Unit 6.3 - Improving Organisational Design
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Job design
The process of determining what a job involves, how it is carried out and how it relates to other relevant jobs.
Includes:
Duties and responsibilities
Methods of carrying out the job
Placement in the organisation
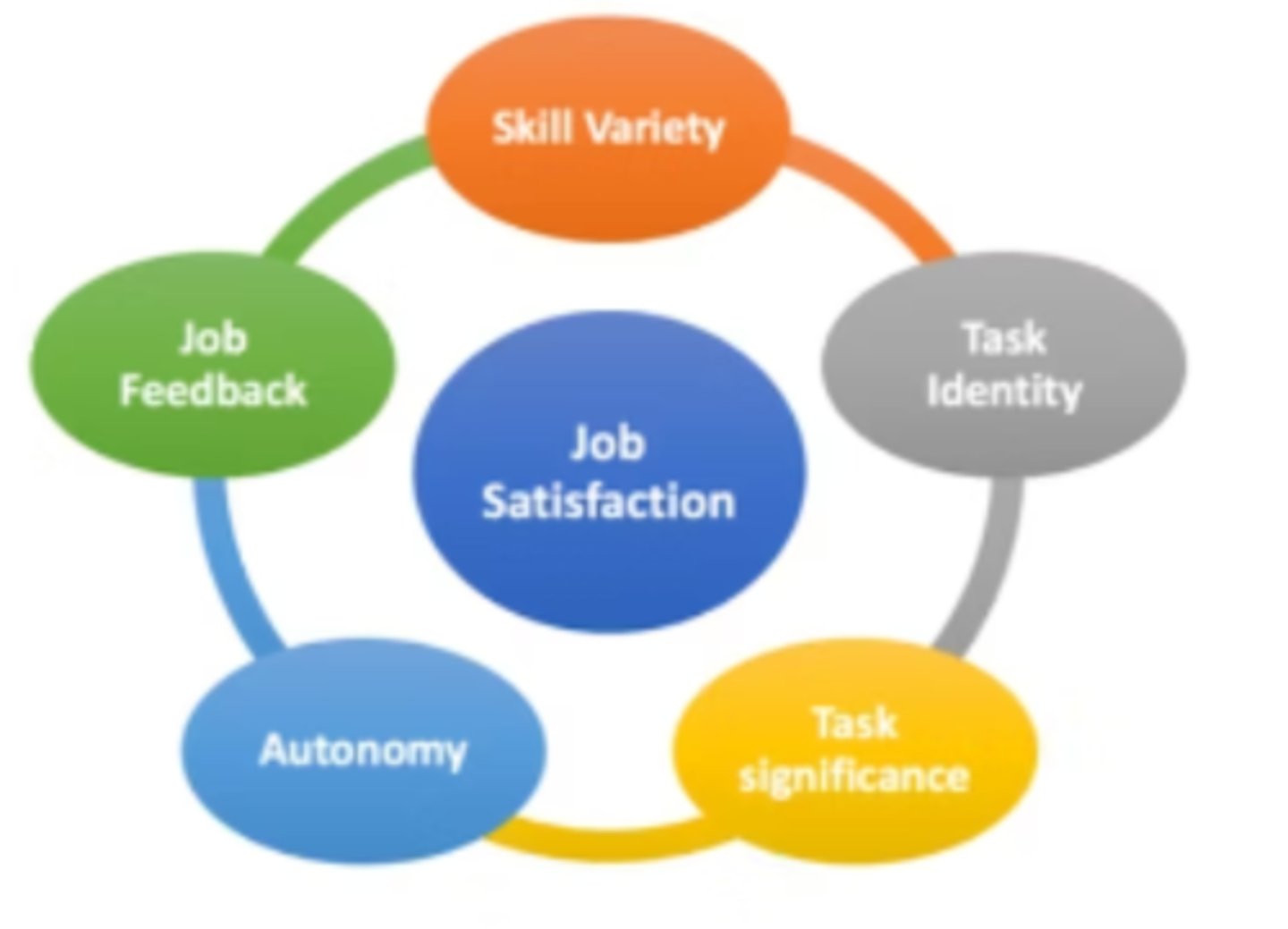
Hackman and Oldham's Job Characteristics Model (Last paper Y13 2024)
A model that is based on the idea that the workplace task itself is key to employee motivation. Specifically, a boring and monotonous job stifles motivation to perform well, whereas a challenging job enhances motivation. - 5 key char
Hackman and Oldham's 5 core job characteristics (last paper Y13 2024)
Skill variety - using an appropriate amount of skills, not too many (overwhelming) and not too few (boring)
Task identify - being able to identify the work at hand as a part of a whole (i.e completing a whole car as a team instead of 1 person only doing 1 part)
Task significance - seeing that work is contributing to the wider objectives
Autonomy - individual has freedom and independence
Feedback - provided with information on progress and how to improve in the future
Hackman and Oldham's Job Characteristics Model (image - last paper Y13 2024)
Job enrichment
Employees job are redesigned to provide them with more challenging and complex tasks
- increase complexity of tasks
- Give employees greater responsibility
Job enlargement
Increasing the number of similar tasks or duties in a job role
Job rotation
Employees switch regularly from one duty to another
Empowerment
Series of actions designed to give employees greater control over their working lives
Organisational design
shaping an organisations employees in a way which helps them to meet their objectives
Organisational structure
The way a business is arranged to carry out its activities
Span of control
how many employees a manager is directly responsible for
Authority
power to make decisions
Hierarchy
division of authority and accountability
Delegation
transferring responsibility or authority to junior employees
Chain of command
the line of authority that moves from the top of a hierarchy to the lowest level
Flat organisational structure
wide spans of control and a short chain of command. There are less levels of hierarchy
Tall organisational structure
narrow spans of control and a long chain of command. There are more levels of hierarchy.
