Protozoans of Medical Importance
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Entamoeba histolytica - disease and mode of transmission
Disease: amoebiasis (amoebic dysentery)
Mode of transmission:
fecal-oral route (ingesting food/water contaminated with feces)
Ingesting cysts from contaminated food/water (cysts can be found in feces of an infected human)
Symptoms:
bloody diarrhea (cyst bypasses stomach acid, hatches in intestines-exycstation, becomes trophozoite and feeds on intestinal lining, causing ulcerations)
Vomiting
Nausea
Morphology
cyst: “bullseye” nucleus.
Up to 4 nuclei in a single, perfectly circular cyst
Mnemonic: ENT = enteric (affects the gut)
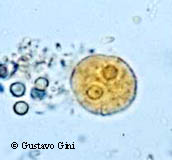
Enteamboea histolytica
Giardia lamblia- disease and mode of transmission
Disease: Giardiasis
also known as "Backpacker's diarrhea" or "Beaver fever".
Mode of transmission:
Drinking contaminated water
Symptoms:
Watery diarrhea (no blood. Parasite doesn’t penetrate intestine)
Greasy stool, foul smelling
Morphology:
Pear shaped
“owl face” nuclei: Looks like 2 eyes staring at you
4 flagella sticking out
Mnemonic: Giardia starts w/ G for Gut
Go traveling you get Giardia (drinking contaminated water in the wilderness where beavers might’ve pooped and released cysts)
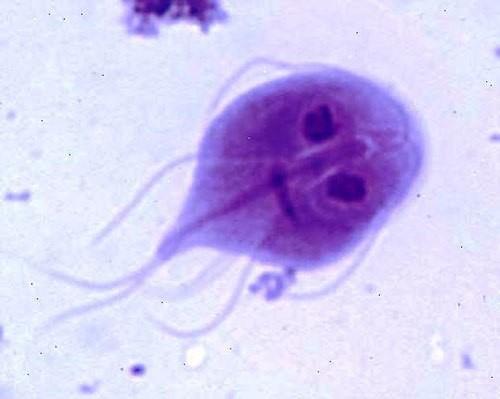
Giardia lamblia
Mnemonic: Giardia lamblia can be contracted when ur out in the wilderness drinking contaminated water and owls are found in the wilderness
Trichomonas vaginalis- disease and mode of transmission
Disease: trichomoniasis
Mode of transmission: sexually transmitted (Sexual intercourse)
Symptoms:
Females: purulent discharge, dyspareunia (pain during sex), dysuria. vulvar irritation
Males: affects male urethra and prostate
Inflammation of urethra, epididymis, prostate
Morphology
four anterior flagella
One posterior flagella along the outer membrane of the undulating membrane
Large nucleus located at the wider, anterior end (towards flagella)
Mnemonic: you MONkey around and have irresponsible seggs = STI of trichomonas
Tricho = hair so these organisms have hair like structures sticking out
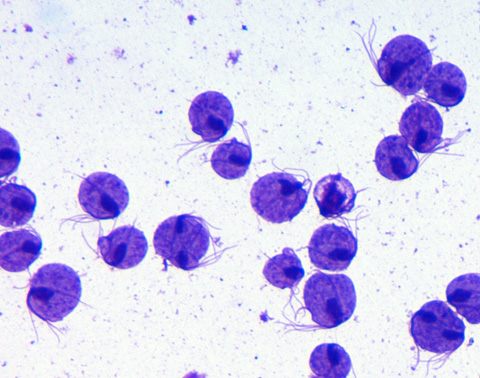
Trichomonas vaginalis
Trypanosoma brucei - disease and mode of transmission
Disease: African sleeping sickness (trypanosomiasis)
Mode of transmission: tsetse fly
bites human and injects trypanosoma in its active (trophozoite) stage
While biting, it injects trypomastigotes (the infective stage of Trypanosoma) into your skin
Infection occurs in 2 stages:
Hemolymphatic stage
Trypanosomes first enter lymph and then blood
Meningoencephalitis stage
happens when trypanosomes infect CNS
Deprive brain of glucose = coma (eternal “sleep”)
