AQA GCSE Geography: Coasts
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/48
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
1
New cards
How do different waves form?
Wind blowing over the sea. Friction with water surface causes ripples that develop into waves. The longer the fetch the more powerful the wave.
2
New cards
What is the fetch?
The distance the wind blows across the water
3
New cards
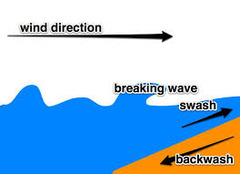
What is the swash?
The wave breaks onto the beach and moves up it
4
New cards
What is the backwash?
Water rolling back from the beach due to gravity
5
New cards
What is a prevailing wind?
A wind coming from the predominant direction
6
New cards
What is a constructive wave?
Long fetch with weak wind, low wave in proportion to length. Strong swash, weak backwash (soaks into sand/slowly drains away)
7
New cards
When do you see constructive waves?
Usually found in summer because of the weaker winds
8
New cards
What is a destructive wave?
Strong prevailing wind with a long fetch. Causes erosion. Tall breaker, weak swash, strong backwash.
9
New cards
What is a tall breaker?
It breaks downwards with a great force
10
New cards
When/Where do you see destructive waves?
In the winter (strong winds) and near oceans because of the strong prevailing wind, e.g Cornwall as it is close to the Atlantic
11
New cards
What are the four processes of erosion?
1. Hydraulic Action (pop!) 2. Abrasion 3. Attrition 4. Solution
12
New cards
What are the four processes of transportation?
1. Traction 2.Saltation 3. Suspension 4. Solution
13
New cards
What are the three types of weathering?
Biological (trees growing), Chemical (limestone dissolving in water), Mechanical (freeze thaw)
14
New cards
What is mass movement?
The downhill movement of weathered material due to the force of gravity
15
New cards
What are the four types of mass movement?
1. Rock Fall 2. Mudflow 3. Landslide 4. Rotational Slip
16
New cards
What is rock fall?
An avalanche of loose rocks, made worse by mechanical weathering (freeze thaw). An example of this was in Burton Bradstock, Dorset Coast in August 2016

17
New cards
What is mudflow?
A fluid or hardened stream or avalanche of mud often made worse by biological weathering. An example of this was in Stehekin, Washington in 2013.
18
New cards
What is landslide?
Blocks of rock slide downhill made worse by biological weathering. An example of this was in Hells Mouth, Cornwall in 2016.
19
New cards
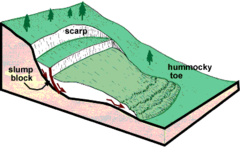
What is rotational slip?
Slump of saturated soil on a weak surface. An example of this is the Holbeck Hall landslide in Scarborough
20
New cards
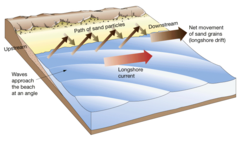
What is long shore drift?
When sediment moves across the beach. First onto it by swash (in the direction of the prevailling wind), when it comes back in backwash it goes at a right angle to the beach. This repeats.
21
New cards
What is a headland?
a narrow piece of land that projects from a coastline into the sea.

