Chapter 15a: Blood Flow単語カード | Quizlet
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
endothelium
inner lining of all blood vessels
artery
- diameter: 0.1-10+ mm
- Mean wall thickness: 1.0 mm
- Endothelium: minimal
- Elastic tissue: medium
- Smooth muscle: lots
- fibrous tissue: little
arteriole
- diameter: 10-100 um
- Mean wall thickness: 6.0um
- Endothelium: minimal
- Elastic tissue: none
- Smooth muscle: little
- fibrous tissue: none
capillary
- diameter: 4-10 um
- Mean wall thickness: 0.5 um
- Endothelium: minimal
- Elastic tissue: none
- Smooth muscle: none
- fibrous tissue: none
venule
- diameter:10-100 um
- Mean wall thickness: 1.0 um
- Endothelium: minimal
- Elastic tissue: none
- Smooth muscle: none
- fibrous tissue: little
vein
- diameter: 0.1-100+ mm
- Mean wall thickness: 0.5 mm
- Endothelium: minimal
- Elastic tissue: little
- Smooth muscle: little more
- fibrous tissue: little
conducting or elastic arteries
- smooth muscle
- proportionally high elastic content
allows for stretch and elastic recoil
- maintains driving force for blood during ventricular diastole
distributing or muscular arteries
- proportionally high smooth muscle content
- vasoconstriction and vasodilation
arterioles
- progress from all three tunics: externa, media and intima to only thin media and intima
