603 Oral Cavity & Pharynx
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
scaphoid fossa
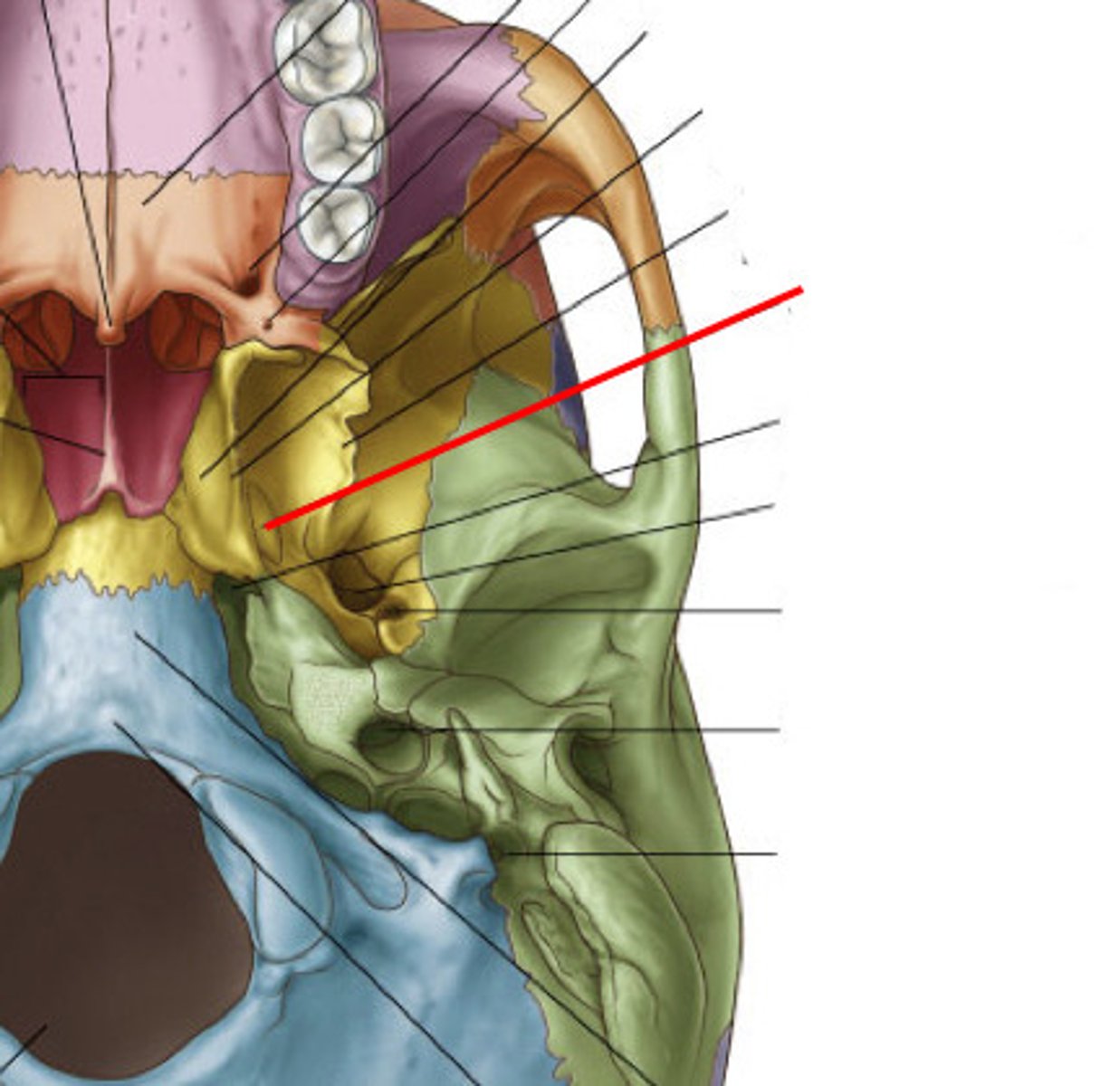
fossa located bwtn the lateral and medial pterygoid plates ==> origin for the tensor veli palatini muscle
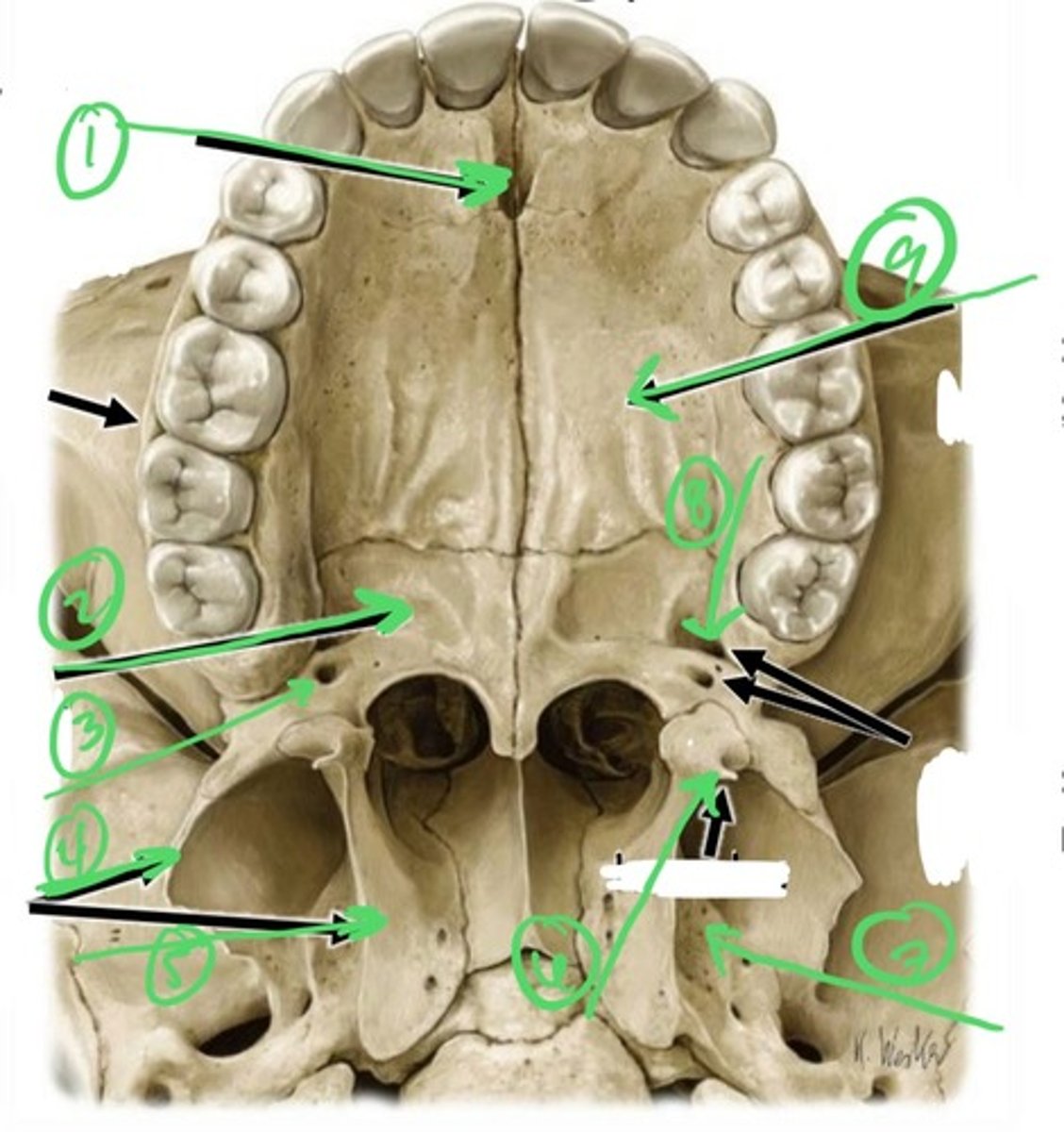
1.) incisive canal
2.) horizontal plate of palatine bone
3.) lesser palatine foramen
4.) medial pterygoid plate
5.) lateral pterygoid plate
6.) hamulus
7.) scaphoid fossa
8.) greater palatine foramen
9.) palatine process of maxilla
mandibular tori
overgrowth of the lingual side of mandibular bone
-associated by grinding (bruxism)
-affects 8-15% of population
torus palatinus
overgrowth of bone in the middle of the hard palate
-hereditary
-may be due to trauma or diet--> concrete reason for growth not known
-affects 20% of the population
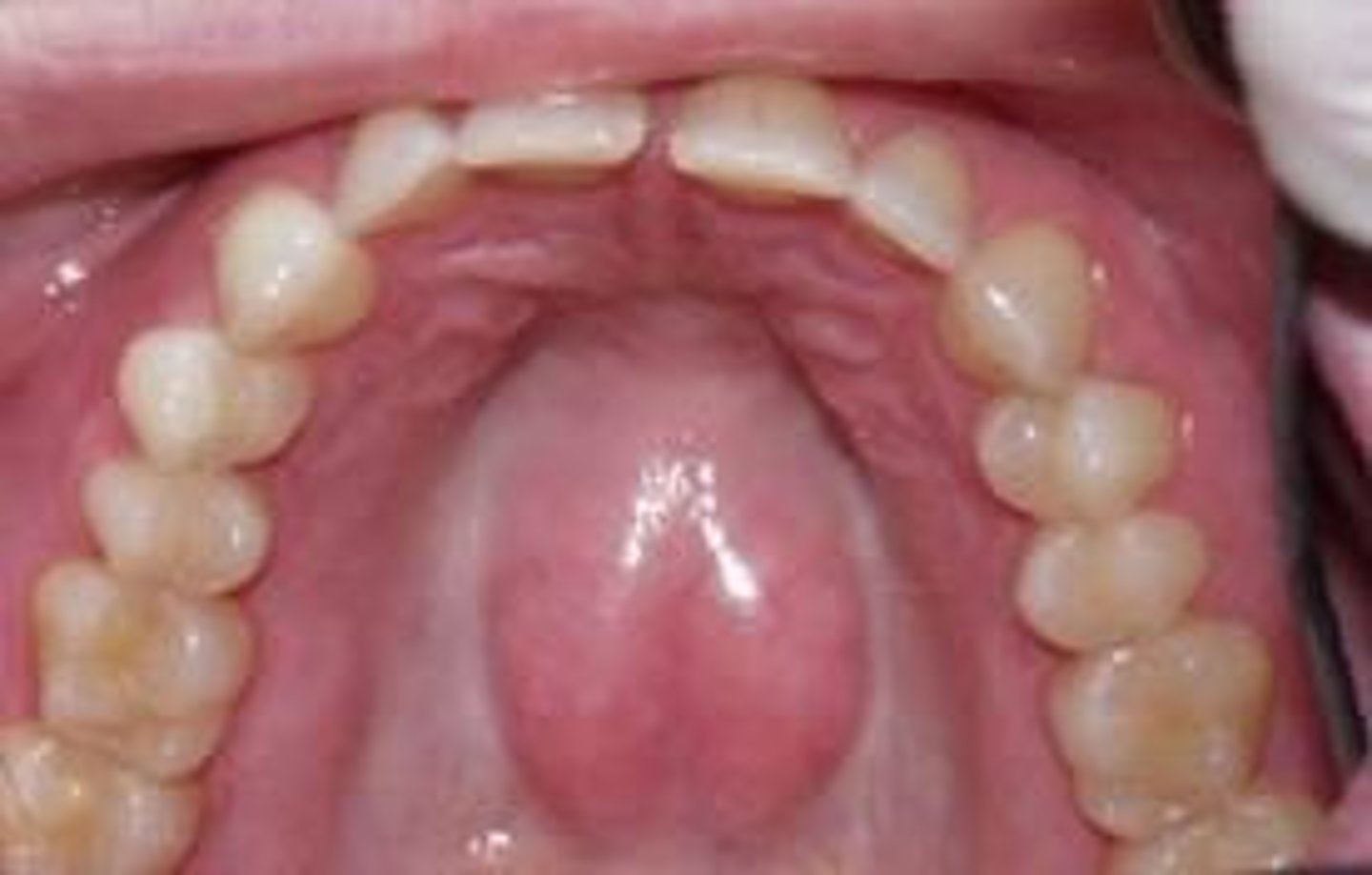
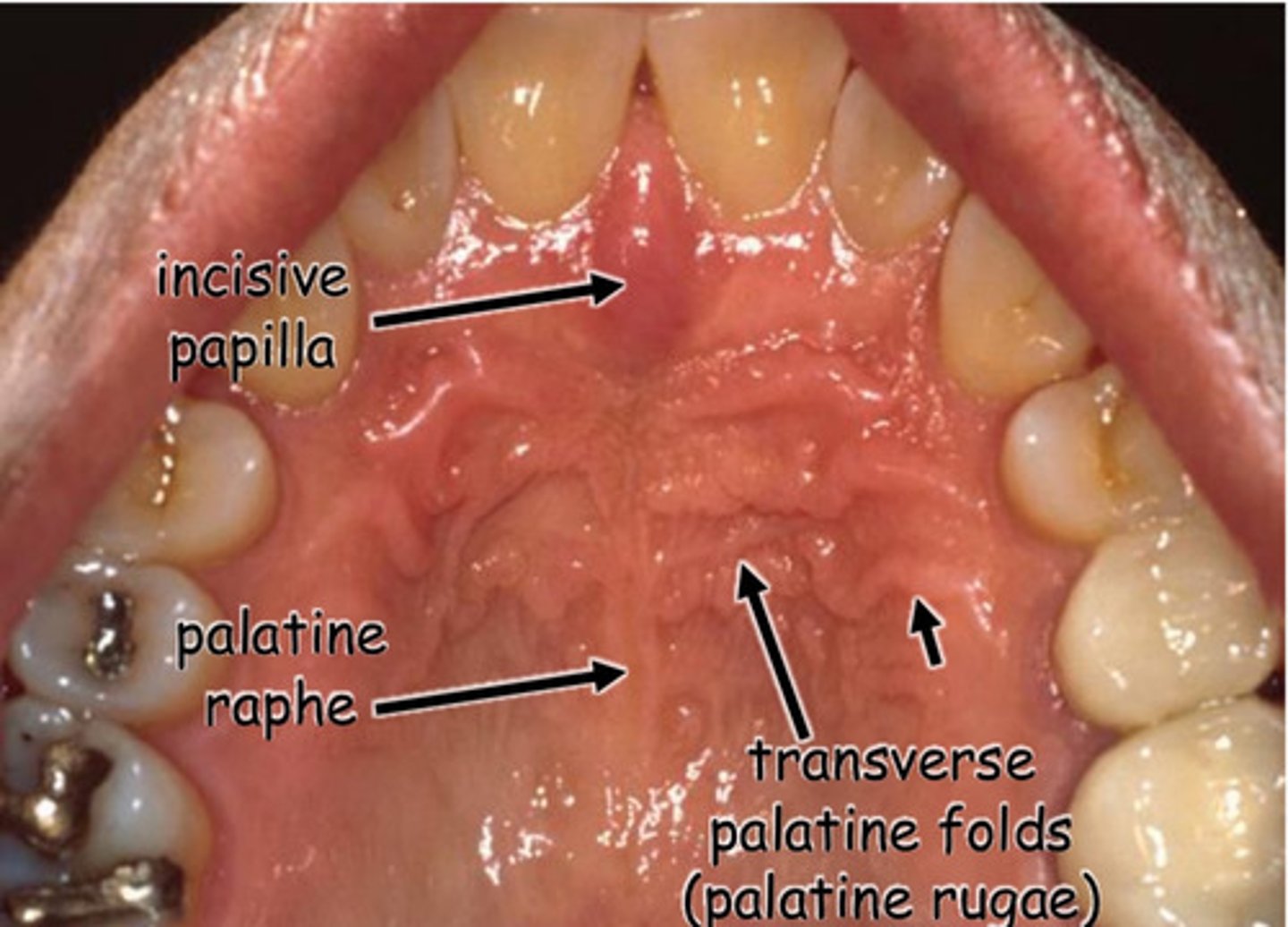
True or False: The pattern of palatine raphe & rugae change throughout life
False ==> palatine raphe & rugae have a fixed pattern that remains throughout life
1.) incisive papilla
2.) palatine raphe
