Moleclar genetics
1/91
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
What does dna do
hereditary inof
intructions for making protiens
What are protiens for
To carry out cellular processes
What si dna made of?
Nucleotide
Whta is a nuleotide made of?
Phospahet
Ribose rugar (deocyribose)
Nitorgen base
Whta aare the 4 nitrogen bases and thier differences?
Double ring:
- adenine
- Guanine
Single ring:
- Thymine
- Cytosine
Making the double helix
Sugard phospahte backbone: one sugar bonds to the next sugar via the phospahte group
the 2 back bones created are bonded to eachother through complimentary nitrogen bases
What are the complimentary bases?
A-t
C-g
In what direction does DNA display?
5’ end to 3’ end (open phospate - empty unbonded phosphate)
Are the backbones prallel?
No anti parallel, right most strand runs 5-3 up to down while left strand runs 3-5 up to down. This allows the nitrogen bases are lined up. (BOTH ARE ATILL READ 5-3)
Differences between RNA and DNA
double vs single strand
Sugar molecule is missing na oxygen on carbon2 (both still clasified as ribose)
Nitrogen base Thymine is Uracil in RNA
Why does DNA prelication need to be almost perfect?
to avoid harmful mutaitons
Process of DNA replication
hydrogen bond break and helix opens
eahc strand acts as a template for new complimentary strand
2 identicl DNA helices now made (each strand ahs a parent and daughter strand)
What enzyme makes the DNA
DNA polymerase III
What does DNA polymerase need to start building DNA
a primer, starting point signal
Explain how each half of the DNA is made
Leading strand: a continuos peice
Lagging strand: made in smaller peices
Why is the lagging strand made in small peices?
becuase fo the anti parallel nature of the DNA
What enzymes are needed for DNA replicaiton?
DNA Polymerase III
primase
helicase
Ligase
What does halicase do
Breakes the hydrigen bonds between the two strands of DNA
Why dont the single strands just bond back together?
Single stranded binding protiens (SSB) stabalize the single strands
Explain the use of primers in DNA replication
Primers are made from Primase. They are Short starnds of RNA that are added to the single DNA strand at the most 5’ end of the seperated DNA
They act as the starting point for DNA polymerase to recognize.
Also knonw as RNA primer
Primer diagram
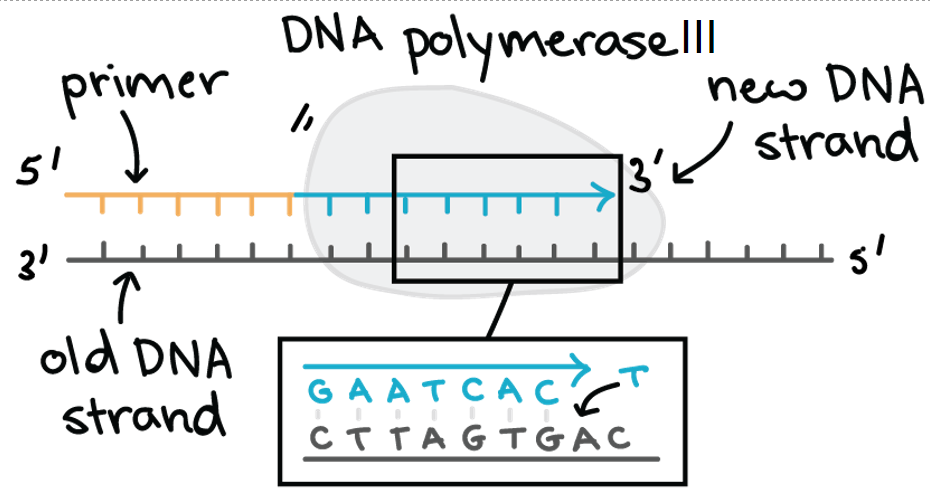
Are laggign strands made 5-3?
Yes, but back wards. The newly formed Lagging strand runs 3-5 tot eh primase is added part way up and DNA polymerase builds backwards to make the Okazaki fragmanets (Short DNA segments)
Do primers stay in the DNA strand?
No, DNA polymerase I removes it.
What is ligase responsible for
Ligase joins the the okazaki fragments together (becasue fot he primers being removed and spaces left)
What are telomers
Telemors are the non coding regions of the dna that are left after RNA primers are removed.
As they shorten, the cell ages and eventually dies
Why deos DNA get shorter after each round of replication?
as telomers are removd, the dna gets shorter each time
What does DNA polymerase do?
removes rpimers
fixes erros: can catch errors in base paring and remove inccorect bases.
will create a base in between fragments and then ligase fills int he rest of the gaps
How is a protien made?
