Chapter 13 - Central Nervous System
1/79
Earn XP
Description and Tags
BIO 047
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
What are the directional terms for the brain?
Dorsal - superior portion
Ventral - inferior portion
Rostral - points toward anterior portion
Caudal - points toward posterior portion
What are the directional terms used for the spinal cord & brainstem?
Dorsal - posterior side
Ventral - anterior side
Rostral - points toward superior portion
Caudal - points toward inferior portion
The spinal cord extends from the foramen magnum to the level of the vertebrae ___ or ___.
L1 or L2
Spinal nerves pass through the ______ ______.
Intervertebral foramen
The tapered inferior end of the spinal cord is the _____ _____.
Conus medullaris
The long filament of connective tissue that runs from the conus medullaris to the coccyx is the _____ _____. What does it do?
Fillum terminale. It secures the cord and prevents jolting.
What are the cervical & lumbar enlargements of the spinal cord? Which limbs do the nerve running through them supply?
They are enlarged sections of the spinal that contain greater amounts of nerves emerging from them.
Spinal nerves from cervical enlargement supply upper limbs
Spinal nerves from lumbar enlargement supply lower limbs
What is the organization of spinal cord segments aligning with the spinal nerves emerging from them?
Cervical - C1-C8
Thoracic - T1-T12
Lumbar - L1-L5
Sacral - S1-S5
Coxxyl - Co1
White matter is composed of ____ and ____ axons. What do they act as in terms of transmitting info?
Myelinated and unmyelinated. They act as the roadways for transmitting info from one gray matter to another
White matter of the spinal cord are made up of fibers that can be classified by type, what are they and how do they differ?
Ascending fibers - carry info from sensory neurons up to the brain
Descending fibers - carry motor instructions from the brain downward to the spinal cord, simulating effectors
Commissural fibers - made up of bundled axons, transmitting info from one side of the cord to another (L and R)
The crossbar of the “H” containing the central canal is known as ______ ______.
Gray commissure
What are the characteristics of the horns belonging to the gray matter of the spinal cord?
Dorsal horn - consists of interneurons
Lateral & ventral horns - contain cell bodies of motor neurons
This matter is shaped like the letter “H” on the spinal cord.
Gray matter
Size of ventral horns can vary according to ______.
The skeletal musculature it’s motor neurons supply to
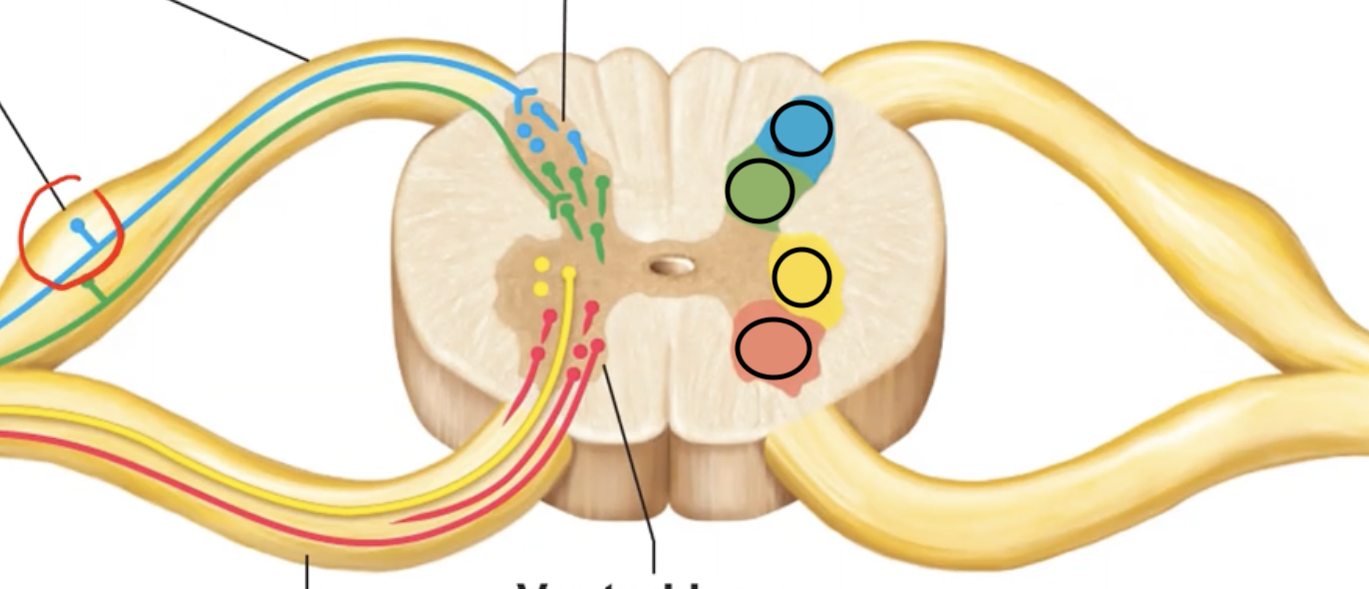
The blue section is supplied by what type of neuron? What type of info do these neurons route?
