3.1-Inflammation
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Elie Metchnikoff
Concluded that the job of inflammation is to bring phagocytic cells to the injured area to engulf invading bacteria
Paul Ehrlich
Humoral immunity, specific antibodies, and non-specific phagocytes at 20th century
Sir Thomas Lewis
Demonstrated that inflammation is brought about by chemical mediators
Histamines produce the triple response of Lewis: red scratch, flare, and wheal
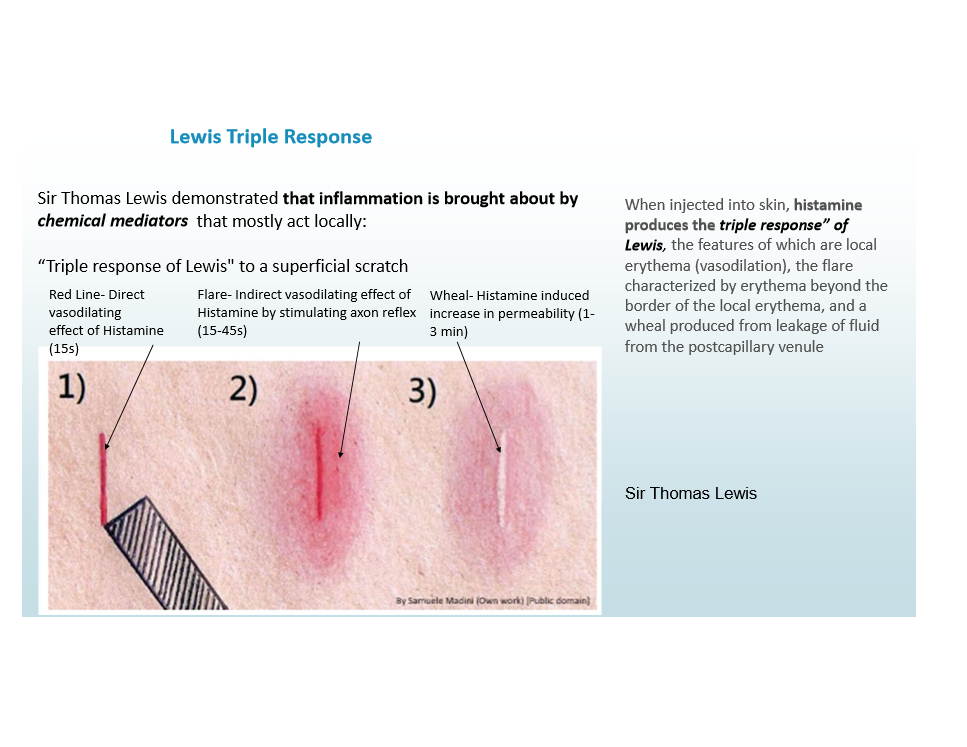
Inflammation
A protective response to eliminate the cause of cell injury and dead cells/tissues, goal is restoring normal tissue function
Fundamentals of inflammation
Components of response
Mediators
Local/systemic
Acute/Chronic
Harmful consequences
Inflammation reaction sequence
Recognition, Recruitment, Removal, Regulate, Repair
Recognition step of inflammation
Offending agent is recognized by host cells/molecules in extravascular tissues