Key features of narrow spans of control (tall structure)
- More promotional opportunities because more layers, but leads to higher wage costs
- Less delegation might mean low morale for junior employees
- Allows tight control, good for quality/safety/security
- Important information may be lost in vertical communication
- Longer chain of command means slower decision making
Key features of wide spans of control (flat structure)
- Individual managers have less time for each junior and must delegate
- More delegation means employees may feel motivated but may become overworked
- Vertical communication (top to bottom and vice versa) is improved
- Lower wage costs + easier vertical communication = higher efficiency
- Shorter chain of command means quicker decision making
Benefits of delegation
Frees up management time
Motivating for workers
Local knowledge
Flexibility and quicker response times
Staff development
Drawbacks of delegation
- Difficult in small organisations
- Customer expectations might not be met
- Attitudes and approach of management might not match delegation style
- Quality of staff and can they be trusted
- Crisis situations may not be handled well
- Confidentiality may not be possible
Centralisation
control is maintained in the middle of the organisation at head office
Decentralisation
control is passed to staff at local levels and to subordinates
Benefits of centralisation
Consistent policies and standardised procedures
Decisions are made quickly without consulting regions
Customers know what to expect
Financial control is easier
Decisions are based on the overall strategy of the organisation
Strong leadership is helpful in times of crisis
Drawbacks of centralisation
- More bureaucratic - often extra layers in the hierarchy
- Local or junior managers are likely to much closer to customer needs and have better knowledge of needs
- Lack of authority down the hierarchy may reduce manager motivation
- Customer service does misses flexibility and speed of local decision-making
Benefits of decentralisation
Motivating for local managers
Audience can be targeted more effectively
Less daily communication needed
Senior managers can focus on wider strategy
Responsive to changes in customer needs
Drawbacks of decentralisation
-Poor decisions by junior managers could harm the whole business.
-Consistent policies may not always followed.