- most regulation of vasoconstriction and vasodilation
- vasomotor tone
Metarterioles
- little smooth muscle
- precapillary sphincters
- supplies blood to capillaries
- acts as a bypass for white blood cells
capillaries
Endothelium
- with basal lamina or basement membrane
- surrounded by pericytes w/ contractile properties
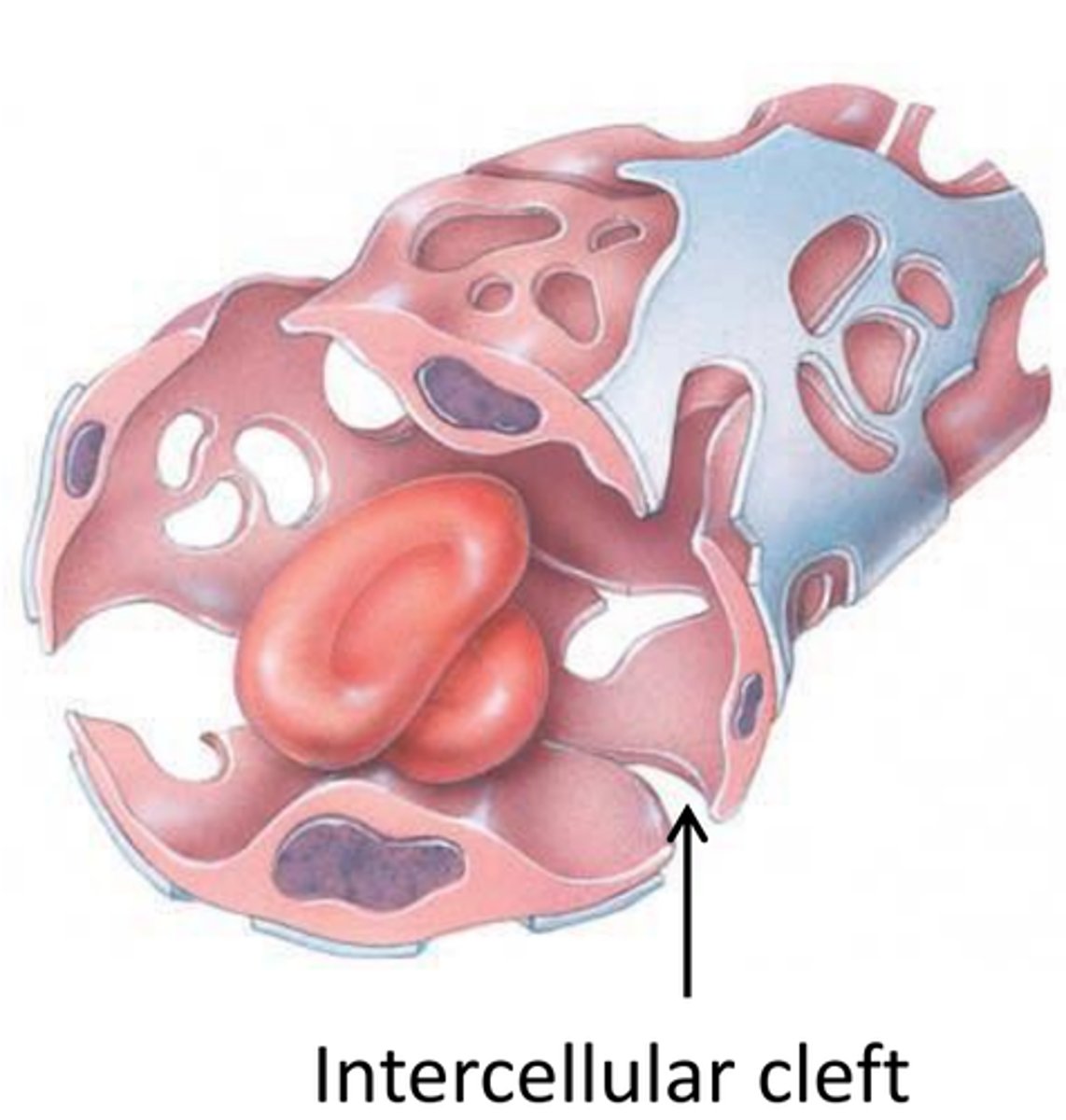
continuous capillaries
most common type of capillary
intercellular clefts
- blood-brain barrier has tight junctions
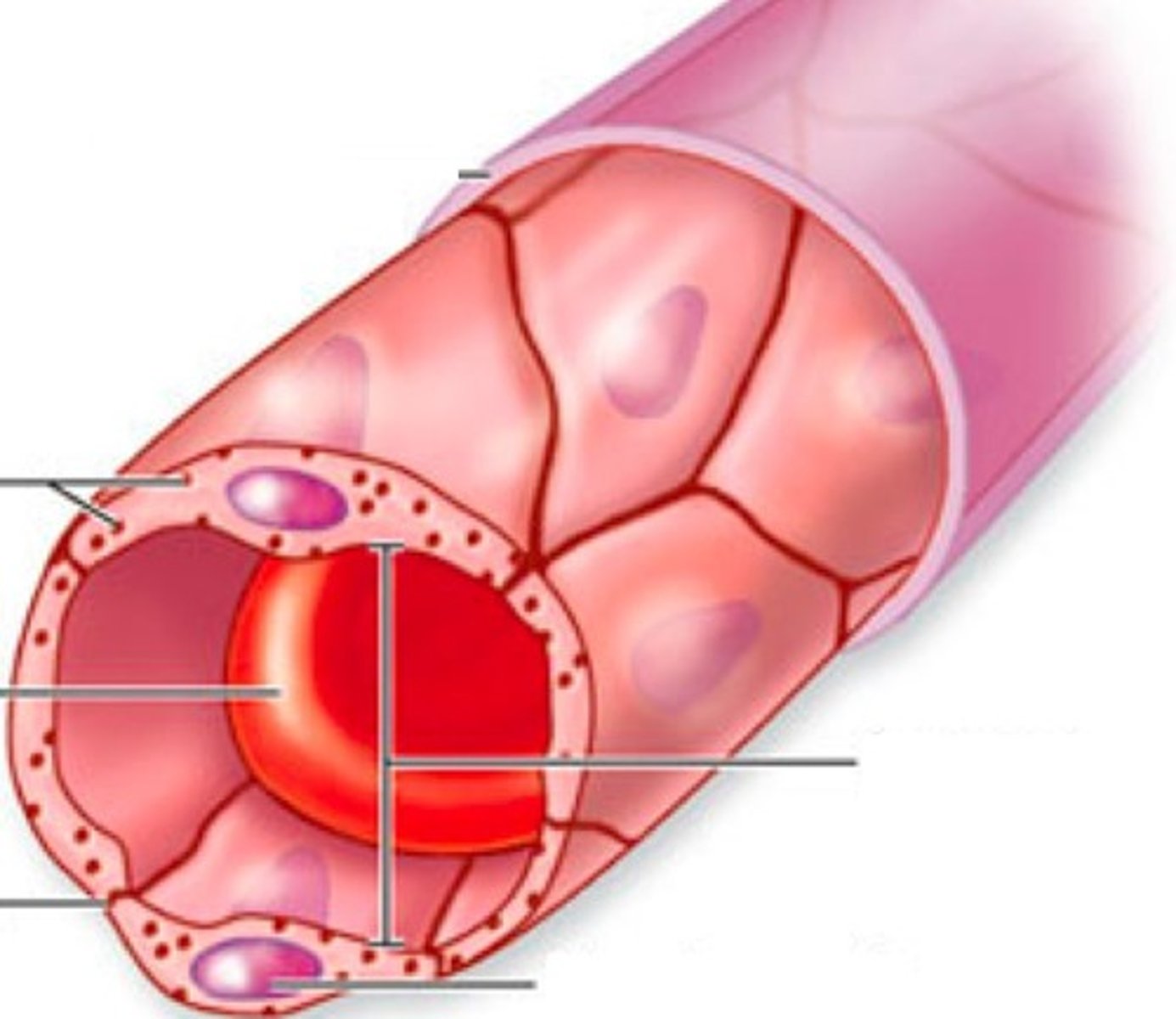
fenestrated capillaries
intercellular clefts with fused vescile clefts
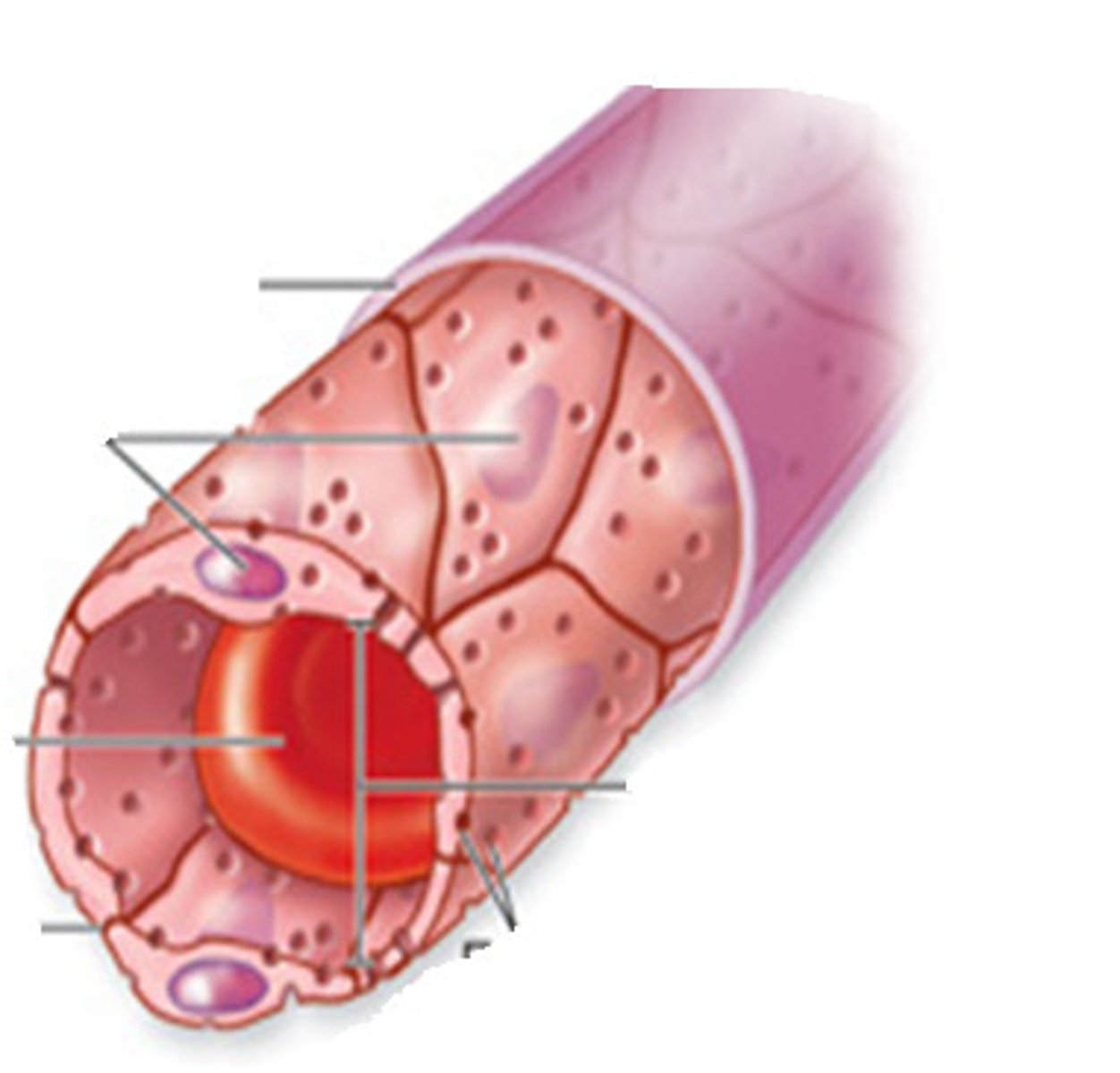
sinusoids or discontinuous capillaries
incomplete endothelial lining and basement membrane
capillary beds
sites of chemical exchange between the blood and interstitial fluid
can be regulated by pre-capillary sphincters
venules
small vessels that gather blood from the capillaries into the veins
progress from only thin media and intima tunics to all three tunics: externa, media, and intima
- smallest venules allow some exchange
veins
- one way valves
- work w/ skeletal muscle and respiratory pumps
- Do you need valves in the jugular veins? YES
blood reservoir: about 60% in veins and venules
more veins and larger diameter than arteries
Angiogenesis
