BIO 1081 Exam3
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
University of Cincinnati Dr. Mosley Spring 2024
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
A somatic cell from a garden pea normally contains 14 chromosomes. How many sister chromatids would that cell contain during G1 of the cell cycle?
A. 0 B. 7. C. 14. D. 28
A. 0
This stage of the cell cycle is characterized by growth, and it contains a checkpoint to verify that all the DNA has been replicated prior to mitosis.
A. Mitosis B. G1
C. S D. Cytokinesis
E. G2
E. G2
Which of the following is not a checkpoint that controls the progression of the cell cycle?
A. The G2 checkpoint checks for DNA damage and determines if all of the DNA is replicated.
B. The restriction point determines if conditions are favorable for cell division and if the DNA is undamaged.
C. Cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases are proteins that are responsible for advancing a cell through the phases of the cell cycle.
D. Cytokinesis involves the formation of cleavage furrow to separate the cells.
D. Cytokinesis involves the formation of cleavage furrow to separate the cells.
What is the final result of mitosis?
A. Genetically different 2n gametic cells
B. Genetically identical 2n gametic cells
C. Genetically different 2n somatic cells
D. Genetically identical 2n somatic cells
D. Genetically identical 2n somatic cells
In eukaryotic cells, chromatin is composed of
A. DNA and proteins.
B. DNA and RNA.
C. DNA and phospholipids.
D. DNA only.
A. DNA and proteins.
Colchicine is a toxin that binds to tubulin proteins and prevents microtubules from elongating. What effect might this have on dividing cells?
A. Chromosomes will not be able to condense, so mitosis will not occur
B. Sister chromatids will not be properly separated into separate daughter cells.
C. Cells will be able to complete mitosis, but cytokinesis will not occur.
D. Replicated chromosomes will not be able to stick together, so sister chromatids will not properly sort into daughter nuclei.
B. Sister chromatids will not be properly separated into separate daughter cells.
__’s phone rang during class
Jamel
In humans, hemophilia is caused by a recessive allele on the X chromosome. Suppose a man with hemophilia has children with a healthy woman whose mother had hemophilia. What is the probability that their second son will have hemophilia?
A. 25% B. 50%
C. 75% D. 100%
A. 25%
In rabbits, there is a gene that controls ear length, with a dominant allele "T" for long ears and a recessive allele "t" for short ears. At another gene locus, there are alleles "B" for black coat and "W" for white coat. Neither the B or W allele is dominant, and BW produces a gray coat. These two allele pairs assort independently. If a gray rabbit that is heterozygous at the gene locus controlling ear length is mated with a white rabbit that is also heterozygous at the gene locus controlling ear length, what is the probability that their first offspring will be gray with long ears?
A. 1/16 B. 3/8 C. 3/16
D. 1/8 E. 1/2
B. 3/8
Pseudohypertrophic muscular dystrophy is a human disorder that causes gradual deterioration of the muscles. Only boys are affected, and they are always born to phenotypically normal parents. Due to the severity of the disease, the boys die in their
teens. Is this disorder likely to be caused by a dominant or recessive allele? Is its inheritance sex-linked or autosomal?
A. Recessive, sex-linked
B. Dominant, sex-linked
C. Recessive, autosomal
D. Dominant, autosomal
A. Recessive, sex-linked
A man who carries an allele of an X-linked gene will pass it on to _____.
A. all of his daughters B. half of his daughters
C. all of his sons D. half of his sons
A. all of his daughters
Mendel's observation of the segregation of alleles in gamete formation has its basis in which of the following phases of cell division?
A. prophase I of meiosis
B. anaphase II of meiosis
C. metaphase I of meiosis
D. anaphase I of meiosis
D. anaphase I of meiosis
When does the synaptonemal complex disappear?
A. Early anaphase of meiosis I
B. Late prophase of meiosis I
C. Late metaphase of meiosis II
D. Mid-prophase of meiosis II
B. Late prophase of meiosis I
The pairing of chromosomes along their lengths which is essential for crossing over is referred to as
A. syngamy. B. recombination.
C. prophase. D. synapsis.
D. synapsis.
Height is a trait that shows continuous variation in humans. In pea plants, on the other hand, the tall allele is dominant over the short allele and there are no intermediate heights. What is the best explanation for this difference?
