The Cell : Cellular Respiration
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/89
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:41 AM on 2/15/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
1
New cards
Metabolism
an emergent property of life that arises from interactions between molecules within the cell
2
New cards
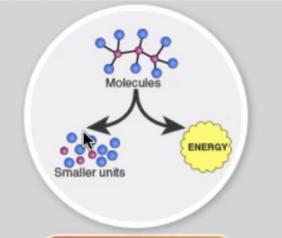
Catabolic pathways
release energy by breaking down complex molecules into simpler compounds.
3
New cards
Cellular respiration
the breakdown of glucose in the presence of oxygen, is an example of a pathway of catabolism
4
New cards
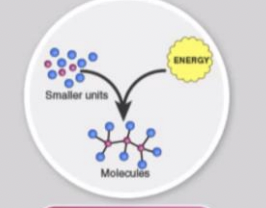
Anabolic Pathways
consume energy to build complex molecules from simpler ones
5
New cards
Synthesis of protien
from amino acids is an example of anabolism
6
New cards
Bioenergetics
the study of how organisms manage their energy resources
7
New cards
Kinetic Energy
energy associated with motion
8
New cards
Energy
the capacity to cause change
9
New cards
Heat (thermal energy)
is kinetic energy associated with random movement of atoms to molecules
10
New cards
Potential Energy
is energy that matter possesses because of its location of structure
11
New cards
Chemical Energy
potential energy available for release in a chemical reaction
12
New cards
Thermodynamics
study of energy transformations
13
New cards
Isolated system
isolated from its surroundings
14
New cards
Open system
energy and matter can be transferred between the system and its surroundings
15
New cards
First Law of Thermodynamics / Principle of conservation of energy
Energy can be transferred and transformed, but it cannot be created nor destroyed
16
New cards
Second Law of Thermodynamics
every energy transfer or transformation increases the entropy (disorder) of the universe
17
New cards
Free Energy Change (Delta G)
A living system’s free energy is energy that can do work when temperature and pressure are uniform as in living cell
18
New cards
Negative delta G (Triangle G)
Initial state to finale state (hint delta G)
19
New cards
Exergonic reaction
proceeds with a net release of free energy and is spontaneous
20
New cards
endergonic reaction
absorbs free energy from its surroundings and is non spontaneous
21
New cards
Endergonic Reaction (will require energy)
What type of reaction is anabolism?
22
New cards
Exergonic Reaction (will release energy)
What type of reaction is catabolism?
23
New cards
closed
Reactions in a (--------) system eventually reach equilibrium and then do no work
24
New cards
Never
metabolism is (----) at equilibrium
25
New cards
catabolic pathway
(-----) in a cell releases free energy in a series of reactions
26
New cards
open systems
Cells are (-------------) experiencing a constant flow of materials
27
New cards
Enzymes
speed up metabolic reactions by lowering energy barriers
28
New cards
Catalyst
a chemical agent that speeds up a reaction without being consumed by the reaction
29
New cards
Enzyme
is a catalytic protein.
30
New cards
Hydrolysis
example of an enzyme catalyzed reaction
31
New cards
TRUE
All enzymes are proteins but not all proteins are enzymes
32
New cards
free energy of activation, or activation energy (EA).
initial energy needed to start a chemical reaction
33
New cards
lowering
Enzymes catalyze reactions by (-------) the EA barrier
34
New cards
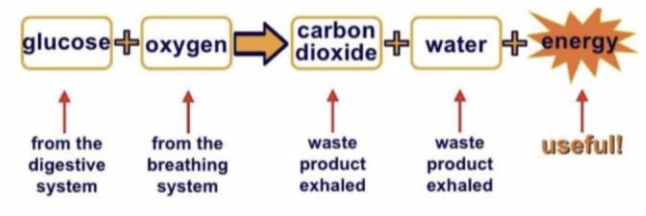
Respiration
the process that the body uses to release energy from digested food (glucose)
35
New cards
Respiration
the reverse reaction of photosynthesis
36
New cards
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
Energy source for all cells. Considered the “energy currency” of the cell.
37
New cards
Adenosine Diphosphate (ADP)
when ATP is converted into (--------) it releases large amounts of energy
38
New cards
Redox Reactions
transfer of electrons during chemical reactions releases energy stored in organic molecules
39
New cards
Oxidation
a substance loses electrons, or is oxidized
40
New cards
Reduction
a substance gains electrons, or is reduced (the amount of positive charge is reduced)
41
New cards
Reducing Agent
the electron donor
42
New cards
Oxidizing agent
electron receptor
43
New cards
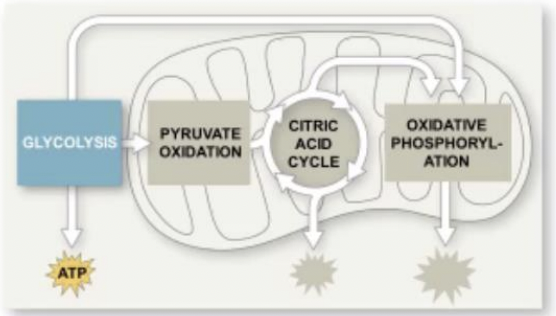
Three
How many stages are there to harvest energy from glucose ?
