Edexcel A Level Biology Topic 8 Exam Questions
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Describe how dopamine acts as a neurotransmitter. (4)
M1: Dopamine released {from presynaptic membrane/ from the synaptic know/ into the synaptic cleft} / diffuses across the synaptic gap
M2: Binds to receptors on the post synaptic membrane
M3: Alters permeability of the post synaptic membrane/ opens {sodium ion channels/ channel proteins} in the post synaptic membrane
M4: Initiating {depolarisation/ action potential} in the post synaptic neurone
The use of drugs such as MDMA (ecstasy) can cause an imbalance of chemicals in the brain.
Describe how the use of MDMA could affect the transmission of impulses in the brain. (2)
M1: MDMA {stimulates release/ prevents re-uptake/ increases concentration} of serotonin
M2: Blocking pre-synaptic receptors/ binding to post-synaptic receptors
M3: Nerve pathways using serotonin are more likely to be stimulated/ more action potentials produced
Individuals who use MDMA may develop the symptoms of depression.
Explain how the use of MDMA could result in the development of these symptoms. (2)
M1: MDMA use results in depletion of serotonin
M2: Post synaptic membrane becomes less responsive to serotonin/ loss of receptors on the post synaptic membrane
M3: Serotonin levels affect mood/ lack of serotonin associated with depression
Describe how low serotonin levels in an individual can affect the transmission of impulses in their brain.
M1: Serotonin is a neurotransmitter/ there will be less neurotransmitter
M2: Less serotonin results in fewer depolarisations of post synaptic membranes
M3: Threshold not achieved/ less chance of action potential being produced in post synaptic neurone
Explain how the treatment of Parkinson's disease overcomes the difficulty of drugs passing from the blood into the brain. (2)
M1: Give {a precursor of dopamine / L-Dopa} which can cross the blood brain barrier
M2: L-Dopa is converted to dopamine in the brain
The transmission of an impulse between a neurone in the optic nerve and a cell in the brain involves ions and neurotransmitter molecules.
Describe how these ions and neurotransmitter molecules are involved in the transmission of an impulse. (4)
M1: Calcium enters pre-synaptic neurone so the vesicles with neurotransmitters can {move towards/ fuse with presynaptic membrane}
M2: Neurotransmitter molecules diffuse across synapse
M3: Neurotransmitter to bind with receptors on post-synaptic membrane on the brain cell
M4: Sodium ions diffuse into the {brain cell/ post-synaptic cell} leading to {a depolarisation/ an action potential}
Contraction of the muscle in the withdrawal response is stimulated by nerve impulses. These nerve impulses can be detected using electrodes.
Explain the electrical changes in an axon that allow these nerve impulses to be detected. (4)
M1: Potential difference across an axon changing
M2: Due to increased permeability to sodium ions/ voltage gated sodium ion channels open
M3: Sodium ions {move into the axon/ cause depolarisation}
M4: Followed by an increased permeability to potassium ions/ voltage gated potassium ion channels open
M5: Potassium ions {move out of the axon/ cause repolarisation of the membrane}
Describe the role of the dendrites in a neurone. (3)
M1: Forms {synapses/ connections} with other neurones
M2: {integrate/ receive} impulses from other neurones
M3: Involved in summation
M4: {Propagate a signal/ initiate an action potential} to the {cell body/ axon}
Compare and contrast the structure of a sensory neurone and a motor neurone. (4)
Similarities:
M1: Both have a cell body containing nucleus
M2: Both have an axon
M3: Both have dendrites at one one of neurone and terminal branches at other end
Difference:
M4: Location of cell body (motor neurone cell body is at one end of the axon whereas in sensory neurone the cell body is located around the axon)
Describe how positron emission tomography (PET) scans can be used to investigate brain structure. (2)
M1: PET makes use of radioactive {tracers/ markers/ glucose}
M2: PET scans detect {emission of positrons/ production of gamma rays}
M3: Provides 3D image
Visual development requires exposure of the visual cortex to environmental signals during a critical period.