Training could also be costly
- Customers may not enjoy lack of consistency
- Local managers may lose touch with the bigger picture
Types of organisational structure
- Functional structure:
- Geographical/region based
- Product-line based
- Matrix structure
(also have generic flat and tall)
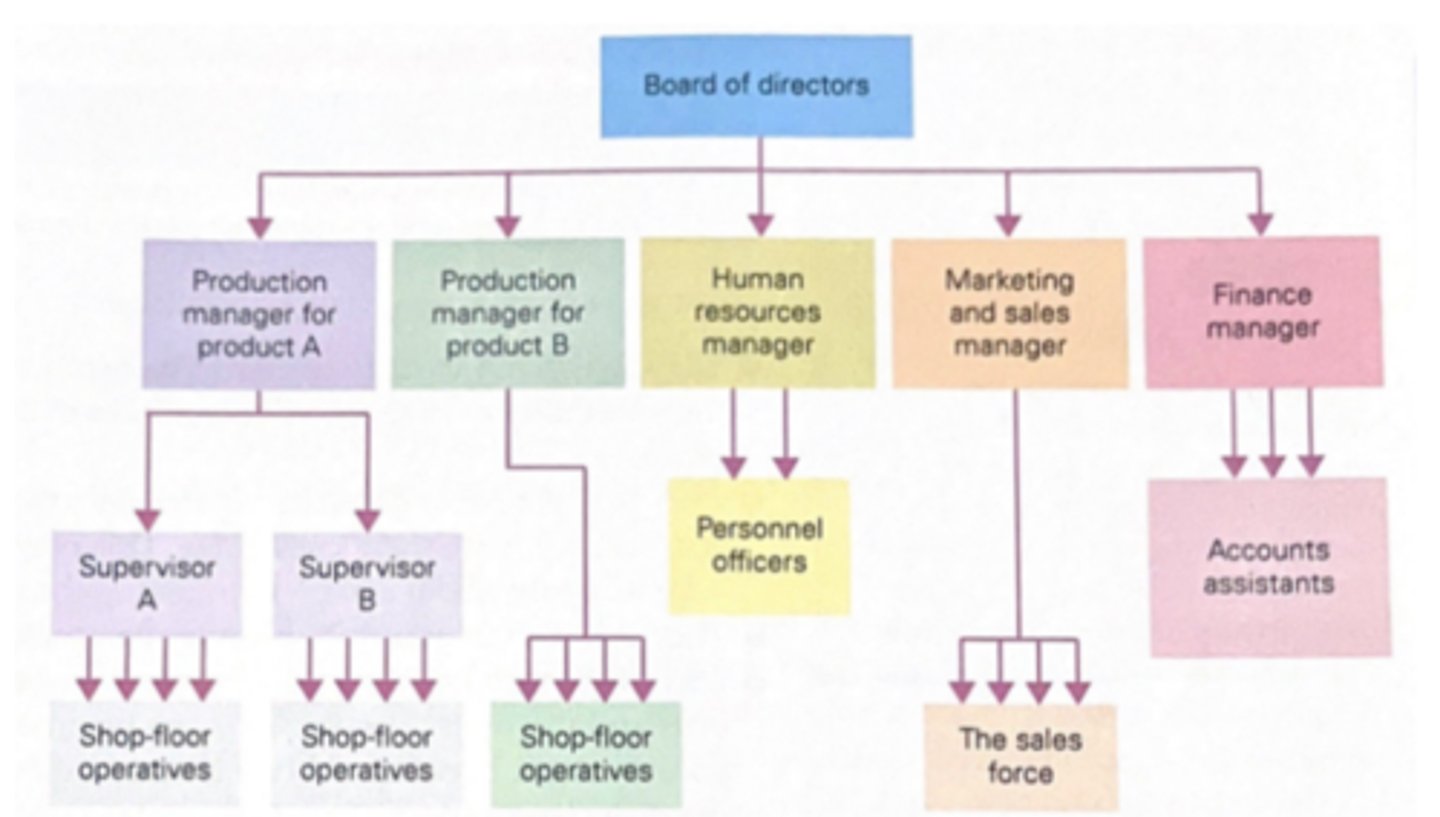
Functional organisational structure
the traditional management structure consisting of a different department for each of the main functions of the business i.e operations, HR, Marketing, Finance
- They are based on hierarchy in which each department operates separately but under the leadership of those above it
- Coordination between different functions must occur at the top (inflexible)
- Size of each function varies to business needs
- Employees have specialist skills
Impact
- Members of each department have the same job area - can share expertise, help problem solve and talk the same business language
- Can identify more with department than the whole business
- Each department can develop its own culture and way of seeing things
- ‘Silo effect’ - where everyone sees the business from their departmental perspective
