MCQ cytology 1st colloqium
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
general classification of cell organelles
cell membrane (plasmalema, plasma membrane)
nucleus
cytoplasm
cell membranes
glycocalyx
solitary membrane
submembraneous protein-filament complex
intercellular contacts
microvilli
cytoplasms
matrix
cytosol/hyaloplasm
general organelles
smooth ER
rough ER
ribosomes
polyribosomes
golgi complex
mitochondria
cytocentre
lysosomes
peroxisomes
coated pits
microtubules
microfilaments
coated vesicles
specialised organelles
myofibrils (actin, myosin)
tonofibril
neurofibril
cilia
flagella
secretory granules
metabolic inclusions
protein granules
glycogen
lipid droplets
pigments
crystals
nucleus
nuclear membrane
outer membrane
perinuclear space
inner membrane
nuclear pores
nuclear matrix
chromatin
chromatin in interphase(euchromatin/heterochromatin)
chromatin in mitosis
nucleolus
granular component (nucleolonema, pars granulosa)
fibrilar component (pars filamentosa)
amorphous components (pars amorpha)
what is receptor mediated endocytosis?
process of accepting substances after recognising them and linking them to their specific membrane receptors
what does the clathrin protein participate in?
coated vesicles
what is exocytosis?
process of releasing secretory granules through the cell membrane
glycocalix
a glycoprotein coat located on top of the plasmalemma and attached to it
what are cytoplasmic inclusions and are they obligatory?
Definition: These are non-living substances found within the cytoplasm of a cell, often serving as storage for nutrients, pigments, or waste products. They can vary in size and composition, including glycogen granules, lipid droplets, and crystals.
Obligatory? No, they are not obligatory structures; their presence depends on the cell type and its metabolic needs.
what is meant by obligatory cell?
Definition: A type of cell that is essential for the functioning of a specific tissue or organ. If removed or absent, it leads to dysfunction or failure of that tissue or organ
involved in processes like metabolism, signaling, or structural support
presence is mandatory for maintaining homeostasis and overall health within the organism.
can you see cell matrix (cytosol) with a light microscope?
Answer:No, the cell matrix (cytosol) is typically not visible with a light microscope due to its transparent nature and low contrast.
cytosol require electron microscopy for better resolution.
what do mitochondria under a light microscope appear as?
tender granules or filaments
what are nissl bodies?
light microscopic image ofof rough endoplasmic reticulum and ribosomes
how are ciliums built?
assembly of microtubules, specifically a 9+2 arrangement of tubulin proteins
do coated vesicles participate in intracellular transport processes?
yes
what is euchromatin?
active form of chromatin in the nucleus
what are microtubules apart of?
cytoskeleton
what does plasma membrane consist of?
lipid bilayer and integral proteins
pinocytosis
uptake of fluid material by cells
which contact does the intercellular space disappear?
Tight Junctions (Zonula Occludens): Specialized structures in epithelial tissues that enable cells to adhere closely, eliminating gaps between their membranes. They play a crucial role in maintaining tissue integrity, regulating the passage of substances, and facilitating signaling and communication.
what are conexones structural components of?
gap junction (nexus)
golgi apparatus stain
silver impregnation AgNO3
what is formation of new mitochondria associated with?
their own budding or simple division
what process is associated with the rough ER?
protein synthesis
what do coated vesicles participate in?
intracellular transport processes
what do lysosomes consist of?
single membrane and hydrolytic enzymes
where is sex chromatin (Barr body) seen in?
female somatic cells
feulgen stain for?
DNA
what do histone proteins take part in?
formation of DNA molecule
interphase nucleus of young, functional activity cells is:
large, pale stained with prominent nucleolus
where do chromosomes move in metaphase?
move to centre of cell equatorial plane
what do mitotic spindle fibres consist of?
microtubules
stain for lipid
Sudan III + H
karyorexis
Definition: A type of cell death characterized by the fragmentation of the nucleus into small pieces
apocrine secretion characterised
Definition: A type of secretion that involves the release of the apical portion of the cell's cytoplasm along with the secretory product.
apoptosis
programmed cell death
fiber of the division spindle are
microtubules
nucleolus
related to formation of subunits of the ribosomes (rRNA)
characteristic of the enzyme acid phosphatase
lysosomes
what do the integral proteins of the plasma membrane interact with?
peripheral proteins
components of the cytoskeleton
glycocalix description
is a polysaccharide layer
takes part in cell adhesion
takes part in cell cooperation
what is nexus?
built of connexones
consist of protein channels for transport of small molecules and ions between the cells
what is the basophilia of the cell cytoplasm due to?