3.) transverse palatine folds (palatine rugae)
4.) transverse palatine folds (palatine rugae)
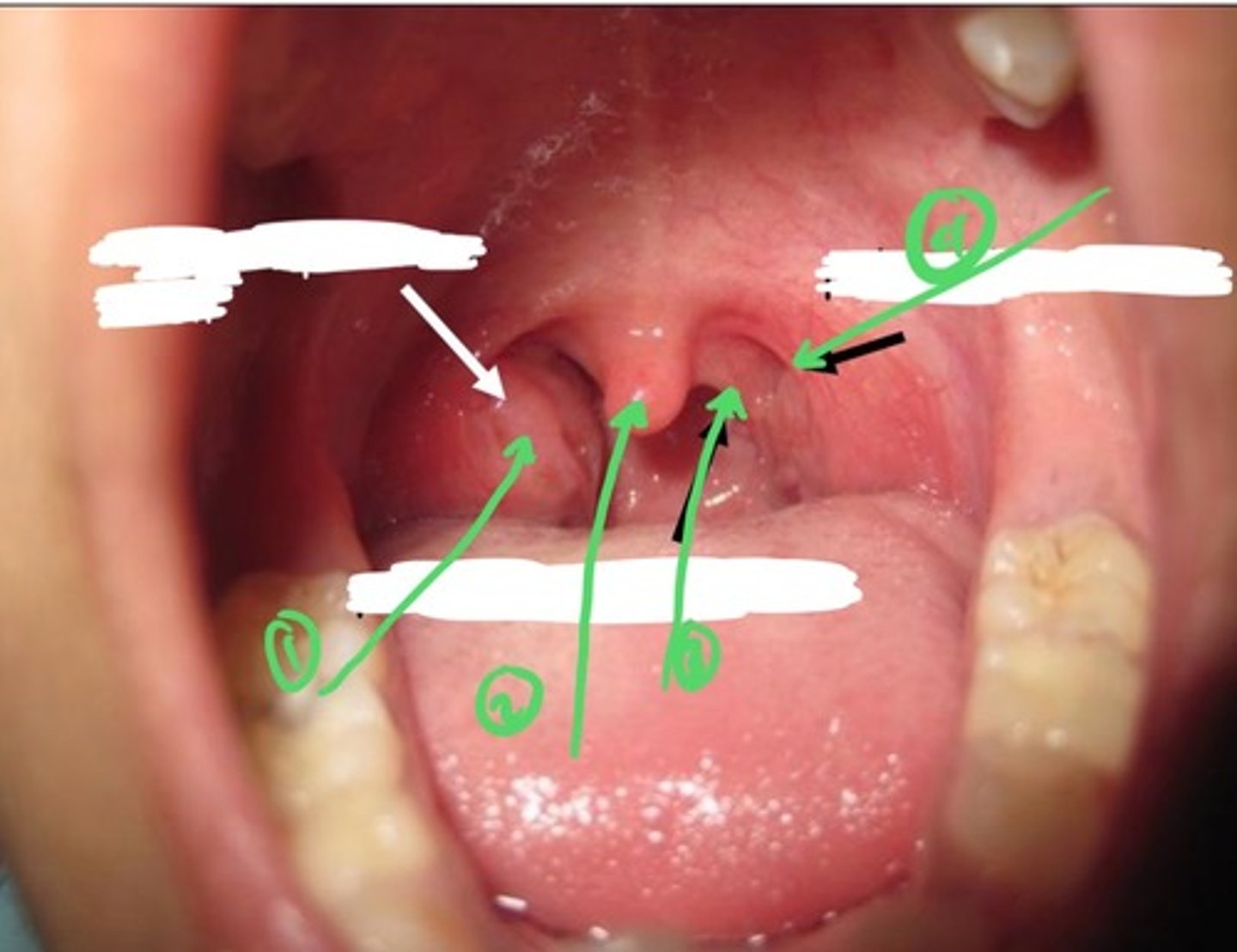
Where are the palatine tonsils located?
palatine tonsils located bwtn the palatopharyngeal arch & palatoglossal arch
1.) tonsil (this one is abnormally enlarged
2.) uvula
3.) palatopharyngeal arch
4.) palatoglossal arch
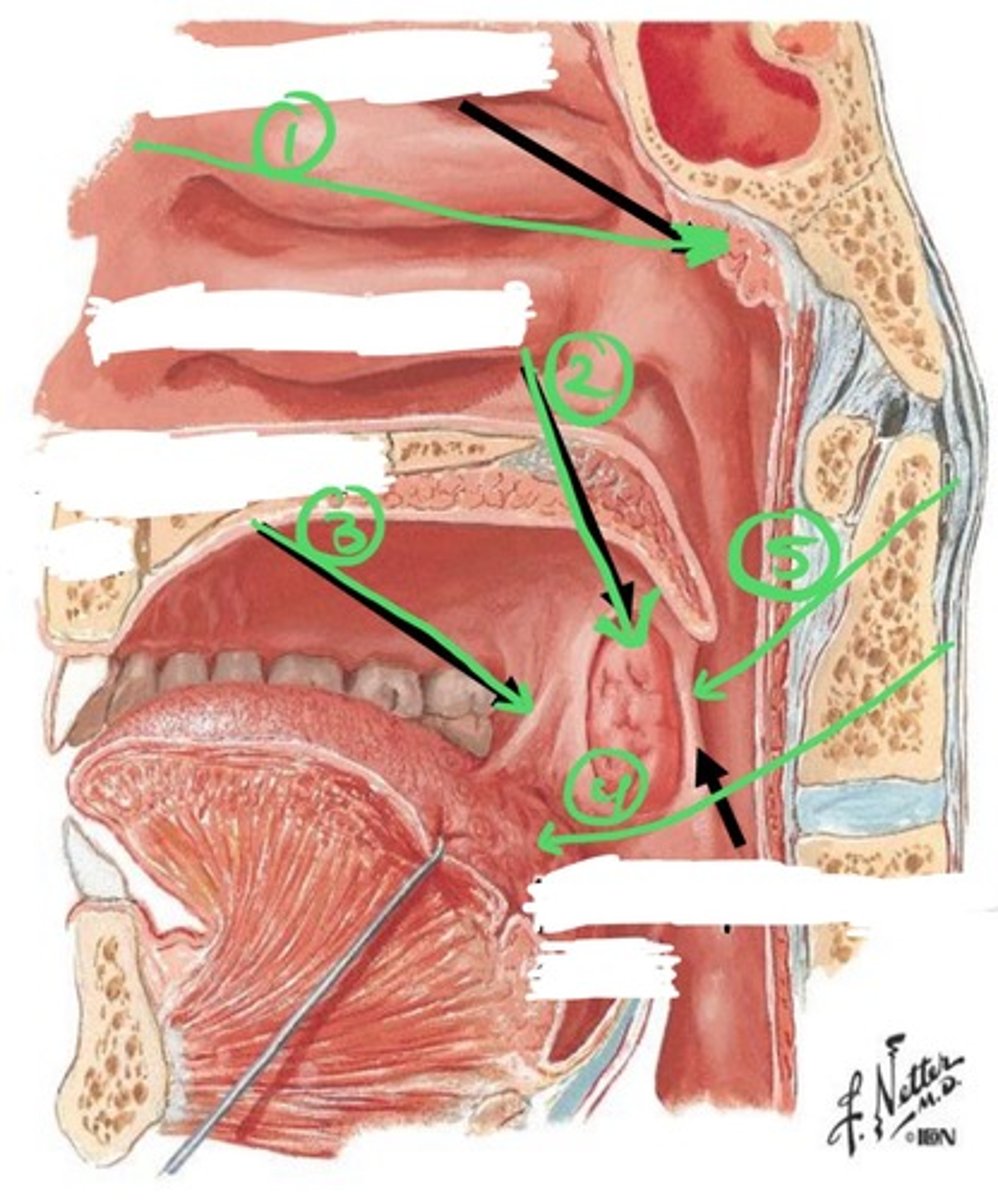
Tonsils
lymphoid tissue w/in the oral cavity & pharynx==> palatine tonsils, lingual tonsils, & pharyngeal tonsils
*epithelial layer differs bwtn each tonsil
ex: palatine tonsil has SSNKE epi & pharyngeal tonsils have respiratory epi
1.) pharyngeal tonsil
2.) palatine tonsil
3.) palatoglossal arch
4.) lingual tonsils
5.) palatopharyngeal arch
True or False: Hemorrhage isn't a common concern during a tonsillectomy because the tonsils are surrounded by limited vasculature
False ==> a lot of blood vessels near the tonsils so hemorrhage is a risk of having tonsils surgically removed
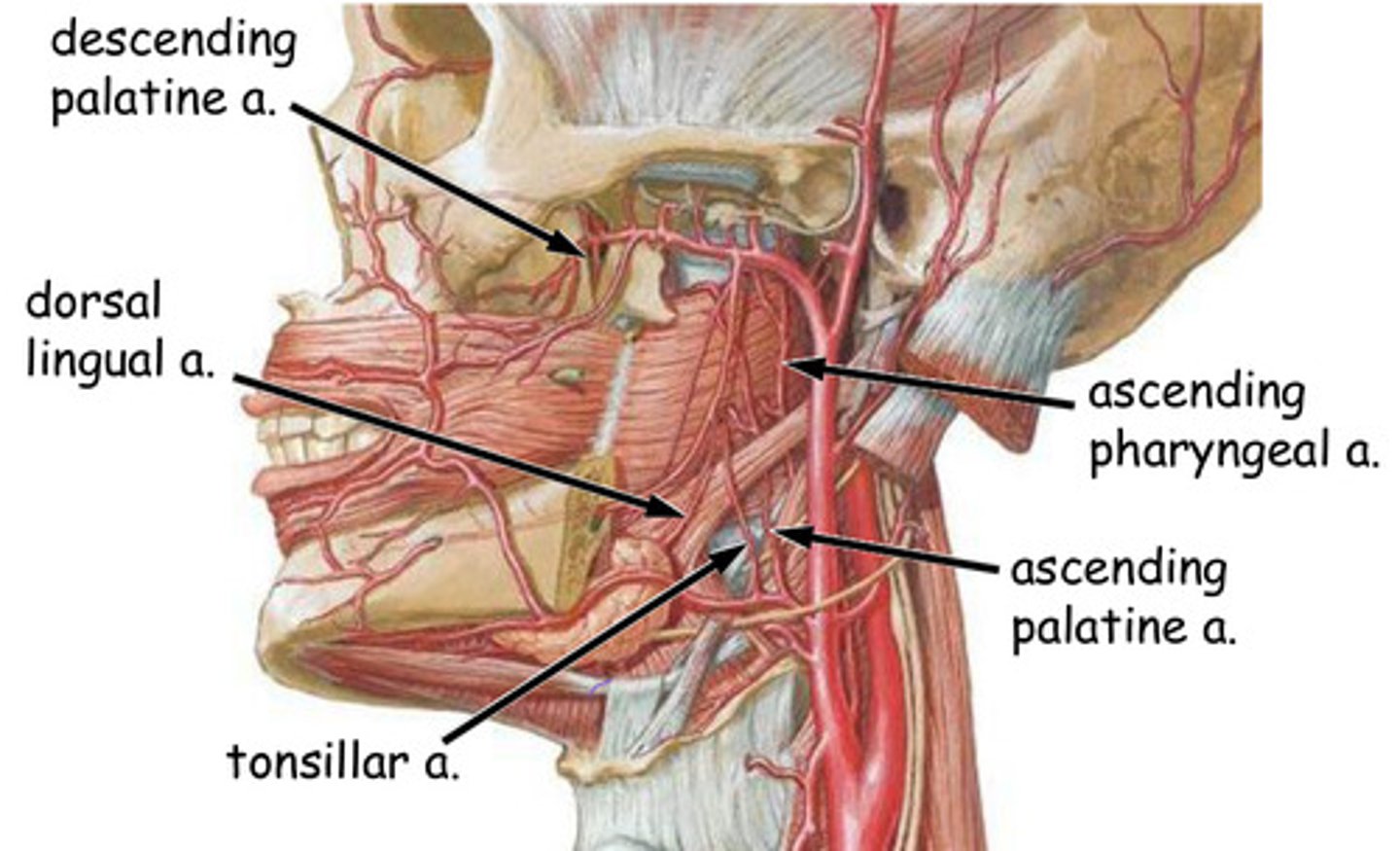
*arteries = "Don't need to know these" (insert suspicious face)
-ascending palatine a.
