AQA GCSE History: Germany
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
When was Germany unified as a nation?
1871
When did Kaiser Wilhelm II come into power?
1888
What were Kaiser's three "great aims" for Germany?
Industrialisation, A Place In The Sun, Control of Political System
When was the first Naval Law introduced?
1898
In what years were old age pensions introduced in Germany?
1889
In which year did Germany overtake Britain in the production of Iron and Steel?
1889
When did World War One start?
1914
When did World War One end?
11th November 1918
What is Weltpolitik?
The policy of participation in world affairs.
Who were the Reichstag?
German Parliament
Who were the Bundesrat?
A group of state sent representatives who helped decide laws
What is Militarism?
The belief a country should have strong armed forces
What problems did Germany face after WW1?
Political Problems (change of government)
Social Problems (families without fathers, brothers etc)
Economic Problems (reparations, loans)
What were the terms of the Treaty of Versailles?
L - Land
A - Army
M - Money
B - Blame (Article 231)
How much land did Germany lose?
13% and 60 million people
What were the limits put on the German army?
No more than 100,000 troops, Conscription was banned, no tanks were allowed, Navy reduced to 15,000, only allowed 6 battle ships and no submarines.
How much money (reparations) did Germany have to pay?
6.6 billion
What did the Germans call the treaty?
Diktat (dictated peace)
What were the Weimar Constitution often described as?
The "November Criminals"
The Weimar Constitution allowed who to vote?
All men and women over the age of 20
What was Article 48?
In an "emergency crisis", it allowed the President to make laws without consulting parliament
What was proportional representation?
The number of seats a party got were proportional to the number of votes they received.
When was the Spartacists Revolt?
1919
What was the Spartacists Revolt?
Communists tried to start a revolution but did not get the support they were hoping for
Who led the Spartacist Uprising?
Karl Liebknecht and Rosa Luxemburg
When did Assassinations on the November Criminals take place?
1919 - 1922
Who mainly assassinated the November Criminals
Right Wing Extremists
When was the Kapp Putsch?
1920
What was the Kapp Putsch?
Wolfgang Kapp marched troops into Berlin and took over the capital, Kapp soon fled abroad
When was the Red Rising In The Ruhr?
1920
What was the red Rising In The Ruhr?
Left wing workers in the Ruhr went on strike
When was the Munich Putsch?
1923 November

What was the Munich Putsch?
Hitler attempted to seize control of Bavarian government and was arrested; his 24-day trial was fully broadcast
During the 1919 - 1923 events of political extremism, who were sympathised?
Right wing were hugely sympathised towards, whereas left wing uprisings were quickly and brutally shut down.
When was Hyperinflation?
1923