Recruitment step of inflammation
Leukocytes and plasma proteins are recruited from circulation
Removal step of infllammation
Leukocytes and proteins are activated to destroy/eliminate the offender
Regulation step of inflammation
Reaction is controlled/terminated
Repair step of inflammation
Tissue damage is repaired
How does recognition of microbes/damaged cells work?
Initiated by DAMPs and PAMPs, activates inflammasome and IL-1 production
Cellular receptors for recognition
TLRs (pattern recognition)
NLRs (damage sensors)
Fc receptors
Complement
Circulating proteins
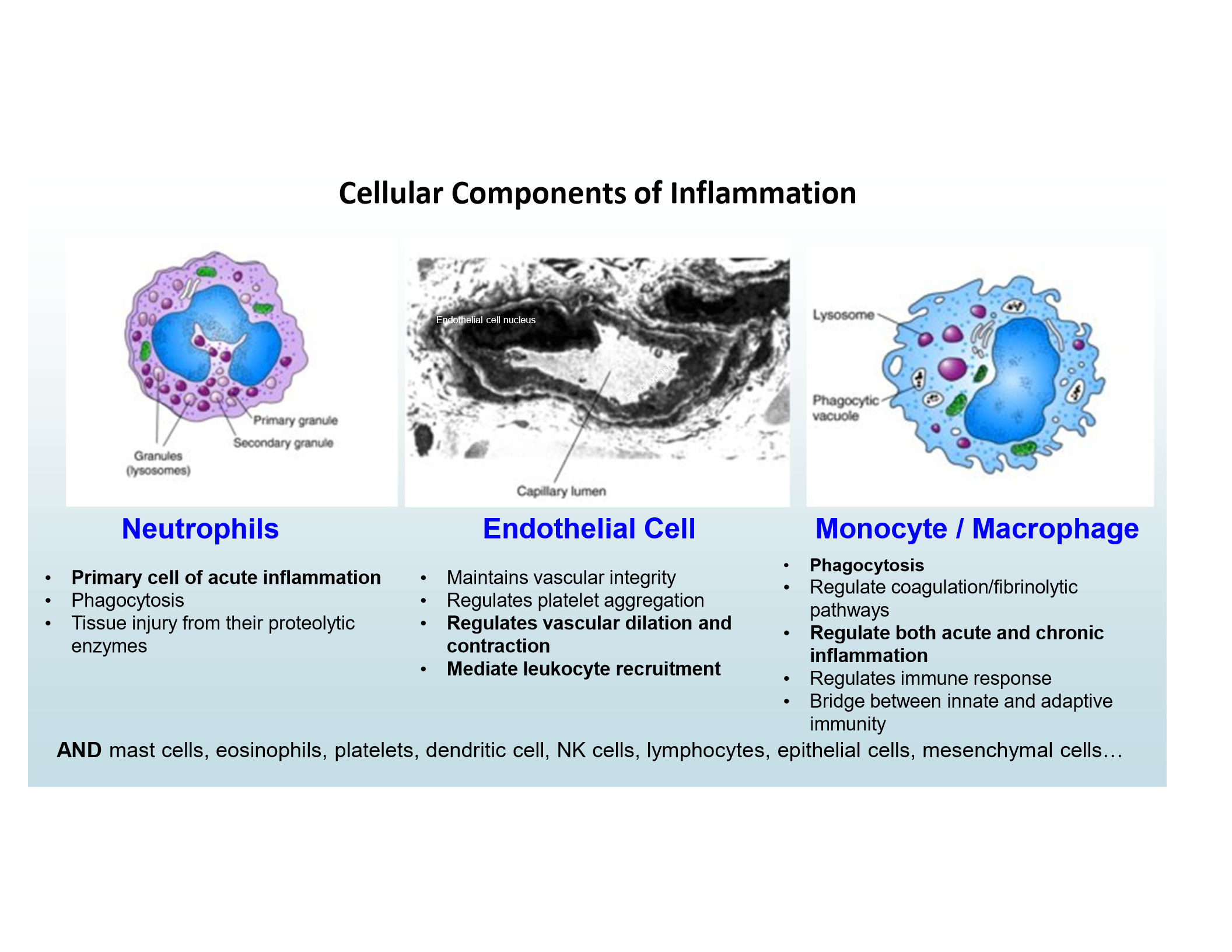
Main inflammatory cells
Neutrophils
Endothelial Cells
Monocytes/Macrophages
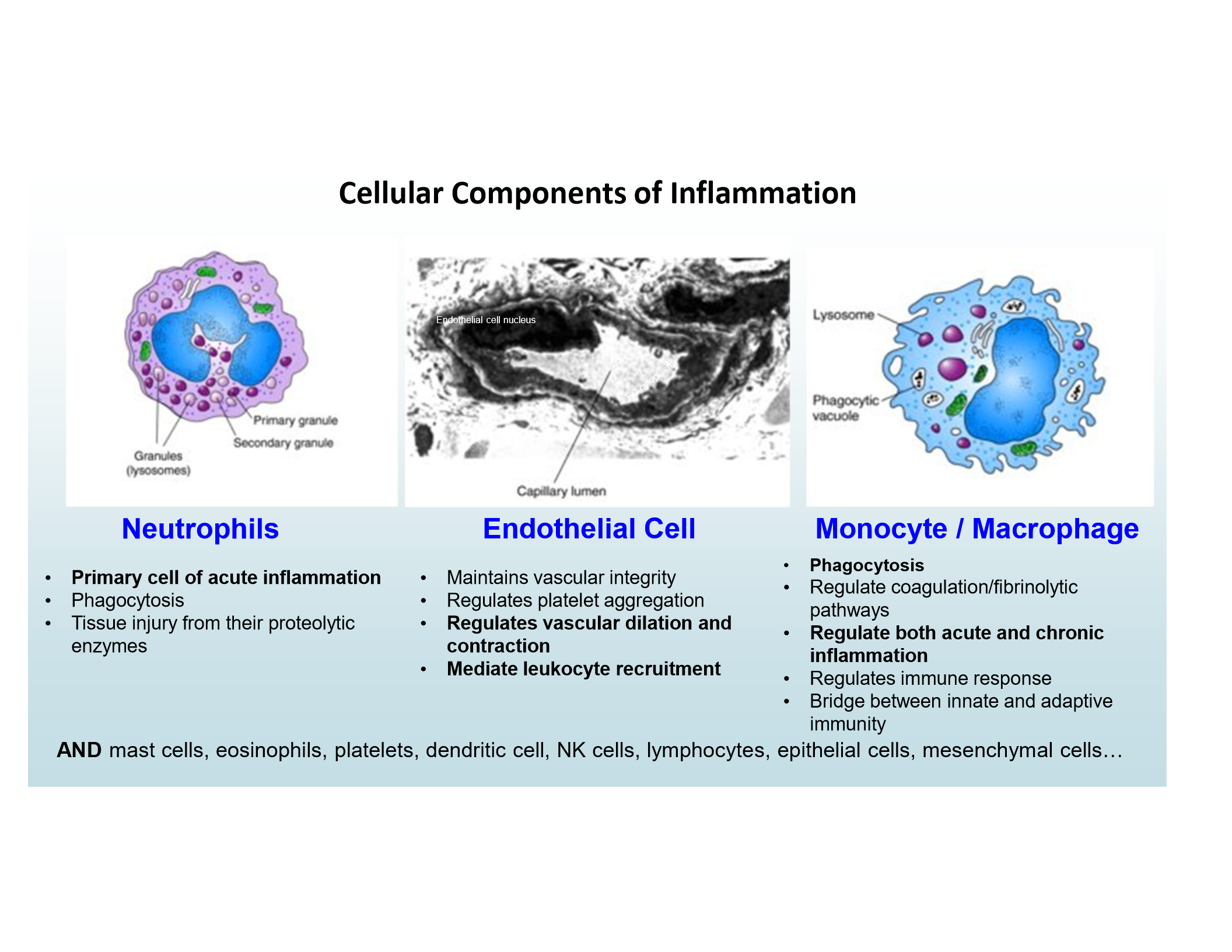
Neutrophils
Primary cell of acute inflammation
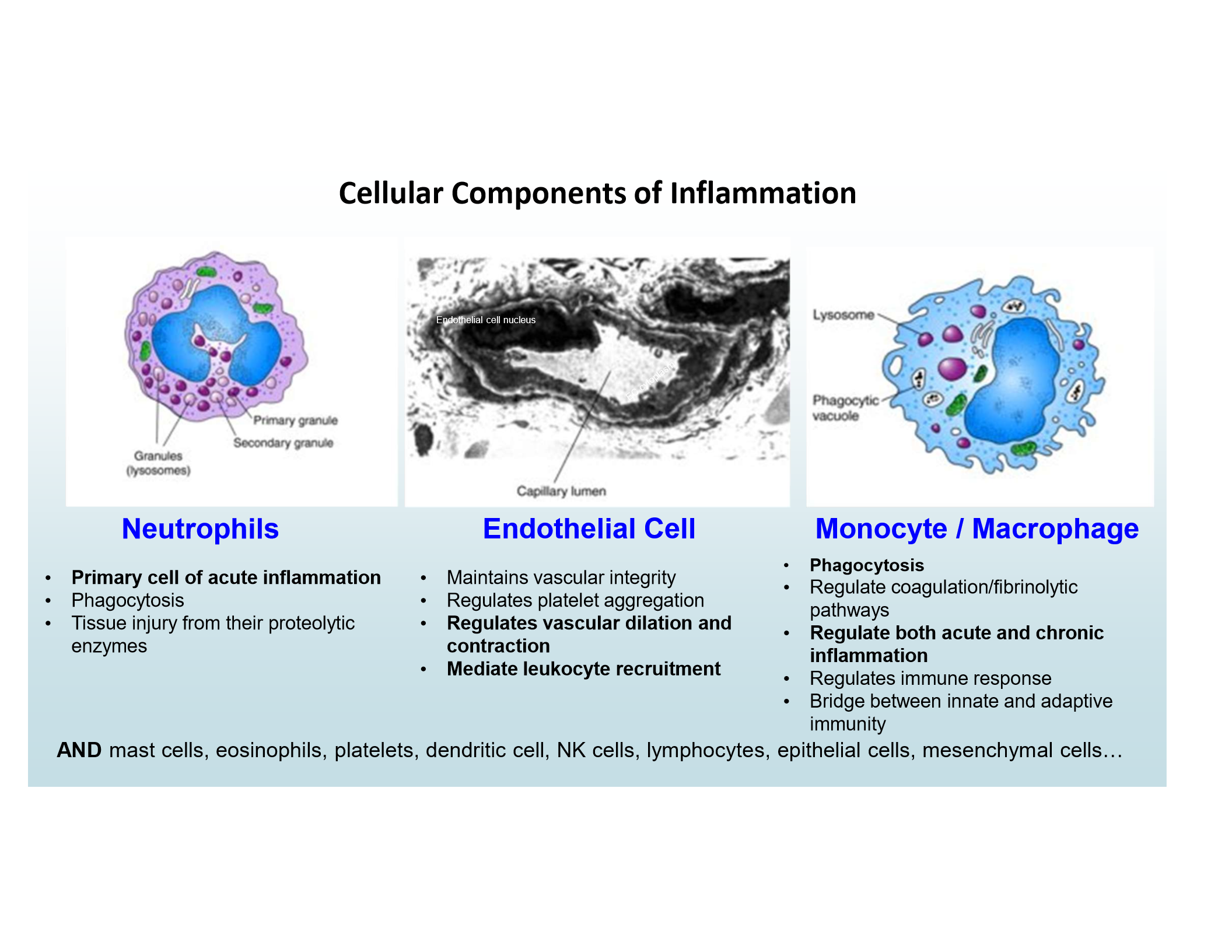
Endothelial Cells
Regulate vascular dilation/contraction, mediate leukocyte recruitment
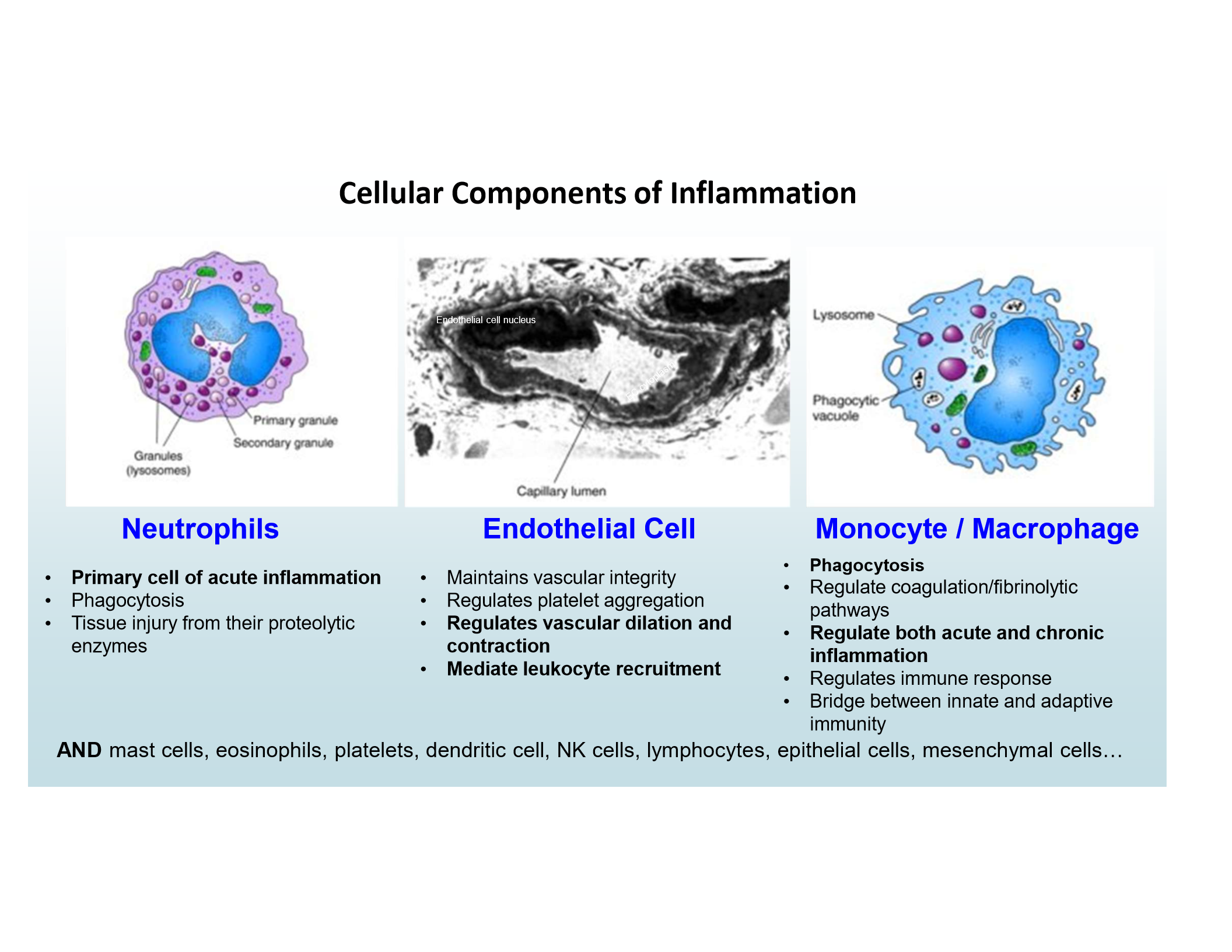
