Physiology of Muscle Contractions
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Gross Anatomy of Muscles
Entire Muscle (covered by epimysium)
Bundles of fascicles (covered by perimysium)
Fascicles are composed by muscle fibres (covered by endomysium)
Muscle fibres can be broken down into myofibrils
Myofibrils are composed of sarcomeres
Sarcomeres are made up of actin (thin) and myosin (thick) filaments
What are The types of Muscle contractions
Isometric Contraction: muscle tension without a change in muscle length
Isotonic Contraction: muscle tension with a change in muscle length, can be either:
Concentric: Muscle shortens while contracting
Eccentric: Muscle lengthens while contracting
Key stuff about muscle contraction
Muscles always pull during a contraction, they never push
A muscle will shorten and move an object if the load is light
A muscle will stay the same length if the load is greater than the muscle strength
How does a muscle contract
In order for a muscle to contract a signal is sent from your brain to the muscle through the motor unit
What is resting membrane potential
The sodium-potassium pump moves 3 sodium ions out of the cell and 2 potassium ions into the cell
Establishes and maintains a concentration gradient, with higher sodium outside and higher potassium inside the cell
Resting membrane potential, -70 mV
What are facilitating Action Potentials
Depolarization: When a neuron receives a signal, voltage-gated sodium channels open, allowing sodium ions to rush into the cell, causing depolarization
Repolarization: As the membrane potential reaches a certain threshold, voltage-gated potassium channels open, allowing potassium ions to flow out of the cell, and sodium channels become inactivated, leading to repolarization
Restoration of Gradients: Sodium-potassium pump restores the ion gradients by pumping sodium out and potassium back in
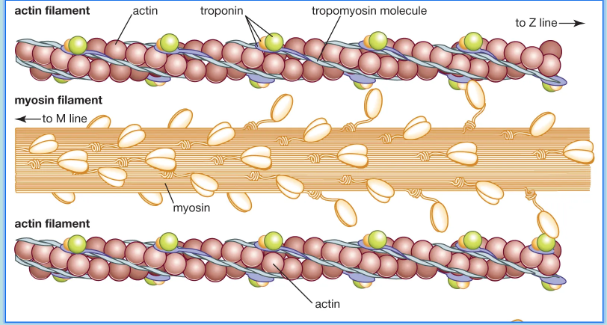
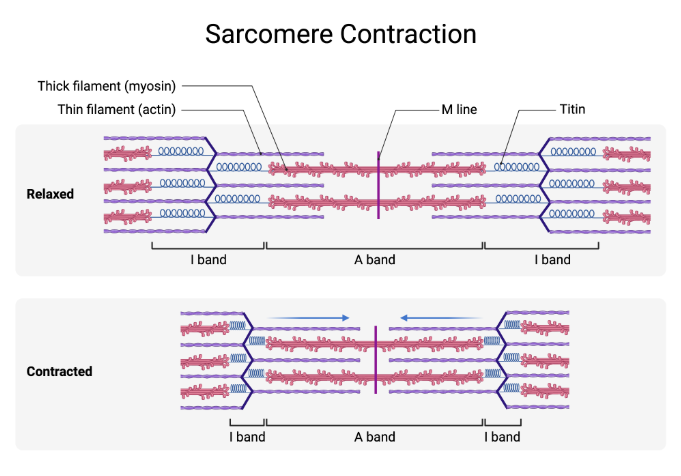
What is the Sliding Filament theory
Actin & Myosin filaments slide past each other, so that the two types of filaments overlap to a greater degree
What are Myosin Corssbridges
Myosin Crossbridges - small bridges that extend from myosin filaments to actin filaments
These “crossbridges” are actually the heads of the myosin filaments (they look like mini golf clubs)
Over & over again, these crossbridges attach, rotate, detach, and reattach in rapid succession
Process results in sliding (or overlapping) of thin & thick filaments (to a greater degree), which shortens the sarcomere
As this process occurs simultaneously in sarcomeres throughout the fibre, the muscle cell shortens
Contracting Sarcomere
Where does Energy from Contractions come from
Release of calcium ions is critical “trigger” in this complex process of muscle contraction (calcium facilitates the interaction of myosin and actin molecules)
Energy source behind the release of calcium (so muscle can contract) is ATP
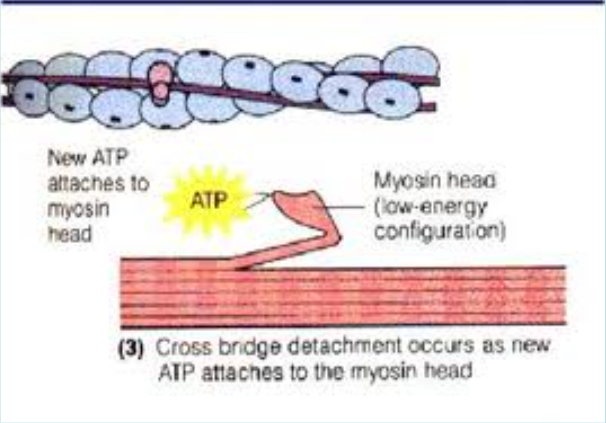
ATP also used to detach myosin from actin molecule (so muscle can relax)
As work of muscle increases, more and more ATP is used up and must be replaced through food metabolism (eating and digesting food)
Atp use to Relax muscle
What is Excitation-Contraction Coupling
Nerve impulse transmitted from nervous system, through neuromuscular junction, to muscle fibre
Electrical signal (impulse from nerve) transmitted by chemical means at the neuromuscular junction
Here, the nerve terminal releases acetylcholine across synapse to muscle fibre4. Transverse Tubulae System transmits signal down into muscle fibre
5. Change takes place in electrical properties of tubulae
6. This change causes a rapid release of calcium ions (energy is provided by ATP), which sets off a series of other chemical reactions that lead to shortening/contraction of muscle fibre
What are Calcium Ions
Release of calcium ions is critical “trigger” in this complex process of muscle contraction
On actin filaments there are troponin and tropomyosin molecules (proteins)
These proteins “inhibit” or regulate the interaction of actin and myosin filaments
If calcium is not present, then actin and myosin do not interact
When calcium is present it interacts with troponin, tropomyosin then moves to not be blocking actin binding sites, thereby allowing actin and myosin to interact and muscle to contract
Calcium’s Interaction on Troponin and Tropomyosin
to allow for muscle contraction