-ascending pharyngeal a.
-tonsillar a.
-dorsal lingual a.
-descending palatine a
True or False: All muscles of the oral cavity are innervated by cranial nerves
True
Cranial Nerves Innervation of Oral Cavity
-Trigeminal Nerve (CN V)
> V2 Maxillary Division--> somatic sensory
> V3 Mandibular Division --> somatic sensory and motor
-Facial Nerve (CNVII)
> motor innervation to buccinator (accessory muscle of mastication)
> taste special sensory via Chorda Tympani
-Glossopharyngeal Nerve (CNIX)
>taste special sensory & somatic sensory to posterior 1/3 of tongue
>visceral motor innervation of parotid gland
-Vagus Nerve (CN X)
>motor --> levator veli palatini, uvula, palatopharyngeus, palatoglossus
>sensory innervation to pharynx
-Hypoglossal Nerve (CN XII)
> motor innervation to tongue muscles (hypoglossus, styloglossus, genioglossus)
In general, what are the targets of parasympathetic fibers from the cranial nerves>
-glands (all except sweat glands)
-smooth muscle
-cardiac muscle
True or False: Clusters of axon fibers from cranial nerves can be called "tracts" or "nerves"
False ==> tracts are clusters of central nervous system neruron axons; Cranial nerves are apart of the peripherial nervous system not the PNS
*Only "cranial nerve" that is actually a tract is the Optic Nerve (CN II)
True or False: Soft palate moves when swallowing and speaking
True
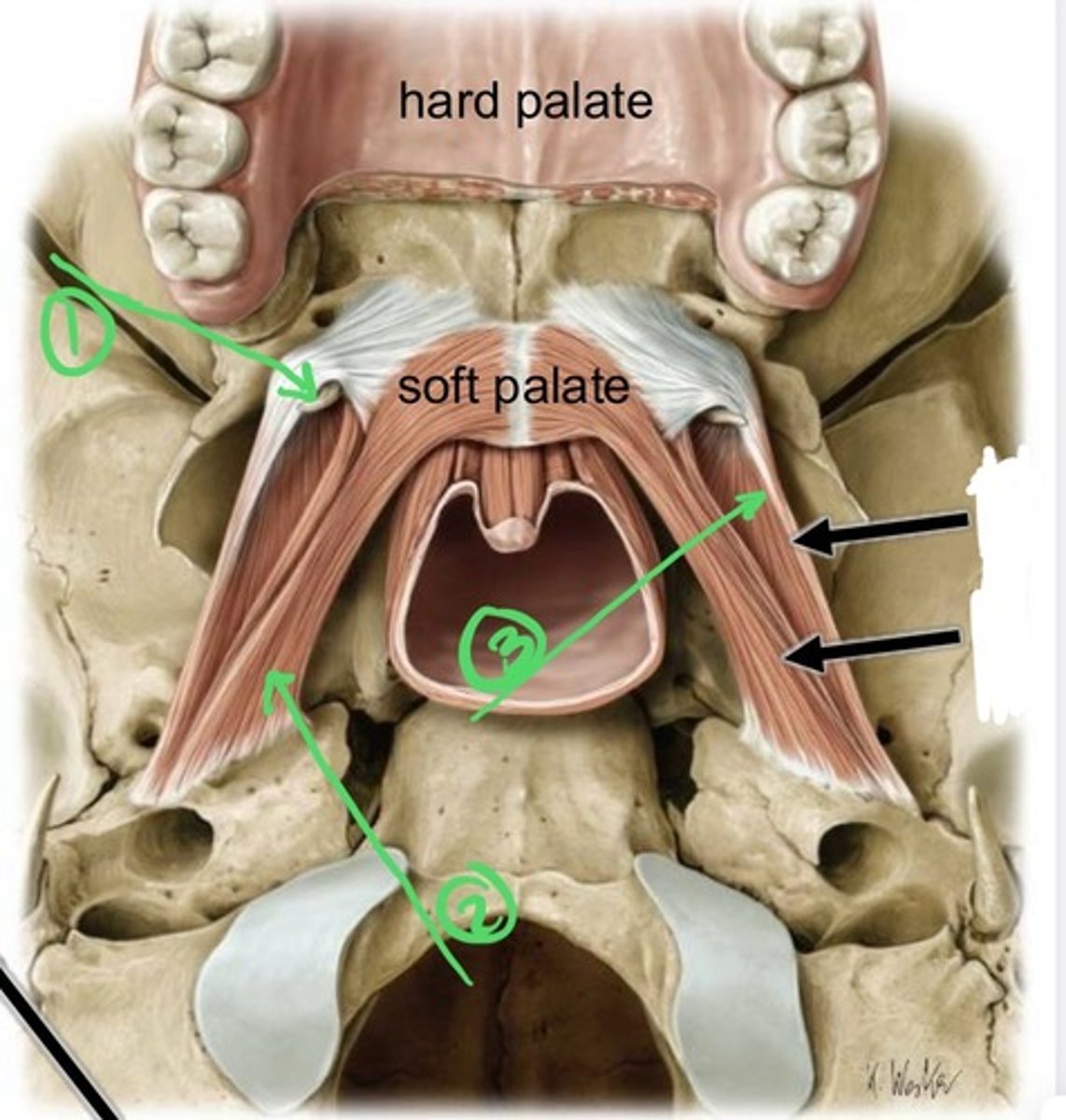
Soft Palate Muscles Innervated by the Vagus Nerve (CN X)
- levator veli palatini
- palatopharyngeus
- palatoglossus
- uvula
1.) tensor veli palatini muscle
2.) levator veli palanti muscle
3.) palatopharyngeus muscle
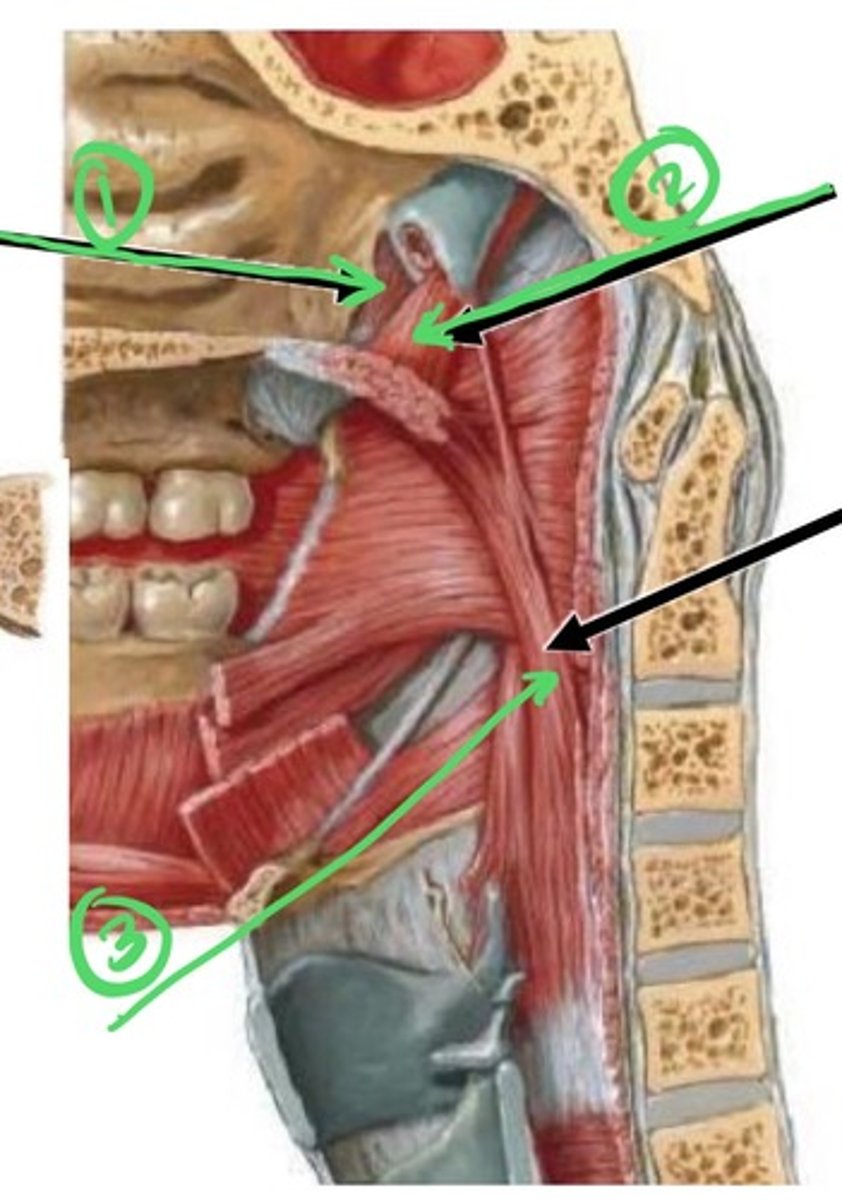
True or False: The Vagus Nerve (CN X) innervates the Levator Veli Palatini & the Tensor Veli Palatini muscles