Monocytes/Macrophages
Phagocytosis and regulation of acute/chronic inflammation
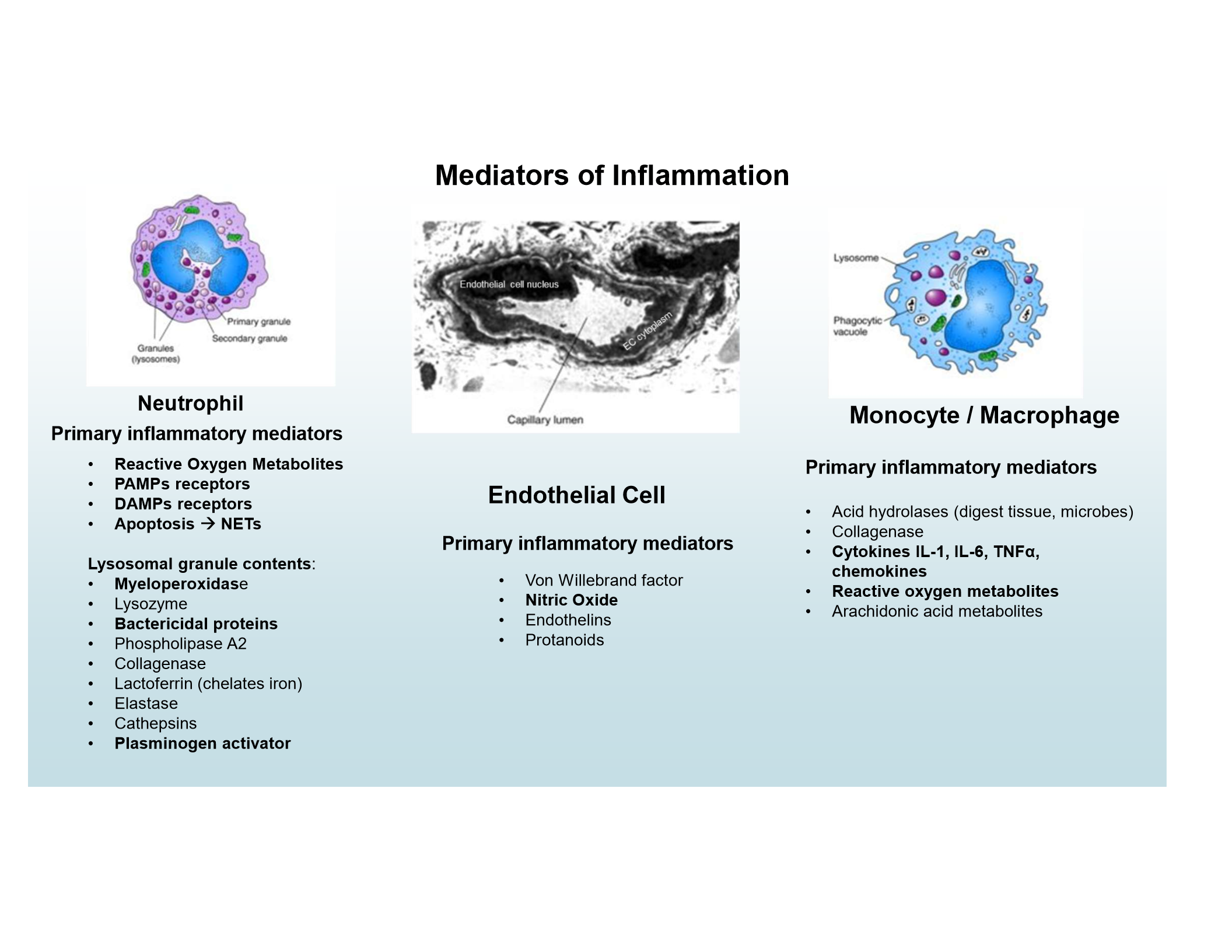
Neutrophil mediators
ROS, PAMP and DAMP receptors, NETs, lysosomal granules (e.g., myeloperoxidase, bactericidal proteins, plasminogen activator)
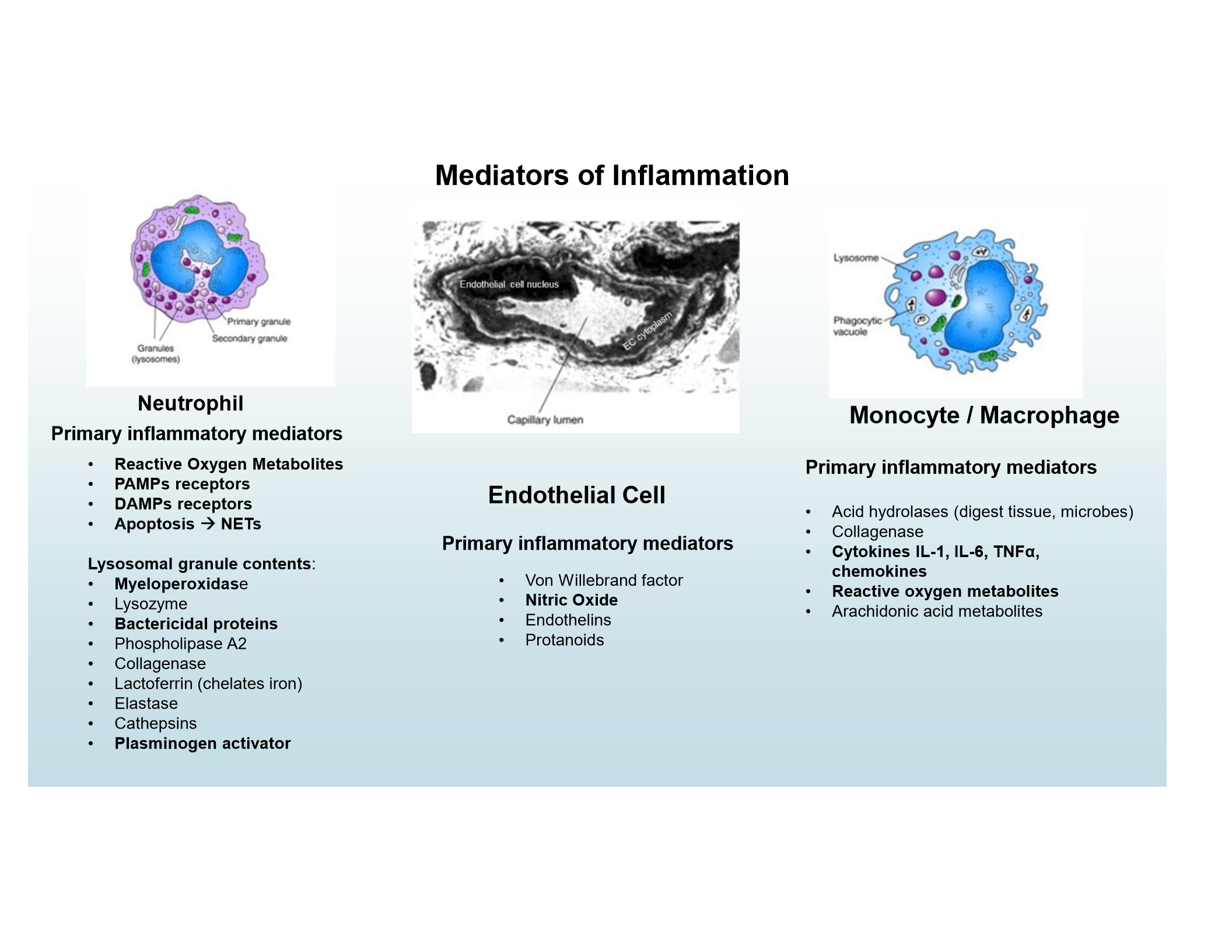
Endothelial mediators
Nitric Oxide
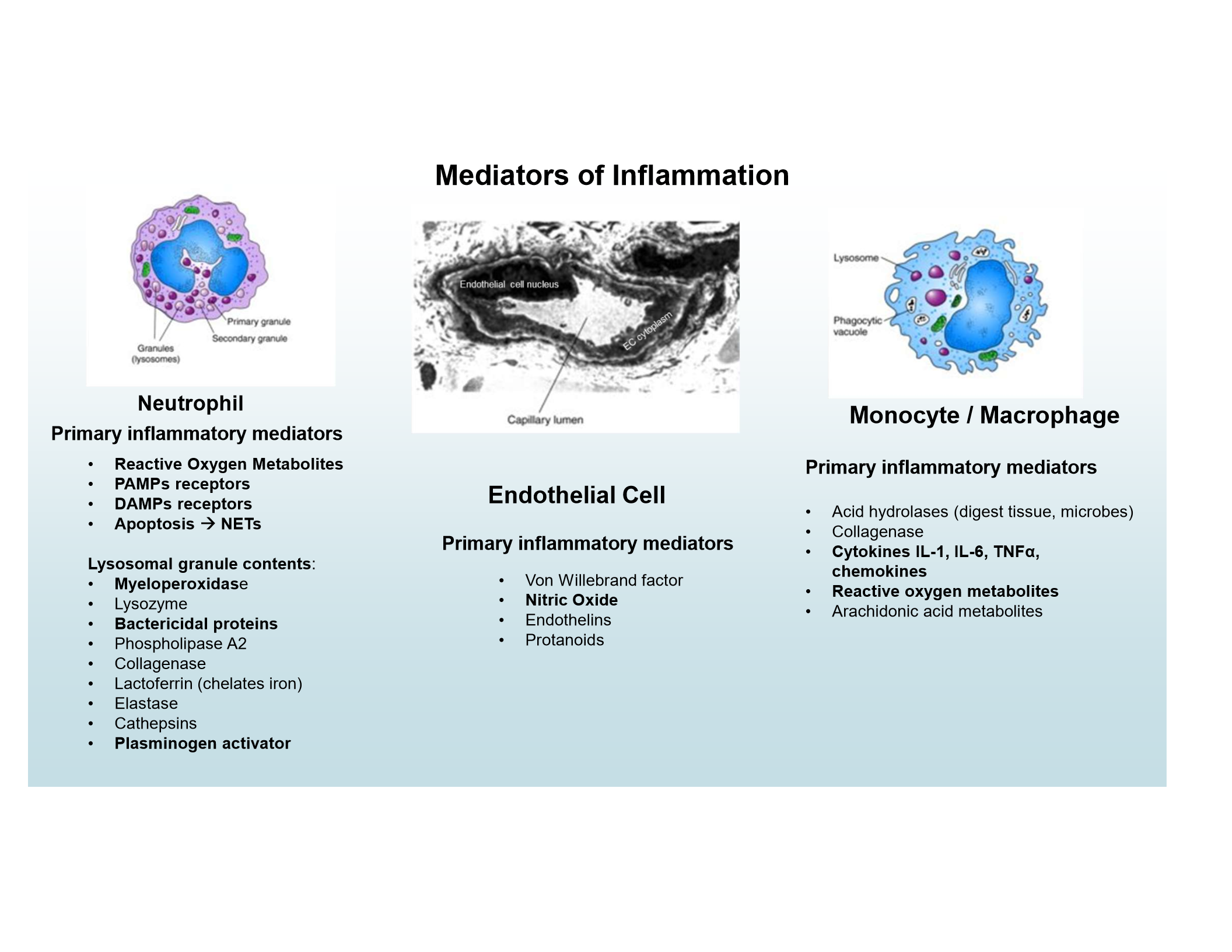
Monocyte/Macrophage mediators
Cytokines (IL-1, IL-6, TNFα), chemokines, ROS
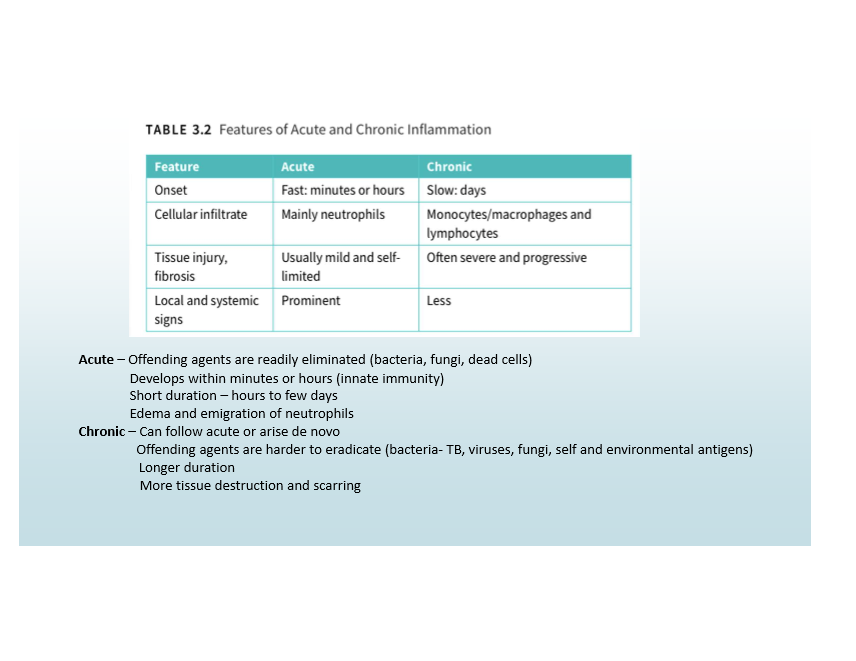
Acute Inflammation
Fast onset, neutrophilic infiltrate, mild/limited tissue injury, prominent signs
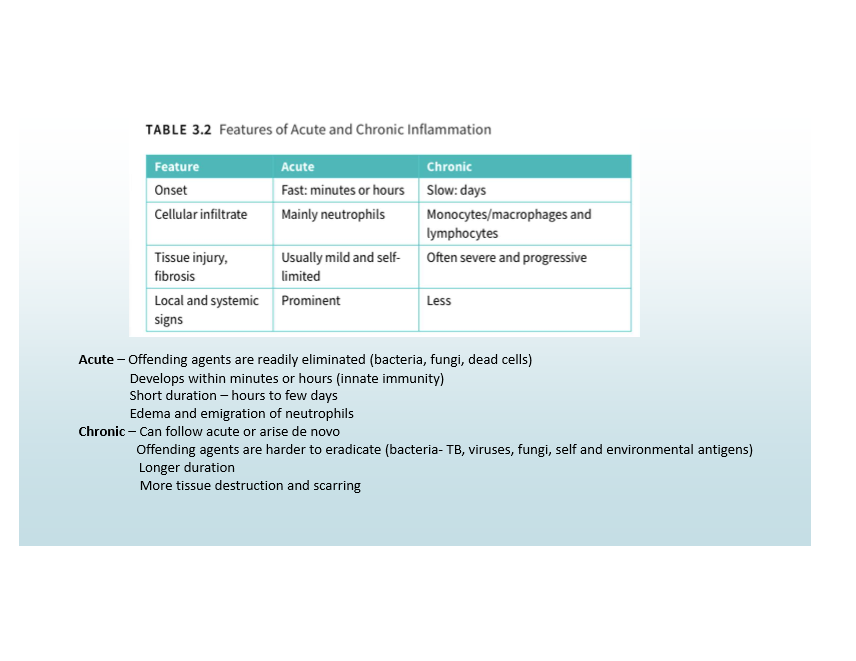
Chronic Inflammation
Slow onset, monocyte/macrophage infiltrate, severe/progressive tissue injury, less obvious signs
Cardinal signs of inflammation
Pain, Heat, Redness, Swelling, Loss of Function
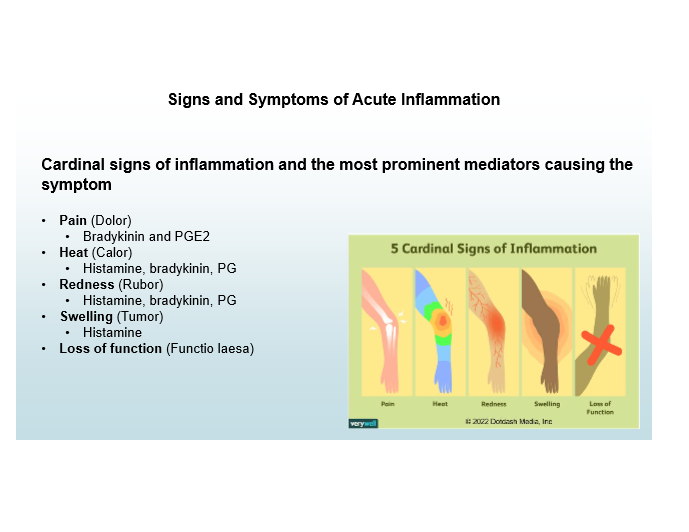
Pain mediators
Bradykinin, PGE2