- Lack empathy with other departments
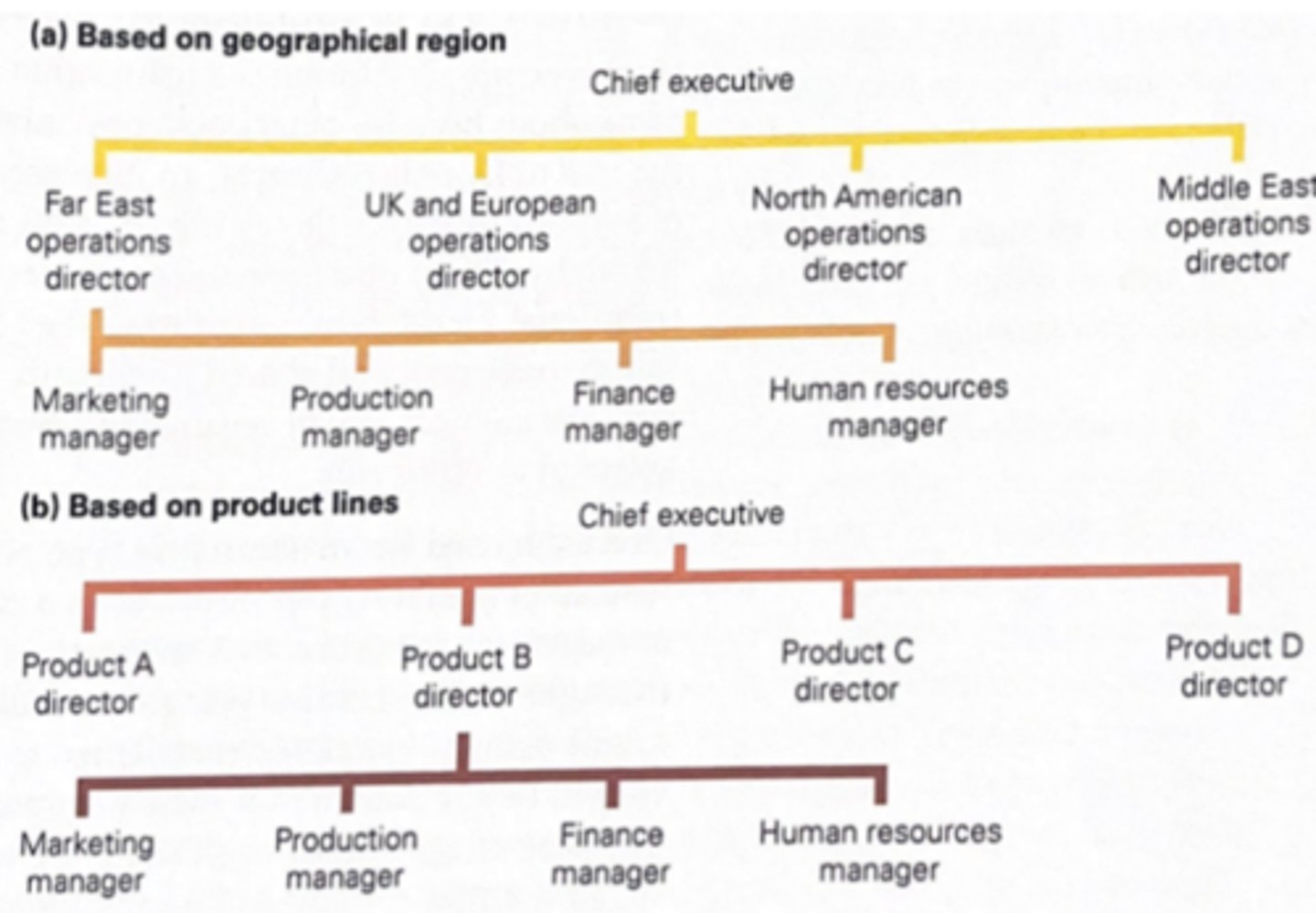
Regional/geographical organisational structure
Structure based on the location of operations, could be different parts of the same country or different countries all together
Impact
- Useful when competing in very distinct regions of a country or around the world
- Meets specific issues and demands in areas as they may vary
- Lead to more in depth market knowledge, better matching of what is offered to the market and more efficient decision making
- Common as businesses expands nationally
- Faces similar issues as product structure
Product based organisational structure
Structure based on different goods or services produced, each is separated into its own department and structure
Impact
- Occurs when a business has very clear product lines that have different customer bases and different challenge and opportunities
- Makes sense if the demands of customer vary significantly
- Groups together those with specific expertise and skills for that group of customers
- Loses a sense of overview of the business as a whole
- Compete rather than cooperate