False ==> Vagus (CNX) innervates the levator veli palatini muscle but not the tensor veli palatini muscle (innervated by V3 of CNV)
palatoglossus muscle
muscle of the glossus & soft palate that
-elevates the tongue & pulls down soft palate to seal the oropharynx
- retraction of tongue & depression of uvula to bring the soft palate & tongue into contact
-isolates vestibule saliva
-prounciate velar consonants (K sound)
-assists in swallowing
*no bony attachment
*innervated by Vagus Nerve (CN X) --> (located near the uvula that's innervated by CN X too, so this makes sense)
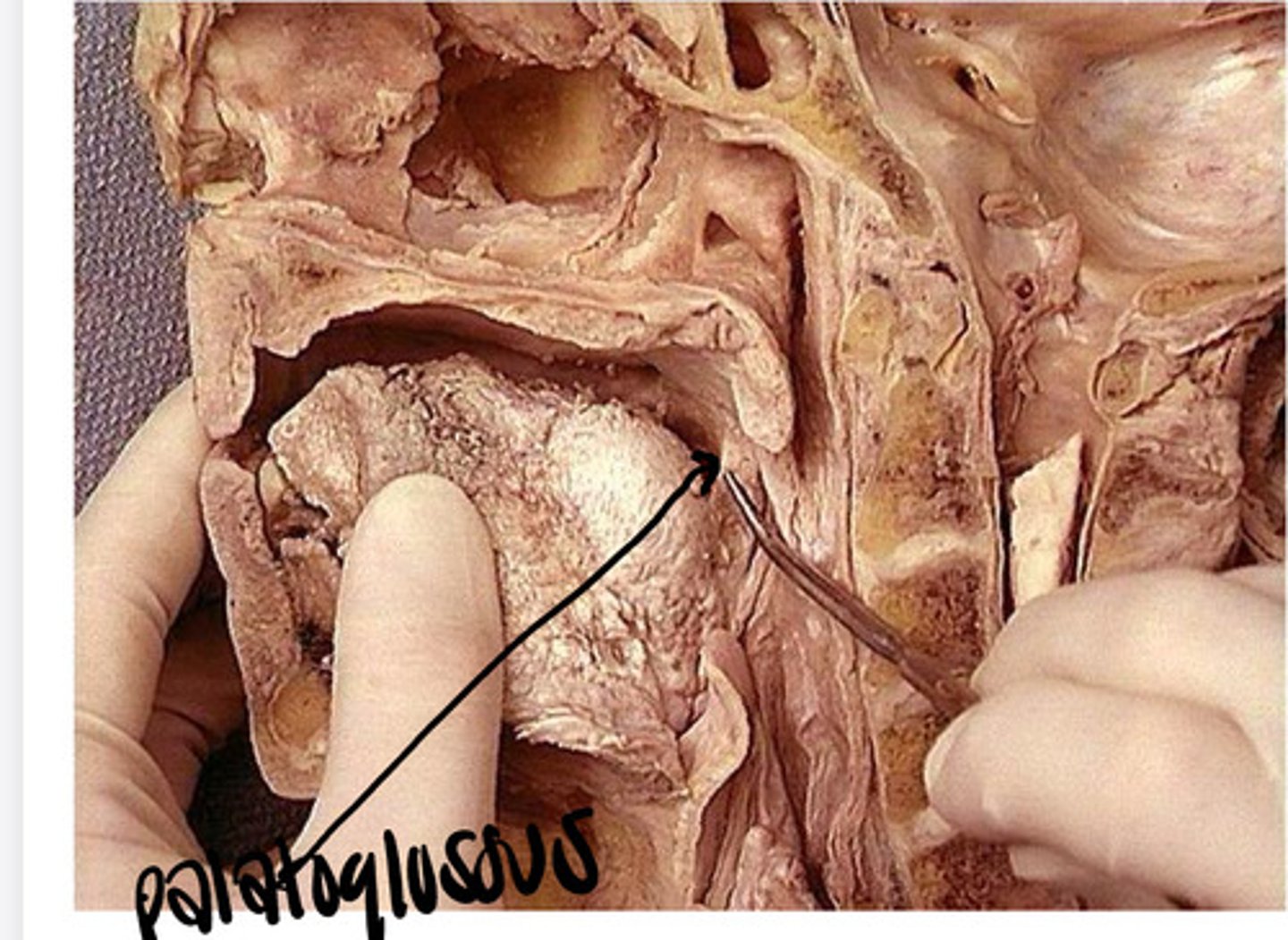
uvula
soft palate muscle that seals the nasopharynx during swallowing & helps prounciate uvular consonants (not used in english)
*can have variations that make it elongated, bifid, or shortened
*innervated by the Vagus Nerve (CNX)
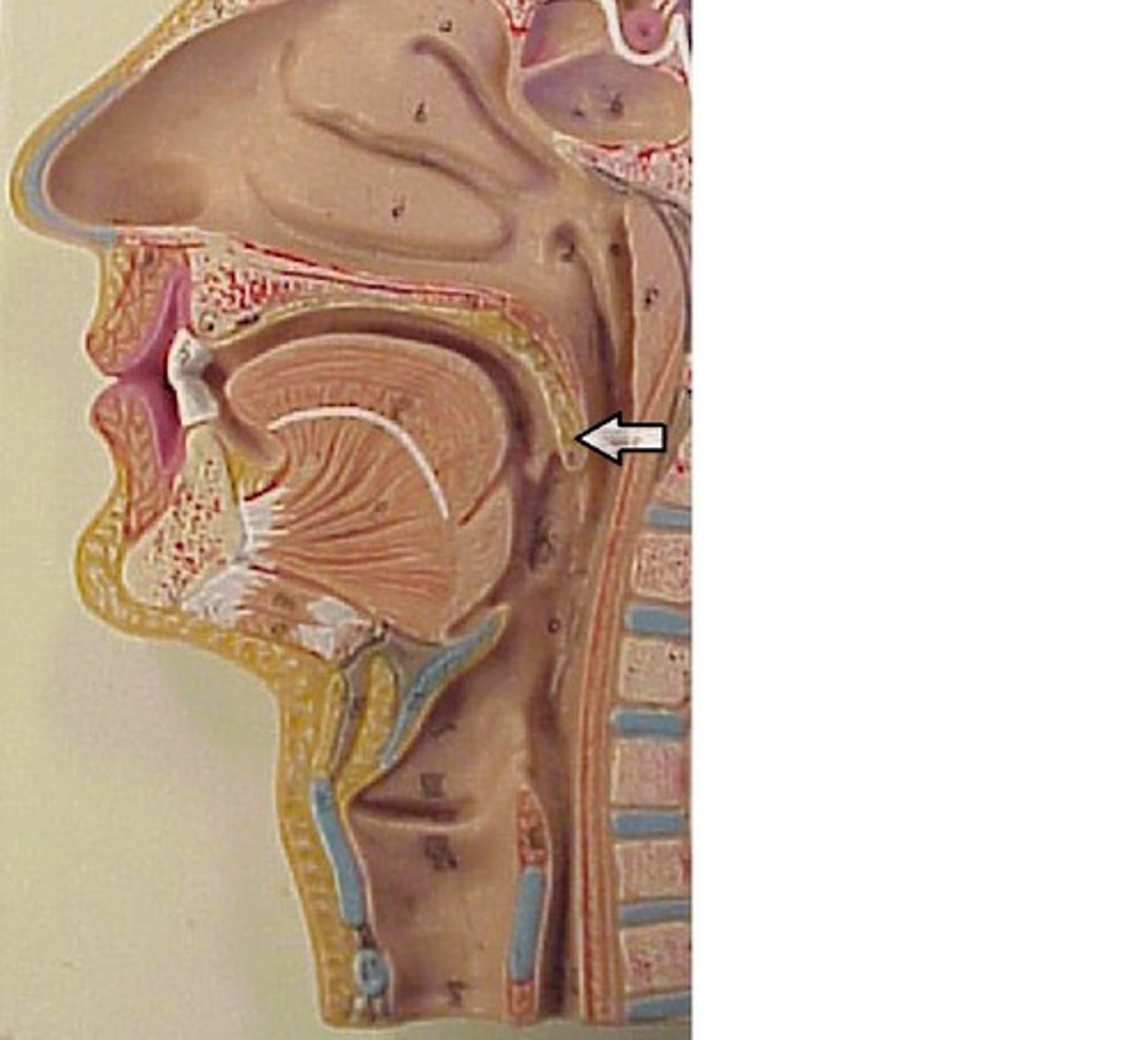
levator veli palatini muscle
muscle of the soft palate that elevates the palate
*innervated by Vagus Nerve (CNX)
Velum
soft palate
tensor veli palatini muscle
muscle of the soft palate that flattens/tenses the soft palate
-origin = scaphoid fossa
-insertion = central tendon (wraps around hamulus of medial pterygoid plate & inserts into its own tendon)
*innervated by Mandibular Division (V3) of Trigeminal Nerve (CNV)
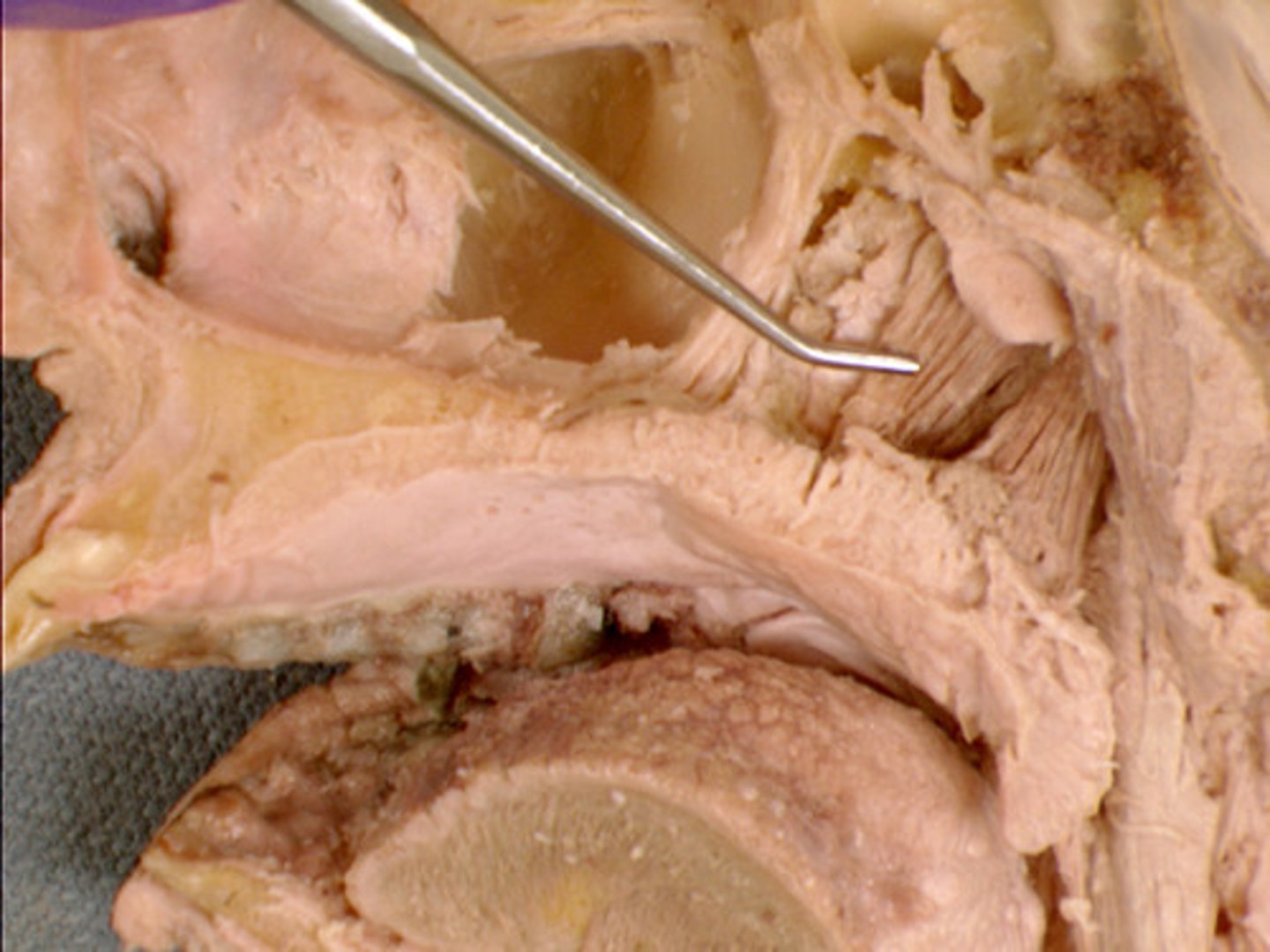
1.) soft palate (velum)
2.) hard palate
3.) levator veli palatini muscle
4.) tensor palatini muscle
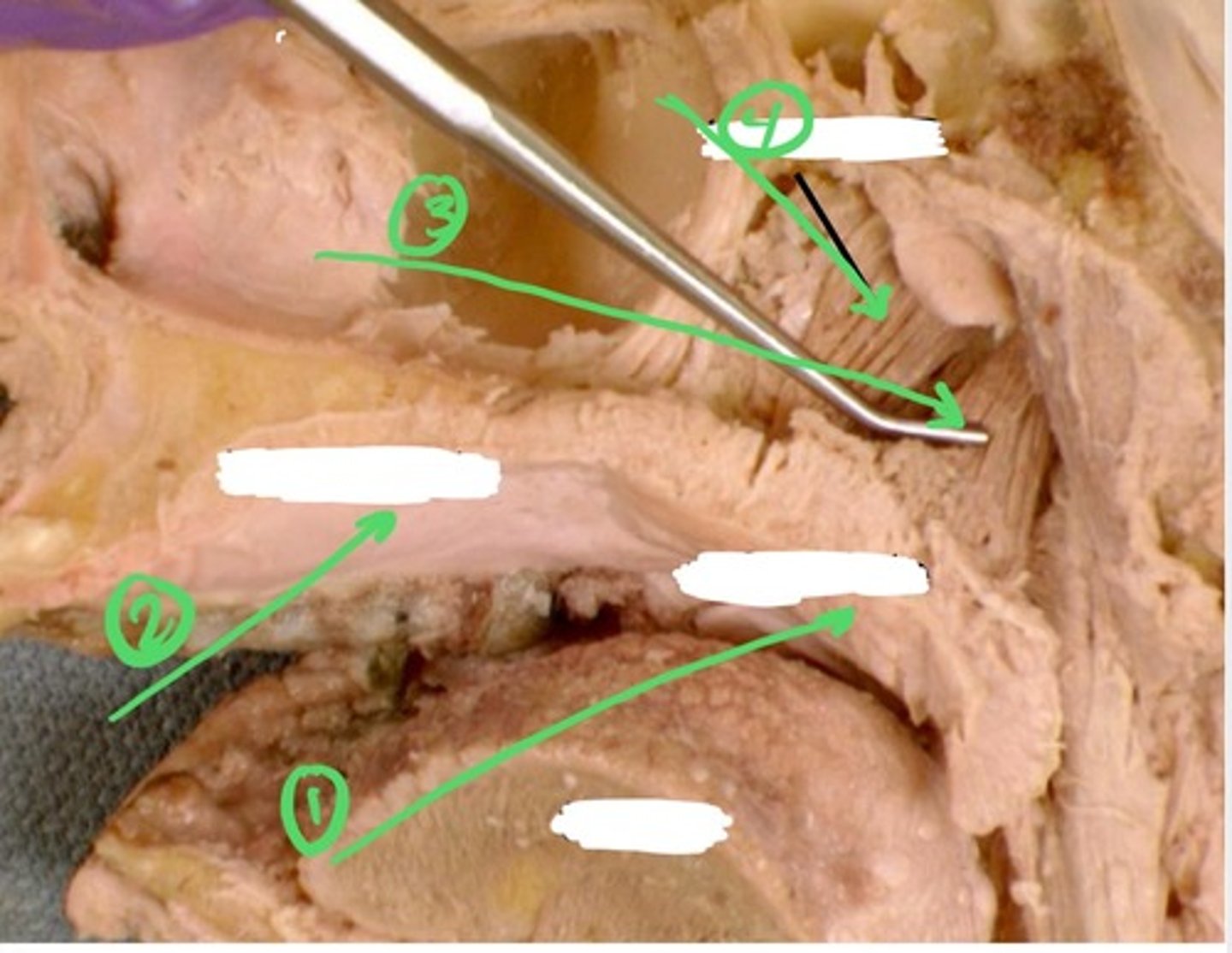
1.) hamulus
2.) levator veli palatini muscle
3.) tensor veli palatini muscle
Extrinsic Glossus Muscles
-styloglossus --> retraction & cupping (attached to styloid process)
-hyoglossus --> depresses the tongue (attached to hyoid bone)