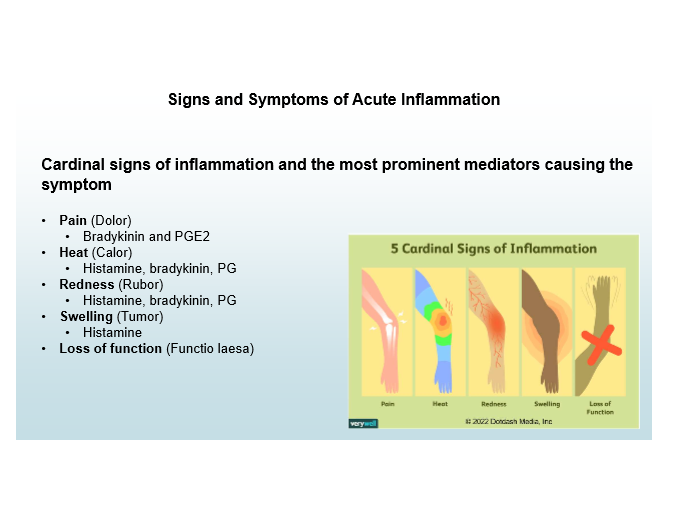
Heat and Redness mediators
Histamine, Bradykinin, Prostaglandins
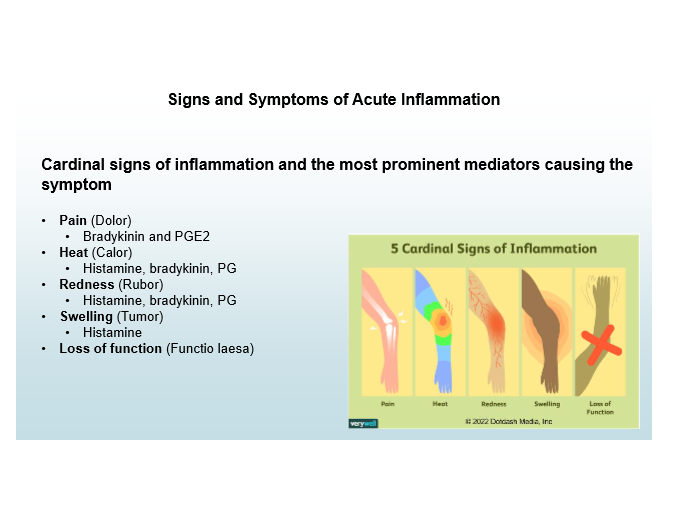
Swelling mediator
Histamine
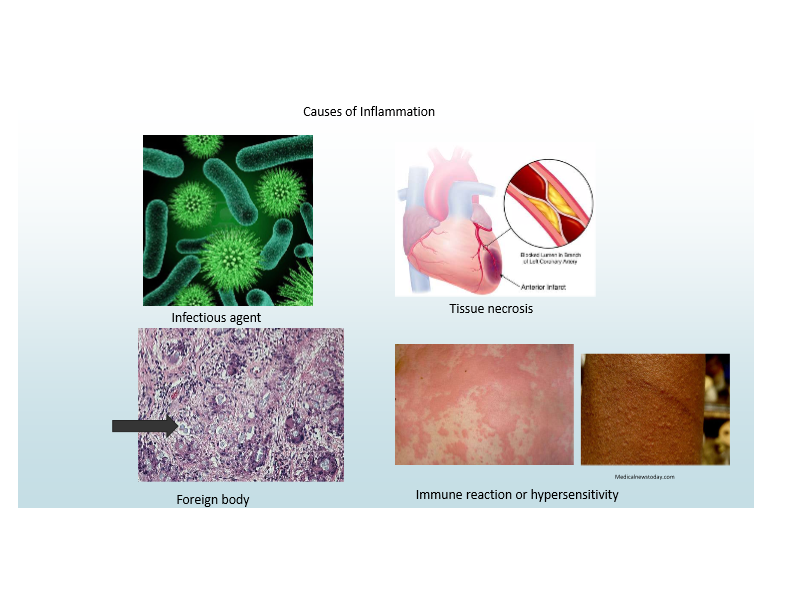
Common causes of inflammation
Infections (PAMPs)
Most common
Tissue necrosis (DAMPs)
Foreign bodies
Immune reactions (hypersensitivity)
Three components of acute inflammation
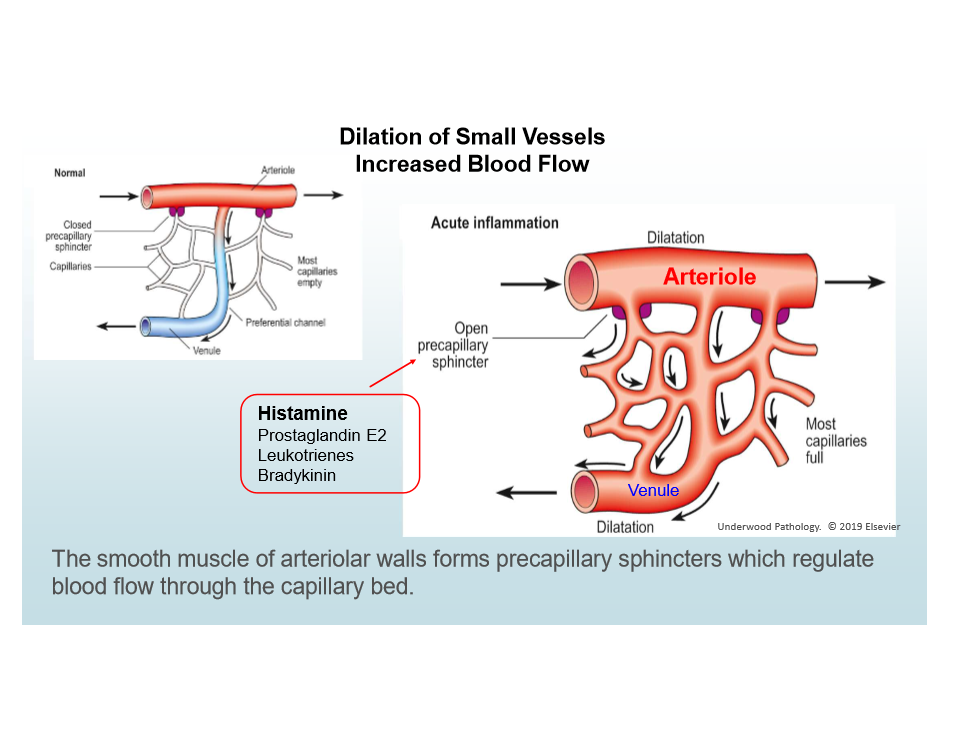
Vasodilation
Increased permeability
Leukocyte emigration
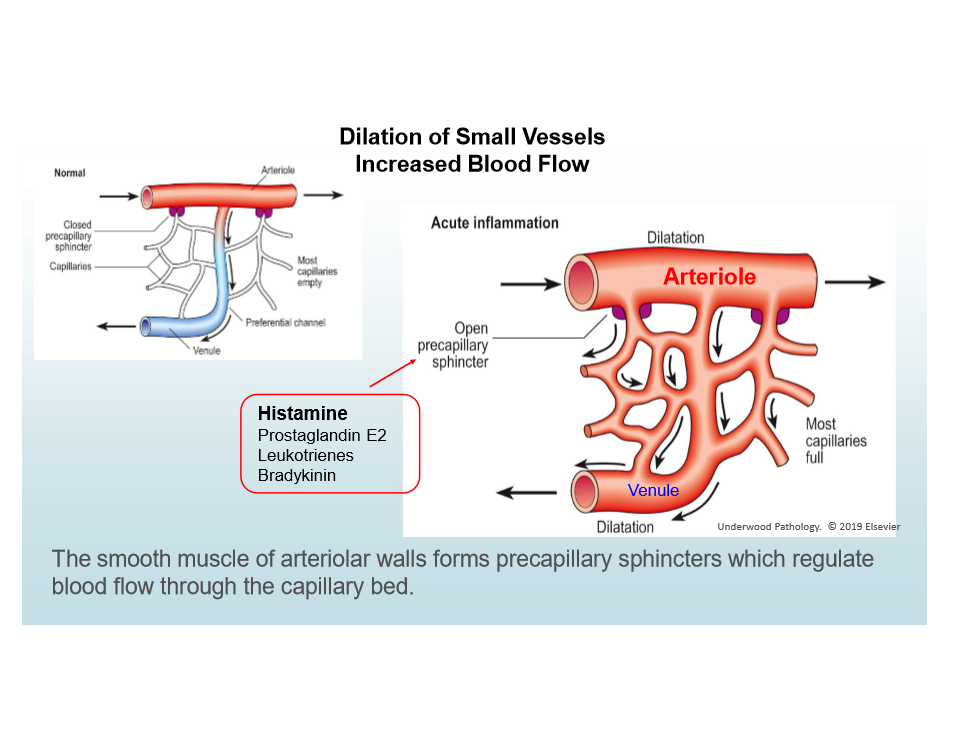
Vasodilation in Acute Inflammatoin
Caused by histamine; increases blood flow; causes heat/redness
Increased vascular permeability in Acute Inflammation
Causes edema; via endothelial contraction or injury
Leukocyte emigration in Acute Inflammation
Leukocytes accumulate at injury site and are activated
Exudation
Escape of fluid, proteins, and blood cells into tissues/cavities
Happens in acute inflammation