22
New cards
What is a bay?
a broad inlet of the sea where the land curves inwards.
23
New cards
How do headlands form?
It starts with a cliff face facing the sea that has alternate layers of soft rock (clay) and hard rock (sandstone, chalk, limestone). As the waves crash into the cliff face, erosion occurs. Due to the soft rock being less resistant, it erodes quickly, causing the hard rock to be left jutting outwards.
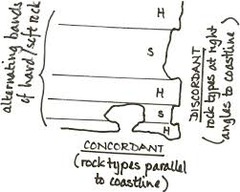
24
New cards
How do bays form?
It starts with a cliff face facing the sea that has alternate layers of soft rock (clay) and hard rock (sandstone, chalk, limestone). As the waves crash into the cliff face, erosion occurs. Due to the soft rock being less resistant, it erodes quickly, causing the hard rock to be left jutting outwards. This leaves bays that form in the soft rocks that curve inwards.
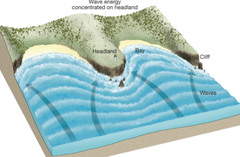
25
New cards
What is a wave cut platform?
Narrow flat area found at the edge of a sea cliff
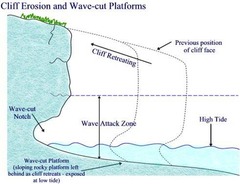
26
New cards
What is a spit?
Long narrow ridges of sand and shingle which is projected into the sea from the coastline.
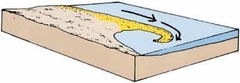
27
New cards
How do spits form?
1. L.S.D carries material across the coastline 2. This build of material creates an extension of the land 3. Spit grows out into sea 4. Spit becomes exposed to changes in wind and wave direction causing the spit to create a recurved end 5. Salt marshes form behind the spit 6. If the spit is growing across an estuary the length will be restricted due to floculation
28
New cards
Example of a spit
Spurn Head, Humber, Holderness Coast
29
New cards
What is a tombolo?
A ridge of sand and shingle joining the mainland to an island

30
New cards
How do tombolo's form?
The spit continues to grow until it connects the mainland and an island (like a bridge)
31
New cards
Example of a tombolo
Chesil Beach - which joins the South Dorset coast to the Isle of Portland.
32
New cards
What is a bar?
A ridge of sand and shingle which has joined two headlands, cutting off a bay

33
New cards
How do bar's form?
1. A spit grows the whole way across a bay 2. A lagoon forms in the bay and as there is low energy a salt marsh is created as there is lots of deposition
34
New cards
Example of a bar
Slapton Sands - Devon.
35
New cards
Can you describe the erosion of a headland?
1. The headland is eroded by the force of the waves 2. This creates a fault in the rock 3. This forms a cave 3. is eroded through, arch 4. Arch head falls, stack 4. Stack is undercut, stump
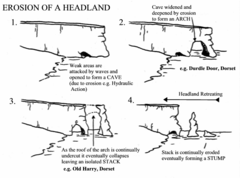
36
New cards
What is cave?
a natural underground chamber in a hillside or cliff, formed due to erosion of a headland

37
New cards
What is an arch?
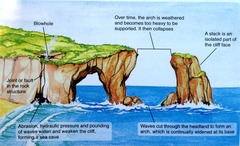
38
New cards
What is a stack?
e.g old harry

39
New cards
What is a stump?
e.g old harry's wife
40
New cards
What is hard engineering?
hard engineering is controlled disruption of natural processes by using man-made structures, e.g groynes, sea walls, rock armour

41
New cards
What are the benefits of hard engineering?
Can prevent lsd (groynes), protect the base of the cliff (sea wall), absorb energy of waves and allow build up of beach (rock armour)

42
New cards
What are disadvantages of hard engineering?
Ugly, expensive, unsustainable, lots of maintenance needed
43
New cards
What is soft engineering?
soft engineering is the use of ecological principles and practices to reduce erosion, working with the environment, e.g beach nourishment, managed retreat

44
New cards
What are the benefits of soft engineering?
don't disturb the natural environment, cheap, natural
45
New cards
What are the disadvantages of soft engineering?
have to compensate farmers (managed retreat), constant maintenance (beach nourishment)
46
New cards
Why are sea levels rising?
As temperatures rise (due to global warming), the sea absorbs heat from the atmosphere causing it to expand and sea levels rise.
47
New cards
What is thermal expansion?
Top layer of water is getting warmer so ice caps are melting, this causes sea level rise

48
New cards
What impact do rising sea levels have?
SOCIAL: death toll, water supplies (too much salt), loss of housing, loss of jobs ECON: decrease of land value, loss of tourism, damaged farm land ENVIRON: adaptation to ecosystems, increased coastal erosion
49
New cards
Where has been affected by rising sea levels?
Maldives - population of 300,000, made up of 1190 islands (199 are inhabited). Flat land (1.5m above sea level is average island height) scientists think it will be completely submerged in 50 to 100 years. Could disrupt their fish export which is their largest export