MT1 - {Tonal Harmony} Ch. 1: Elements of Pitch
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
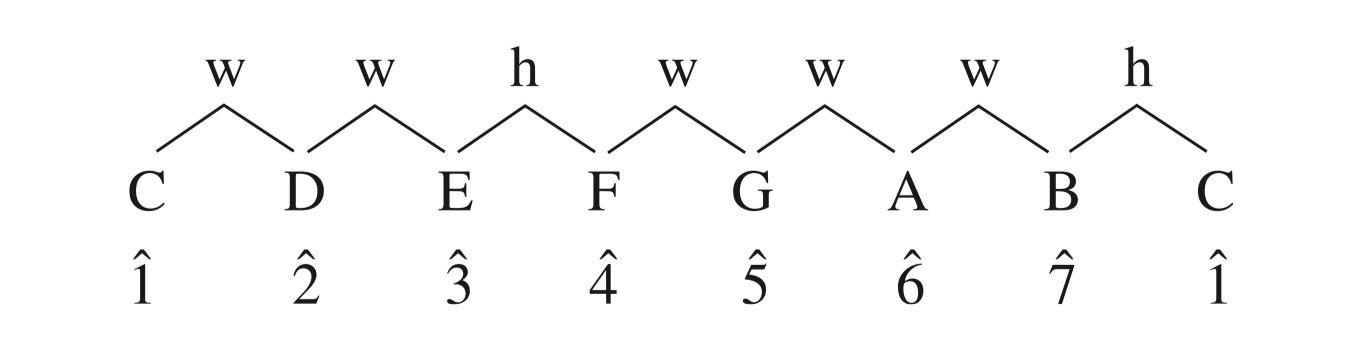
A specific pattern of small steps (half steps) and larger one (whole steps) encompassing an octave
Major scale
The distance from a key on the piano to the very next key, white or black (using white keys on the piano, there are two half steps in each octave)
Half step
Skips the very next key and goes instead to the following one
Whole step
Four-note patterns
Tetrachords
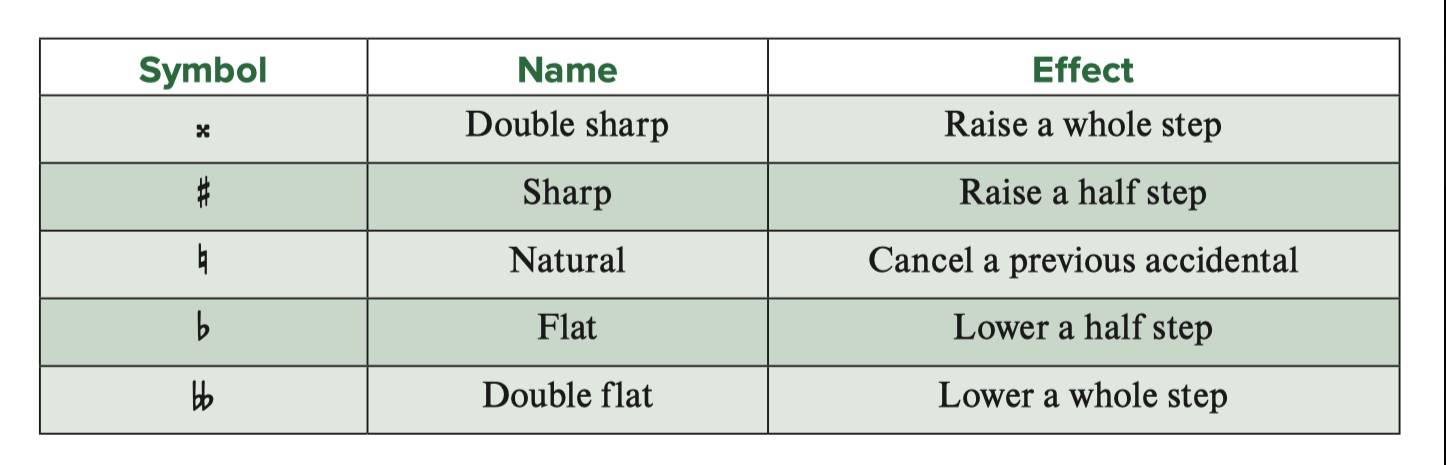