- Duplication of resources
- Senior managers should look to share resources and centralise some functions such as payroll
Functional based organisational structure (diagram)
Regional and product based organisational structures (diagram)
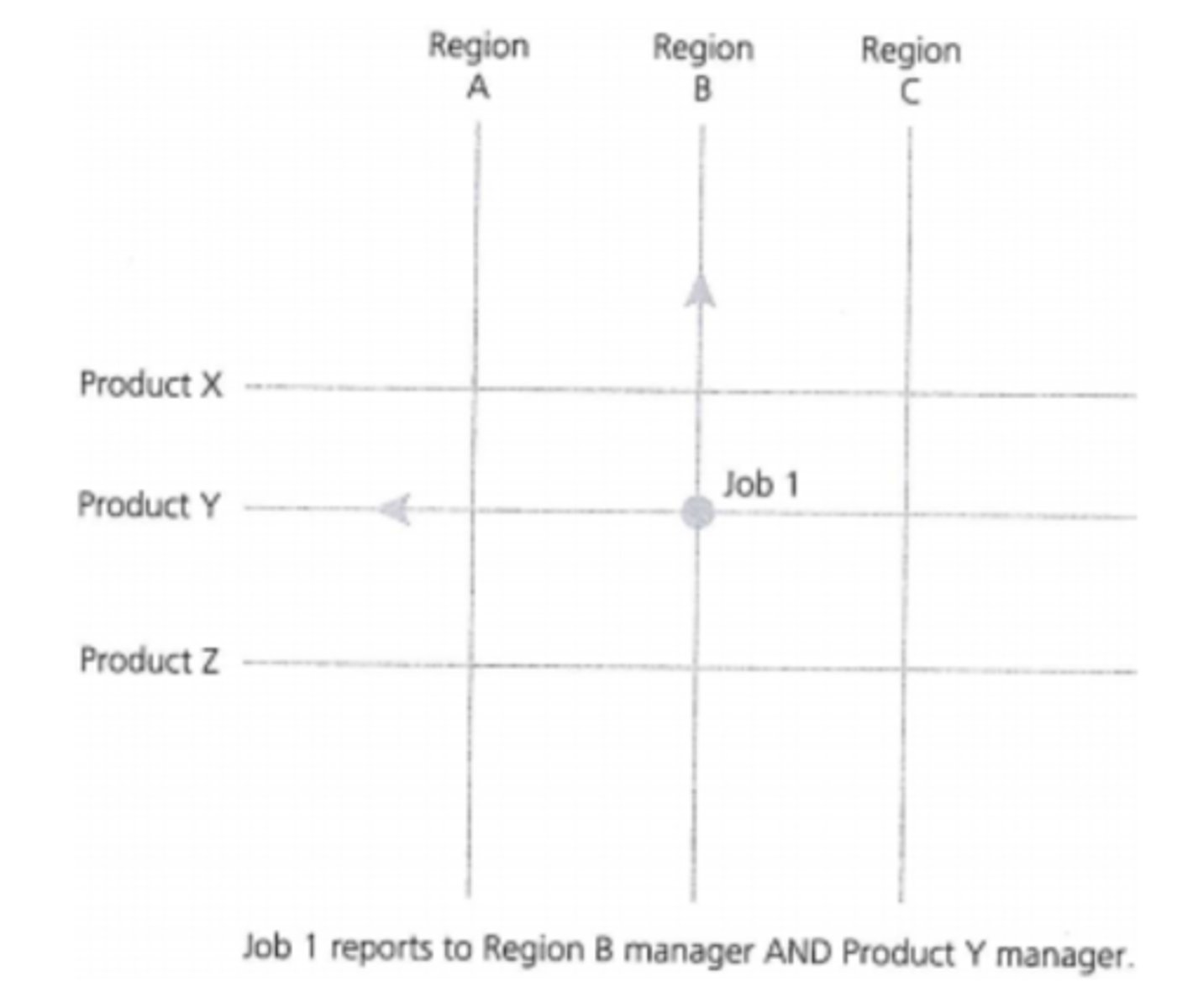
Matrix organisational structure
- Combination of two or more types of structure at once, leading to job holding have more than one boss
- Tends to be used alongside functional, not instead of it
Impacts
- Enables individual projects to be better coordinated
- Lines of authority can become unclear
- Different departments can share knowledge
- Motivating
- Two bosses can be overwhelming
- Managers report to at least two superiors
- Can’t just focus on your area but also the other areas
- Want to share understanding and learn from others in other places
- Tries to avoid ‘silo effect’ - compartmentalising too much can lead to inefficiencies
- Issues from having two superiors who may have different priorities
Matrix organisational structure (diagram)
Influences on organisational structure, delegation and decentralisation
Business objectives
Size of the organisation