Increased vascular permeability cause
Endothelial cell contraction (main), endothelial injury (secondary)
Mediators: histamines, bradykinin, NO, PGs
Exudate
High-protein fluid with cells/debris; implies inflammation and increased vascular permeability
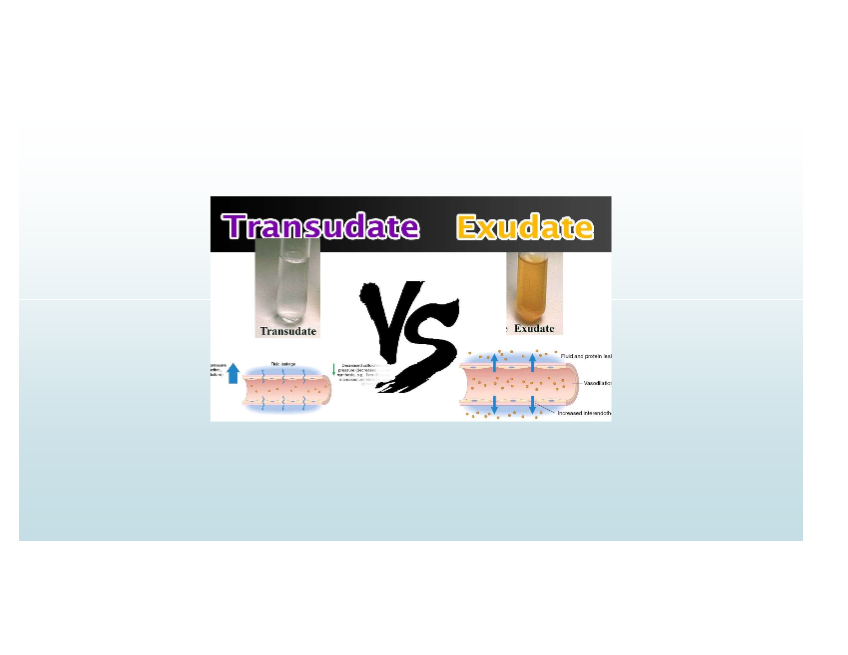
Transudate
Low-protein fluid; caused by osmotic/hydrostatic imbalance; non-inflammatory
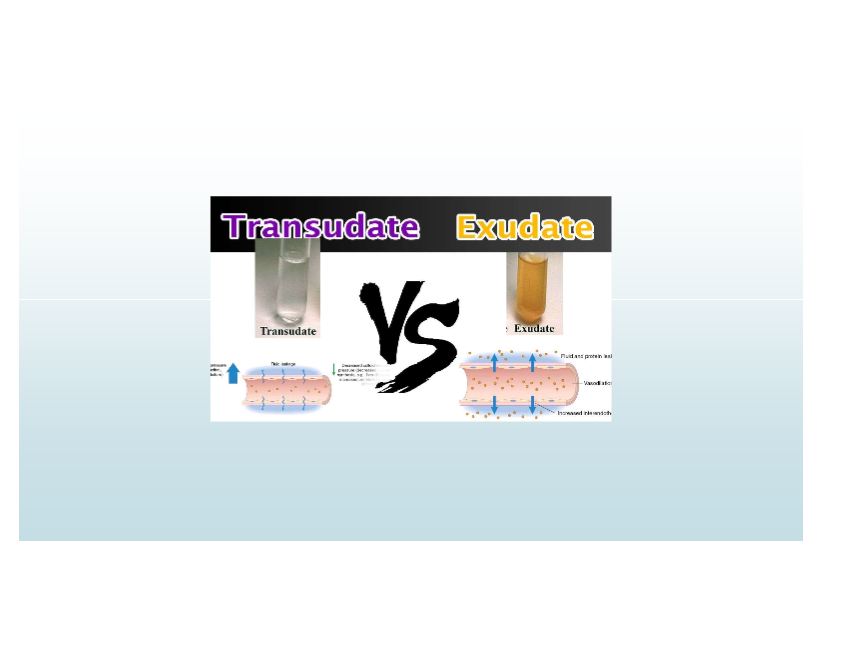
Causes of transudate
CHF (pitting edema), Cirrhosis (ascites fluid)
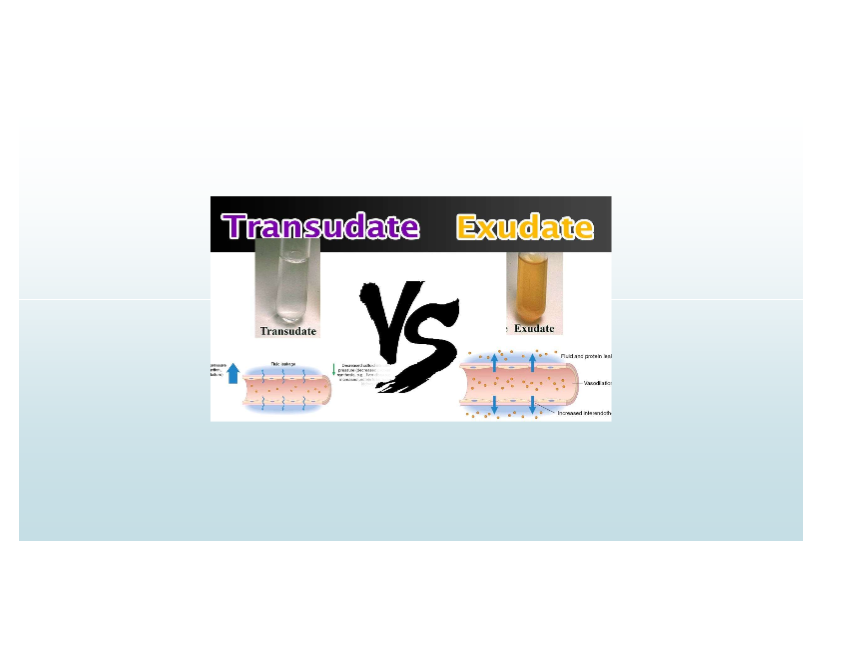
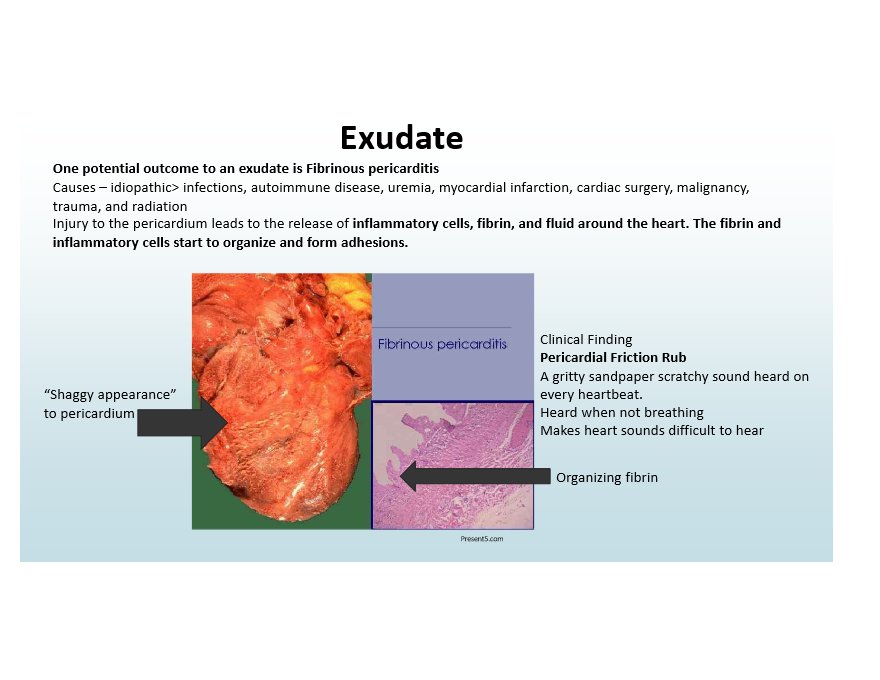
Outcome of exudate
Fibrinous Pericarditis—pericardial friction rub and adhesions
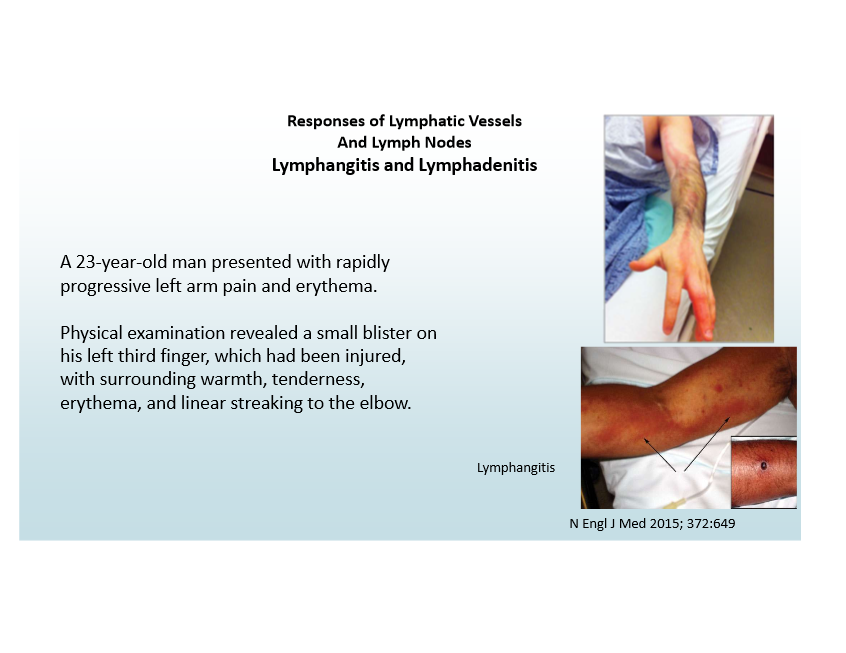
Lymphatic role in inflammation
Can become inflamed (lymphangitis), lymph nodes enlarge (lymphadenitis)
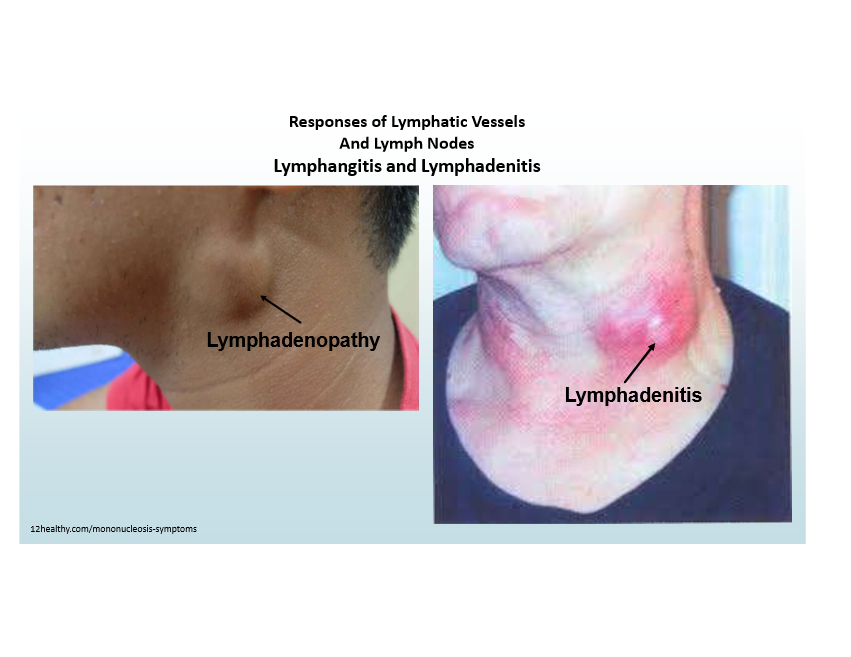
Signs of lymphangitis
Red streaks near wound, painful enlarged lymph nodes
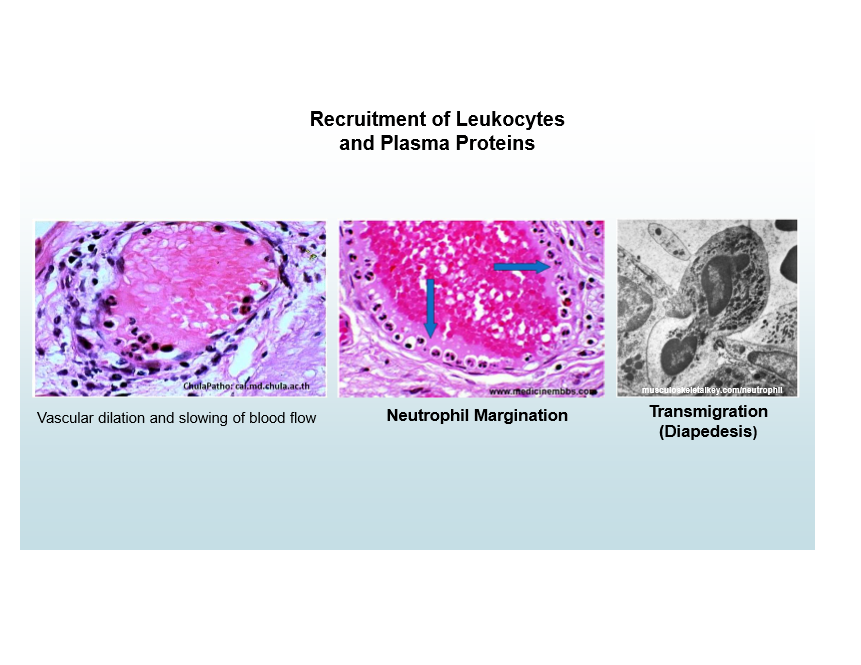