A symbol that raises or lowers a pitch by a half or whole step
Accidental
To identify the first degree of a scale
Key
A pattern of sharps or flats that appears at the beginning of a staff and indicates that certain notes are to be consistently raised or lowered
Key signature
Notes that have the same pitch but that are spelled differently, like E and F♭
Enharmonic (enharmonically equivalent)
To write or play music in some key other than the original
Transpose
A diagram like the face of a clock to help memorize key signatures
Circle of fifths
A seven-note musical scale consisting of a whole, half, whole, whole, half, whole, whole step pattern
Natural minor scale
A musical scale that starts from the natural minor scale, has its seventh degree raised by a half step (A, B, C, D, E, F, G♯)
Harmonic minor scale
An ascending form and a descending form, ascending form is up by the 3rd, and descending from is the same as the natural minor scale (down by the 7,6, and 3)
Melodic minor scale
Pattern of w-h-w-w
Minor pentachord
Share the same key signature
Relative keys
A major key and a minor key that share the same tonic (starting note)
Parallel keys
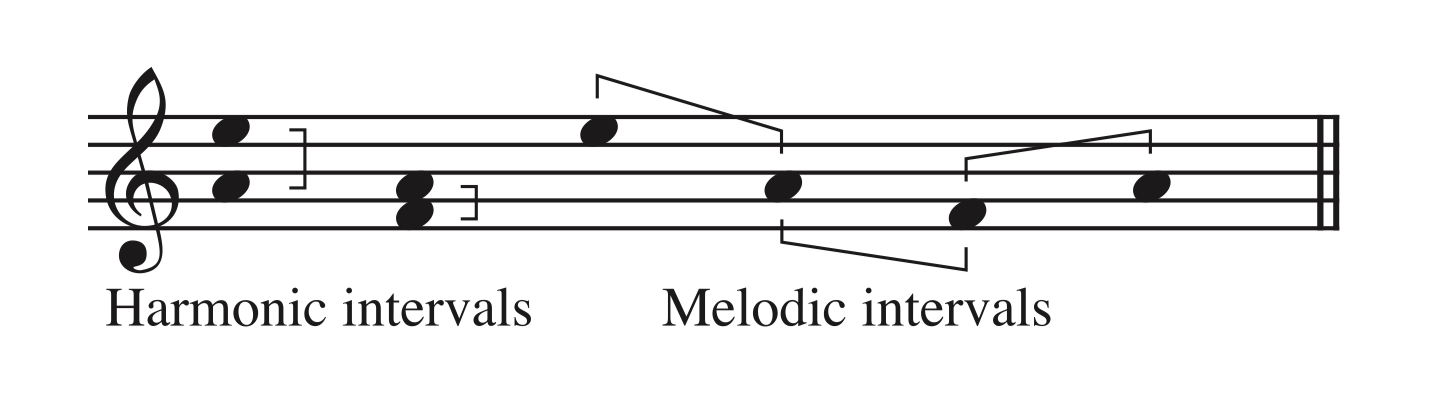
The measurement of the distance in pitch between two notes
Interval
Notes are performed at the same time
Harmonic interval
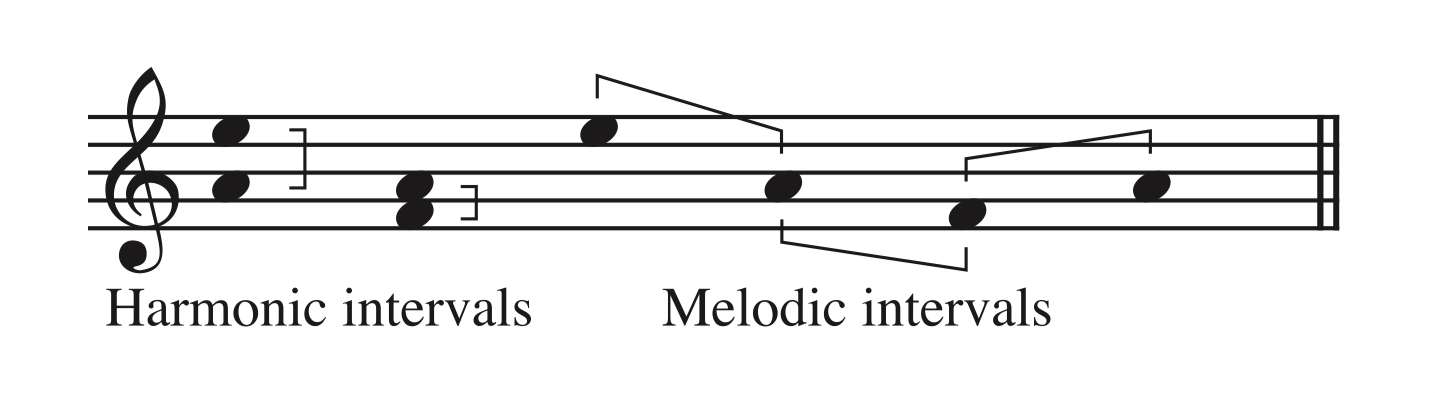
When the notes are played successively
Melodic interval
Two or more musical parts perform the same note at the same time, either in the same octave
Unison
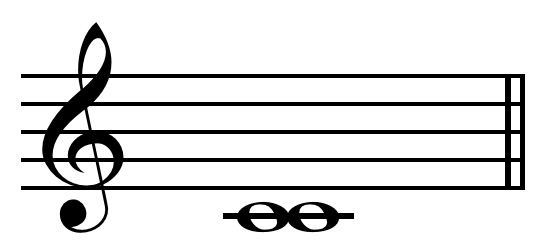
The internal between two notes of the same name, where the higher note has a frequency double that of the lower note
Octave
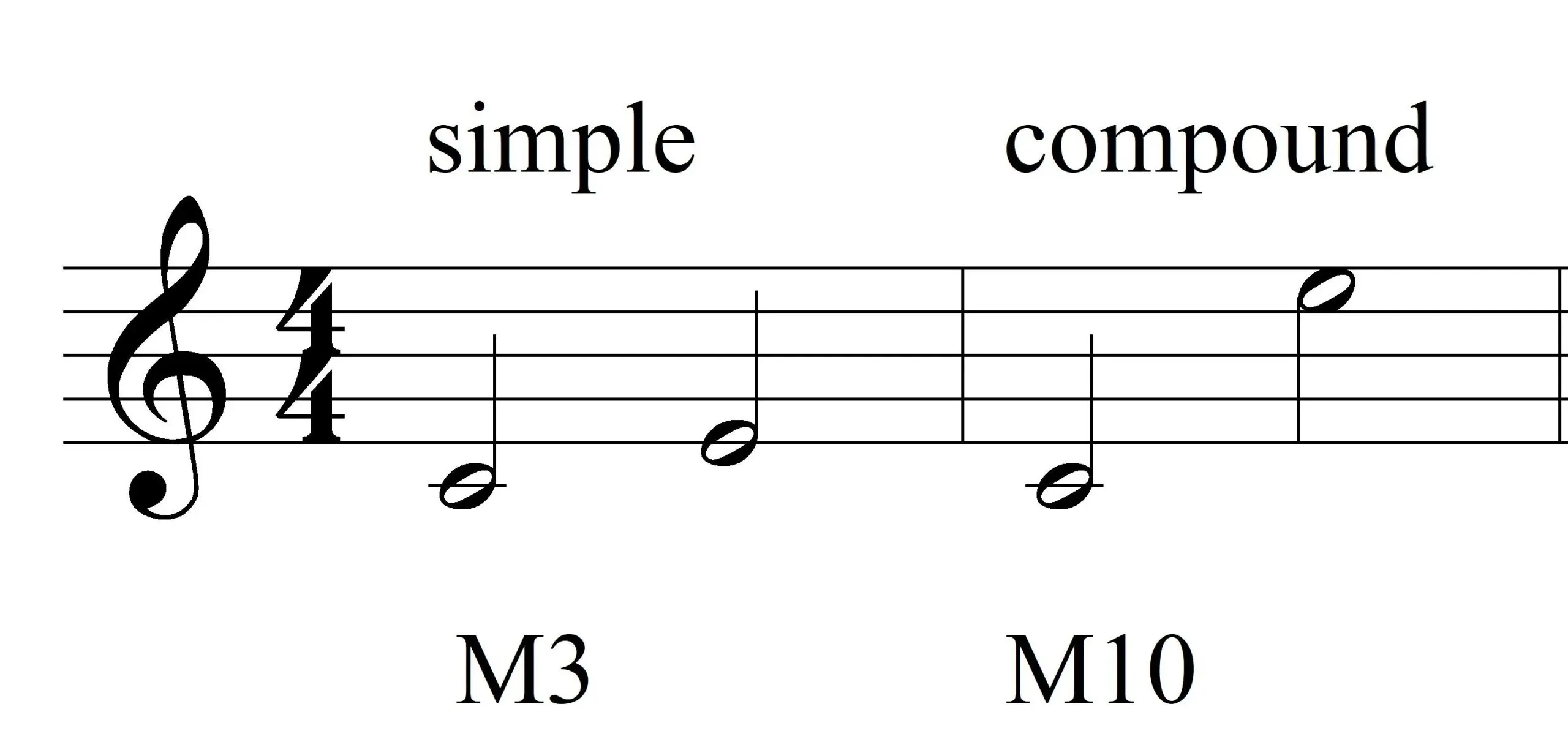