-genioglossus --> protrusion & depression of central portion of the tongue; allows you to stick your tongue out (attached to the superior genial tubercles of the mandible)
*innervated by the Hypoglossal Nerve (CNXII)
*blood supply = lingual artery
Intrinsic Glossus Muscles
muscles that make up the tongue (the portion that we can see in the oral cavity, not the extrinsic muscles)
*innervation
-motor--> hypoglossal (CN XII)
-taste --> chorda tympani of CNVII (front 2/3); glossopharyngeal (back 1/3)
-somatic sensation --> lingual nerve of V3 (front 2/3); glossopharyngeal nerve (back 1/3)
*blood supply = lingual artery
(slides didn't name the individual muscles that make up the intrinsics)
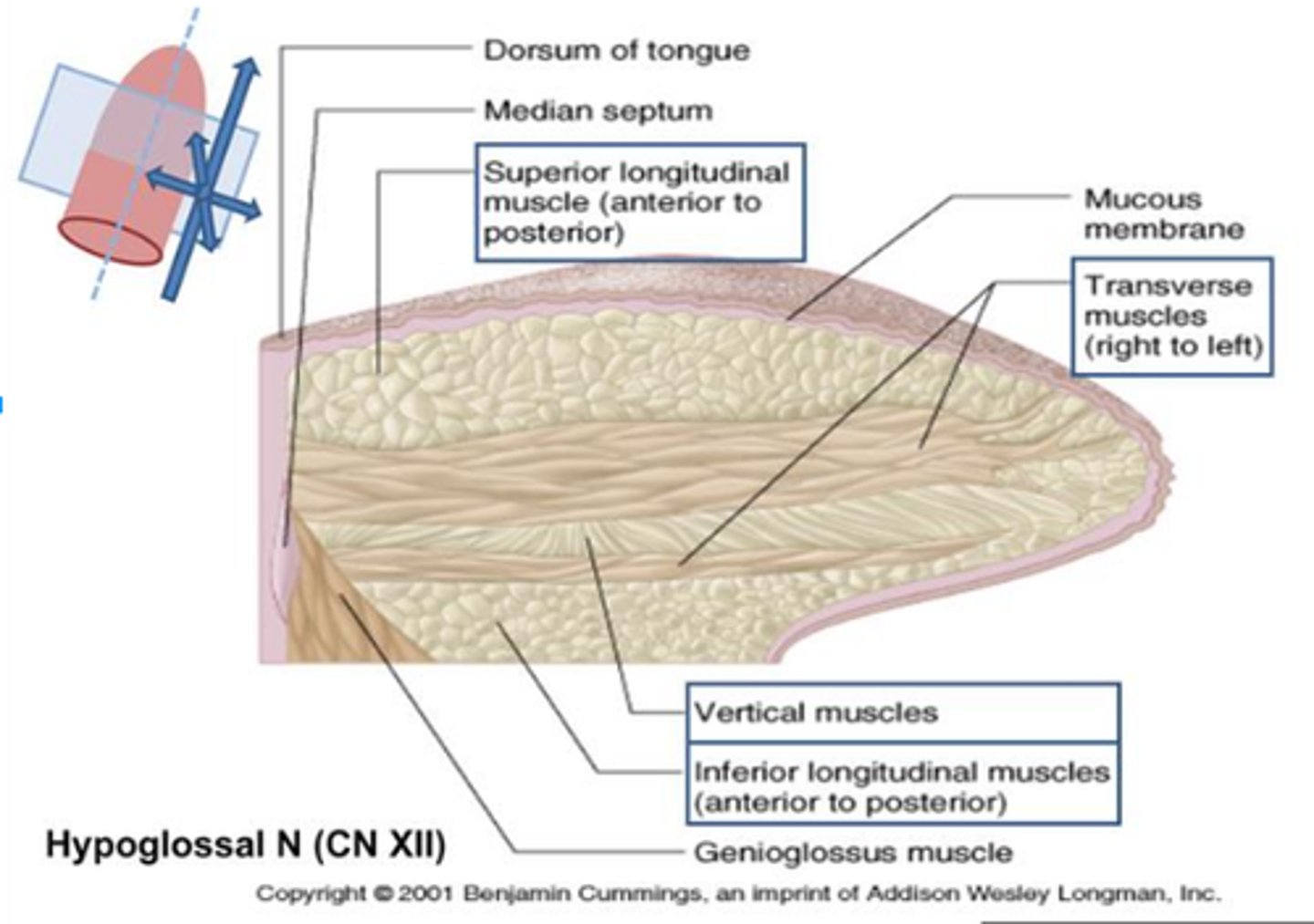
1.) intrinsic glossus muscles
2.) genioglossus muscle
3.) geniohyoid muscle
4.) hyoid bone
5.) hyoglossus muscle
6.) styloglossus muscle
7.) styloid process
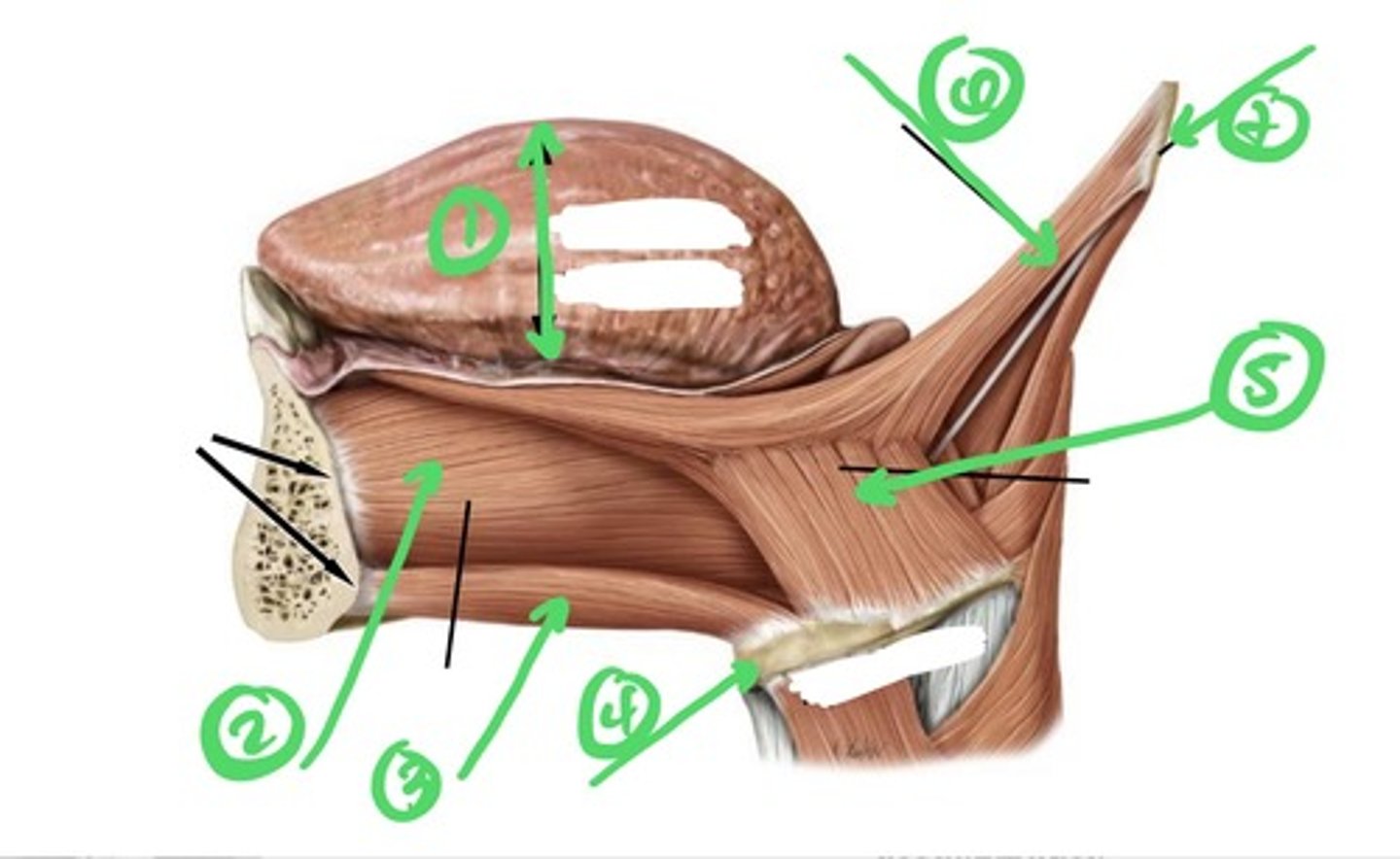
Which muscle retracts & cups the tongue?
styloglossus muscle
-extrinsic glossus muscle
-origin = styloid process
-innervated by hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
Which muscle depresses the tongue?
hyoglossus muscle
-origin = hyoid bone
-innervated by the hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
Which muscle protrudes & depresses the central portion of the tongue?
genioglossus muscle (allows you to stick your tongue out)
-origin = superior genial tubercles of mandible
- innervated by hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
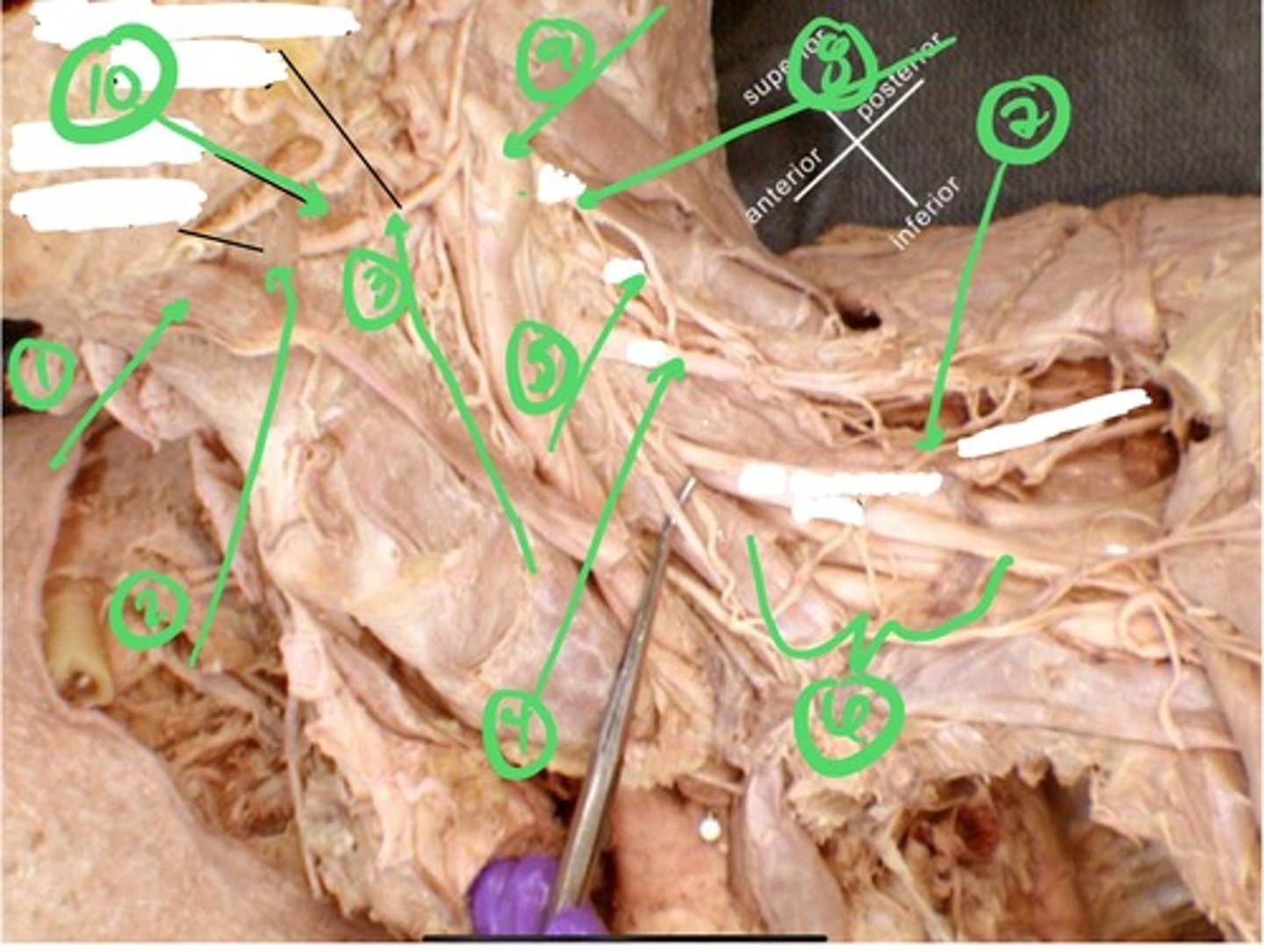
1.) anterior belly of digastric muscle
2.)mylohyoid muscle
3.) hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
4.) C3 spinal nerve
5.) C2 spinal nerve
6.) C5 spinal nerve & upper brachial plexus
7.) suprascapular nerve
8.) C1 spinal nerve
9.) internal carotid artery