Who was hyperinflation a win for?
Those who had borrowed money from the government
Those who had to pay off debts
Who was hyperinflation a loss for?
Those with savings
Those on a fixed income
Small businesses
Economic hardship bred?
Political Extremism
What were the six factors leading to Hitler's rise to power?
The Depression
Unpopular Government
Hitler's Appeal
Fear Of Communism
Role of the SA
Propaganda
Who was in charge of Nazi propaganda?
Joseph Goebbels
In Weimar Culture, what was there none of?
Censorship
What is censorship?
Removing parts of media that are seen as unacceptable
What types of music became popular under Weimar Culture?
Cabaret and Jazz
What did women become in 1920s Germany?
"Untraditional"
What is negative cohesion?
Bringing people together by a shared hatred
What is propaganda?
Information used to promote a political party / view
What is a chancellor?
An important minister who helped the President run the country
Who were the SA?
Hitler's private army
When was the Wall Street Crash?
October 1929
What caused the Wall Street Crash?
Americans hadn't made as much money from their shares as they hoped, so quickly tried to sell them back. Millions couldn't sell them back for how much they paid and were left ruined as debt collectors took their homes.
What agreement in 1925 demonstrated that Germany was now a friendly power by guaranteeing borders with France and Belgium?
Locarno pact
Which agreement of 1928 was signed by 64 countries and promised to solve disputes by peaceful means?
Kellogg-Briand pact
Who was foreign minister between 1924 - 1929?
Gustav Stresemann
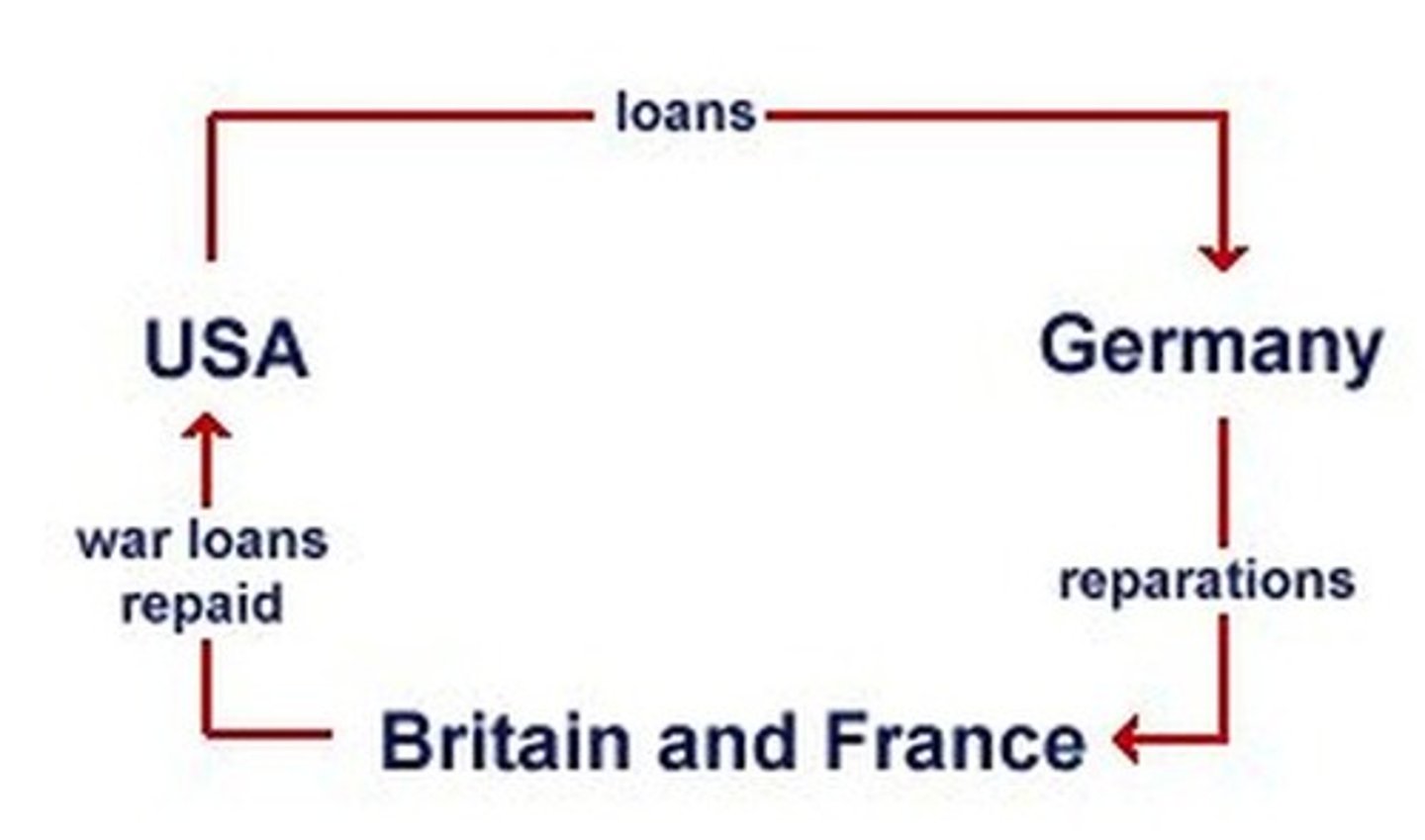
What was the Dawes Plan?
It was a American's investors plan to find a way for the German's to continue to pay reparations.
When was the Dawes plan?
1924
How much money did the Dawes plan give Germany in marks?
800 million marks
Thanks to American loans, what was Stresemann able to do?
Create international relations and industrialise. This created lots more job opportunities
Many people thought Stresemann put "wallpaper over cracks", why?
Too reliant on American loans and unemployment increased
What plan reduced reparations in 1929?
Young plan
How much did the Young plan reduce reparations to?
£2 billion
Who was Chancellor from March 1930- May 1932 (during the Great Depression)?
Bruning
In the early 1930s, what did Chancellor Bruning try to pursue?
A tough economic policy - he stopped paying reparations and introduced tariffs to protect German farmers.
What was the problem with Bruning's tough economic policy?
It had no short term effects, so Bruning received criticism
The Reichstag called new elections in 1930, which were disastrous. What did this allow Hitler to do?
Exploit the fear in Germany
How many seats in the Reichstag did the Nazi's get in November 1932?
196
Who became chancellor in May 1932?
Franz von Papen
Franz von Papen was unable to rule effectively, so called another election when?
July 1932
Who became chancellor in December 1932?
Kurt von Schleicher
Why was Kurt von Schelicher's reign so short?
Forced to resign
When was Hitler appointed as Chancellor?
30th January 1933