Describe the role of visual stimulation on the development of the visual cortex during the critical period. (3)
M1: Ocular dominance columns develop in visual cortex
M2: Neurones form synapses with these {cells/ columns}
M3: {stimuli/ action potential/ impulses} along neurones required to strengthen connections with cells of ocular dominance columns
M4: Stimulation during the critical period is needed to form effective connections in the visual cortex (connections become weaker if stimuli not received)
Functional MRI (fMRI) measures brain activity by detecting changes in what? (1)
Changes in blood flow
The non-protein part of the light-absorbing pigment in the rod cells of the retina is called what? (1)
Non-protein part is called retinal
Explain how fMRI can be used to identify the part of the brain involved in interpreting information from the visual cortex. (3)
M1: fMRI detects {blood flow/ oxygen use} in the brain
M2: Increased brain activity results in increased {blood flow/ demand for oxygen/ aerobic respiration} in the area of activity
M3: Oxyhaemoglobin absorbs fewer radio waves/ fMRI detects areas where less signals absorbed
Describe the role of sodium ions in the functioning of a mammalian rod cell. (4)
M1: Sodium ions are pumped out of the {rod cell/ inner segment}
M2: in the light/ when stimulated sodium ions do not move back into the rod cell
M3: in the dark/ when not stimulated sodium ions can move back into the {rod cell/ outer segment}
M4: In the light/ when sodium ions do not move back in, the rod cell is hyperpolarised / (in the dark/ when sodium ions can move back in) the rod cell is depolarised
Cells in the tip of the oat coleoptile release IAA.
Explain how the IAA affects the growth of the coleoptile. (4)
M1: IAA diffuses from the tip of the coleoptile
M2: Therefore can be taken up by cells in the zone of elongation
M3: Which causes cells to elongate
M4: Details of action in zone of elongation (e.g. leads to lowering of the pH in the cellulose cell wall)
M5: Therefore causes the coleoptile {to grow towards light/ increase in height}
Describe the role of IAA (auxin) in the phototropic response of plants. (4)
M1: IAA produced in the tip of the shoot
M2: IAA accumulates on the dark side of the shoot
M3: IAA stimulates cell elongation
M4: Causing shoot to grow towards the light source
Describe the functions of the enzymes used to genetically modify bacteria. (4)
M1: Restriction endonuclease used to {cut plasmid/ isolate gene}
M2: Forming sticky ends
M3: Ligase enzymes used to add isolated gene to plasmid
M4: Ligase forms phosphodiester bonds between nucleotides
M5: Recombinant {DNA/ plasmid} produced
Describe how bacteria can be genetically modified to produce a cytokine for the treatment of neurological and mental disorders. (4)
M1: Isolate the gene for cytokine from the human DNA
M2: Use a bacterial plasmid as a vector
M3: Cut the human DNA and the plasmid using the same restriction enzyme
M4: Splice the gene and plasmid together using DNA ligase
M5: Put the modified plasmids into the bacterial cells
Describe why a region of the brain might appear lighter in an image obtained by a fMRI scan. (3)
M1: Due to more activity
M2: An increase in {oxygenated blood / blood flow} to the region
M3: fMRI signals {not absorbed/ reflected} by the oxygenated blood