Leukocyte movement
Controlled by adhesion molecules and chemokines

Leukocyte margination and rolling
Along the periphery of vessels
E-selectin and P-selectin

Transmigration mediator
PECAM-1

Integrins role
Enable strong adhesion to endothelial molecules

Initial rolling mediator
Selectins
Firm adhesion mediators
Integrins
Transmigration (Diapedesis)
Migration of leukocytes across endothelium
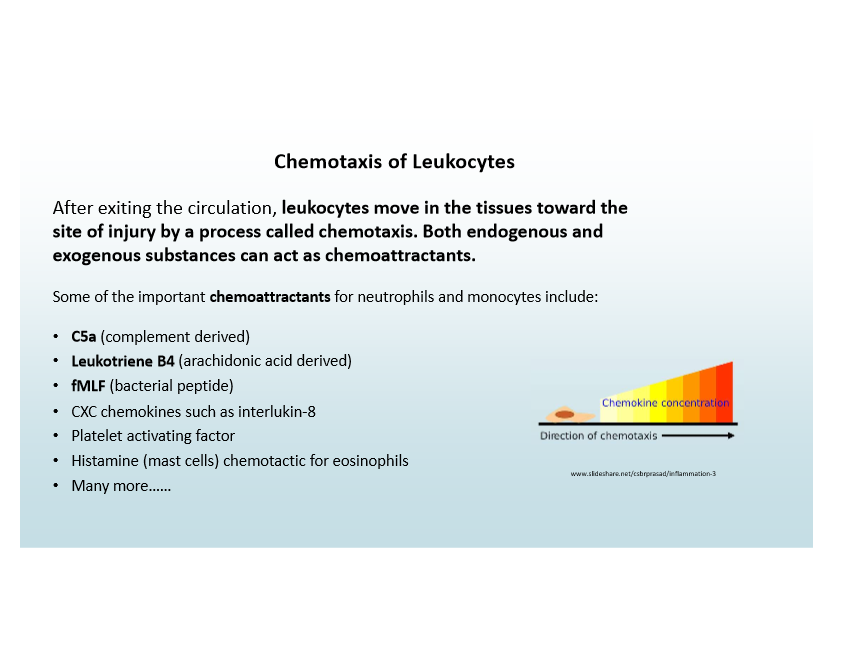
Chemotaxis
Leukocytes move toward injury guided by chemoattractants
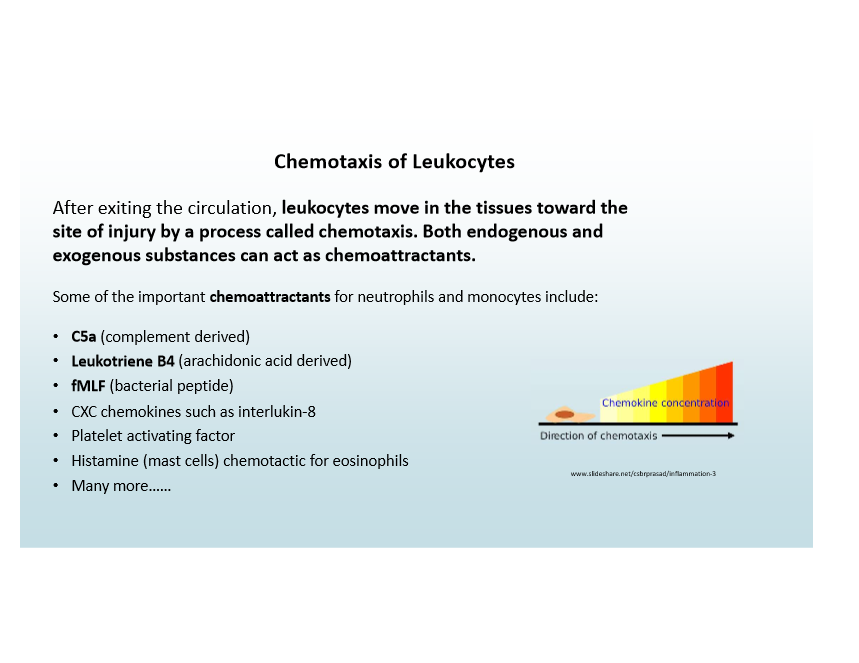
Chemoattractants Examples
C5a (from complement)
Leukotriene B4
fMLF (from bacteria)
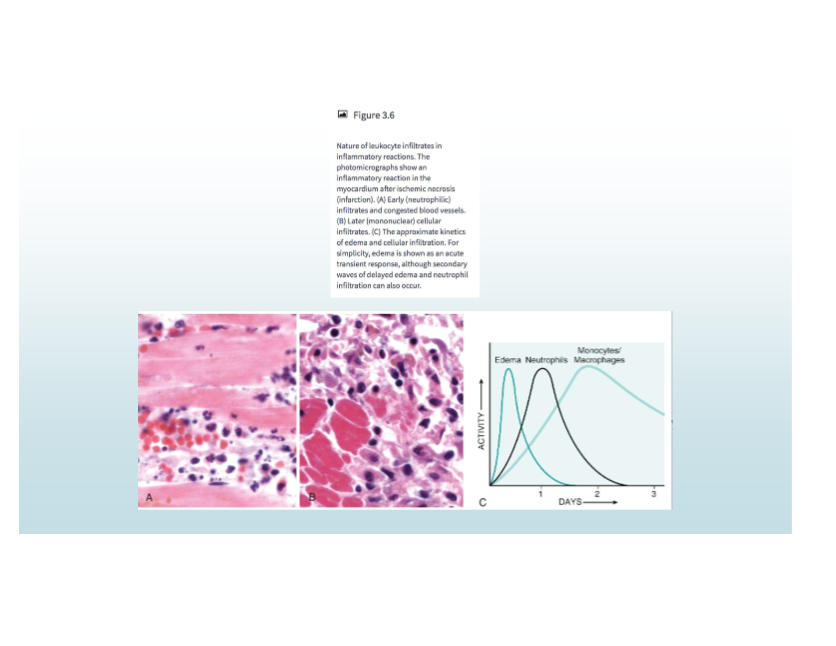
Inflammatory cell timeline
Neutrophils first, then monocytes/macrophages
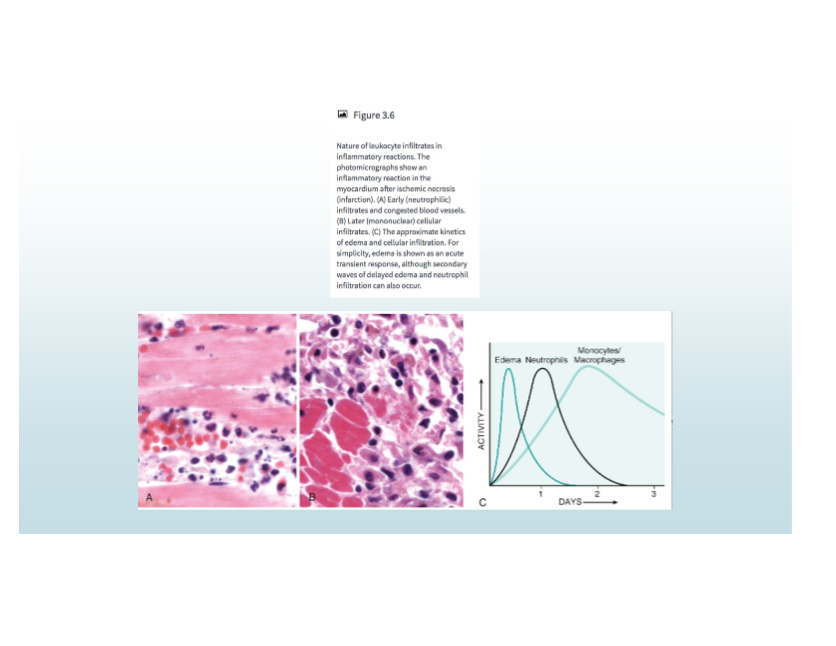
Exceptions to neutrophil-first response in inflammation (and what they’re replaced with)
Pseudomonas (persistent neutrophils)
Viruses (lymphocytes)