A. The alleles that control height in pea plants are epistatic.
B. The alleles that control height in pea plants are pleiotropic.
C. The alleles that control height in humans are pleiotropic.
D. Height is a polygenic trait in humans.
D. Height is a polygenic trait in humans.
A mutation causes a gene to become overactive, contributing to uncontrolled cell growth. Which term best describes this gene?
A. tumor-suppressor gene
B. oncogene
C. proto-oncogene
D. alternatively spliced gene
B. oncogene
Which of the following is most likely to occur when a tumor-suppressor gene is mutated?
A. The tumor-suppressor gene may be overactive.
B. The resulting tumor-suppressor protein would further suppress cell proliferation.
C. The resulting tumor-suppressor protein would activate an oncogene.
D. The tumor-suppressor gene and resulting protein may lose its function and ability to suppress cell proliferation.
D. The tumor-suppressor gene and resulting protein may lose its function and ability to suppress cell proliferation.
Hemophilia is caused by a
A. recessive allele on the X chromosome.
B. dominant allele on the X chromosome.
C. codominant allele on the X chromosome.
D. recessive allele on an autosome.
A. recessive allele on the X chromosome.
In sickle cell anemia, the defective hemoglobin differs from the normal hemoglobin by
A. the color of the pigment.
B. the size of the molecule.
C. a single amino acid substitution
D. the total number of amino acids.
C. a single amino acid substitution
If an individual allele has more than one effect on the phenotype, this is called
A. Epistasis B. Multiple alleles
C. Polygenic D. Pleiotropy
D. Pleiotropy
A human female with only one X chromosome is said to have a condition called
A. X chromosome inactivation.
B. Turner syndrome.
C. Klinefelter syndrome.
D. Down syndrome
B. Turner syndrome.
If there are 20 chromosomes in a cell in G1 phase, how many centromeres are there?
A. 10 B. 20
C. 30 D. 40
B. 20
If there are 16 centromeres in a cell at anaphase, how many chromosomes are there in each daughter cell following cytokinesis?
A. 8 B. 16
C. 32 D. 48
A. 8
Movement of the chromosomes during anaphase would be most affected by a drug that prevents
A. cell wall formation.
B. elongation of microtubules.
C. shortening of microtubules.
D. formation of a cleavage formation
C. shortening of microtubules.
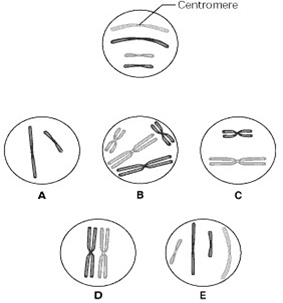
The lettered circle in the figure shows a diploid nucleus with four chromosomes. There are two pairs of homologous chromosomes, one long and the other short. One haploid set is symbolized as black and the other haploid set is gray. The chromosomes in the unlettered circle have not yet replicated. Using the figure below, which lettered circle represent telophase?
A. A B.B C. C
D. D E.E
E.E
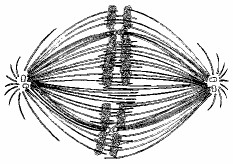
If the cell, whose nuclear material is shown in the figure below continues toward completion of mitosis, which of the following events would occur next?
A. Synthesis of sister chromatids.
B. Nuclear envelope breakdown
C. Formation of telophase nuclei
D. Spindle fiber formation
C. Formation of telophase nuclei
Which of the following is true concerning cancer cells?
A. They are not subject to cell cycle controls.
B. When they stop dividing, they do so at random points in the cell cycle; they are not subject to cell cycle controls; and they do not exhibit density-dependent inhibition when growing in culture.
C. When they stop dividing, they do so at random points in the cell cycle, and they are not subject to cell cycle controls.
D. They do not exhibit density-dependent inhibition when growing in culture.
B. When they stop dividing, they do so at random points in the cell cycle; they are not subject to cell cycle controls; and they do not exhibit density-dependent inhibition when growing in culture.
Why do neurons and some other specialized cells divide infrequently?