The distance between two notes that are one octave or less
Simple intervals
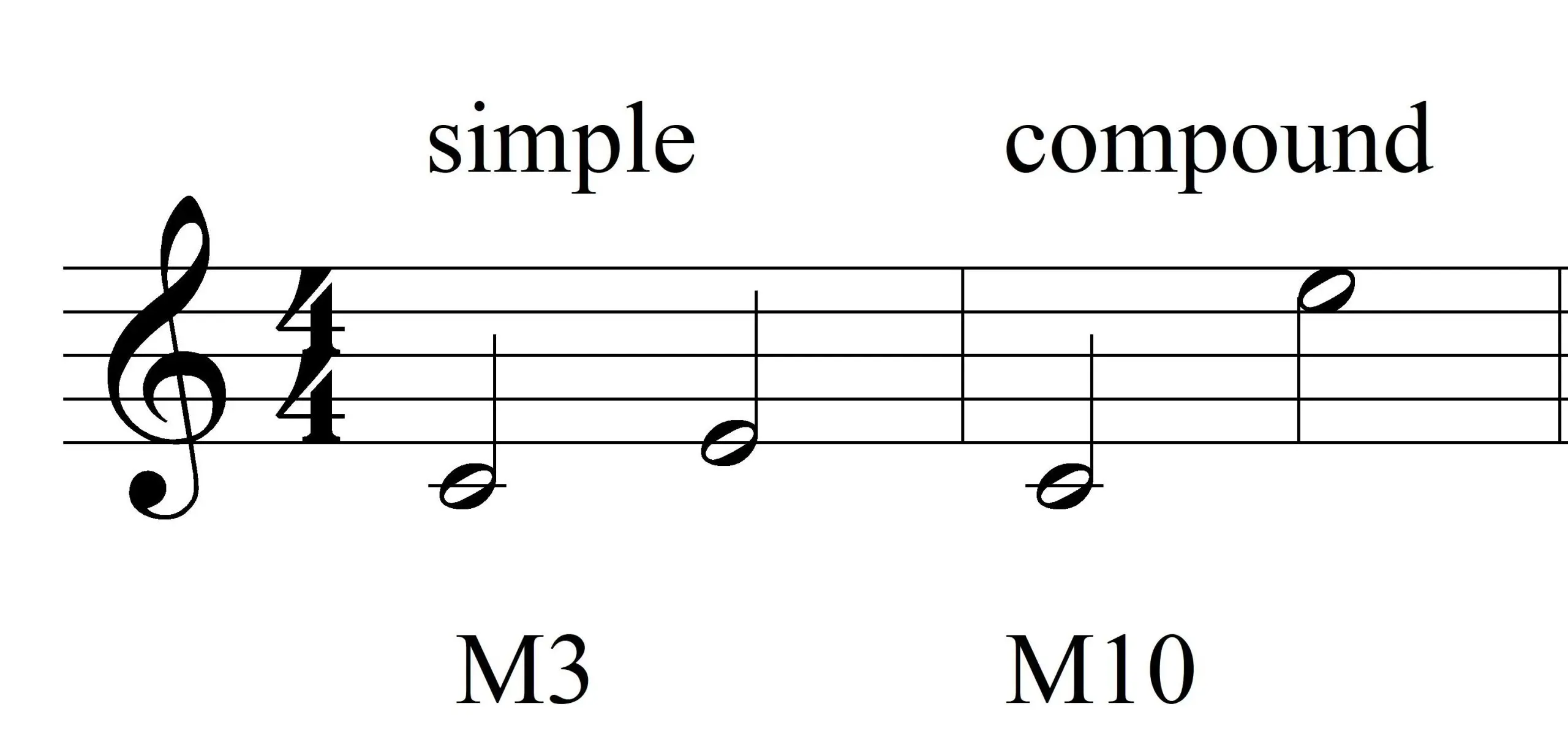
Larger intervals
Compound intervals
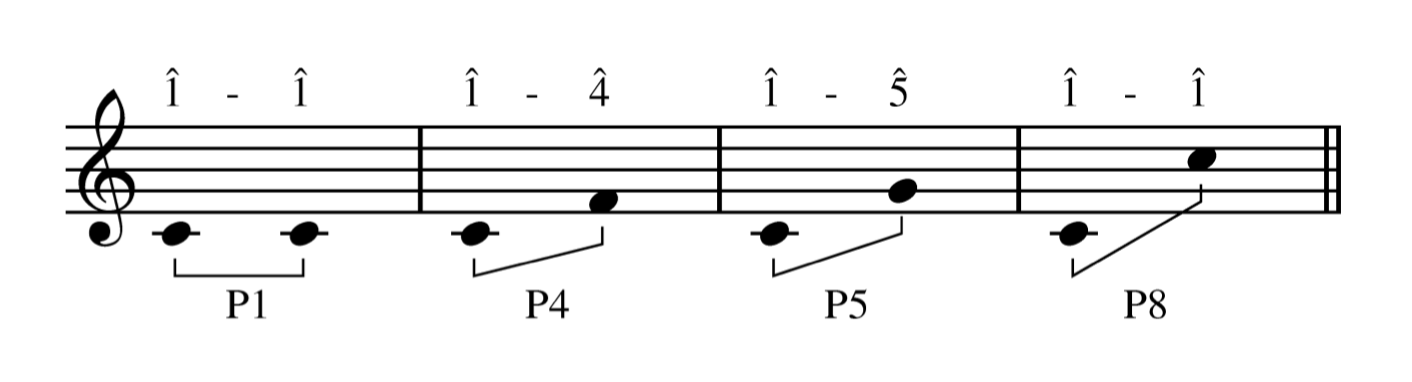
Used only in connection with unisons, 4ths, 5ths, 8ves
Perfect
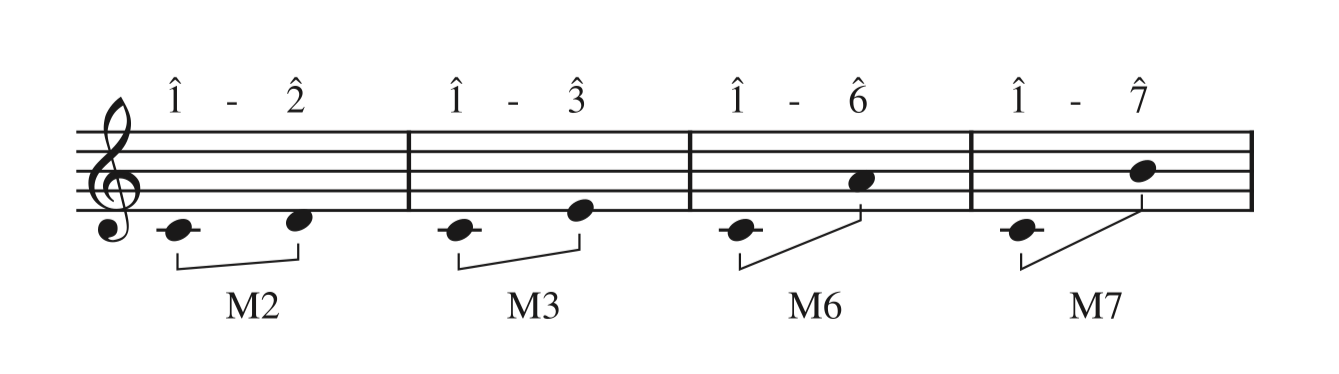
Used only in connection with 2nds, 3rds, 6ths, 7ths, and their compounds
(Modified) Major/minor
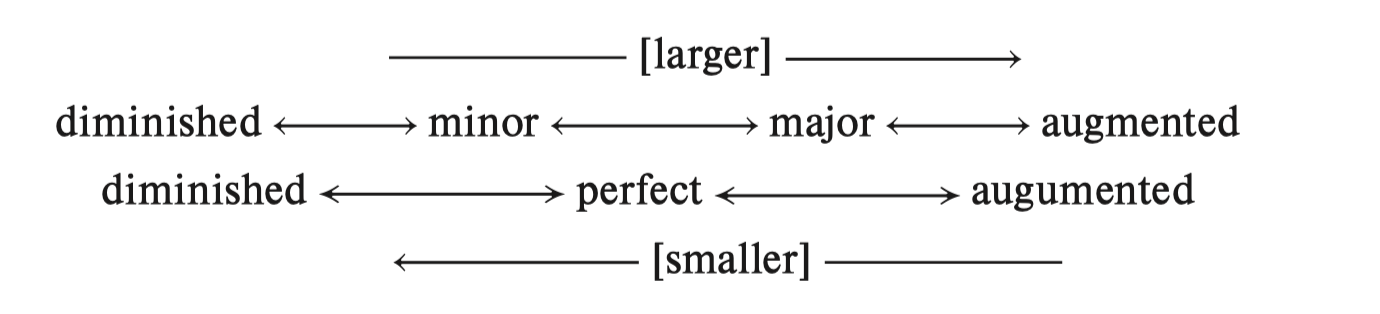
A perfect or a major interval is made a half step larger without changing the numerical name
Augmented
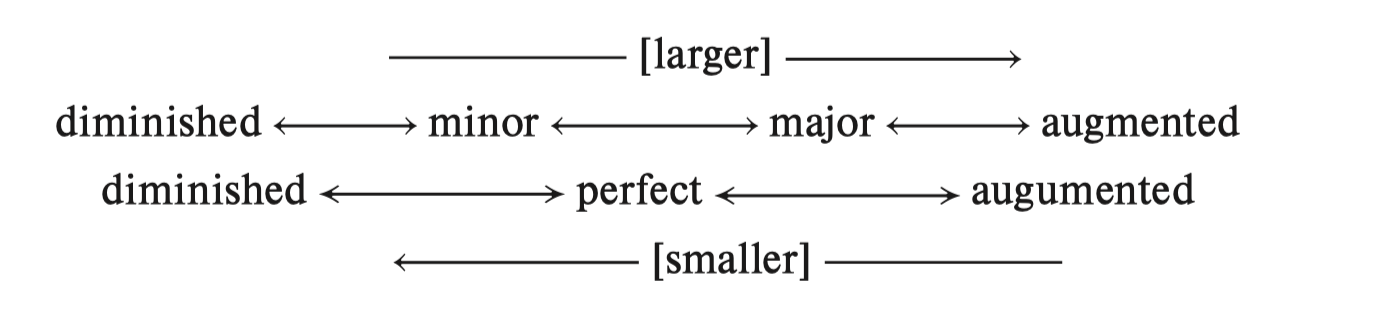