Somatic sensory, which routes info like pain on skin.
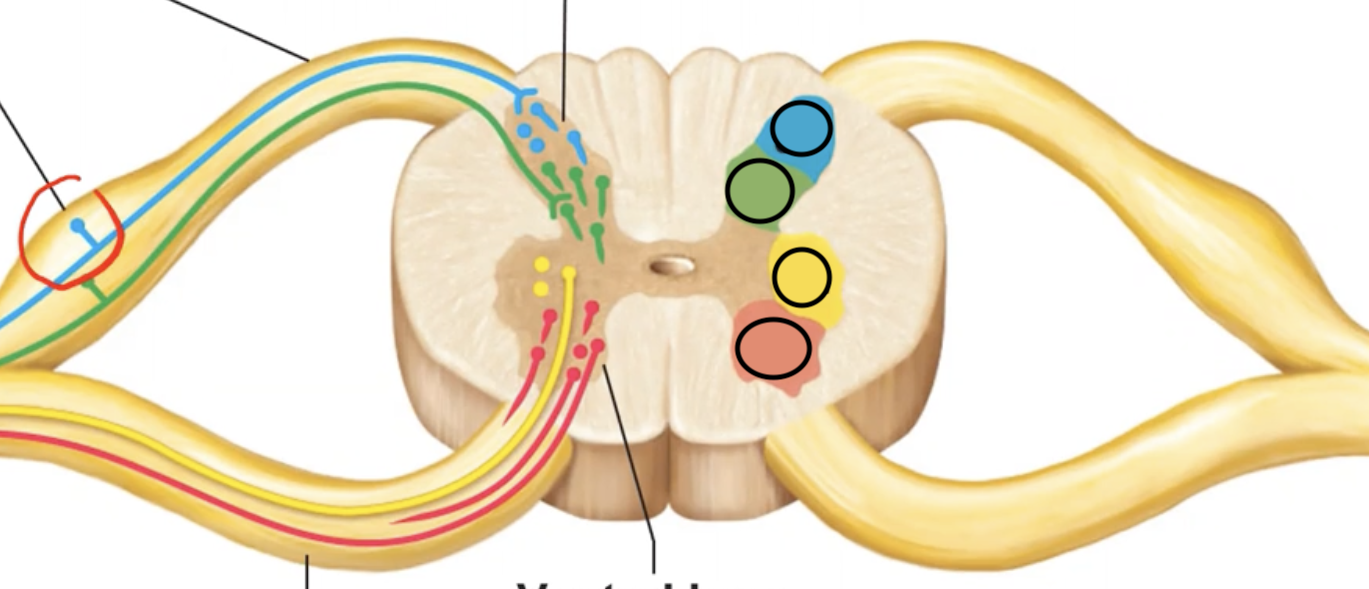
The green section is supplied by what type of neuron? What type of info do these neurons route?
Visceral sensory, which routes info like pressure on heart.