formation of new blood vessels
Promote: mitogenic (mitosis) growth factors
- vascular endothelial growth factors
- fibroblast growth factor
- potential treatment for artery diseases
- development of collateral blood vessels
- inhibit: cytokines
- angiostatin: stasis
- endostatin: stasis
- potential treatment for some cancer
- block development of blood vessel growth and access to nutrients
relationships among pressure, flow and resistance
Recall:
- pressure gradient
- resistance to flow
- velocity and cross-sectional area
- Flow = ∆P/R
- MAP = CO x R
Blood pressure basics
arterial pressure
The pressure of the blood against the arterial walls.
systolic pressure
pressure resulting from ventricular systole - contraction
diastolic pressure
pressure resulting from ventricular diastole - relaxation
pulse or pressure wave
- vibration in the arteries
- alternation between ventricular systole and diastole
- travels 10x faster than the blood
- pulse is the direct reflection of the ventricular action
- pulse deficit
Pressure: decreases the further away it gets from the heart
Effect of distance and friction on pressure and pressure waves
Pulse pressure (PP)
- strength of the pressure wave
PP = SP-DP
- mmHg 160/120 vs 120/80 vs 100/60
MAP
driving force for arterial blood flow
- effect on perfusion of organs and tissues
- DP + 1/3 PP or (SP + 2DP)/3
- mmHg
- 160/120 vs 120/80 vs 100/60
- 133.33 vs. 93.33 vs. 73.33
PP = systolic - diastolic
How do you find pulse pressure?
MAP = DP + 1/3 PP
How do you find MAP?
Syphygmomanometry
laminoar flow vs. disrupted flow
1st Korotkoff sound: systolic pressure
2nd Korotkoff sound: diastolic pressure
less than 120/80 mm Hg
normal blood pressure
120-129/less than 80
elevated BP/ pre- hypertension
130-139/80-89
hypertension stage 1
140 + / at least 90
hypertension stage 2
Health risks
- hemorrhagic strokes
- aneurisms
- kidney failure
- heart failure
over 180 and/or / over 120
hypertensive crisis
ineffective flow against gravity
- below 90/60 mmHg
MAP = 70mmHg
MAP = below 60 is problematic = ineffective ciruclation
Hypotension
1. blood volume
2. cardiac output (HRxSV)
3. volume of blood into vs volume of blood out of arteries
4. volume of blood in venous reservoir
What can influence MAP?
Mass balance of water: volume into body vs. volume out
increase volume = increase pressure
How does blood volume influence MAP?
CO = HR x SV
HR increases = SV increases = CO increases
Heart rate: parasymp vs symp input
Stroke volume:
- EDV: venous return, frank starling law of the heart
- heart contractility: ejection fraction
How does cardiac output affect MAP?
