High School Chemistry
1/358
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Based on Khan Academy's High School Chemistry Course
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
359 Terms
Atom
A basic unit of matter made of subatomic particles (protons, neutrons, and electrons)
Nucleus
Protons and neutrons in the middle of an atom
Electron cloud
Where electrons are most likely to be found
Proton
Subatomic particle with a charge of 1+ and a mass of 1 unified atomic mass unit (u)
Electron
Subatomic particle with a charge of 1- and a mass of 0.0005 unified atomic mass unit (u)
Neutron
Subatomic particle with a neutral charge and a mass of 1 unified atomic mass unit (u)
What is an element identified by?
The number of protons in its nucleus
Abbreviation for atomic number
Z
Atomic number
The number of protons
Chemical symbol
Every element's unique one or two letter abbreviation
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons
Mass number
The sum of the number of neutrons and protons in an atom
Isotope notation

Ion
An atom with an electric charge
Cation
A positively charged ion with more protons than electrons
Anion
A negatively charged ion with more electrons than protons
How is the charge of an ion calculated?
# of protons - # of electrons
Bohr Model
Electrons are represented as dots that sit on a ring around the nucleus
Energy Levels/Shells
The circles in a Bohr Model
How many electrons can each energy level in an atom hold?
1st = 2, 2nd = 8, 3rd = 18, 4th = 32
Valence shell
The outermost shell in an atom
Valence electrons
The outermost electrons of an atom (found in the valence shell)
Core electrons
Electrons that are not in the valence shell
Radiation
Energy that travels through space
Electromagnetic radiation
Energy transferred by oscillations in the electromagnetic field
Photon
A particle of EM radiation
Speed of light in a vacuum (c)
3 × 108 m/s
Wavelength
The distance from one peak of a wave to the next peak
Frequency
The number of wave cycles in a period of time
Relationship between photon energy and frequency
Photon energy increases as frequency increases
Electromagnetic radiation types from lowest frequency to highest frequency
Radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, gamma rays
How do emission spectra occur?
Energized electrons drop an/multiple energy levels, releasing photons
How do absorption spectra occur?
Cool gas absorbs photons in order for its electrons to jump up energy levels
Lewis dot diagrams
Diagrams that consist of the chemical symbol of an element surrounded by dots for each of the valence electrons that the element has
Orbitals
Areas where electrons are likely to be found
1s orbital
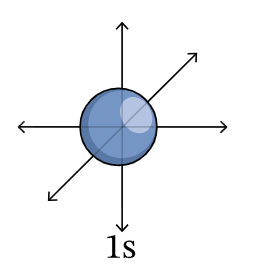
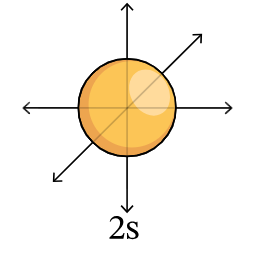
2s orbital
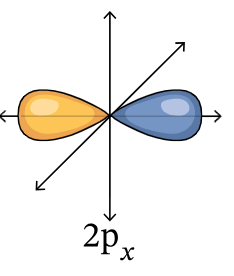
2px orbital
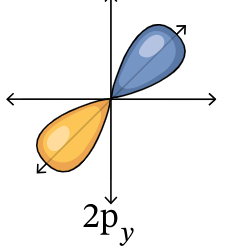
2py orbital
2pz orbital
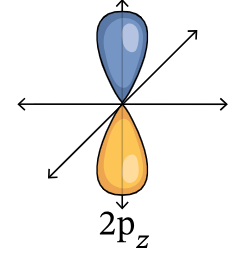
When discussing orbitals, what represents energy levels?
The coefficient
Subshell
2s is a subshell, 2px, 2py, and 2pz make up a subshell
Electron configurations
Where electrons are located around the nucleus of an atom
What do the exponents in electron configurations mean?
