(BIO 386) Lecture 10 - Running Waters
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Hydrography
Change in structure of the channel and effects on flow (patterns)
Role of running waters in global cycles
short retention time
responsible for fluxes between terrestriala and ocean reservoirs
dissolved and particulate substances
rivers and streams associated with wetlands
Dissolved substances
weathering/organismal uptake
Particulate substances
deposition/feeding/erosion
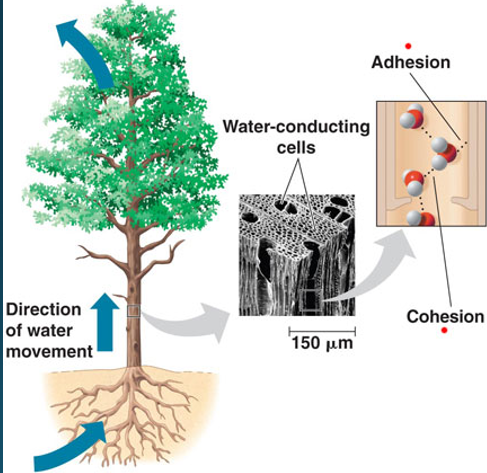
Transpiration water budget
Movement of water vapor through stomata of leaves to the atmosphere
Trade-off: water conservation vs. nutrient acquisition
Plants differ in amount of transpiration
Evapotranspiration water budget
Total flux of water from an ecosystem
Made up of evaporation and transpiration
Watershed water budget
The area of the landscape that contributes to flow of water at a particular point in the stream
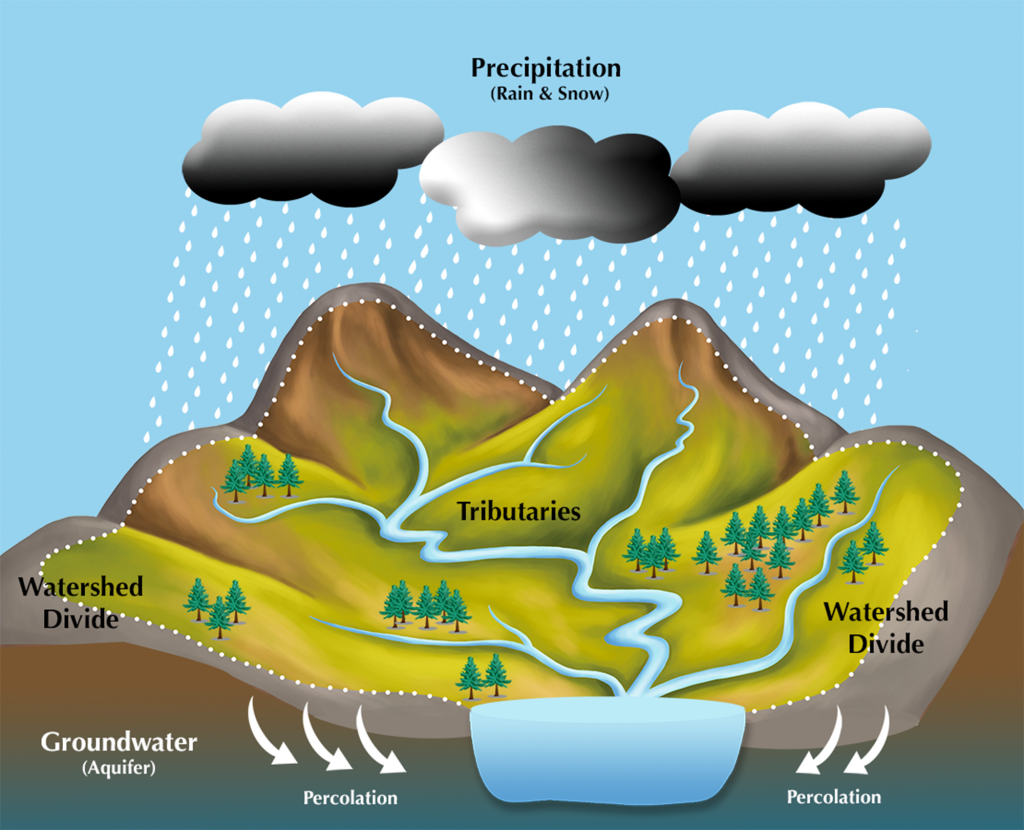
Groundwater recharge
depends on soil structure and nature and depth of bedrock
Plants affect terrestrial water balance
Difference between precipiation and discharge due to transpiration by plants in summer; plants suck up all the water.