CO vs. peripheral resistance
- ∆ CO → ∆ flow into arteries
- CO affected by heart rate & stroke volume
- ∆ R → ∆ flow out of arteries
- R affected primarily by arteriole diameter
How does volume of blood into vs volume of blood out of arteries affect MAP?
venous vasoconstriction
- ∆ in distribution of blood in arteries vs. veins
- Affected by venous vasoconstriction or vasodilation
- EDV
- Venous return
- Frank-Starling law of the heart
How does volume of blood in venous reservoir affect MAP?
1. Local control of arteriolar resistance: matches tissue blood flow to the metabolic needs of the tissue. In the heart and skeletal muscle, these local controls often take precedence over reflex control by the CNS
2. Sympathetic reflexes mediated by the CNS maintain MAP and govern blood distribution for certain homeostatic needs, such as temperature regulation.
3. Hormones - particularly those that regulate salt and water excretion by the kidneys - influence BP by acting directly on the arterioles and by altering autonomic reflex control
What are some influences on arteriole resistance?
Local or intrinsic control
local regulation to adjust to local needs
Myogenic autoregulation: on-off regulation
- arteriole smooth muscle stretch and mechanically gated Ca channels
- increase blood flow, increases muscle stretch --> opens mechanically gated Ca channels
- intracellular Ca increases, blood flow increases, diameter increases, arteriole resistance decreases
- decrease blood flow, decrease muscle stretch, close mechanically gated Ca channels, opposite effects
Active hyperemia
response to increased metabolic need
- increased metabolic activity → vasodilation → increased blood flow
- stimuli for arteriole dilation
- accumulated metabolic byproducts: CO2, adenosine, H, K
- Paracrine agents: CO2, bradykinin, NO
- after increasing blood flow: remove vasodilators and return to tonic state
Reactive hyperemia
Response to lack of flow
occlusion: decreased blood flow and accumulate metabolic byproducts
stimuli for arteriole dilation
- accumulate metabolic byproducts: CO2, adenosine, H, K
- paracrine agents: CO2, bradykinin, NO
after increasing blood flow
- remove vasodilators and return to tonic state
Active
increase tissue metabolism → increase release of metabolic vasodilators into ECF → arterioles dilate → decreased resistance creates increase in blood flow→ O2 and nutrient supply to tissue increases as long as metabolism is increased
Reactive
decrease tissue blood flow due to occlusion → metabolic vasodilators accumulate in ECF → arterioles dilate, but occlusion prevents blood flow → remove occlusion → decrease resistance creates increase blood flow → as vasodilators wash away, arterioles constrict and blood flow returns to normal
occlusion = close up
when occluded for a few seconds to a few mins. O2 levels fall and metabolic paracrine signals such as CO2 and H accumulate in the interstitial fluid
Active vs. reactive hyperemia
Arteriole pressure autoregulation: on-off regulation
decreased arterial pressure → vasodilation→ increased blood flow
stimuli for arteriole dilation
- same as for active hyperemia
- but different in that metabolic activity is constant but blood flow can't keep pace
- increased arteriole pressure → vasoconstriction → decreased blood flow
stimuli for arteriole constriction or return to tonic state
- increased O2 and removal of vasodilating chemicals
Sympathetic influence on arteriole resistance
Tonic control: vasomotor tone
- sympathetic system regulates most changes
- parasympathetic input is not necessary for vasodilation
- NE NT and E neurohormone with a1 adrenergic receptors
- vascular sm. muscle
- increased symp. input → increased vasoconstriction
- decreased symp. input → decreased vasoconstriction (return to tone or allow to vasodilate)
- E neurohormone with B2 adrenergic receptors
- vascular smooth muscle of liver and cardiac and skeletal muscle
- increased symp. input → decreased vasoconstriction (allow to vasodilate)
- decreased symp. input → increased vasoconstriction (return to tone)
Why mixed responses? Fight or flight
Hormone influence on resistance
extrinsic control
Atrial Natriuretic peptide (ANP)
- vasodilation
- influences function of kidney for water regulation → blood volume (more water in blood)
Angiotensin II (ANG II)
- potent vasoconstriction
- influences function of kidney for water regulation → blood volume (less water in blood)