44
New cards
Glycolysis
Stage in harvesting energy from glucose where the breaking down of glucose into two molecules of pyruvate happens
45
New cards
The citric acid cycle
Stage in harvesting energy from glucose where the completion of breakdown of glucose happens
46
New cards
Oxidative phosphorylation
Stage in harvesting energy from glucose where most of the ATP synthesis (90%) happens
47
New cards
Glycolysis
(“sugar splitting”) breaks down glucose into two molecules of pyruvate
48
New cards
Pyruvate
Glycolysis breaks down glucose into two molecules of (------)
49
New cards
two molecules
Glycolysis breaks down glucose into (----) molecules of pyruvate
50
New cards
Glycolysis
occurs whether or not O2 is present
51
New cards
Energy investment phase & Energy payoff phase
Two major phases of glycolysis
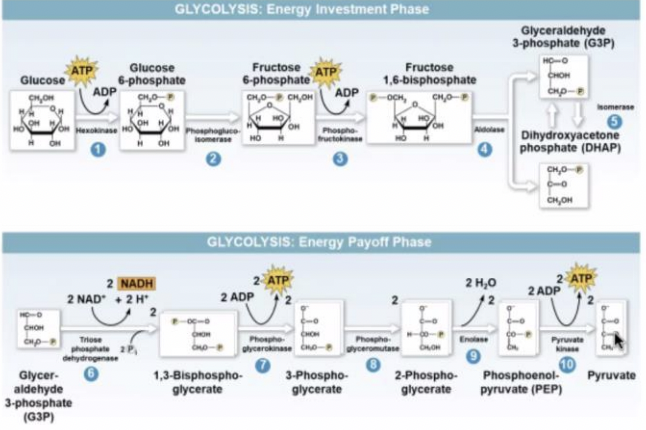
52
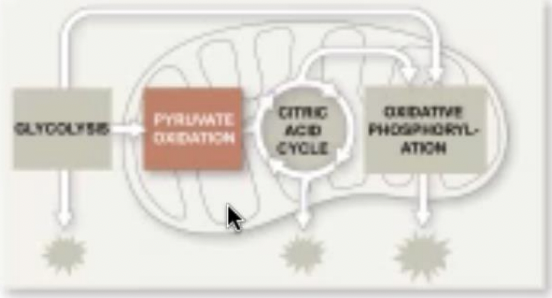
New cards
Mitochondrion
where pyruvate enters in the presence of oxygen & where oxidation of glucose is completed
53
New cards
acetyl coenzyme A (Acetyl CoA)
pyruvate is converted to (------) to begin the citric acid cycle
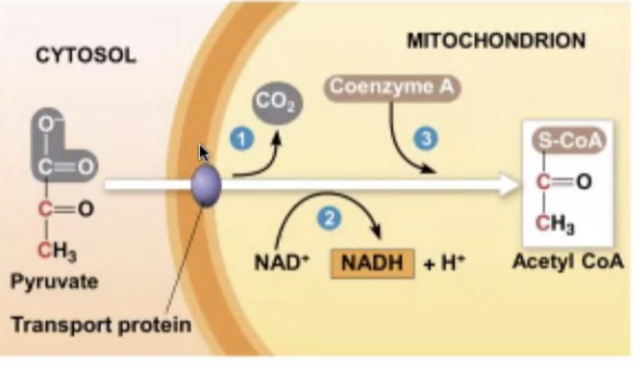
54
New cards
Fermentation and anaerobic respiration
enable cells to produce ATP without the use of oxygen.
55
New cards
anaerobic respiration or fermentation
glycolysis couples with (-------) to produce ATP
56
New cards
Anaerobic respiration
uses an electron transport chain with a final electron acceptor (ex. sulfate)
57
New cards
Fermentation
uses substrate-level phosphorylation instead of an electron transport chain to generate ATP
58
New cards
eight steps
How many steps are there in the citric acid cycle?
