Chapter 21: The Origin and Evolutionary History of Life
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Autotroph
an organism capable of producing its own organic compounds from inorganic materials (photosynthesis for example)
Coacervate
a specific type of photobiont containing enzymes allowing synthesis pathways
Endomembranous theory
single membrane organelles originated by the plasma membrane budding inward and breaking off
Endosymbiont
an organism that lives in or on another
Endosymbiosis theory
double membrane organelles arose from a symbiotic relationship in which the endosymbiont living inside the cell lost its autonomy and became incorporated as an organelle within that cell
Heterotroph
an organism not capable of producing its own organic molecules from inorganic materials (will be a consumer)
Microsphere
one type of protobiont; produced by adding water to abiotically formed polypeptides
Protobiont
a vesicle of abiotically produced polymers
Stromatolite
a column of prokaryote cells that become fossilized (living stromatolites are extremely rare)
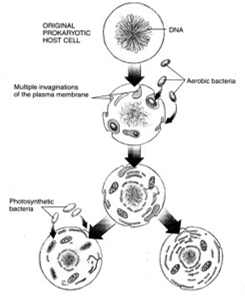
Which evidence supports the theory with aerobic bacteria illustrated in this figure
A.) The Miller-Urey experiment
B.) Burgess shale fossils
C.) Ediacarian Fossils
D.) The presence of DNA in some organelles
E.) All of these
D.) the presence of DNA in some organelles
What substances whose chemical structure may serve as a catalyst in a reaction
-pyrite (fools gold)
-clay
-charges surface attraction: ions Zn+ and Fe+ (catalysts)
Describe the Iron-SUlfur Hypothesis
organic found near hydrothermal vents (deep ocean)
protected the environment, were precursors of biological molecules bubble up, tube worms thrive there today
CO2, sulfur, mineral (nickel and iron)
Describe the Prebiotic Soup Hypothesis
water was an organic soup, over time it mixed and molecules spontaneously formed
miller ury eperiments
Miller-Urey conditions
soup mixture, heat source, lightning, rain, time
Miller-Urey Results
All 20 amino acids
Bases for RNA and DNA
lipids
If phosphate was added, ATP
Anaerobic
original: survives without O2
Aerobe
Requires O2
Heterotroph
original cells/organisms: use previously formed material (organic and inorganic)
Autotroph
Synthesize own organic nutrients from inorganic molecules
What are protobionts
spheres made of abiotically produced polymers (contains water)
Structural Properties of protobionts
-physically separate internal and external environments
-spontaneously divide when becomes too large (binary fission in organisms)
2 types of protobionts
-microspheres: proteinoids from sphere
-liposomes: lipids from sphere (may for a bilayer)
What are coacervates
(combination of organic molecules from sphere): closes structure to a cell
-biologically active molecules trapped inside (metabolic process possible)
-species type of brotobiome
Coacervate features
-Excitable: electrochemical gradients
-osmotically active: respond to osmotic and chemical changes
-biologically active: enzymes and reactants trapped inside(directed cellular reactions)
Explain the Metabolism First Hypothesis
Coacervates could provide the mechanism for metabolism (ATP ←> ADP)
-molecules necessary for metabolism (reactions within produced functional organization inside sphere)
-intrasphere energy source couple to reaction is possible
Explain RNA 1st Hypothesis
self replicating RNA arose first
-ribozymes need metal ions, drove self-replication and chemical reactions
-later independent enzymes catalyzed reaction… (RNA stores info: single strand =easy)
Other support: can take many shapes based on sequence, variety in sequence due to errors, can be synthesized in labs
Explain DNA 1st Hypothesis
Initial DNA synthesis: RNA replicated a duplicate strand and made DNA via reverse transcriptase
Negatives of DNA synthesis 1st Hypothesis
no enzymatic properties (no self-replication)
Positives for evolution of DNA
-double stranded=molecular stability
-fewer mutations than RNA and know DNA is needed to establish replication and cell lineage
Explain Heterotophs and the first cells
(rely on preformed molecules)= cant produce organic compounds from inorganic sources (CO2)
-consumed spontaneously→ formed organic molecules →cyano bacteria came on the seen
(anaerobic environment)
Explain the energy source transition for the first cells (4)
-Fermentation: heterotrophic and anaerobic
-Chemoautotrophs: use inorganic molecules for energy production (CO2 fixation)
-Photosynthesis: cyanobacteria split water (released O2) → transitions to aerobic environment
-Chemosynthesis: tube worms around thermal vents house bacteria (oxidize H2s)
Cyanobacteria
These organisms were most likely the source of the first free oxygen in the atmosphere
Explain the autogenesis (endomembranous) theory: single membrane organelles
the plasma membrane budded inward and broke off: single membrane organelles could have been breaking off of plasma membranes around primitive cell
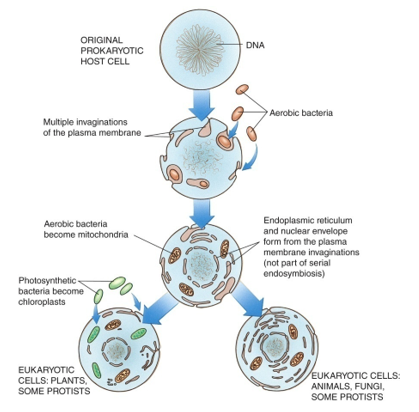
Explain the autogenesis (endomembranous) theory: double membrane organelles
Srial endosymbiosis: one organism is an endoparasite of another (endoparasite lost autonomy but remains part of host)
-chloroplasts: photosynthetic bacteria engulfed by heterotrophic cells
-mitochondria: aerobic bacteria initially engulfed by anaerobic cells
Compare and contrast mitochondria, chloroplasts, and bacteria
-size=similar
-genetics: DNA circular in all three, RNA ribosomes similar in all three
-enzymes and transport systems: similar to those of bacterial membrane
-replications: similar to bacteria fission or splitting
-antibiotic effects: effective against bacteria but impact mitochondrial/chloroplast activities