10.) hyoglossus muscle
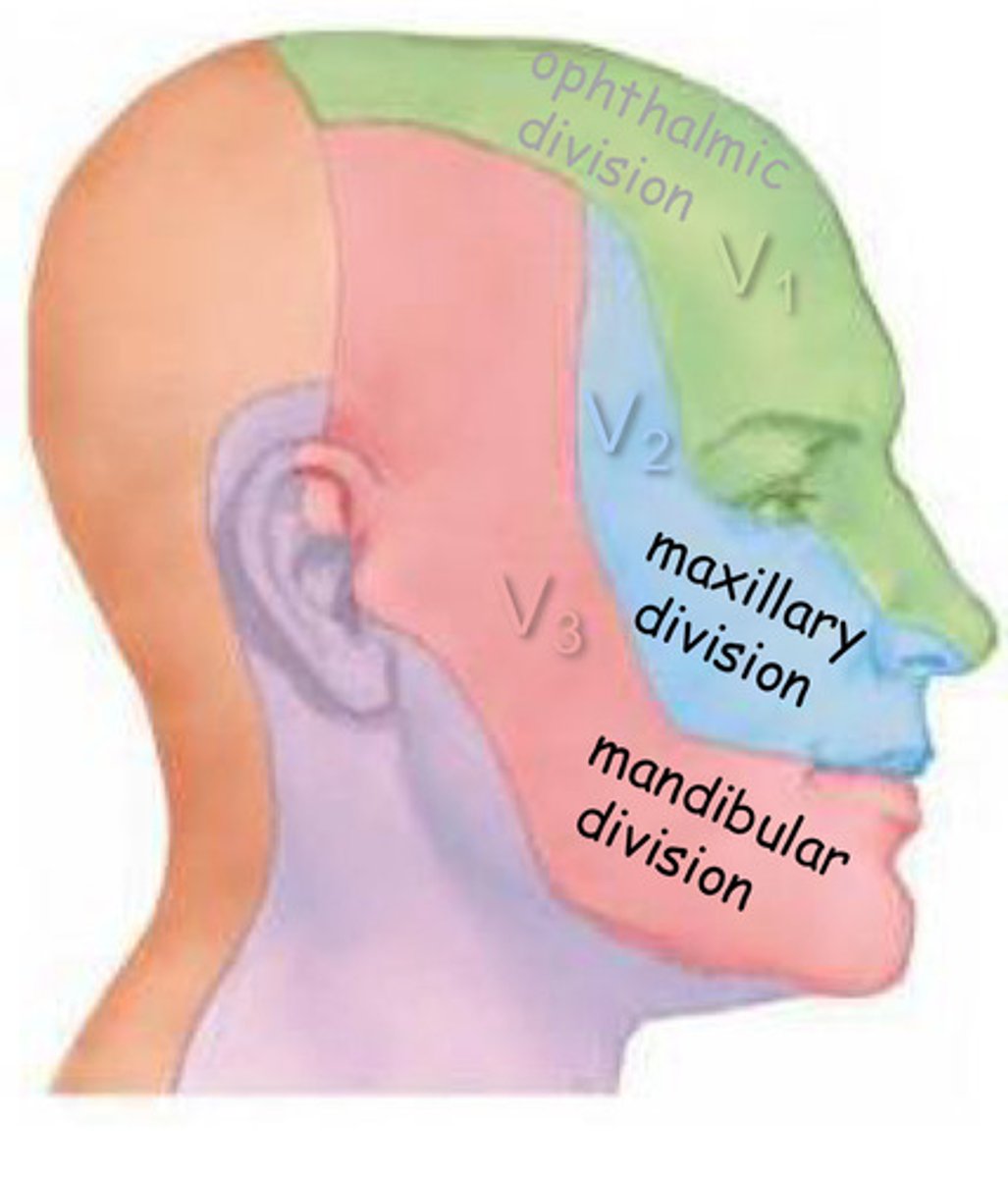
True or False: The lip & cheek muscles are innervated by the Maxillary (V2) and Mandibular Division (V3) of the Trigeminal Nerve (CNV)
False ==> The lip & cheek muscles are innervated by the Facial Nerve (CN VII)
-lip muscles --> orbicularis oris, levator labii superioris, depressor labii inferioris muscles
-cheek muscles --> buccinator muscle
True or False: All the major muscles of mastication involve movement of the mandible
True
*all major muscles of mastication innervated by Mandibular Division (V3) of Trigeminal Nerve (CNV)
-temporalis
-masseter
-medial/lateral pterygoids
Sensation of the Oral Mucosa
-Trigeminal Nerve (CNV)
-Facial Nerve (CNVII)
-Glossopharyngeal Nerve (CNIX)
Trigeminal Nerve (CNV)
major somatic sensory nerve to the face & internal cranium
-Maxillary Division (V2) --> max teeth, hard/soft palate, upper lip, & everything else in that region
-Mandibular Division (V3) --> mandibular teeth, lower lip, & everything else in that region (except the posterior 1/3 of tongue cuz that gets sensation from the glossopharyngeal nerve CNIX)
Salivary Glands
-sublingual gland --> innervated by CNVII
-submandibular gland --> innervated by CNVII
-parotid gland --> innervated by CNIX
- approximately 1000 minor salivary glands --> labial, palatine, & pharyngeal glands (innervated by CNVII)
*secrete about 1 liter of saliva a day (not much secretion when sleeping)
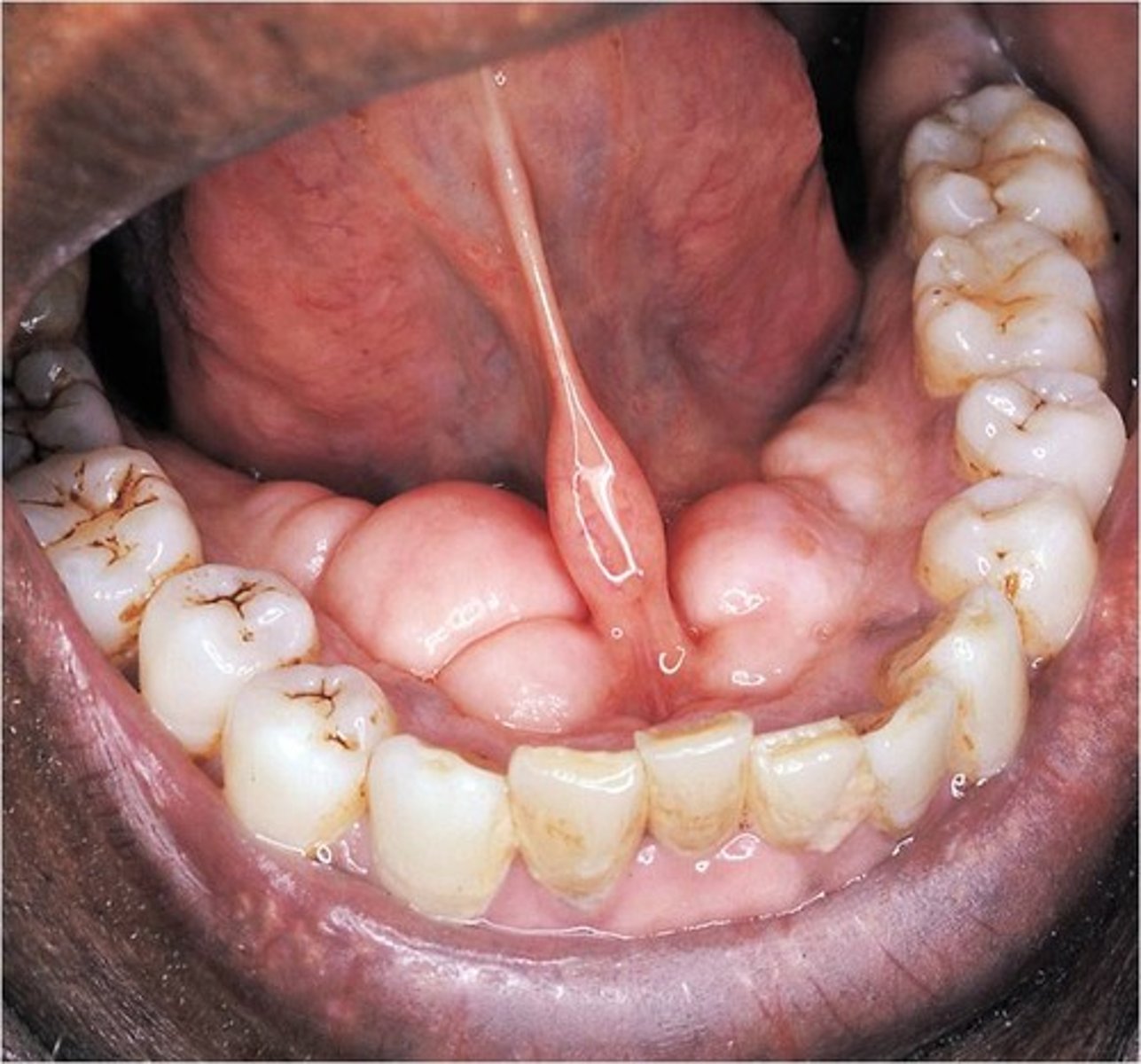
sublingual caruncle
opening for submandibular gland beneath the tongue
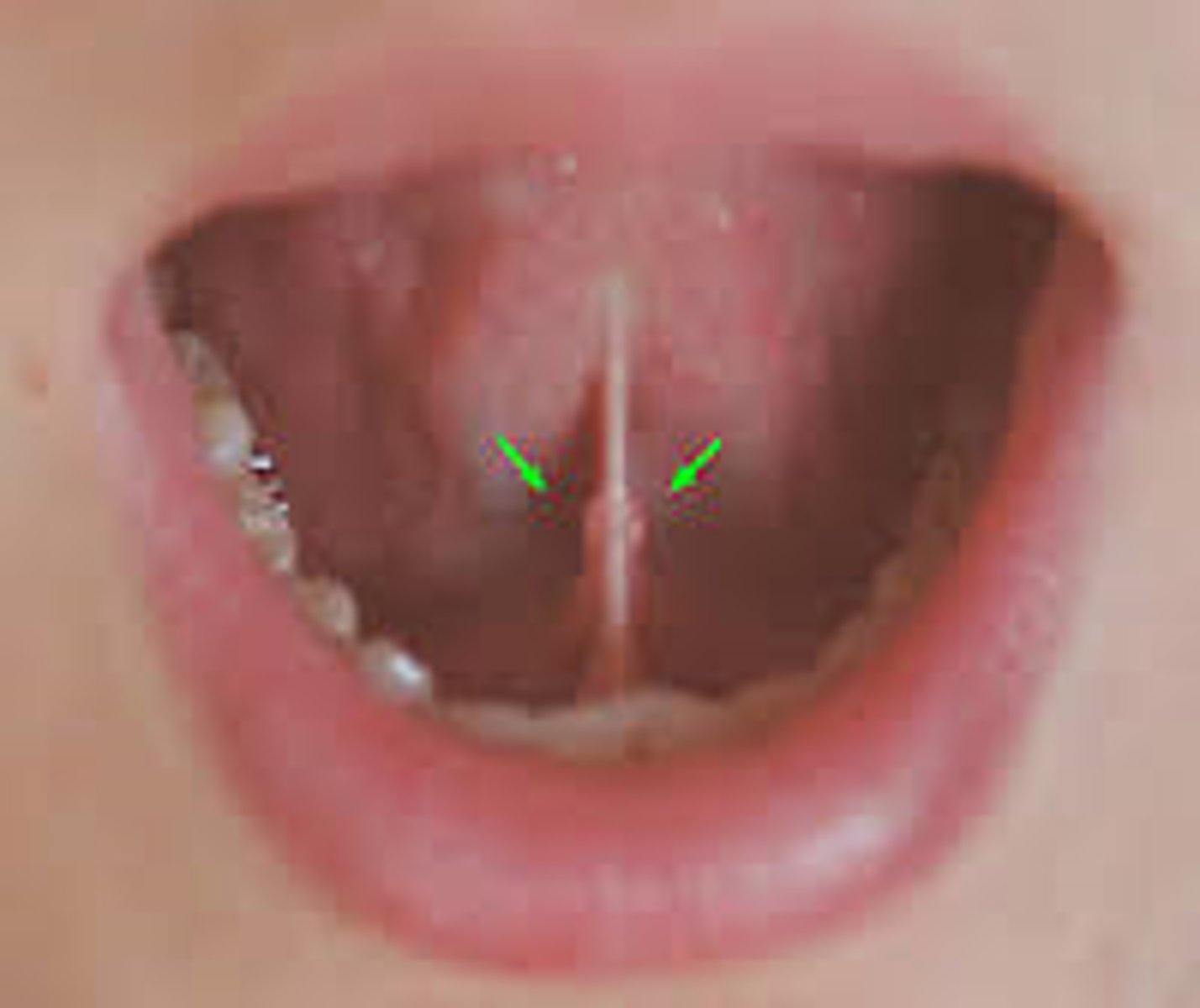
1.) lingual nerve
2.) submandibular duct
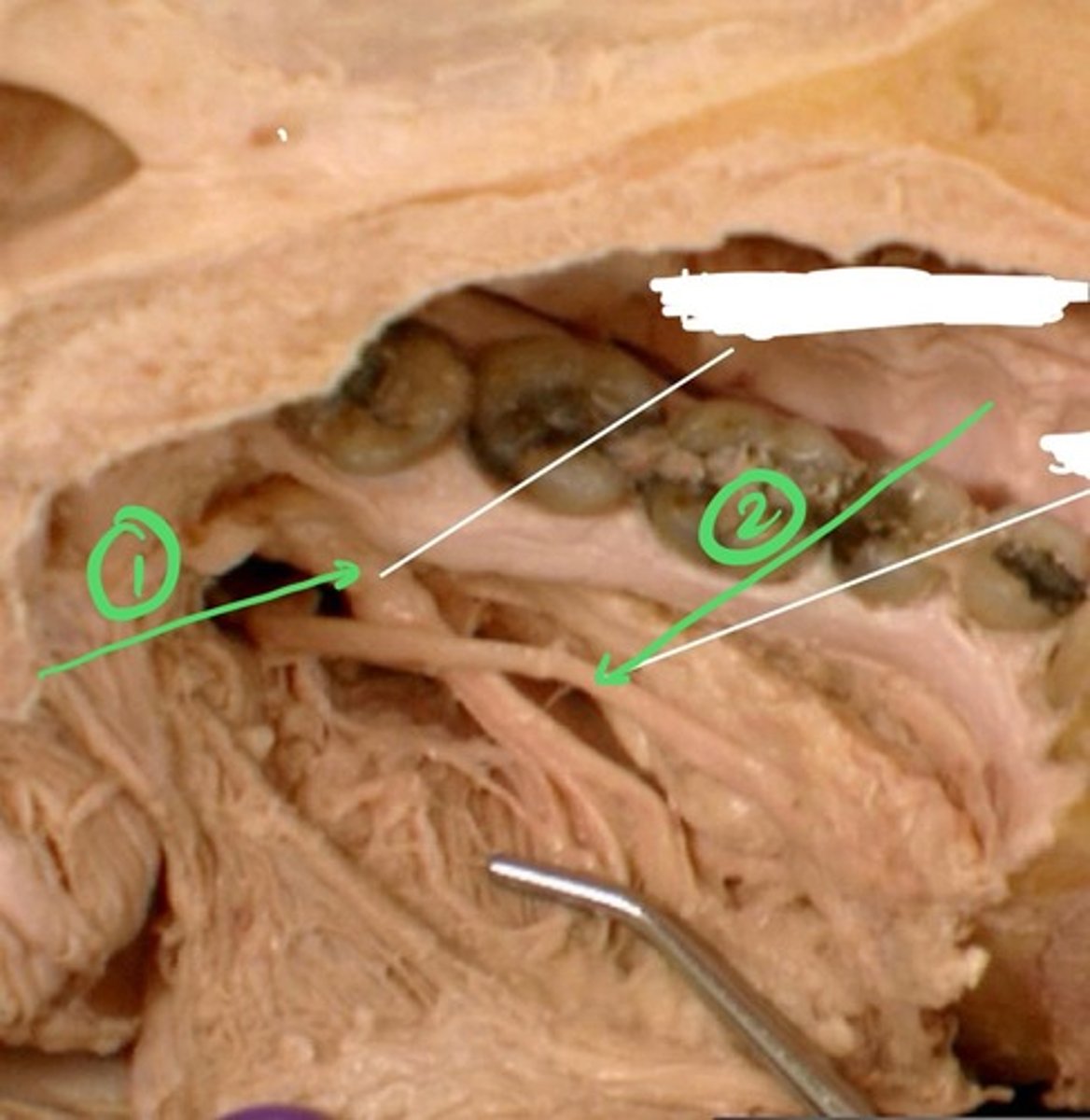
Where do the preganglionic fibers that innervate the parotid gland synapse?