Mnemonic: “African Try to BRUise your sleep”
to remember T.brucei causes African sleeping sickness
Morphology:
Wiggly shaped
Small Kinetoplast located at posterior end (behind/posterior to the nucleus)
Often observed in blood smears
3 subspecies of T.brucei
Trypanosoma brucei gambiense
causes chronic African trypanosomiasis
“West African sleeping sickness”
Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense
causes acute (rapid) African trypanosomiasis
“East African sleeping sickness”
Mnemonic: East is on the Right so it causes Rapid African trypanosomiasis
Trypanosoma brucei brucei
parasite primarily of cattle and occasionally other animals
Under normal. Conditions doesnt infect humans
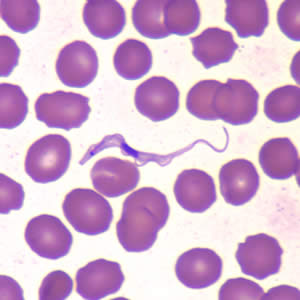
Trypanosoma brucei
Trypanosoma cruzi- disease and mode of transmission
disease: chagas disease
Mode of transmission: “kissing bug”
punctures thin skin (Eg: lip, eyelid) of individual
When it defecates, its feces contains the parasite, which could enter the wound of the host
Balantidium coli- disease and mode of transmission
disease: balantidiasis
Mode of transmission: fecal-oral route
ingesting poop contaminated food/water
Symptoms
diarrhea
Morphology
trophozoite contains cilia (Coli = Cilia)
Kidney/B shaped nucleus
Mnemonic: Balantidium = B shape
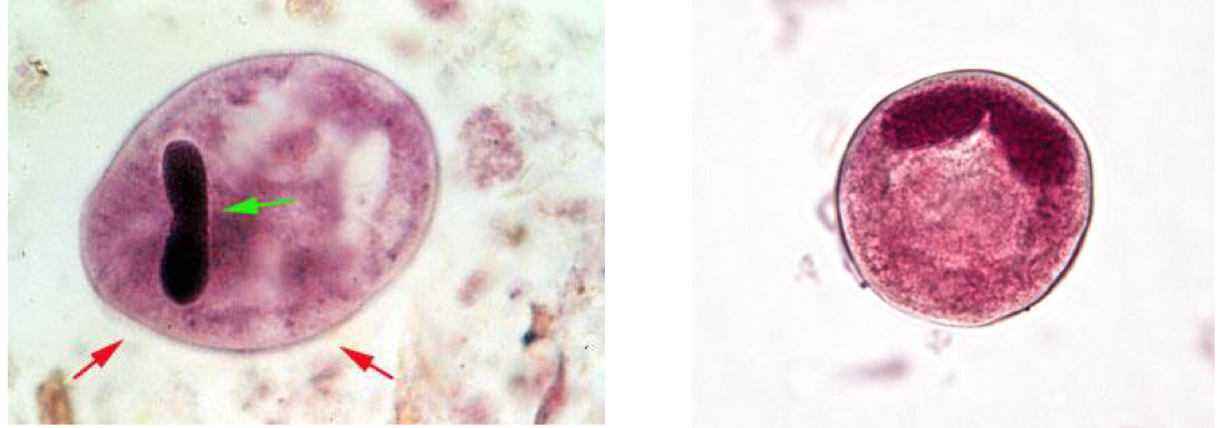
Balantidium coli
Right = cyst
Left = trophozoite
Plasmodium spp. - disease and mode of transmission
disease: malaria
parasites invade liver and rbc, causing hemolysis
mode of transmission: female Anopheles mosquito
infection: infected mosquito bites human, injects parasite into blood.
blood —> liver cells—> red blood cells (ring stage)—> hemolysis (shizont)
morphology:
ring stage: looks like a ring inside the rbc
shizont: a multinucleated cell inside the rbc
gametocyte: banana/sausage shaped. seen in blood smear.
mnemonic: PLASModium = parasite in plasma (blood) causes Malaria (plasMA MAlaria)

plasmodium spp
Plasmodium species (4) and which causes most severe infections?
Plasmodium Malariae
Plasmodium Falciparum
Plasmodium Vivax
Plasmodium Ovale
Most severe infections = P.falciparum
Toxoplasma gondii- disease and identification
disease: toxoplasmosis
congenital toxoplasmosis: Congenital (present at birth) toxoplasmosis is passed through the placenta to the fetus. Some babies won’t have any symptoms at birth, but are at high risk for developing them later on.
mode of transmission: eating undercooked meat, ingestion/inhalation of oocysts (found in cat feces)
Cat poop can contaminate soil, water, plant material and the food we eat.
morphology:
crescent moon shape
tapered anterior and blunt posterior end
mnemonic: TOXic waste in cats
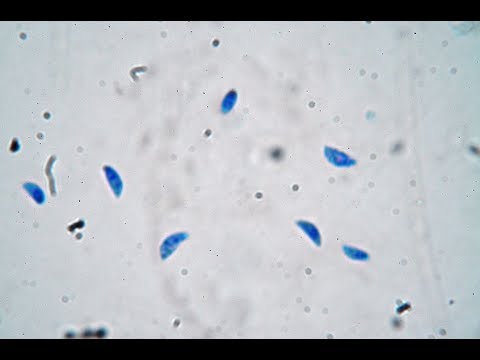
Toxoplasma gondii