Dna has the code
code has to get ot ribosome where its built
Describe Crick’s dentral dogma
Dna is slip and RNA is transcribed which leaves the nucleus tot he ribosome where it is translated into amino acids to build the protien
how to RNA code for amino acids?
3 nitrogen bases code fro 1 Amino acid. they are called Codons
Stop codons
The stop result of a codon is a signal for the RNA strad to stop beign rpoduced
What is trancription
the porcess of copying info from dna into an RNA
Does all of the DNA info need to transcribed?
No, only the specific sequences (genes)
How does RNA recognize where to transcribe?
Startign point is called the promoter sequence or Tataa box
what recognizes the tataa box and transcribes the dna info?
Enzyme called RNA polymerase
what does RNA polymerase make?
Pre-MRNA
How does RNA polymerase and the tataa box work together?
RNA polymerase binds to tataa and transcribes the sequecne comign after the taataa box. the RNA strand created is complimentary to thr DNA
In what direction is the RNA polymerase creatign Pre MRNA?
5→3
Compare error managemnt in protien creation vs dna replication
Transcription has NO proofreading so mistakes are made, BUT not always a probelm because fo the redundancy of genetic code
are there okazaki fragments in RNA productions?
no, RNA is single stranded
What is MRNA?
Messenger RNA that is transcribes from DNA
Describe the role of Terminator sequences (STOP) in DNA transcription
Terminator sequences are signals fro RNA polymerase and Pre MRNA to detach from DNA strand. RNA - P recognizes it as a stop
Before makign its way to the cytosol, what happens to MRNA
Mrna needs to be protected fro the cytosol: A 5 cap and Poly A tail are added to 5’ and 3’ ends right before the Strat codon and aftert the stop codon
Splicesomes remove introns and reconnect extrons to leave just codons
What is an extron
useful genetic coding sequences
Introns
non coding sequences of RNA
What is needed for RNA translation?
Transfer RNA + Ribosomes + mRNA
what is tRNA
free floating molecules that read the mRNA
mRNA tells the tRNA what amino acid to carry
how does tRNA recognize the codon sequencs of mRNA
using its anti codon that is complimentary to the mRNA codon.
What does Trna do in protien creation?
tRNA anticodon binds to mRNA codon (because complimentary)
3’ end is the attachment site of the amino acid whicht hen unbind and binds tot he next amino acid int he ribosome
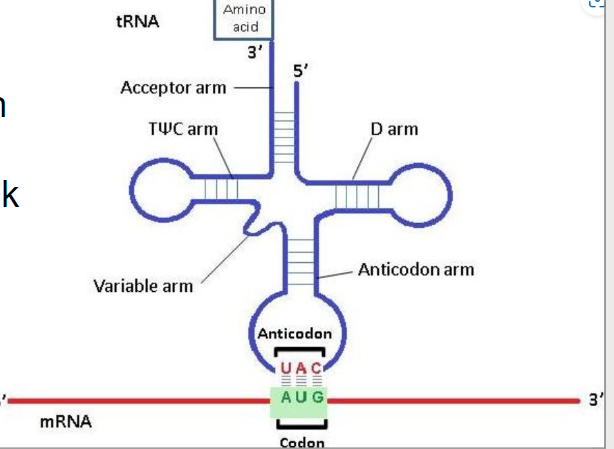
Whta is the ribosome is made of
protien rRNA
explain how the ribosome work
Mrna slides in between the two units. tRNA fits into p site where it bind to MRA codons in aticodons. Then another tRNA sits int he a site. amino acid bind to amino acid int he a site. then trna leaves throught eh e site
when does the tranlastion process stop?
when a stop codon ont he mRna is reached an stops mroe amino acids from being created
Release factor free the poly peptide chain (poly peptide start folding and stuff)
Brief summary of protien syntheiss
Transcription
mrna protected
intorns removed - mrna to cytoplasm
mrna in ribosone
trna and mrna make poly petide chain in ribosome
what is a mutation
A permanent change in the genetic material
difference between: germ vs somatic cell mutations
germ: passed on to offsrping - in reproductive cells
somatic: not passsed on to futue offspring passed on to aughter cells - in cell mitosis
what causses a mutation?
Physical or chemical mutagens:
physical - high energy radiation or UV radiation
chemical - carcinogens (molecule that can enter the nucleus and induce mutations)
Type of mutations!