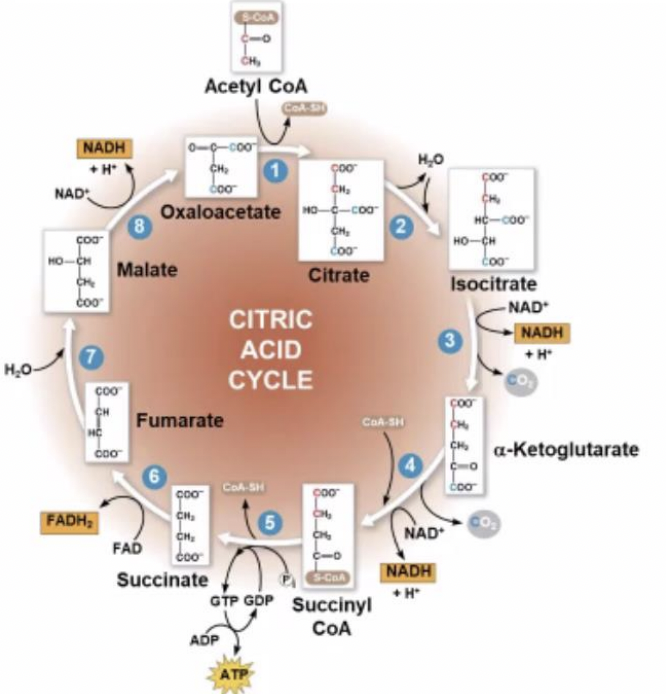
59
New cards
NADH and FADH 2
produces by the cycle relay electrons extracted from food to the electron transport chain
60
New cards
oxidative phosphorylation
NADH and FADH 2 then donate electrons to the electron transport chain which powers ATP synthesis via (-----)
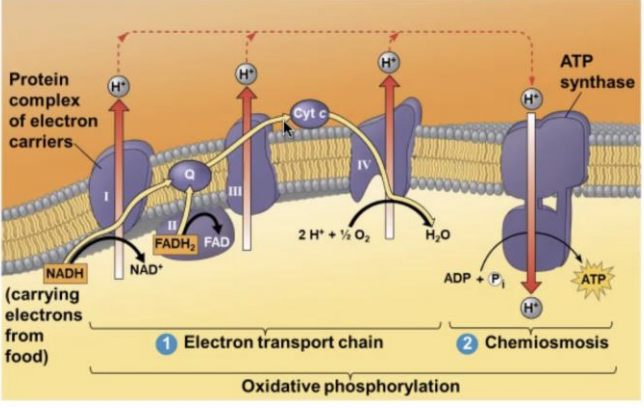
61
New cards
yes
Can we catabolize other macromolecules other than glucose?
62
New cards
Proteins
is digested to amino acids; amino groups can fee glycolysis or the citric acid cycle
63
New cards
Fats
are digested to glycerol (used in glycolysis) and fatty acids (used in generating Acetyl CoA)
64
New cards
1 glucose, 2 ADP, 2 ATP, 2 NAD+
what are the reactants of glycolysis?
65
New cards
2 ATP
how many atp will glycolysis produce?
66
New cards
2 NADH
how many NADH will glycolysis produce?
67
New cards
2 pyruvate
how many pyruvate will glycolysis produce?
68
New cards
acetyl COA
pyruvate oxidation in glycolysis is where 2 pyruvate produces 2 what ?
69
New cards
2NADH
pyruvate oxidation in glycolysis is where (-----) is produces
70
New cards
2 pyruvate, 2 coA, & 2NAD+
what are the reactants of pyruvate oxidation?
71
New cards
2 CO2
pyruvate oxidation produces how many CO2?
72
New cards
2 acetyl coA
pyruvate oxidation produces how many acetyl coA?
73
New cards
2 NADH
pyruvate oxidation produces how many NADH?
74
New cards
Krebs Cycle / Citric Acid Cycle
the main purpose of this cycle is to make NADH & FADH
75
New cards
cytoplasm / cytosol
where does glycolysis takes place?
76
New cards
Anaerobic (does not need oxygen)
is glycolysis anaerobic / aerobic?
77
New cards
mitochondria
where does pyruvate oxidation occurs?
78
New cards
aerobic (needs oxygen)
is citric acid cycle aerobic or anaerobic?
79
New cards
2 acetyl coA, 6 NAD+ & 2 FAD+
what are the reactants of citric acid cycle?
80
New cards
6 NADH &. 2 FADH
how many NADH &. FADH does citric acid cycle produce?
81
New cards
4 CO2 & 2 ATP
how many CO2 & ATP does citric acid cycle produce?
82
New cards
aerobic (needs oxygen)
is oxidative phosphorylation aerobic or anaerobic?
83
New cards
inner mitochondria
where does oxidative phosphorylation occurs?
84
New cards
1 O2 , 10 NADH, 2 FADH
what are the reactants of oxidative phosphorylation
85
New cards
38 ATP
oxidative phosphorylation produces how many ATP ? (maximum)
86
New cards
26 - 34 ATP produced
oxidative phosphorylation produces how many ATP ?
87
New cards
Water
other than ATP what does oxidative phosphorylation also produce?
88
New cards
oxidative phosphorylation
Electrons are transferred from the NADH and FADH to protein complexes and electron carriers
89
New cards
oxidative phosphorylation
Electrons are used to generate a proton gradient as protons are pumped across to the intermembrane space
90
New cards
ATP synthase
Protons can travel through an enzyme called