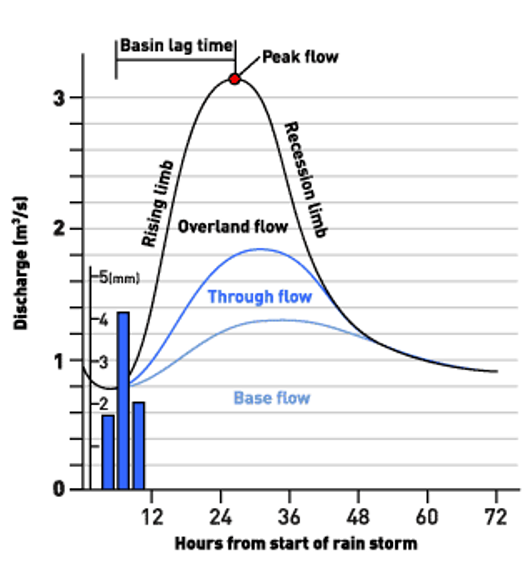
Water flow paths
Baseflow: from groundwater
Overland flow: over surface
Through flow (interflow?): through surface soils
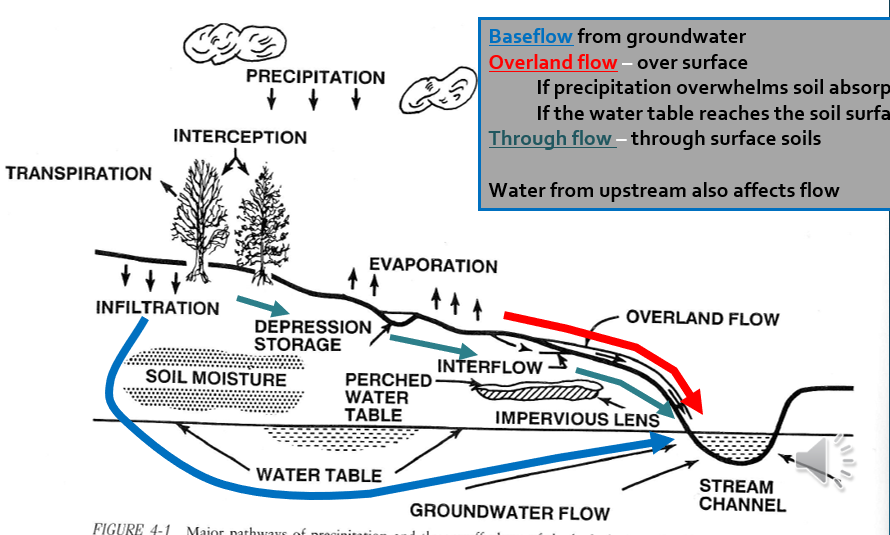
Baseflow
From groundwater, varies as water table rises and falls
Overland flow
Over surface, responds fastest but only due to soil hardening or saturation
Through flow
Faster to respond to precipitation and recedes faster than baseflow
Stream Order
How far a stream is from its origin
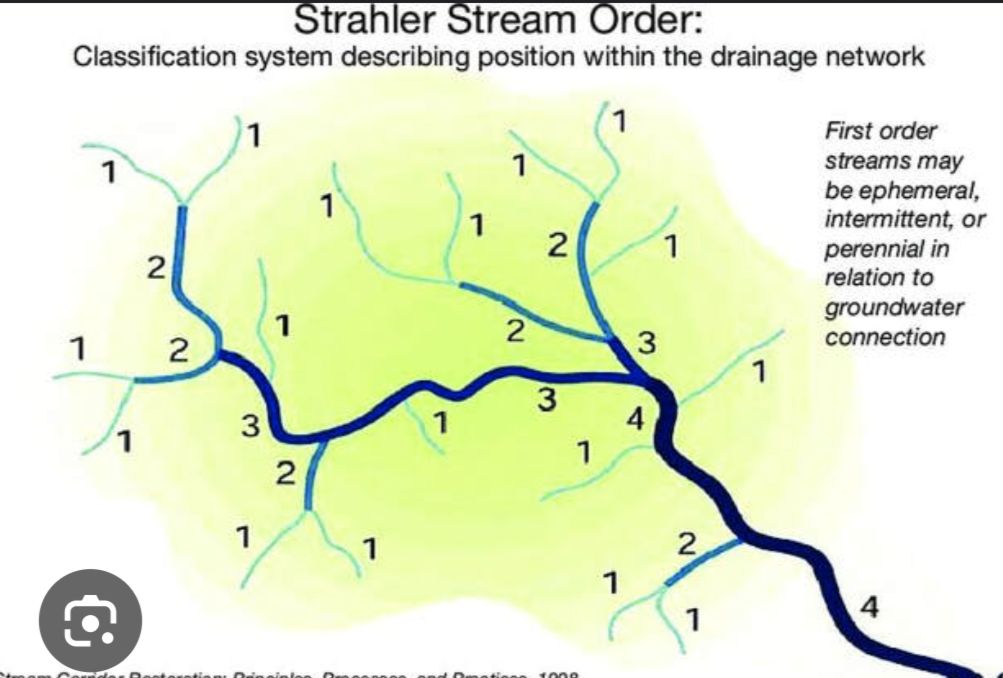
Stream characteristics that change with order

Flow of running water influences…
the shape of the stream channel itself, because they carry particles
Eddies
Whirlpools of flowing water that are caused by differences in speed
Eddies cause variations in current speed, which leads to
Movement of particles:
When flow is fast: Erosion
When flow is slow: Settling and deposition
Resistance of surrounding materials affect
Structure of rivers/streams
When resistant to erosion: streams follow solid banks
When erodable: streams meander and positions change over time
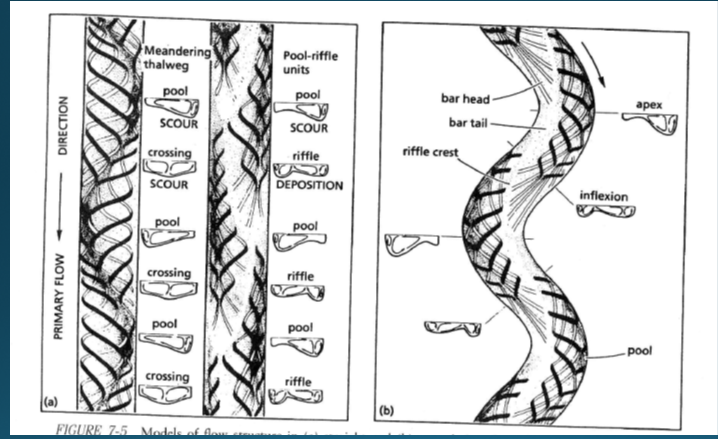
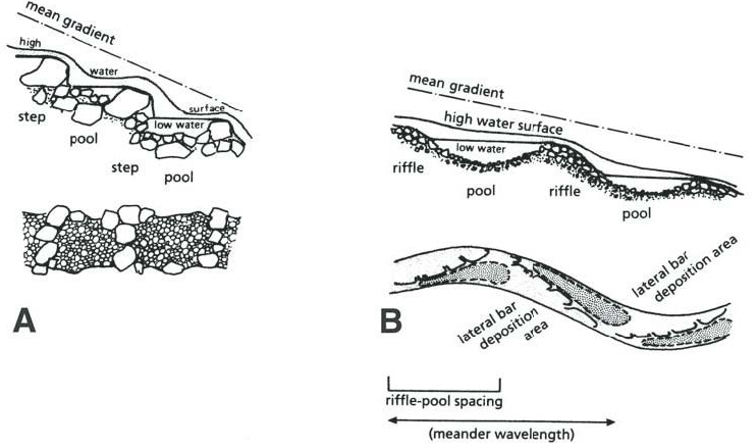
Riffles
Zones of erosion and loss of material (Only coarse material remains)
Pools
Places of slow water flow and deposition of slit
Floodplains
