chapter 5.3 - variability
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
measures of variability
summarize and describe extent to which scores in a distribution differ from each other and the mean
range
distance from lowest to highest score, problematic because lacks precision and extreme scores distort variability
interquartile range
range of the middle 50% of observations (25th to 75th percentile), attempts to get around problem of range being dependent on extreme scores, to compute find median and use median to split into 2 halves and then find the difference in the two half’s medians, problematic because eliminates half the data
variance
an index that reflects the degree of variability in a group of scores, average of the squared deviations (distances) about the mean, larger variance=more spread out scores
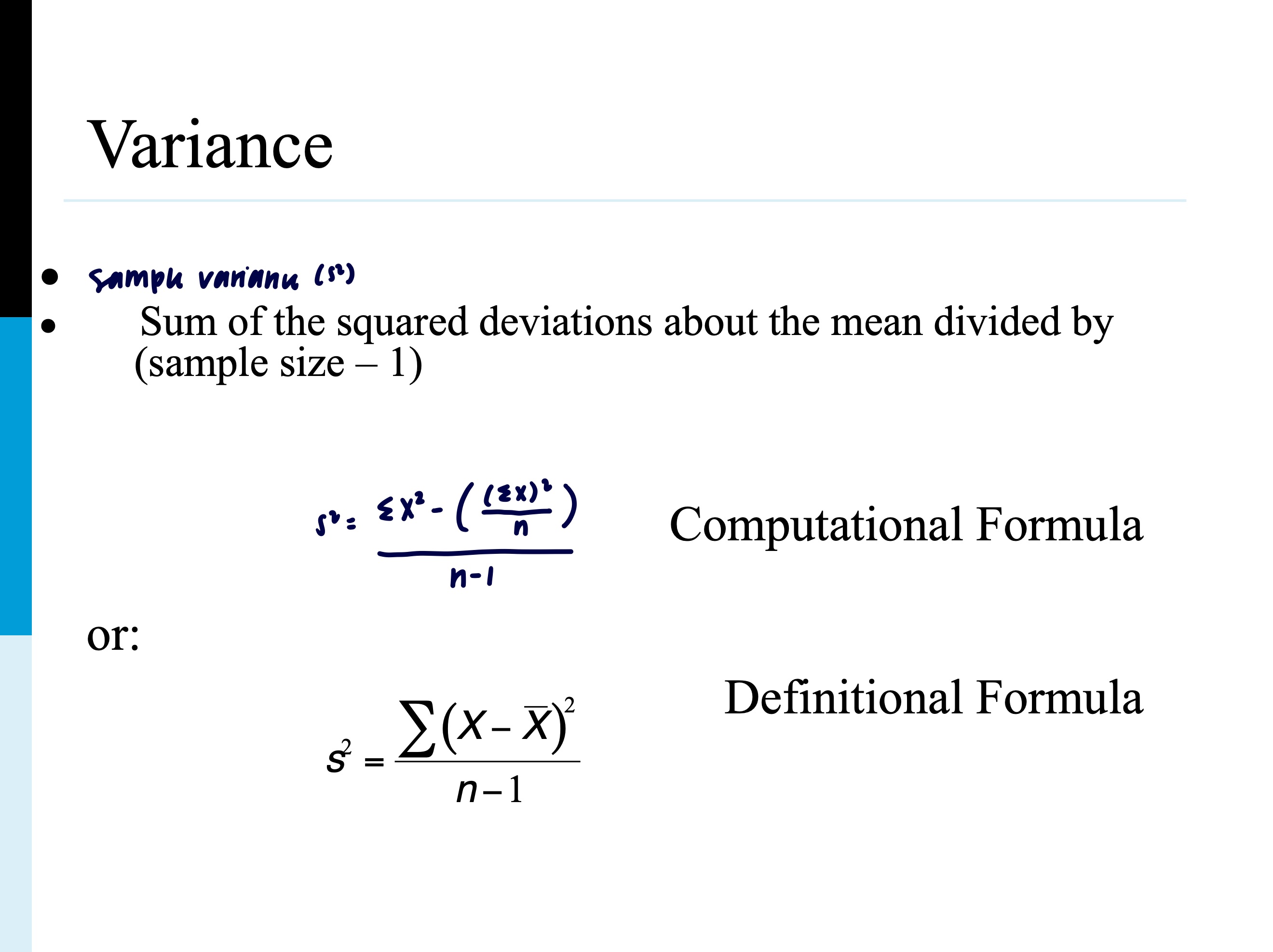
sample variance (s2)
sum of the squared deviations about the mean divided by samplesize-1