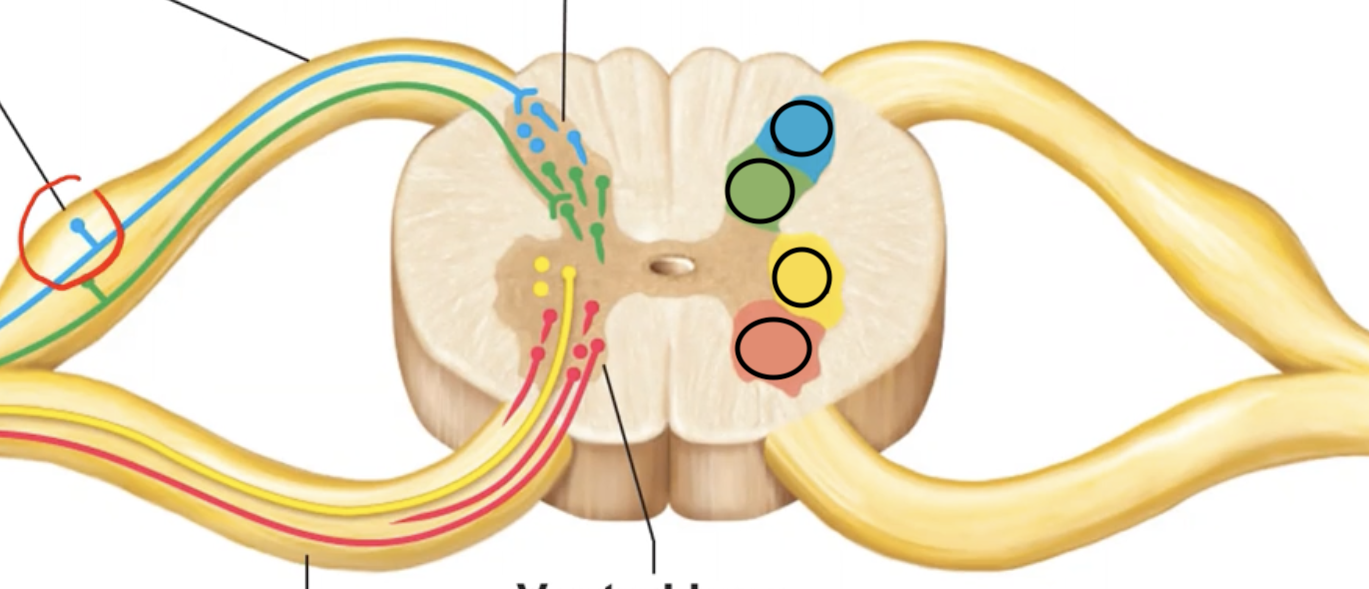
The yellow section is supplied by what type of neuron? Where do these neurons route info to?
Visceral motor, which routes info TO smooth cardiac muscles & glands.
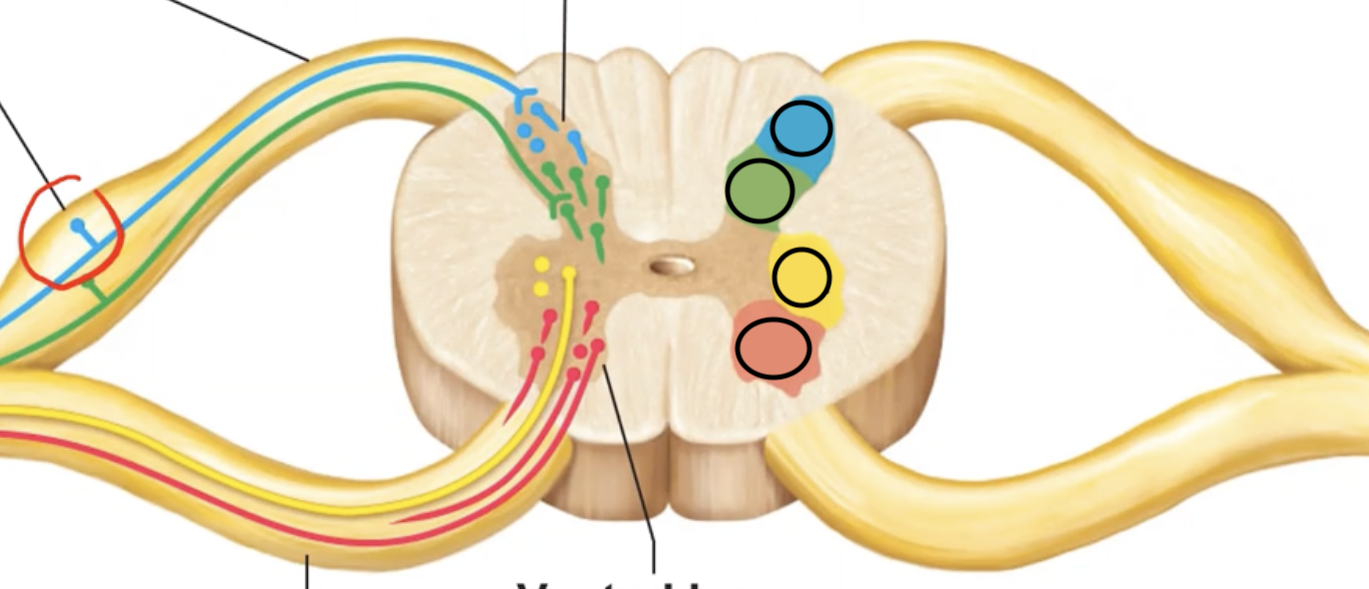
The blue section is supplied by what type of neuron? Where do these neurons route info to?
Somatic motor, which routes info TO skeletal muscles.
Shallow grooves are also known as _____.
Sulci / sulcus
Deep grooves are known as _____.
Fissures
The median sulcus of the spinal cord is located ______ while the median fissure is located _____.