A. They no longer carry receptors for signal molecules.
B. They can no longer bind Cdk to cyclin.
C. They show a drop in MPF concentration.
D. They have been shunted into G0.
D. They have been shunted into G0.
Which is the first checkpoint in the cell cycle where a cell will be caused to exit the cycle if this point is not passed?
A. G0 B. previous M
C. G1 D. S
C. G1
Tumor-suppressor genes
A. often encode proteins that stimulate the cell cycle.
B. are cancer-causing genes introduced into cells by viruses.
C. are frequently over expressed in cancerous cells.
D. can encode proteins that promote DNA repair or cell-cell adhesion.
D. can encode proteins that promote DNA repair or cell-cell adhesion.
The human X and Y chromosomes
A. include genes that determine an individual's sex.
B. are about the same size and have approximately the same number of genes.
C. are both present in every somatic cell of males and females alike.
D. are called autosomes.
A. include genes that determine an individual's sex.
Which of these statements is false?
A. At sexual maturity, ovaries and testes produce diploid gametes by meiosis.
B. Single, haploid (n) sets of chromosomes in ovum and sperm unite during fertilization, forming a diploid (2n), single-celled zygote.
C. In humans, each of the 22 maternal autosomes has a homologous paternal chromosome.
D. In humans, the 23rd pair, the sex chromosomes, determines whether the person is female (XX) or male (XY).
A. At sexual maturity, ovaries and testes produce diploid gametes by meiosis.
In a human karyotype, chromosomes are arranged in 23 pairs. If we choose one of these pairs, such as pair 14, which of the following do the two chromosomes of the pair have in common?
A. Length, centromere position, and staining pattern only.
B. They have nothing in common except they are X-shaped.
C. Length, centromere position, staining pattern, and traits coded for by their genes.
D. Length and position of the centromere only.
C. Length, centromere position, staining pattern, and traits coded for by their genes.
Which of these is a way that the sexual life cycle increases genetic variation in a species?
A. By decreasing mutation frequency
B. By allowing crossing over
C. By conserving chromosomal gene order.
D. By increasing gene stability.
B. By allowing crossing over
The karyotype of one species of primate has 48 chromosomes. In a particular female, cell division goes awry and she produces one of her eggs with an extra chromosome (25). The most probable source of this error would be a mistake in which of the following?
A. Mitosis in her ovary
B. Either anaphase I or II
C. Metaphase I of one meiotic event
D. Telophase I of one meiotic event
B. Either anaphase I or II
When we see chiasmata under a microscope, that lets us know which of the following has occurred?
A. Asexual reproduction
B. Prophase I
C. Separation of homologs
D. Meiosis II
B. Prophase I
Independent assortment of chromosomes is a result of
A. the random and independent way in which each pair of homologous chromosomes lines up at the metaphase plate during meiosis I.
B. the random nature of the fertilization of ova by sperm.
C. the random distribution of the sister chromatids to the two daughter cells during anaphase II.
D. the relatively small degree of homology shared by the X and Y chromosomes.
A. the random and independent way in which each pair of homologous chromosomes lines up at the metaphase plate during meiosis I.
Which of the following occurs in meiosis but not in mitosis?
A. Chromosome replication
B. Synapsis of chromosomes
C. Alignment of chromosomes at the equator
C. Condensation of chromatin
B. Synapsis of chromosomes
What do we mean when we use the terms monohybrid cross and dihybrid cross?
A. A dihybrid cross involves organisms that are heterozygous for two characters and a monohybrid cross involves only one.
B. A monohybrid cross results in a 9:3:3:1 ratio whereas a dihybrid cross gives a 3:1 ratio.
C. A monohybrid cross produces a single progeny, whereas a dihybrid cross produces two progeny.
D. A monohybrid cross involves a single parent, whereas a dihybrid cross involves two parents.
A. A dihybrid cross involves organisms that are heterozygous for two characters and a monohybrid cross involves only one.
The individual with genotype AaBbCCDdEE can make many kinds of gametes. Which of the following is the major reason?
A. The tendency for dominant alleles to segregate together
B. Different possible assortment of chromosomes into gametes
C. Crossing over during prophase I
D. Recurrent mutations forming new alleles
B. Different possible assortment of chromosomes into gametes
In certain plants, tall is dominant to short. If a heterozygous plant is crossed with a homozygous tall plant, what is the probability that the offspring will be short?
