10[H3O+]
pOH (potential of hydroxide ion)
a scale used to determine the hydroxide ion concentration in a solution
pOH = - log10[OH-]
Kw (ionic product of water)
the equilibrium constant for the self-ionisation reaction of water
[H3O+] X [OH-] = 1 X 10-14 @ 25 degrees Celsius
Ka
acid dissociation constant
when Ka is large, pKa is small (strong acid)
pKa = -log10 Ka
Kb
base dissociation constant
when Kb is large = strong base
pKb= -log10Kb
equivalence point - titrations
acid and its conjugate base are at completely equal concentrations
buffer
solutions/mixtures that maintain the pH approx. constant despite small addition of an aid or a base
RESISTS CHANGES IN pH
usually a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base
When small quantities of H3O+ or OH- are added to the buffer, they cause a small amount of one buffer component to convert into the other
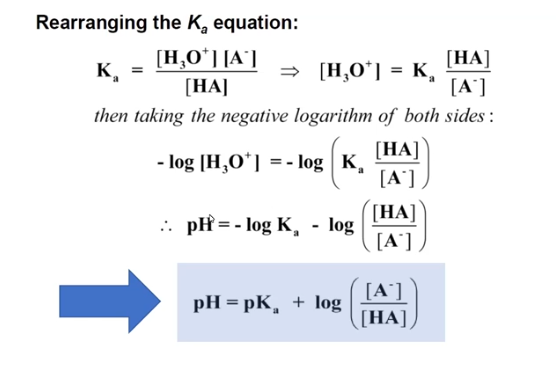
hendersson-hasselbalch equation

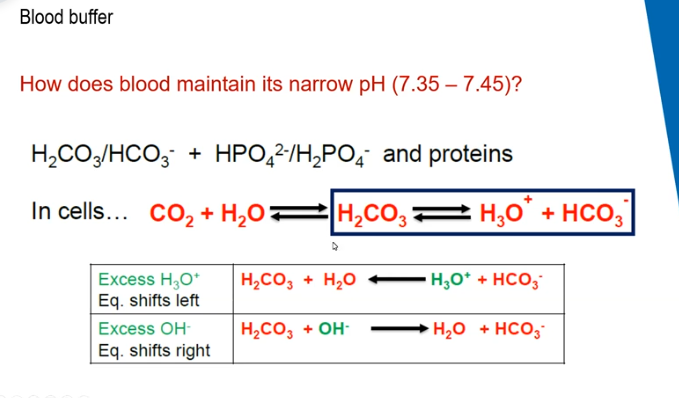
blood buffer