How many electrons are in each subshell
Aufbau principle
Electrons fill lower-energy atomic orbitals before filling higher-energy ones (works best for the first 20 elements)
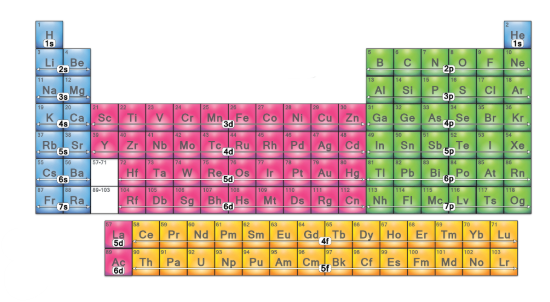
Which electron configuration block is this? (blue)
s-block
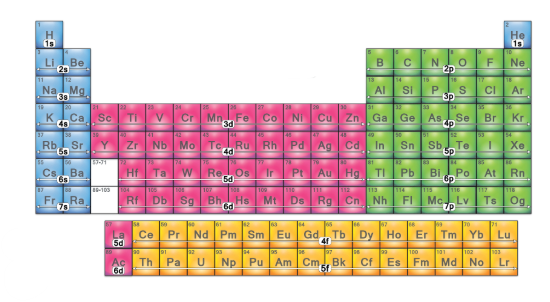
Which electron configuration block is this? (pink)
d-block
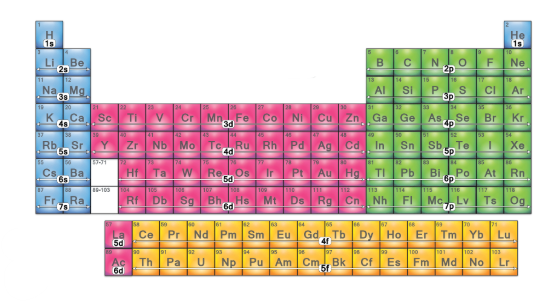
Which electron configuration block is this? (green)
p-block
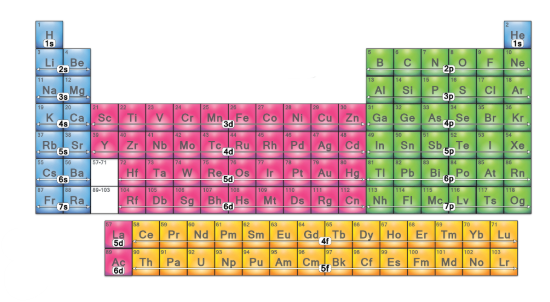
Which electron configuration block is this? (yellow)
f-block
How to write electron configuration in shorthand?
Write the electron configuration for the previous noble gas
Octet rule
Most of the elements important in biology need 8 electrons in their outermost shell in order to be stable
Groups
The vertical columns on the periodic table
Periods
The horizontal rows on the periodic table
Alkali metals
Group 1 on the periodic table
Alkaline earth metals
Group 2 on the periodic table
Halogens
Group 7 on the periodic table (very reactive nonmetals)
Noble gases
Group 8 on the periodic table (very unreactive)
Going across a period, atomic radius tends to… (and why)
Decrease because of increased nuclear charge (more proton pull)
Going down a group, atomic radius tends to… (and why)
increase due to increased shielding and the addition of new shells
Ionization
The process of removing an electron from a neutral atom or compound
Ionization energy
The energy required to remove an electron
Going across a period, ionization energy tends to… (and why)
Increase (more proton pull)
Going down a group, ionization energy tends to… (and why)
Decrease (more orbital rings so more shielding)
How can the charge of an atom be predicted by its number of valence electrons?
How many electrons an atom needs to gain or lose in order to achieve a full octet
Ionic bonds
The attraction between oppositely charged ions
What structure is an ionic solid?
Crystal lattice structure
Advantage of a lattice structure for ionic solids
Maximizes the attractive forces between opposite charges and minimizes the repulsive forces between like charges
How are cations named?
Element name + "ion" (ex: sodium ion)
Polyvalent
Able to form cations of different charges
How is the magnitude of charges for polyvalent ions represented?
Roman numerals
How are anions named?
Root of the element's name + ide
Monatomic ions
A single atom with a net charge
Polyatomic ions
A group of atoms with a net charge
Hydroxide chemical formula and charge
OH-, with a charge of -1
Acetate chemical formula and charge
C2H3O2-, with a charge of -1
Nitrite chemical formula and charge
NO2-, with a charge of -1
Nitrate chemical formula and charge
NO3-, with a charge of -1
Carbonate chemical formula and charge
CO3-2, with a charge of -2
Sulfite chemical formula and charge
SO32-, with a charge of -2
Sulfate chemical formula and charge
SO4-2, with a charge of -2
Phosphate chemical formula and charge
PO43-, with a charge of -3
Ammonium chemical formula and charge
NH4+, with a charge of +1
Cyanide chemical formula and charge
CN-, with a charge of -1
Bicarbonate chemical formula and charge
HCO3-, with a charge of -1
Hypochlorite chemical formula and charge
ClO-, with a charge of -1
Chlorite chemical formula and charge
ClO2-, with a charge of -1
Chlorate chemical formula and charge
ClO3-, with a charge of -1
Perchlorate chemical formula and charge
ClO4-, with a charge of -1
Permanganate chemical formula and charge
MnO4-, with a charge of -1
Chromate chemical formula and charge
CrO42-, with a charge of -2
Dichromate chemical formula and charge
Cr2O72-, with a charge of -2
Hydrogen Peroxide chemical formula and charge
H2O2, with a charge of 0 (each oxygen atom has a charge of -1 and each hydrogen atom has a charge of +1)
The atoms within a polyatomic ion molecule are held together by…
Covalent bonds
When naming acids, if the name of the anion ends in the -ide suffix
Write as hydro---ic acid
When naming acids, if the name of the anion ends in the -ate suffix
Write as ---ic acid
When naming acids, if the name of the anion ends in the -ite suffix
Write as ---ous acid
Covalent bonds
Shared electron pairs between atoms
Molecule
A group of two or more atoms covalently bonded together
Diatomic elements
Elements that do not exist alone in nature as individual atoms, and are found as a covalently-bonded pairs
Compound
A chemical substance composed of two or more different elements