Lecture 11: Cytoskeleton (microtubules)
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Cytoskeleton Function
maintains cell shape, organization, provides support for internal/external movement
proteins:
actin
microtubules
Cytoskeletal Filaments
microfilaments
composed of actin
microtubules
composed of tubulin
intermediate filaments
composed of various proteins; desmin, lamin, keratin
Microtubules Structure
polymers of the protein tubulin
tubulin subunit is a heterodimer formed from two closely related globular proteins called ⍺-tubulin and β-tubulin
hollow tubes
have polarity due to the orientation of the subunits
⍺-tubulin end = - end
grows and shrinks less rapidly
β-tubulin = + end
grows and shrinks more rapidly
built from 13 parallel protofilaments, each composed of ⍺β-tubulin heterodimers stacked head to tail, then folded into a tube
helical microtubule lattice make them stiff and hard to bend.
helix forms from a slight stagger in the protofilament lateral contacts
Microtubule Growth
rapid growth occurs by the addition of tubulin dimers at the ends
3 phases:
lag phase
elongation phase
plateau phase
dynamic instability
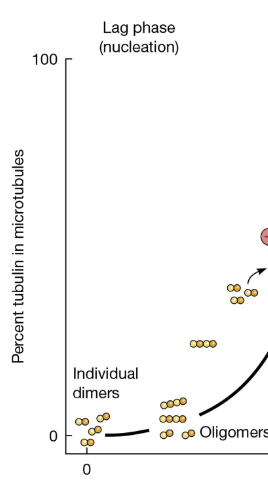
Lag phase
nucleation
process in which several tubulin molecules interact to form a microtubule seed
assemble into protofilaments
addition of GTP-tubulin to + end of a protofilament causes the end to grow in a linear conformation that assembles into the cylindrical wall of the microtubule
nucleation is slow, and depends on the y-tubulin ring complex
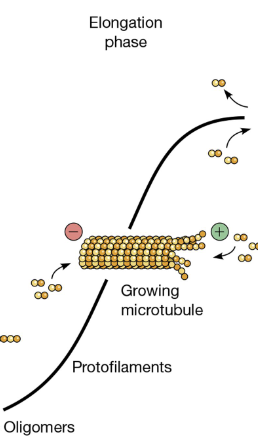
Elongation Phase
microtubules lengthen by adding GTP-bound tubulin dimers, forming a stable GTP-cap at the plus-end, allowing them to grow and probe the cell
growing microtubules
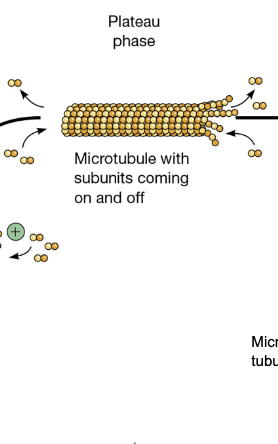
Plateau Phase
the final stage of in vitro microtubule assembly, where the concentration of free tubulin subunits reaches a stable point, and the overall polymer mass stops changing significantly
microtubules with subunits coming on and off
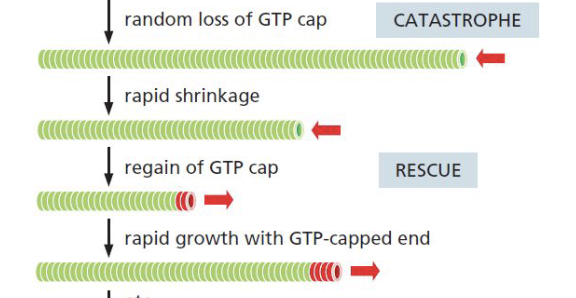
Dynamic Instability
process which individual microtubules alternate between cycles of growth and shrinkage
Catastrophe
change from growth to shrinkage
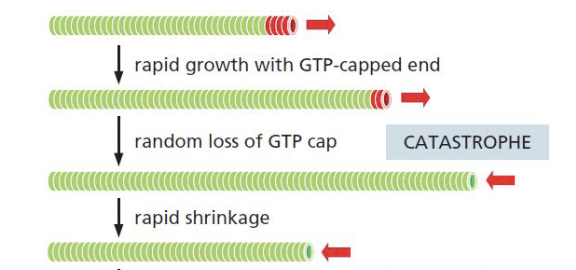
Rescue
change from shrinkage to growth
Protofilament Shape
GTP hydrolysis after assemble changes the conformation of the subunits and tends to force the protofilament into a curved shape that is less able to pack into the microtubule wall
Microtubule Organizing Centre
MTOC
where microtubules are generally nucleated from
where y-tubulin is most enriched
most animals possess a single, well-defined MTOC: centrosome
Centrosome
single, well defined MTOC of most animals
composed of 2 centrioles and surrounded by a dense mass of protein
pericenrtiolar material
unless the cell is dividing, y-tubulin is only found in the centromere
Microtubule Associated Proteins
MAPs
bind and stabilize microtubules
Map2 and Tau works to se the spacing of the microtubule bundles
because of this, Tau mutations cause neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s
\
Microtubules Orientation
axon microtubules have uniform orientation
dendrite/others have mixed orientations
dendrites also contain organelles, unlike axons
Microtubule Motors
2 types:
kinesins
dyneins
move vesicles/organelles in the secretory pathway
Kinesins
move towards the + end of microtubules
motor domain which splits ATP and converts the energy into motion
cargo-binding domain connects to the object being moved
small size
regular movements
capable of transporting mitochondria/other organelles to the periphery
must be inhibited for - end transport
kinesin-binding proteins prevent kinesin-microtubule binding
Dyenin
cytoplasmic dynein moves towards the - end
ATPase domain body
ATP binding changes conformation structure to dissociate microtubule binding
tail which binds to cargo
large size
irregular movements
mediates rapid movement of melanosomes
melanosome: organelle which synthesizes and stores melanin
coordinated movement because microtubules are uniformly polarized
Axonal Organelle Transport
neurons transport vesicles with neurotransmitters to the synapse
a vesicle contains both types of motor proteins
motor proteins can be inactivated to get them back
Cilia/Flagella
hairlike appendages with a bundle of microtubules at their core
flagella: found on sperm and many protozoa
have an undulating motion
cillia: beat with a whiplike motion
axoneme: core of both, composed of microtubules and their associated proteins
Axonemal dyenin
bends the axoneme which moves the cilium and flagellum