Dorsally, ventrally
The spinal cord is protected by what structures?
Vertebrae, meninges, and CSF.
What are meninges? What are the different layers of them?
Meninges are fibrous membranes surrounding the spinal cord.
Dura mater: single outermost layer & the most durable
Arachnoid mater: directly deep to the dura mater (tightly attached)
Pia mater: innermost layer clinging tightly to chord, leaving a large space between itself and the arachnoid mater
What space is found superficial to the dura mater and largely contains fat?
The epidural space
True or false, the subarachnoid space harbors CSF & large blood vessels?
True!
True or false, the subdural space should be filled with fluid and should not be empty?
False, the subdural space is a POTENTIAL fluid space but SHOULD be empty in healthy individuals.
What are the functions of cerebrospinal fluid?
Provides a liquid cushion & increases buoyancy for CNS organs, nourishes the brain & spinal cord, removes waste, and carries chemical signals between parts of the CNS.
What are the four regions the brain is divided into and how else can it be organized?
Modern version
Cerebrum
Diencephalon
Brainstem
Midbrain, pons, & medulla
Cerebellum
Older version
Forebrain - Cerebrum + diencephalon
Hindbrain - Pons, medulla, & cerebellum
Midbrain - In between forebrain & hindbrain
The ventricles of the brain are lined with _____ _____.
Ependymal cells
When it comes to matter in the brain, GRAY matter is _____ located while WHITE matter is _____ located.
Centrally; externally
What are the only two gray matter structures of the brain?
Gray nuclei - deeply situated & sparsely dispersed gray matter
Cortex - additional outer layer of gray matter formed from neuronal cell bodies
The lateral ventricles are located in _____ _____.
Cerebral hemispheres
The third ventricle lies in _____.
Diencephalon
The third ventricle connects to _____ _____ through the ______ _____.
Lateral ventricles, interventricular foramina.
The fourth ventricle is positioned by the ____ ____ and is flanked by openings called ______.
Brain stem, apertures
This structure filters blood to produce CSF.
Choroid plexus
What are the components that make up choroid plexuses?
Ependymal cells & blood capillaries
What are some general functions of the brain stem?
Produces autonomic behaviors necessary for survival (heart rate, breathing rate, etc.)
Passageway for all fiber tracts running between the cerebrum & spinal cord
Heavily involved w/ the innervation of the face & head (10/12 cranial nerves attach to it)
Describe the external landmarks of white matter pertaining to the medulla.
Pyramids - bulging structures of white matter that lie on its ventral surface
Inferior cerebellar peduncles - fiber tracts connecting the medulla & cerebellum
Pyramids of the medulla harbor pyramidal motor tracts, what are they and what do they do?
Pyramidal motor tracts are nerve fibers running from the midbrain, descending through the pyramid, and then crossover before reaching the spinal cord. They transport voluntary motor output from the cerebrum and carry them to effectors.
The inferior cerebellar peduncle allows for communication between the _____ and _____ _____.
Cerebellum, spinal cord
The cell bodies of cranial nerves __-__ cluster within _____ _____ ____, which is composed of ____ ____.
The cell bodies of cranial nerves VIII-XII cluster within cranial nerve nuclei, which is composed of gray matter.
The core of the medulla contains much of the _____ _____, which influence autonomic functions like ______ ______.
Reticular formation, cerebral alertness
The pons is known as a bridge between the ______ and _____. It contains the nuclei of which cranial nerves?
Midbrain, medulla. It contains the nuclei of the trigeminal nerve (V), abducens nerve (VI), and facial nerve (VII).
The middle cerebellar peduncles indirectly allow for communication between the _____ and _____.
Cerebellar, cerebrum
The midbrain lies between the ____ and the ____.
Diencephalon, pons
These are the eraser-shaped structures on the ventral portion of the midbrain.
Crus cerebri (or cerebral peduncles)
The superior cerebellar peduncles indirectly allow for communication between the ____ and ____.
Cerebrum, cerebellum
Red nucleus is a structure belonging to the ____, which helps maintain cerebral alertness.
Midbrain
Substantia nigra is a structure belonging to the midbrain which is crucial for _____ _____, and when degenerated, is the culprit for Parkinson’s disease.
Motor control
The midbrain contains the cranial nerve nuclei for the ____ and ____ nerve.
Oculomotor (III), trochlear (IV)
Corpora quadrigemina is the term used when _________. What do the two separate sets of colliculi function as?
All four colliculi are collectively seen. The superior colliculus is for visual reflex and the inferior colliculus is for auditory reflex.
What do crus cerebri harbor?