Describe why a combined PET and CT scan may be better for diagnosing cancer than a PET or CT scan on its own. (3)
M1: (using both provides information on) function (PET) and structure
M2: PET scan shows areas that are {more (metabolically) active / dividing more }
CT scan gives {location / size}
M3: Each scan uses a different technique / techniques described (e.g. CT uses X-rays and PET radioactively labelled metabolite such as glucose)
Describe the interaction of the muscles in the eye that led to the dilation of the pupils. (3)
M1: Antagonistic pairs of muscle
M2: In the iris
M3: Radial muscles contract and circular muscles relax

Explain the changes in the sodium and potassium ion concentrations in the cytoplasm of the neurone from point W to point X on the graph. (4)
M1: Voltage gated sodium ion channels open and sodium ions {diffuse into /move in} from outside the cell
M2: (therefore causing an) increase in sodium ion concentration
M3: Voltage gated potassium ion channels open and potassium ions {diffuse out / move out} from the inside
M4: (therefore causing an) decrease in potassium ion concentration at or after {7 milliseconds / 40 mV}
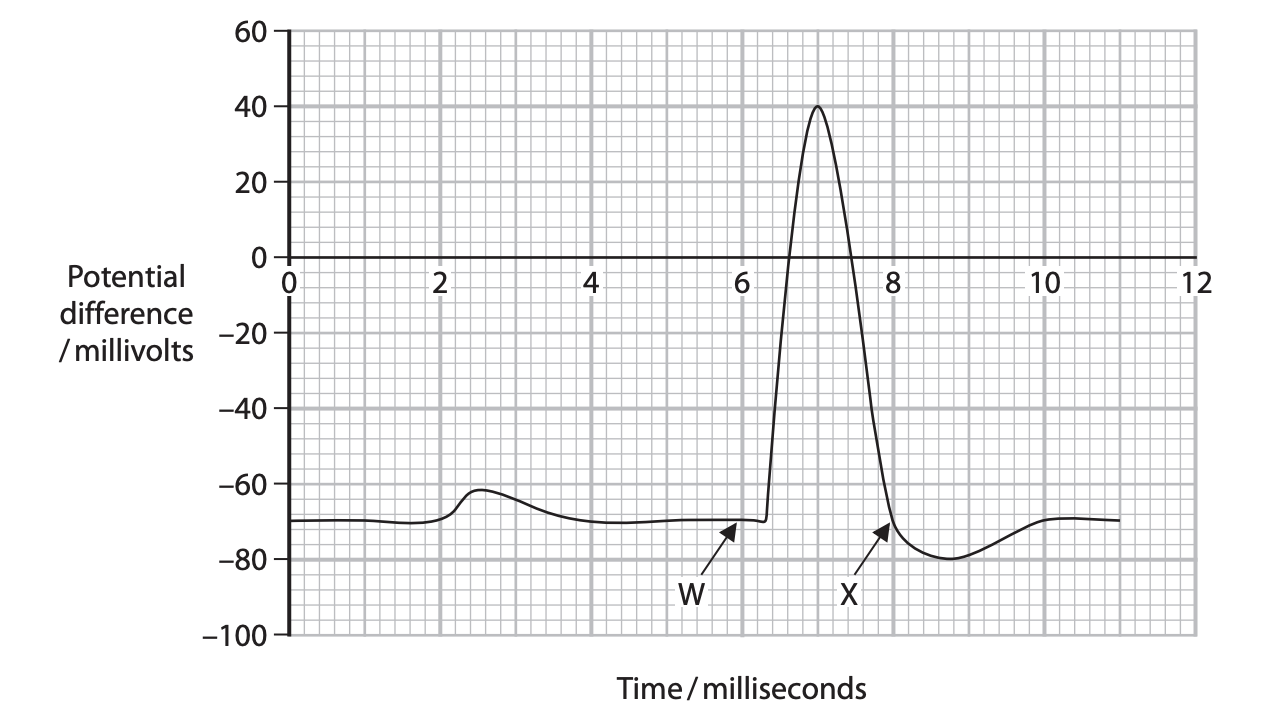
Explain why the neurone becomes hyperpolarised after point X on the graph. (3)
M1: Potassium ions continue to leave the {axon/ cytoplasm}
M2: Therefore preventing another depolarisation occurring/ it is the refractory period
M3: Allowing time for neurone to reset
M4: So that nerve impulses travel in one direction only
Explain the role of ATP in the transmission of impulses along neurones. (2)
M1: ATP required for sodium/potassium pumps
M2: To move ions against concentration gradient
M3: To maintain potential difference across axon membrane (ALLOW maintains resting potential)
Rod cells form synapses with bipolar neurones.
Describe how movement of sodium ions in a rod cell affects depolarisation in a bipolar neurone. (4)
M1: (in the dark) sodium ions moving {in through sodium ion channels / into the outer segment}
M2: Sodium ions {removed / pumped out} at inner segment
M3: So rod cell depolarises
M4: Causing { neurotransmitter / glutamate } to be released
M5: Inhibits depolarisation in (adjacent) bipolar neurone
Describe the role of the photosensitive pigment phytochrome in the flowering of long‑day plants. (2)
M1: increased red light (due to a long day / short night) / limited exposure to far-red light
M2: Phytochrome red converted to phytochrome far-red in the day / little conversion of far red form to red form during the (short) night
M3: {accumulation / high concentration} of phytochrome far red stimulates flowering
Explain the importance of habituation response in an animal. (2)
M1: Allows an animal (to learn) to ignore (repetitive) non-threatening stimuli
M2: Therefore allowing it to focus on (potentially) more relevant stimuli (ALLOW therefore allowing it to conserve {energy / resources} )
Describe the role of myelination in the conduction of a nerve impulse.
M1: Provides (electrical) insulation
M2: Enables saltatory conduction
Describe the role of ion channels in the conduction of a nerve impulse. (5)
M1: Sodium (ion) channels open
M2: (then) sodium ions diffuse in
M3: (causing) depolarisation of the membrane
M4: Sodium (ion) channels close and potassium (ion) channels open
M5: (then) potassium ions diffuse out
M6: (causing) repolarisation of the membrane