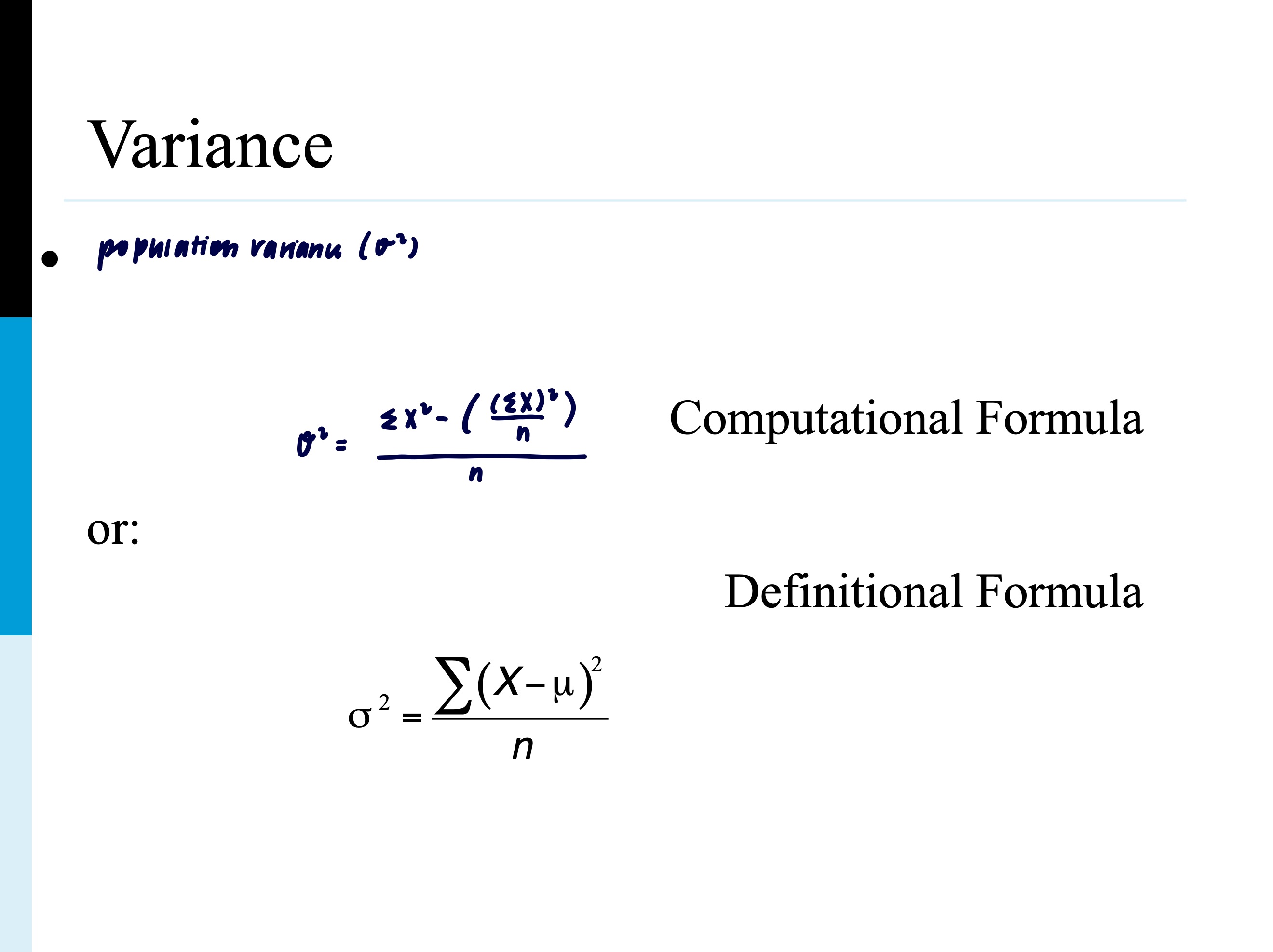
population variance (σ²)
very similar to sample but not samplesize-1
standard deviation
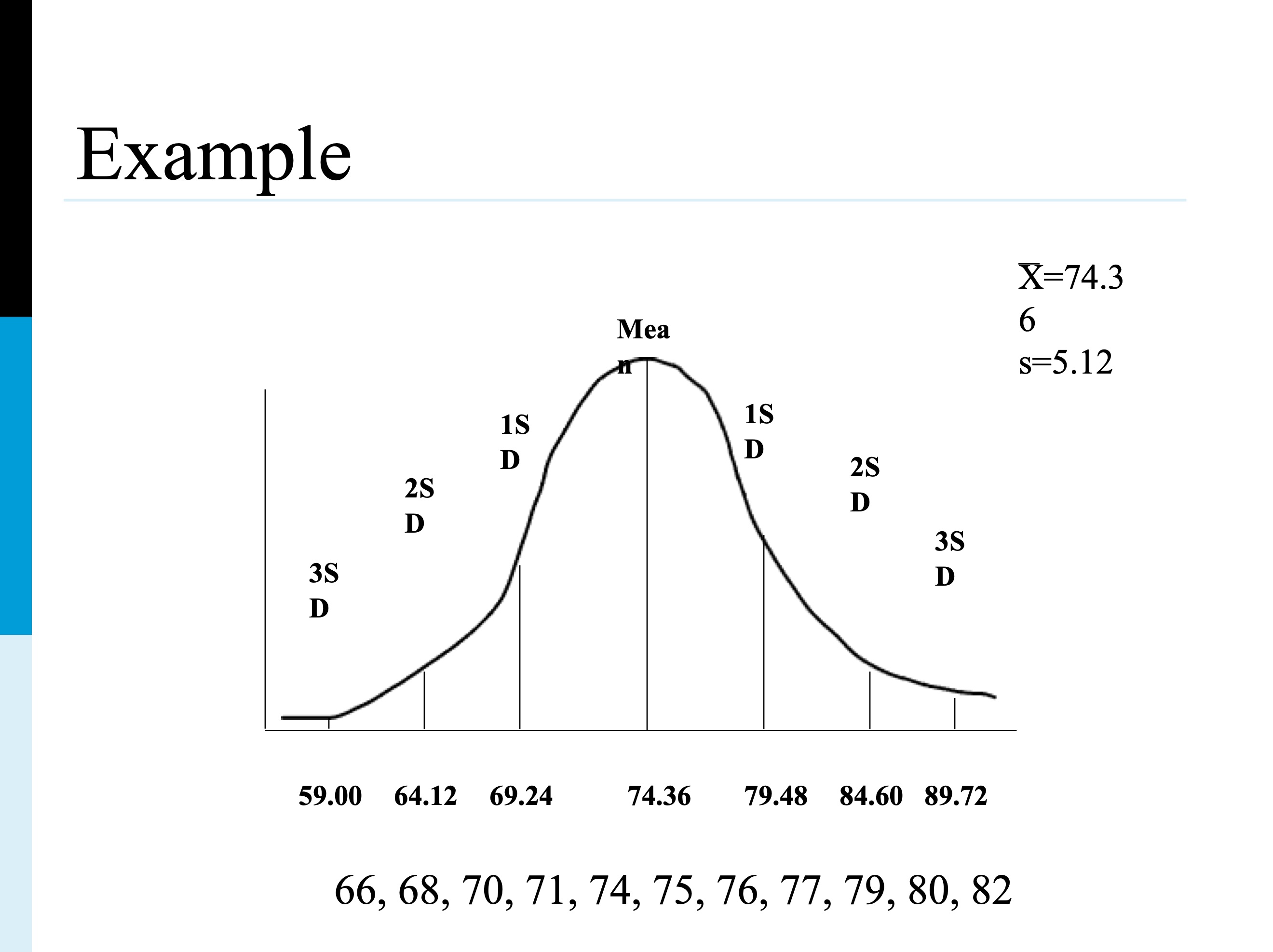
take square root of the variance, is a measure of the average deviation of each score of the mean
approx. 68% scores will fall within 1 SD of mean
approx. 95% falls within 2 SD of mean
approx. 99.7% falls within 3 SD of mean
extreme scores
add variability to distribution and increase variance and SD