Nature of the organisation
Culture
Management style
Skill of workforce
External environment
Stakeholders
How managing HR helps to meet objectives (diagram)
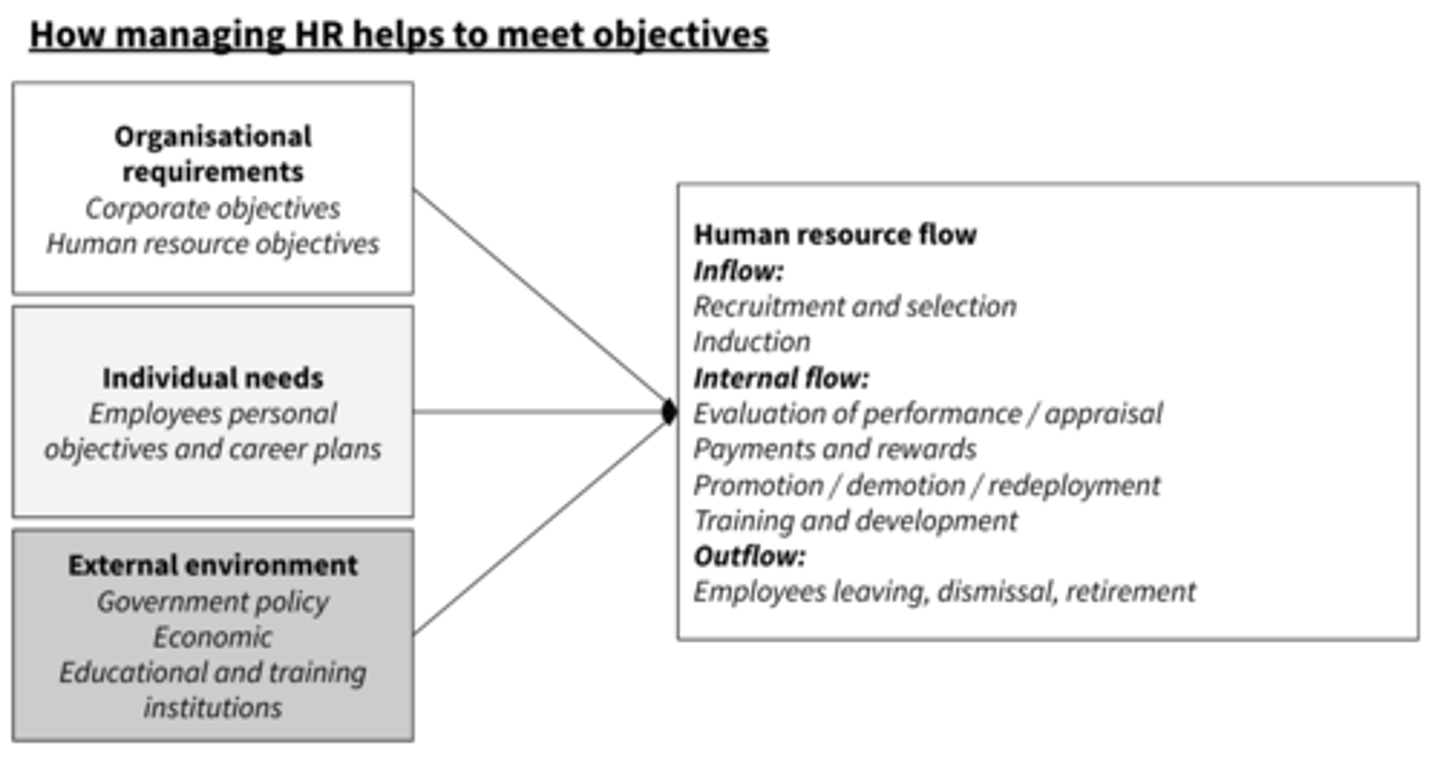
Internal influences on HR plans
Strategic plan and corporate objectives
Marketing and production plans
Financial position
Number of workers
Labour turnover
External influences on HR plans
Market conditions
Labour market / demographics
Economy and government policy
Legislation
Local factors
Recruitment and selection
The process of filling an organisation's job vacancies by appointing new staff
Internal recruitment
filling a job vacancy by selecting a person who is already employed by the organisation
External recruitment
filling a job vacancy by advertising outside the organisation
Benefits of internal recruitment
The employee's abilities are known already
Motivating for employees
Quicker and less expensive process
Shorter induction period is needed
Less risky
Benefits of external recruitment
It often provides a large choice of well qualified candidates
New ways of thinking are introduced
Helps to avoid negative colleague dynamics
Valuable information on competition
Training
Process whereby an employee gains job related skills and knowledge
Possible reasons to train
New products / services
Change of organisational structure
Developing / introducing new technology
Changes to procedure i.e customer service
High labour turnover
Low morale
Changes in legislation
On-the-job training
training that takes place in the work setting, learn by observing experienced employee
Off-the-job training
Training that takes place away from the work area by visiting a separate organisation
Benefits of on-the-job training
Cheaper
More specific to business
Bad habits
Willingness of instructor
Benefits of Off-the-job training
More expensive
More generic
Higher quality (done by experts)
Less immediate pressure
Benefits of training
- Helpful for new employees
- Employees are skilled
- Motivating
- Increases efficiency and productivity
- Improved chances of promotion
- Reduces cost in the long run
- Encourages employees to be flexible
- Improves reputation of the company (reduced defects, better customer service etc)
- Encourages employees to work towards corporate aims
- Employee business reputation as good employer