Frameshift: insertion , deletion
Base substitution: missense, silent, nonsense
Frameshit insertion
extra base makes everythign misalign
Frameshift deletion
base removed, makes everythign misalign
Base substitution missense
on randome chaneg creates a diff amino acid
Base substitution silent
one randome base chaneg makes the same amino acid
Base substitution nonsense
one random base change makes a stop codon
why do we care abt determining DNA sequences
solve crimes
paternity suits
fetal creening (genetic disroders)
research to fidn cures
How to break DNA
restriction enzyme slice the DNA at restiction sites
restiction sites can then be used to isloate specific sequences of interest
what are the 3 steps of studying DNA sequences
break
multiply
sort/analyze
how is dna amplified
bacteria is used as a vector to multiply interseted DNA
what are plasmids
plasmids are the circular portions of DNA (Bacteria vectors)
explaint he process of DNA stuff
rescriction enxyme splits the plasmids at restrction site, same enzyem used on another dna of interest, dna sequence intereted to plsmid to be replicated
how does the restricted dna sequence stick to the split plasmid?
sticky ends of the dna atracted to plasmid are compllimentary. they form hydrogen bonds and ligase fils in any gaps
what is it called when plasmid and target DNA are combined
Recombinant DNA
now how is the dna cloned?
recombinant plasmid is intersted back into the bacteria vecto and multiplies it
What are the diff ways DNA is aomplified?
bacterial vector
PCR
PCR method of amplifying
DNA, primers mucleotied and Taq polymerase are added into test tube
dna heated to 90* to seperate strands
cooled to 37* and primers are added
heated to 70* to activate DNA polymerase makign 2 identical strands
cycle repeats itself
Sortign & analyzing DNA: gel elctophoresis
DNA fragmaents travel trhough a special gel towards a postive charge (dna has a negative charge)
the seperation of fragments creates a patern of bands call DNA fingerprint. Everyones fingerprint is diff
smaller dna fragaments move faster and farther
How is Gel electrophoresis used
perental disputes, matching dna, research for gene diseas)
what is gene expression?
the process of turning on a a gene to produce RNA
why does a cell controll how / when a gene is exressed?
to be mor energentically fabourable
Examplesof egen exrepssion
lactase
arctic fox
Gene expression regulation: Eukaryotes
can eb inhibited on protien synthesis pathways (trasncription/translation)
trascription control: block / prevent transcription
post transcription controll: mRNA dstroyed,
Post trancriptopk controll: poly a tail/5cap shortened
post translation control: poly peptide degration
post translation control: delay of folding
RNA transport control: mRNA not allowed out of nucleus (nucleus pore blocked)
Gene expression regulation: prokaryote
ONLY IN TRANSCRIPTION REGULATION. on or off
protiens neede for a specific funtion are encoded togethin blocks of codons called operons. every codon neede for lactase protien will be right after eachtoher int he lac operon
all be cuase prokaryotes are simple and dont have aneclues so both strancriptiona dn trasnlation happens simultaneously
regions of operons
coding regions
premoter / start site (tataa box)
operator ( dna region that determins if trancription hapens) repressor will bind there to block rna polymerase form recognizing the tataa box
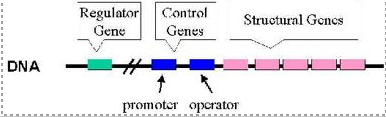
What are the molecules that affect the operon?
repressor - binds to operator region and block transcription
activators - recruits RNA polymerase to the promotorer to start transcription
inducers - small molecules that acticate or repress transcription baed on need
what is needed for lac operon to be activated
low/absent glucose elvels
lactose
how does lac operon work
if conditions ar emet, the inducer allolactase binds to lac repressor beating it up so it leaves the fight like the whimp it is. then the RNA polymerase and transcribe
what kind of relationship does th eallolactie and represor rpotien have
ezyme and subtrate
Tooisomerase vs helicases
Helicases are enzymes that separate the nucleic acid strands for replication. Topoisomerases are enzymes that relax the supercoiling in DNA strands
Why are chromosome mutations potentially more serious the gene
because chromosome mutations affect much larger regions of DNA potentially carrying hundreds or even thousands of genes
what are the 4 type sof chromosoem mutations
Deletion
Duplication
Inversion
Translocation
What is agarose gel and how does it work?
used to resolve DNA fragments on the basis of their molecular weight
Where is the DNA placed in the gel electrophoresis apparatus?
wells
Explain why not all the bands in the mother’s or father’s profiles have a counterpart in the baby’s DNA profile.
because the baby gets 50 of each parent
Explain why blood typing may not be a viable method of determining which baby belongs to which parent.
blood typing does not distinguish between people of different genotypes. For example, a person may be Type B blood but that person could either be BO or BB