A. 1/4 B. 0
C. 1/2 D. 1/6
B. 0
Labrador retrievers are black, brown, or yellow. In a cross of a black female with a brown male, results can be either all black puppies, 1/2 black to 1/2 brown puppies, or 3/4 black to 1/4 yellow puppies. These results indicate which of the following?
A. Epistasis is involved.
B. There is incomplete dominance.
C. Yellow is dominant to black.
D. Brown is dominant to black.
A. Epistasis is involved.
Cinnabar eyes are a sex-linked recessive characteristic in fruit flies. If a female having cinnabar eyes is crossed with a wild-type male, what percentage of the F1 males will have cinnabar eyes?
A. 25% B. 100%
C. 50% D. 75%
B. 100%
A woman is found to have 47 chromosomes, including three X chromosomes. Which of the following describes her expected phenotype?
A. Excessive emotional instability
B. Sterile female
C. Healthy female of slightly above-average height
D. Masculine characteristics such as facial hair
C. Healthy female of slightly above-average height
Males are more often affected by sex-linked traits than females because
A. X chromosomes in males generally have more mutations than X chromosomes in females.
B. female hormones such as estrogen often compensate for the effects of mutations on the X chromosome.
C. males are hemizygous for the X chromosome.
D. mutations on the Y chromosome often worsen the effects of X-linked mutations.
C. males are hemizygous for the X chromosome.
Normally, only female cats have the tortoiseshell phenotype because
A. only males can have Barr bodies.
B. multiple crossovers on the Y chromosome prevent orange pigment production.
C. the males die during embryonic development.
D. a male inherits only one allele of the X-linked gene controlling hair color.
D. a male inherits only one allele of the X-linked gene controlling hair color.
Which of the following statements is true of linkage?
A. Crossing over occurs during prophase II of meiosis.
B. The closer two genes are on a chromosome, the lower the probability that a crossover will occur between them.
C. All of the traits that Mendel studied–seed color, pod shape, flower color, and others–are due to genes linked on the same chromosome.
D. Linked genes are found on different chromosomes.
B. The closer two genes are on a chromosome, the lower the probability that a crossover will occur between them.
An inversion in a human chromosome often results in no demonstrable phenotypic effect in the individual. What else may occur?
A. The individual is more likely to get cancer.
B. There may be deletions later in life.
C. Some abnormal gametes may be formed.
D. All inverted chromosomes are deleted.
C. Some abnormal gametes may be formed.
Which of the following produces a Mendelian pattern of inheritance?
A. A chloroplast gene mutation
B. A trait acted upon by many genes
C. A mitochondrial gene mutation
D. Viral genomes that inhabit egg cytoplasm
B. A trait acted upon by many genes
Cytosine makes up 42% of the nucleotides in a sample of double-stranded DNA from an organism. Approximately what percentage of the nucleotides in this sample will be thymine?
A. 8% B. 42%
C. 16% D. 31%
A. 8%
In trying to determine whether DNA or protein is the genetic material, Hershey and Chase made use of which of the following facts?
A. DNA contains purines, whereas protein includes pyrimidines.
B. DNA contains phosphorus, whereas protein does not.
C. DNA contains sulfur, whereas protein does not.
D. RNA includes ribose, whereas DNA includes deoxyribose sugars.
B. DNA contains phosphorus, whereas protein does not.
What is meant by the description "antiparallel" regarding the strands that make up DNA?
A. The 5' to 3' direction of one strand runs counter to the 5' to 3' direction of the other strand.
B. One strand is positively charged and the other is negatively charged.
C. One strand contains only purines and the other contains only pyrimidines.
D. Base pairings create unequal spacing between the two DNA strands.
A. The 5' to 3' direction of one strand runs counter to the 5' to 3' direction of the other strand.
Which of the following statements is true of histones?
A. Histones are found in mammals, but not in other animals or in plants or fungi.
B. The mass of histone in chromatin is approximately nine times the mass of DNA.
C. Histone H1 is not present in the nucleosome bead; instead, it draws the nucleosomes together.
D. Each nucleosome consists of two molecules of histone H1.
C. Histone H1 is not present in the nucleosome bead; instead, it draws the nucleosomes together.