How many people were unemployed by the time Hitler came to power(January 1933)?
6 million
When was the Reichstag Fire?
27th February 1933
Who was found at the scene of the Reichstag Fire?
Marinus van der Lubbe
What law did Hitler pass in March 1933? What power allowed him to do this? What did this do?
Law for the Protection of the People and the State (allowed to pass because of Article 48) which allowed him to ban the Communist Party.
After the 1933 election, what percentage of the votes did the Nazi party have?
44%
Thanks to proportional representation, who did the Nazi party team up with in order to gain a majority?
Nationalist party
Catholic Centre party
When was the Enabling Act?
1933
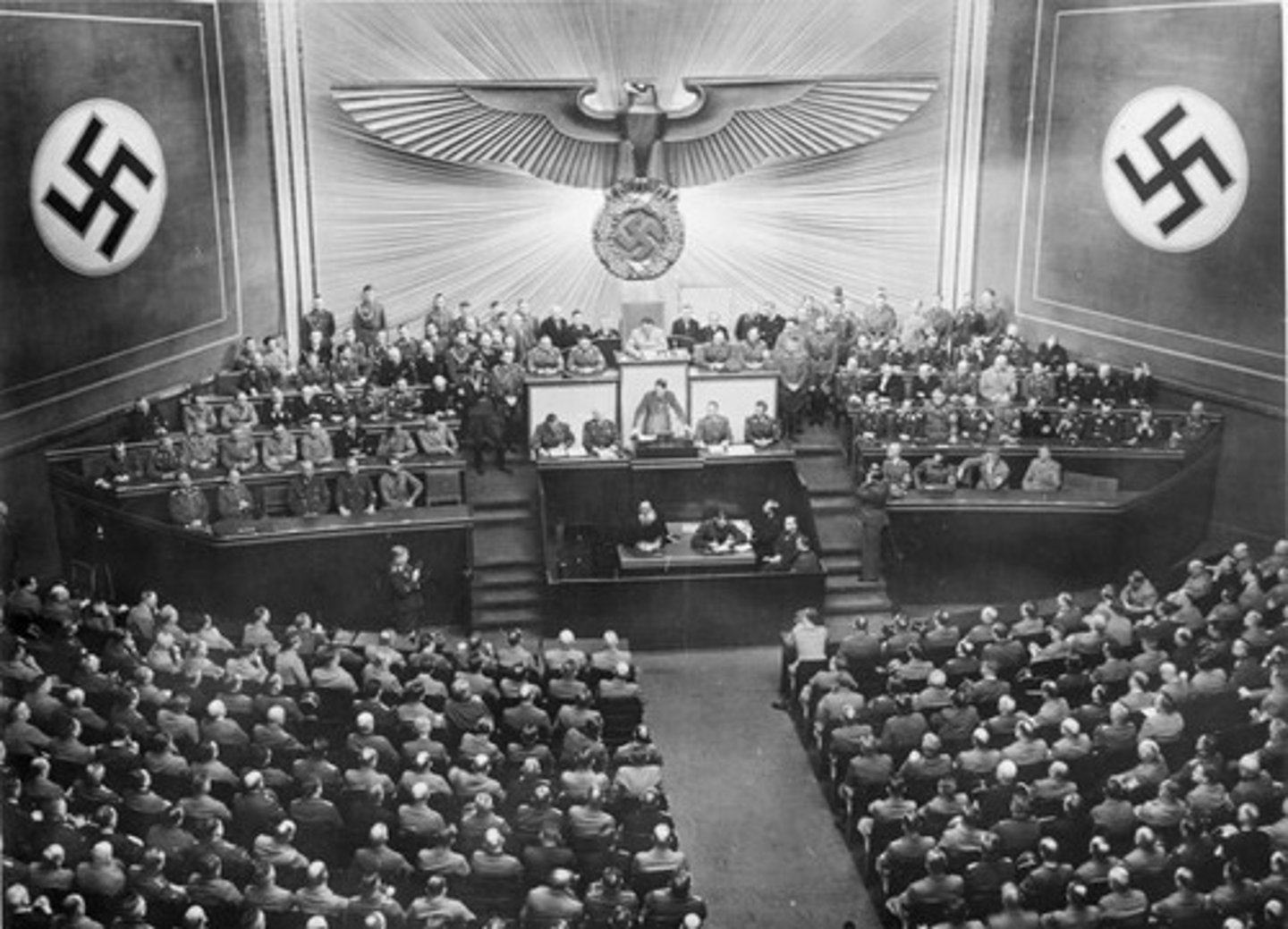