Periodically flooded areas
water is reduced due to friction of nearby river bottom
particles sink out because of slower flow
Fertile, nutrient-rich
Riverflow is directly related to…
flux of materials
Particle load
Mass flux of particles per year (flow x concentration)
Load is higher for steeper rivers with fast flow
Load is lower for flatter rivers with slower flow
Succession of vegetation
Starts with open land affected by fire, ice, etc. starts to grow annual plants →
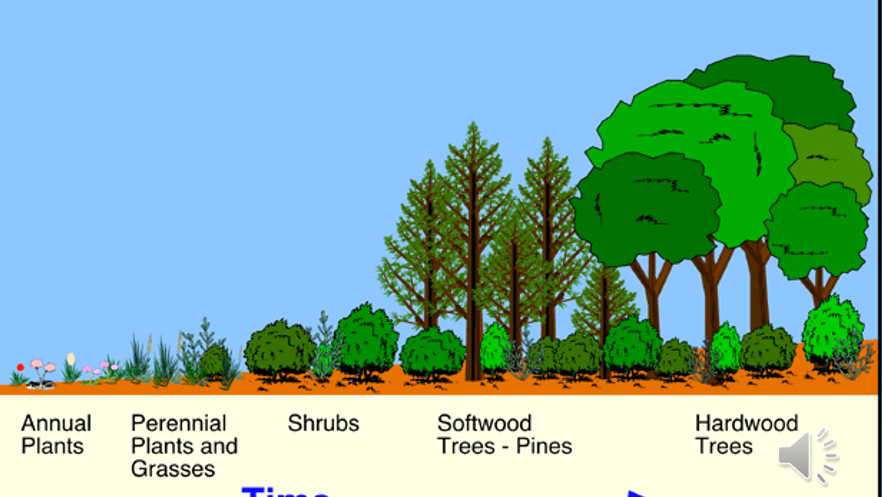
Succession affects nutrient retention
Mid succession:
Limiting nutrient is needed to make more biomass → Starts to decrease
Later succession:
Outputs to streams < input from atmosphere
Limiting elements increases
Plants are CHANGING characteristics of water in soils that are reaching the streams → Output to streams =i input from atmosphere
Dissolved organic carbon (DOC) makes up…
70-90% of organic matter in surface waters
Allocthonous
inputs originate from outside system
Autochthonous
inputs originate from inside system
Three sources of food
1) Algae/plants growing in stream
2) Dissolved organic matter from watershed
3) Particulate organic matter from watershed
Scrapers
eat algae and bacteria off of rocks and plants
Shredders
Shred and ingest large organic material
digest associated algae, bacteria, fungi