Hypersensitivity (lymphocytes/macrophages/plasma cells)
Helminths/allergies (eosinophils)
Function of chemokines
Chemoattractants that cause leukocyte chemotaxis
Major phagocytes in inflammation
Neutrophils and Macrophages
Neutrophil characteristics
Bone marrow origin, short-lived, rapid, ROS use, NETs, lysosomes
Macrophage characteristics
Longer-lived, prolonged response, cytokine production, less ROS
Leukocyte activation
Microbe/dead cell recognition triggers leukocyte response (e.g., Dohl bodies-RNA in activated cell)
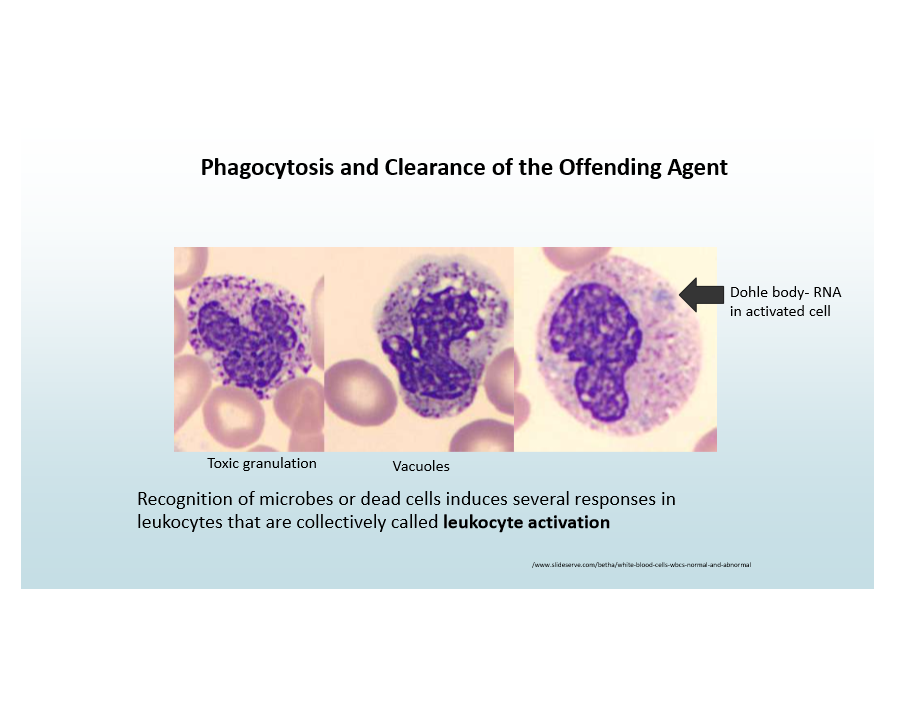
Phagocytosis steps
Recognition/attachment to leukocyte
Engulfment into leukocyte
Killing/degradation
Killing of microbe mechanism
ROS and RNS, lysosomal enzymes for phagocytosed material
When is the efficiency of phagocytosis better?
When microbes are coated with opsonins
C3b
Plasma lectins like mannose-binding-lectin
Immunoglobulin (IgG) reacting with microbe