What was the Enabling Act?
A law that allowed Hitler to close down the Reichstag, trade unions and opposition parties. This Act gave Hitler the right to make laws without the Reichstag's approval for the next four years.
Who was the leader of the SA?
Ernst Rohm
When was the Night of the Long Knives?
30th June 1934
When did President Hindenburg die?
2nd August 1934
After Hindenburg's death, Hitler gave himself a new title. What was this title?
The Fuhrer
After Hindenburg died, what did Hitler do in order to gain the loyalty of the army?
Army Oath
How do the Nazis manage unemployment rates?
Remove women and Jews from statistics
Rearmament and Conscription introduced
Reich Labour Service (RAD)
When were conscription and rearmament introduced?
1935
In what city did the Nazi's hold a rally in every August?
Nuremberg
What was the Beauty of Labour Movement?
Improved working conditions
What was the Strength Through Joy Movement?
Organised leisure time for workers
What was the Reich Food Estate?
Farmers can sell produce at a guaranteed price

What is the Reich Entitled Farm Law?
Gives farmers state protection for their farms
What was the 'Blood and Soil' programme?
Protects the farmers pleasant way of life and makes them feel important

When was rationing introduced?
1939
How many Germans flee from East to West in WW2?
3 million
Who were the SS?
Hitler's personal army

What is Autarky?
Self-sufficiency. When a country doesn't need to trade / import
Who was appointed Economics minister in 1937 with the goal of achieving 'Autarky'?
Hermann Göring
What is Lebensraum?
Living space. Nazis invaded countries and stole materials
What is conscription?
Compulsory enrolment into the army
What was the 'Law for the Encouragement of Marriage'?
Couples were given 1000 marks when they got married and were allowed to keep 250 marks for every child they had
What was the 'Honour Cross of German Mothers'?
Allowed women to receive awards for how many children they had