facilitate decomposition by making particles smaller
Collectors
Collect particles floating in water or in sediment
deposit feeders: feed on sediment
filter feeders: collect particles
River continuum concept
Primary source of carbon to food webs shift with distances from source waters
results in shifting ratios of production and respiration (P:R)
some sections are more dependent on local production, some on remote production
Upper river
light is low and vegetation nearby
primary source of carbon: terrestrial plant material
P:R <1 (heterotrophic)
Shredders dominate
Middle river
Light is high as river widens
Carbon produced by photosynthesis within river
P:R>1 (autotrophic)
Scrapers dominate
Lower river
River deep and filled with sediments
Source of carbon from upstream
P:R<1 (heterotrophic)
Filter feeders collectors dominate
Nutrient movement
Nutrients move downstream fastest when dissolved/suspended in flowing water
Organisms take up dissolved substances into sediments, preventing downstream loss
Algae/plants
Bacteria
Fast flow loosens sediments and organisms, taking them downstream, and vice versa.
Channel shape influences
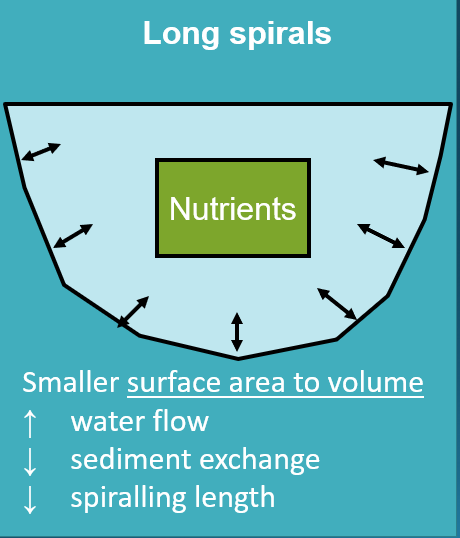
Spiraling and nutrient loss
Long Spirals:
Smaller surface area to volume
Shorter Spirals:
Larger surface area to volume