presence of abundant rough ER
numerous ribosomes
nuclear pores description
selective transport of substances across the nuclear envelope
formed at sites where the inner and outer membranes of the nuclear envelope are joined
nucleolus
build part of chromosomes 13,14,15,21 and 22
where ribosome formed
component of nucleus
main function of smooth ER
synthesis of lipids and steroid hormones
synthesis of glycogen and mucus
intracellular transport
dyctysome description
component of the golgi apparatus
flattened cisternae with outer forming and inner secreting surfaces
release secretory granules from the outer surface
mitochondria specific features
posses own genetic apparatus
formation of new mitochondria through own budding or simple division
take part in ATP synthesis
common features of mitochondria and peroxysome
contain matrix with numerous enzymes
general membrane cell organelles
lysosome features
intracellular digestion
contain hydrolytic enzymes
related to processes of cell aging and death
peroxysome specific features
contain oxidative enzymes
contain matrix with crystalloid
microtubule specific
sustain cell shape
intracellular transport of molecules and organelles
participate in formation of spindle fibres during the mitosis
how is mitochondria visualised?
iron-hematoxylin
Altmann method acid fucsin
typical for nuclear membrane
double layered
continous with the rough ER
nuclear pores
based on their function the plasma membrane proteins are classified as
receptors
transport
connecting
enzymes
transductive
what are the types of cell junction (intercellular contacts)?
Tight Junctions (zonula occludens) - Seal adjacent cells, preventing leakage of molecules between them.
Desmosomes (zonula adherens/macula adherens) - Anchor intermediate filaments, offering strong adhesion under stress.
Gap Junctions (nexus) - Allow direct communication between cells through channels
Zipper interlocking (interdigitations)
what does an electron microscope image of nucleolus show?
granular part (pars granulosa)
fibrous part (pars fibrosa)
main changes in nucleus and cytoplasm during prophase
nucleolus disappear
nuclear envelope disappear
mitotic spindle fibres form
chromosomes coild and condense becoming visible (spirem figure)
general membrane cell organelles
endoplasmic reticulum
golgi apparatus
mitochondria
lysosome
peroxisome
coated vesicles
electron microscope of Golgi complex
cisternae
microvesicles
vacuoles
main components of the cytoskeleton
microtubules
microfilaments
cell inclusions are:
glycogen granules
lipid droplets
pigments
crystals
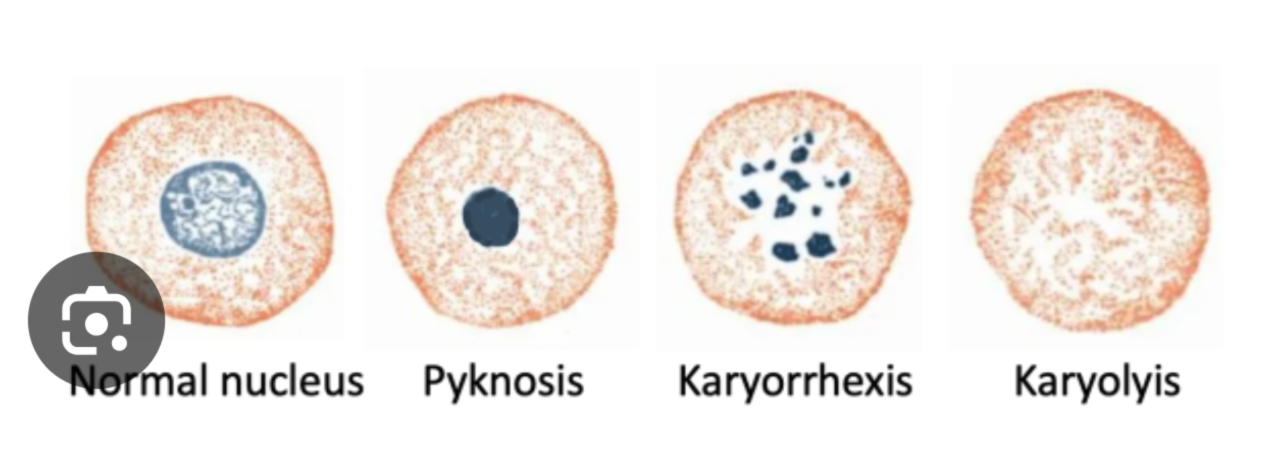
what are the light microscopic changed in ageing cell?
pyknosis
karyorexis
karyolysis
what are the types of exocrine secretions?
merocrine
apocrine
holocrine
what are some specialised cells?
myofibril
tonofibril
neurofibril
cilia
flagella
secretory granules
what is the organelle when by light microscope obs of spinal ganglion stained with AgNO3 and reticular network is seen near the nucleus?
Golgi apparatus
electron microscopy of bowl-like complex with parallel cisternae with vesicles and vacuoles
Golgi complex
what is the EM of cylindrical structure at right angles composed of 9 sets of 3 microtubules?
centrioles
light microscope seen Sudan III + H staining orange droplets with blue nuclei are seen
lipid inclusions
what is the stage in mitosis where the chromosomes are localised in the opposite poles of teh spindle fibres
anaphase
9×2 + 2 arrangement of microtubules can be seen with EM what is the organelle?
cilia
oval with cristae and two membranes seen with EM
mitochondria