otic ganglion
Where do the preganglionic fibers that innervate the sublingual & submandibular glands synapse?
submandibular ganglion
Pharynx (Overview)
runs from above the soft palate to the epiglottis
-three parts
> nasopharynx
> oropharynx
> laryngopharynx
-structures
>palatine tonsil
>palatopharyngeus muscles
> circular muscles --> superior, middle, & inferior constrictors (outer layer of muscles)
> longitudinal muscles --> salpingopharyngeus, palatopharyngeus, stylopharyngeus (inner layer of muscles)
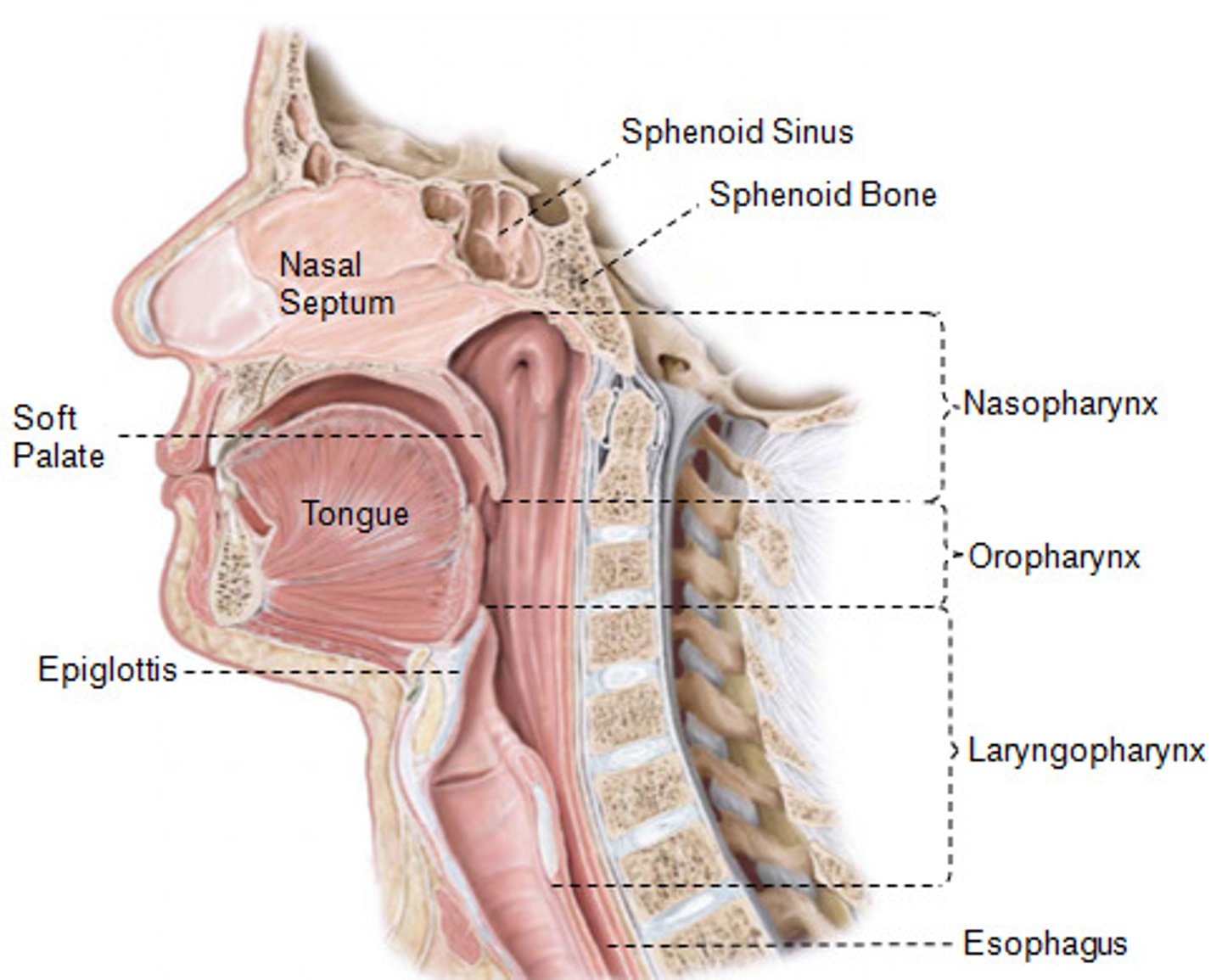
1.) nasopharynx
2.) oropharynx
3.) laryngopharynx
4.) epiglottis
5.) glossus
6.) soft palate (velum)
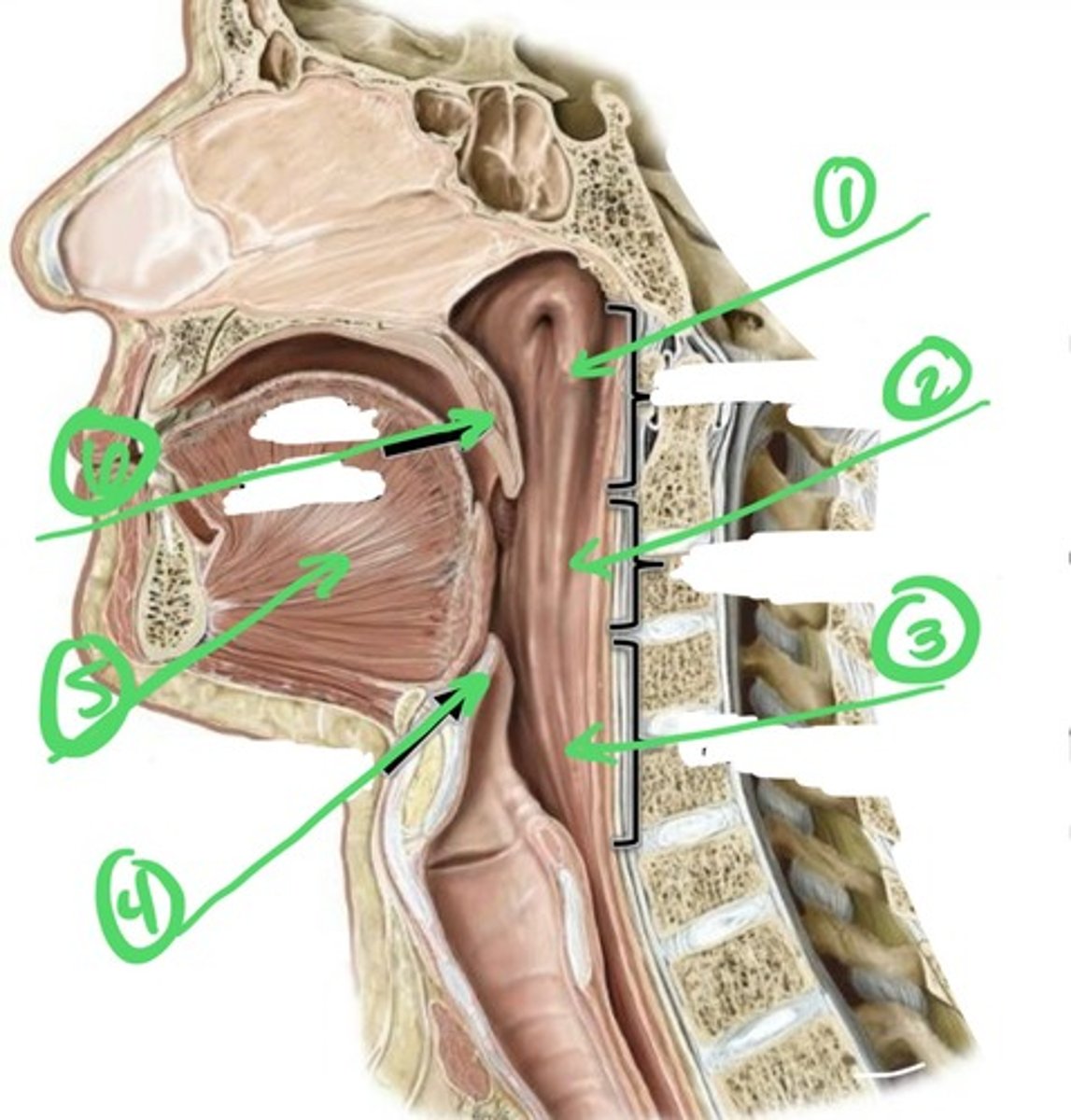
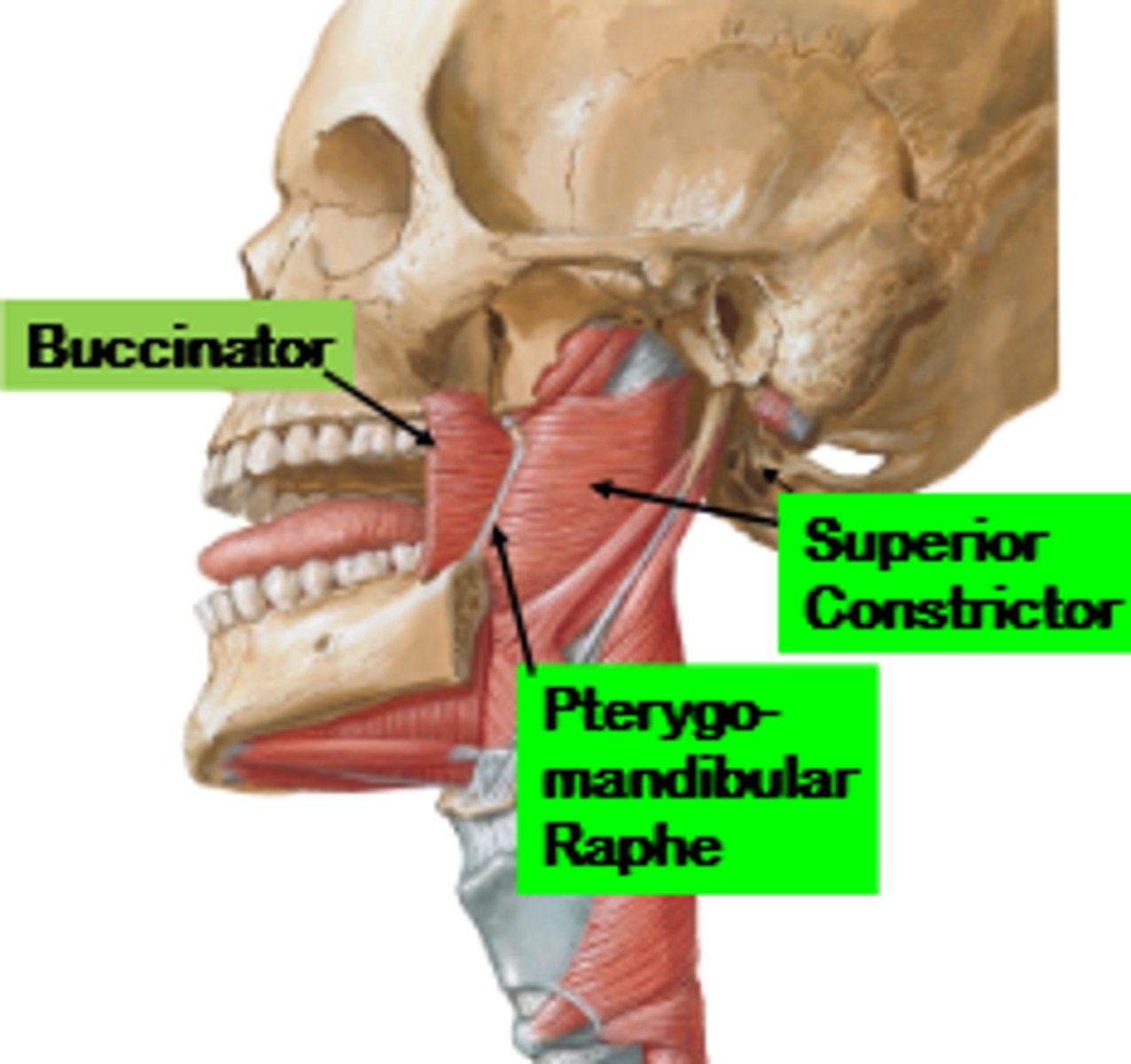
pterygomandibular raphe
origin for superior constrictor muscle (a pharynx circular muscle) & buccinator muscle
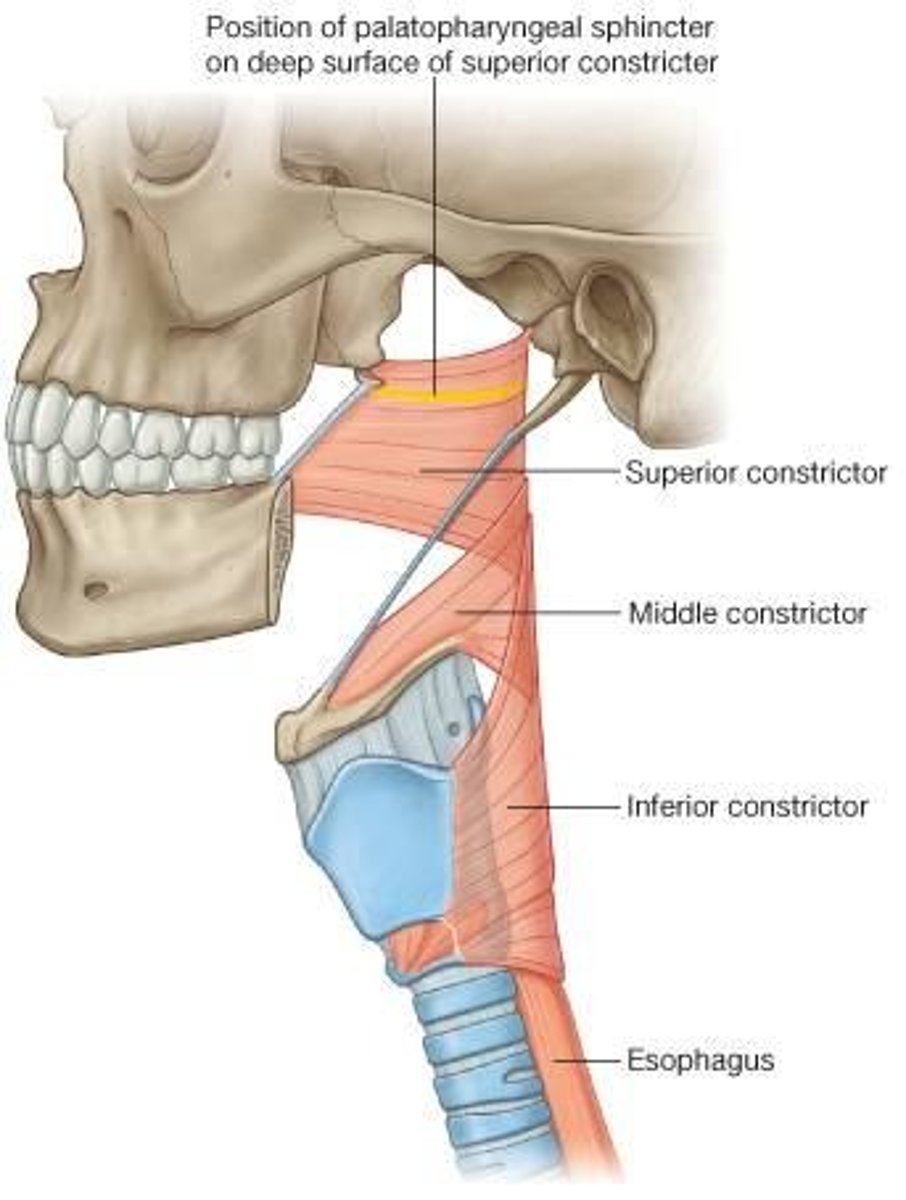