A perfect or a minor interval is made a half step smaller without changing ints numerical name
Diminished
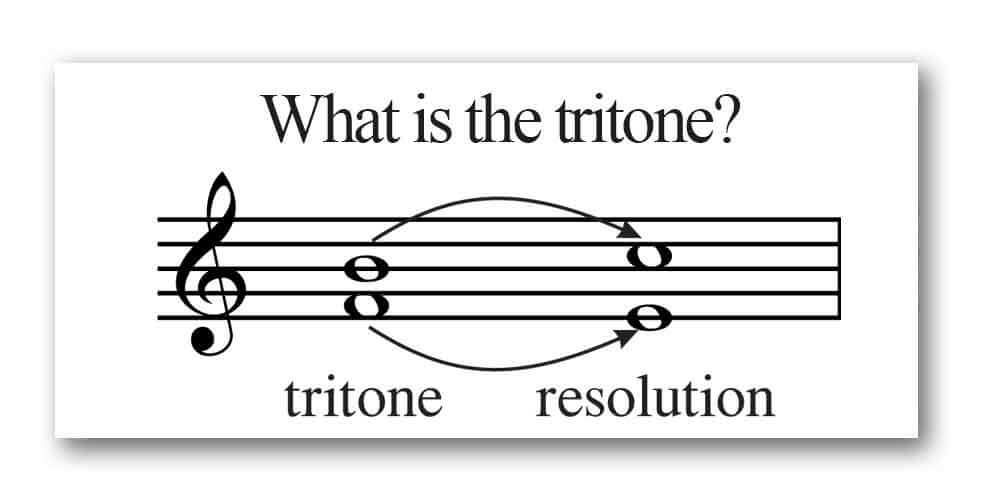
Used for the +4 or its enharmonic equivalent; a dissonant, unstable interval spanning three whole steps, equivalent to half an octave
Tritone
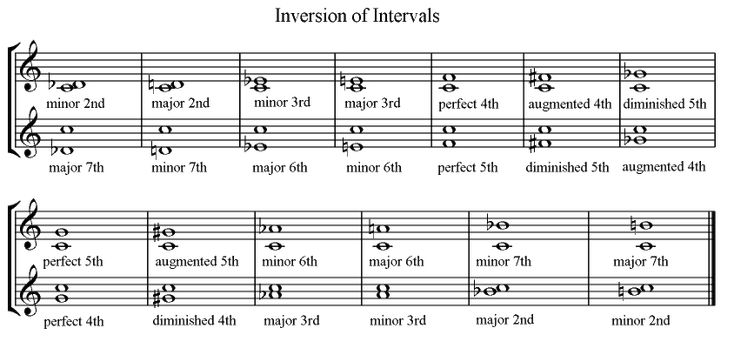
Descending intervals, especially large ones, often easier to spell and identify through use
Interval inversion
Pleasing to the ear and not pleasing to the ear,
Consonant/Dissonant
The lowest note played or notated
Bass
Highness or lowness of a sound (particular pitches named by using the musical alphabet, consisting of letters A through G)
Pitch
Space from any C up to the next B (numbered with the lowest C on piano)
Octave register
An arrangement of five lines and four spaces (pitches are notated on the staff)
Staff
Short horizontal lines extending the music staff to notate pitches above or below its five liens and four spaces
Ledger lines
Determine exactly what pitch is represented by each line or space
Clefs
two staves joined by a brace, with a table clef on the top staff and a bass clef on the bottom
Grand staff