Fibers of the pyramidal motor tract
The vermis of the cerebellum partitions the ____ _____ ____ ______ ______.
Left and right cerebellar hemispheres
This structure gives rise to the cauliflower-looking appearance of the cerebellum.
Folia
The cerebellum is composed of these 3 regions. Specify what type of matter they are.
1) Cortex - gray matter
2) Arbor vitae - internal white matter
3) Deep cerebellar nuclei - deeply situated gray matter
What are the main functions of the cerebellum?
Coordinate & smooth out movements controlled by the other body parts
Help maintain equilibrium (balance)
The diencephalon is composed of these 3 paired gray matter structures.
Thalamus
Hypothalamus
Epithalamus
All sensory messages, except for _____, will pass through the thalamus & be processed before they are conveyed to the cerebrum.
Olfaction
This is the small pit-shaped structure adhering the pair of thalami together.
Interthalamic adhesion
The hypothalamus lies under the thalamus, between the ______ _____ and the ______ ______.
Optic chiasma, mammillary body
True or false, structurally the pituitary gland is found in the CNS but is functionally part of the endocrine system?
True!
List some of the functions of the hypothalamus.
Control of the ANS
Control of emotional responses
Control of motivational behavior
Control of he endocrine system via manipulation of pituitary gland secretion
Regulation of body temp
Regulation of hunger & thirst sensations
Regulation of sleep-wake cycles
Formation of memory
The epithalamus secretes the hormone ______. How does this aid the hypothalamus?
Melatonin. It aids the hypothalamus in control of circadian rhythm.
True or false, the convoluted appearance of the brain is due to sulci & gyri?
True
The cerebral cortex is the home of our ____ mind and enables us to…
Concious
Be aware of ourselves & our sensations
Initiate & control voluntary movements
Communicate, remember, & understand
The cerebral cortex contains these three kinds of functional areas made up of interneurons.
Sensory areas
Association areas
Motor Areas
The primary somatosensory cortex is involved with conscious awareness of _____ _____ senses. The somatosensory association area integrates different sensory inputs for _____ and _____.
General somatic; touch and pressure
The primary visual receives _____ _____ that originates on the _____. The visual association area functions to _________________________.
Visual info, retina; continues the process of visual information (analyzing color, form, movement, etc.).
The primary auditory cortex is involved with conscious awareness of ______. The auditory association area lies in the center of the _______ ______ and is involved in ______ and _____ speech.
Sound; Wernicke’s area, recognizing and understanding speech
The motor areas of the cerebral cortex are into these four parts. Specify their location and additional info needed to know about them.
Primary motor cortex
Located in precentral gyrus
Controls motor functions
Premotor cortex
Located anteriorly to the precentral gyrus
Controls & plans more complex movements
Frontal Eye Field
Controls voluntary movement of the eyes
Broca’s Area
Found in L cerebral hemisphere
Manages speech production
Cerebral white matter allows for communication between…
Different areas of the cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex and the brain stem & spinal cortex
What are the different types of tracts found in cerebral white matter & their characteristics?
Commisures - composed of commissural fibers & allow communication between the cerebral hemispheres
Association fibers - connect different parts of the same hemisphere
Projection fibers - run vertically & allow for communication between higher regions of the brain & spinal cord
Deep gray matter of the cerebrum consists of basal ____ and basal _____ _____.
Basal ganglia, basal forebrain nuclei
Degeneration of this structure is the culprit for Alzheimer’s disease.
Basal forebrain ganglia
The function organization of the brain is divided into the ____ ____ and the _____ _____. How do they differ location-wise and what do they do specifically?
Limbic system
More localized, spread widely in the forebrain
Controls our emotions
Reticular formation (Reticular Activity System)
Spans the brainstem
Maintains conciousness & alertness
What are the structures making up the limbic system & their function?
Diencephalic structures
Hypothalamus - controls motivational / pleasurable behavior
Cerebral structures
Cingulate gyrus - helps us shift our thoughts, tells us pain is unpleasant
Amygdala - processes info related to fear / anger, activates our sympathetic nervous system
Hippocampus - allows us to consolidate & retrieve memory
Describe the meninges protecting the brain.
Dura mater - composed of two layers fused together
Arachnoid mater - deep to dura mater
Pia mater - clings tightly to the brain, following into its fissures & sulk
This structure extends from the arachnoid mater & into the dural sinuses, and recycle / return CSF to blood.
Arachnoid villi
True or false, BBB (Blood-Brain Barrier) is an absolute barrier that prevents all blood-borne toxins from entering the brain.
False, BBB prevents MOST toxins from entering the brain but can be penetrated by nutrients, nicotine, alcohol, etc.