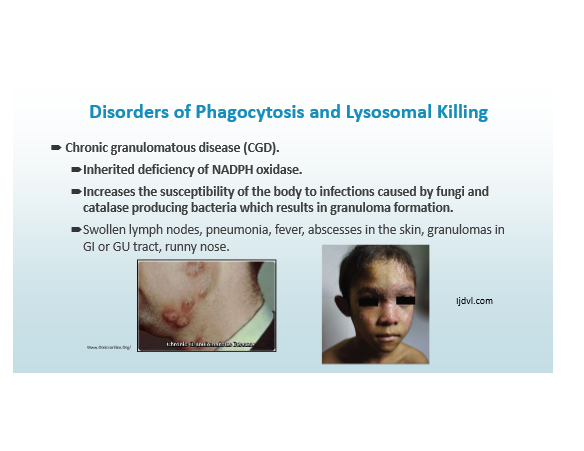
Chronic Granulomatous Disease
Inherited deficiency of NADPH oxidase
Increases susceptibility of body to infections caused by fungi and catalase producing bacteria, resulting in granuloma formation.
Chediak-Higashi Syndrome
Impaired phagocytosis; infections, neutropenia, giant granules, albinism

Myeloperoxidase Deficiency
Reduced killing; severe Candida if diabetic
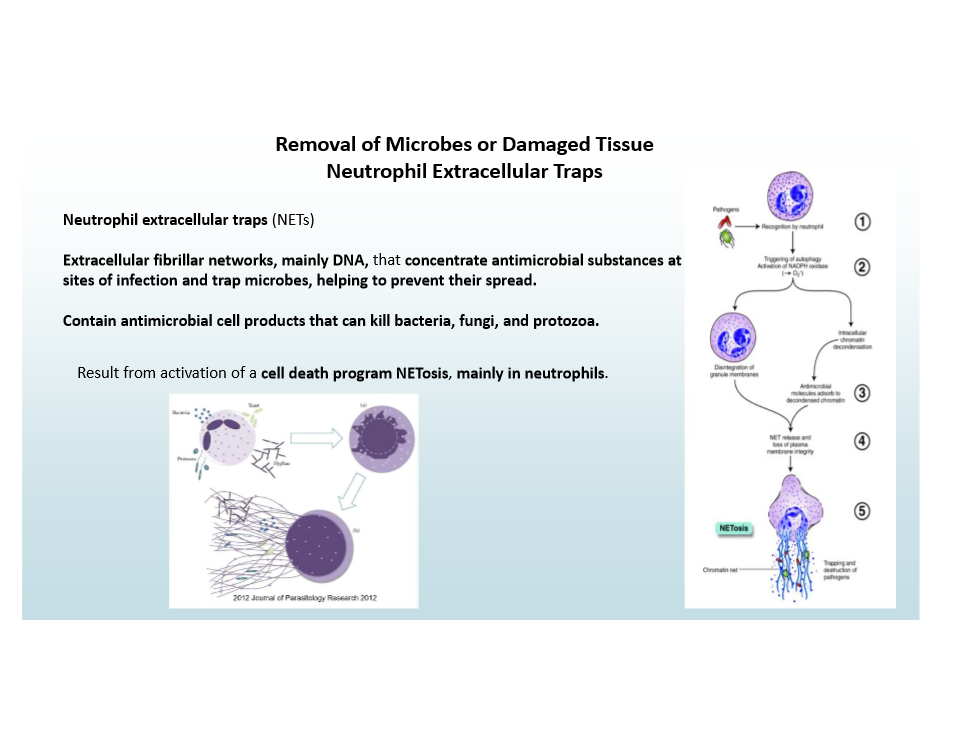
Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs)
Extracellular DNA networks trap/kill microbes
NETosis is activated to cause this!
Leukocyte-mediated injury Mechanisms (3)
Collateral damage to host tissues (ex. TB)
Autoimmunity
Hypersensitivity
How leukocytes damage tissues
Use same mechanisms as in defense (ROS, enzymes)
Inflammation resolution mechanisms
Short half-life mediators
Neutrophil apoptosis
Anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-10, TGF-β)
Switch to lipoxins