where does the middle constrictor muscle of the pharynx originate?
greater horn of the hyoid bone
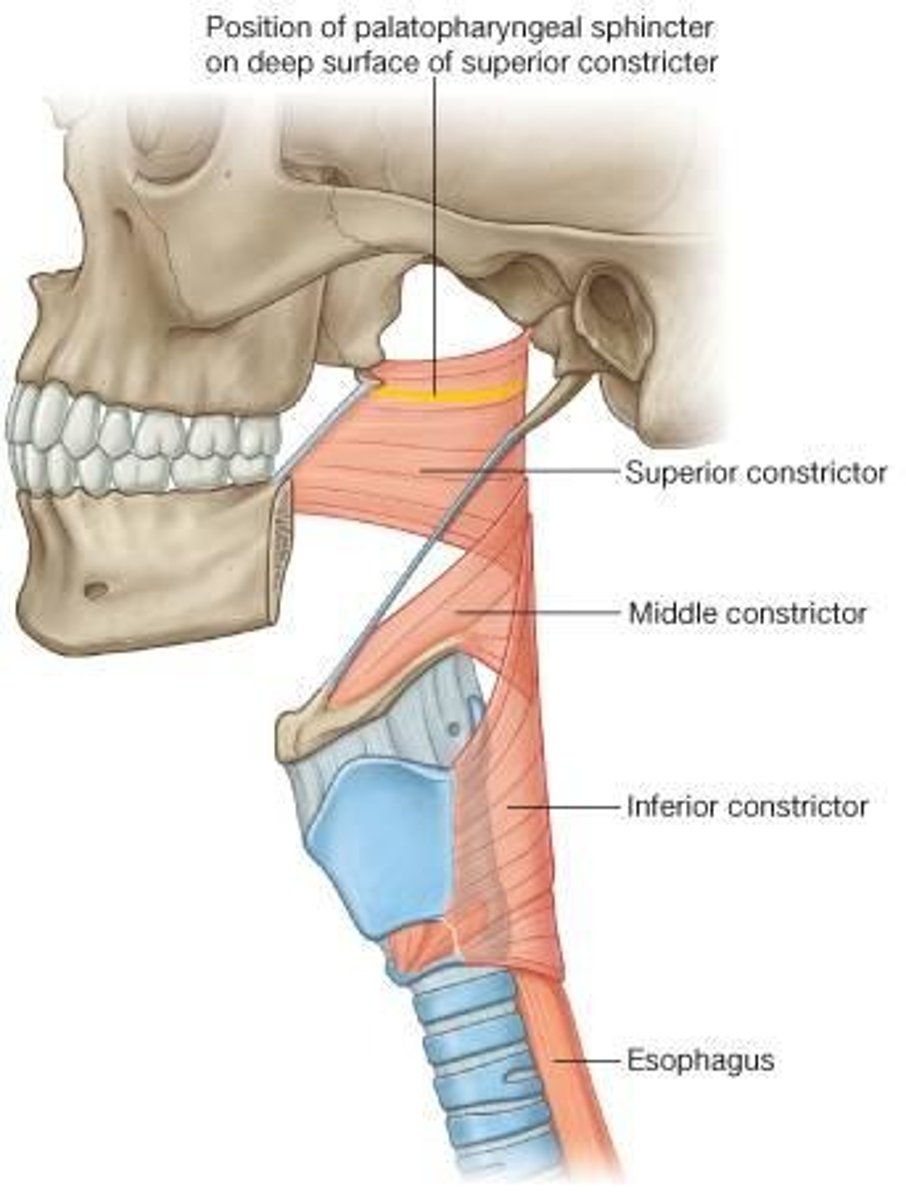
where does the inferior constrictor muscle of pharynx originate?
oblique line of the laryngeal cartilage
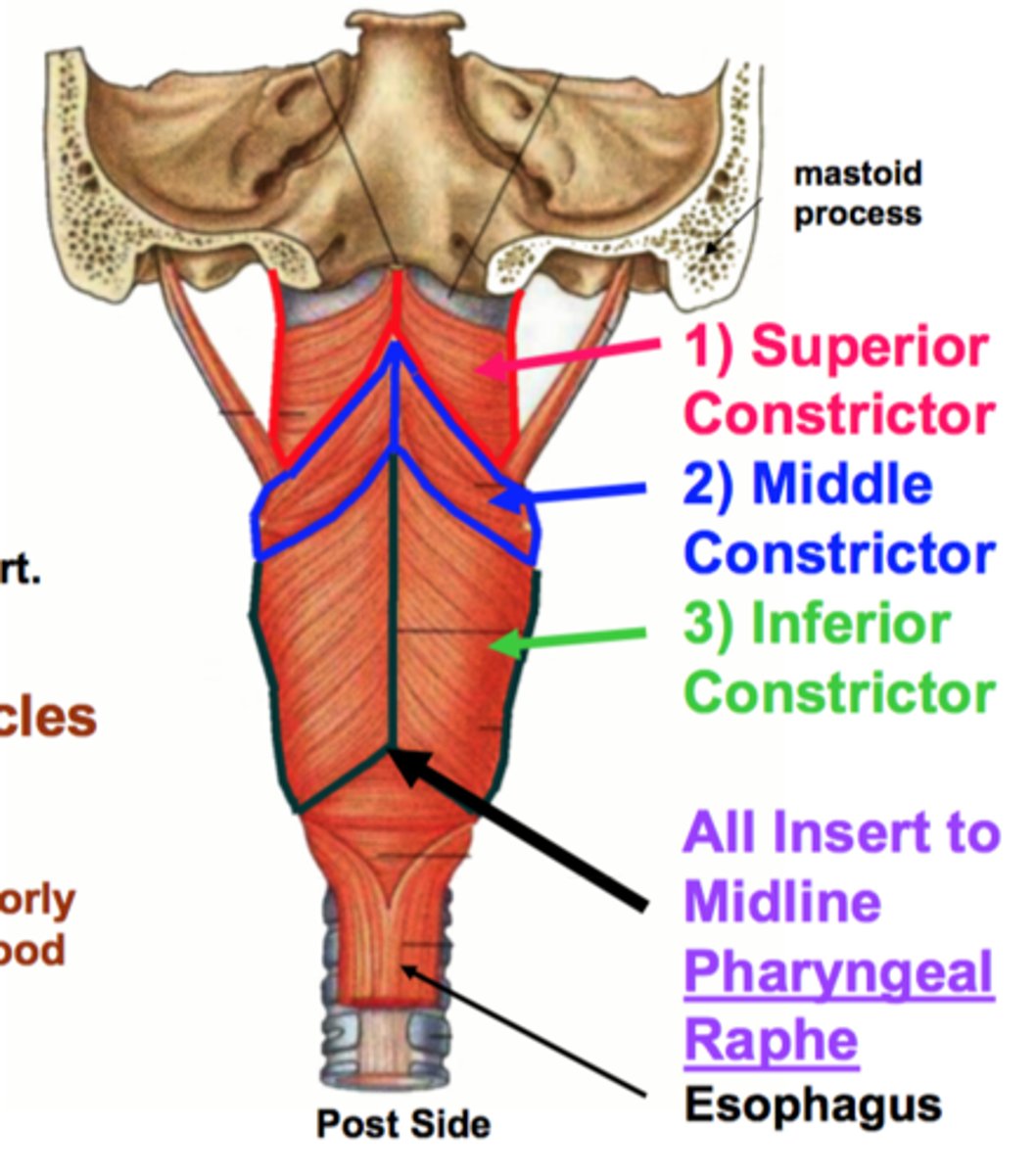
where do all the circular muscles of pharynx insert?
pharyngeal raphe
Circular muscles of Pharynx
superior, middle, & inferior constrictor muscles that contract to reduce the diameter of the pharynx; contract sequentially to move food in the epiglottis
-superior constrictor --> origin = pterygomandibular raphe
-middle constrictor --> origin = greater horn of hyoid bone
-inferior constrictor --> origin = oblique line of the laryngeal cartilage
pharyngeal tubercle
origin for the pharyngeal raphe (where the circular muscles of the pharynx insert)
longitudinal muscles of pharynx
muscles of the pharynx that elevate & shorten/widen the pharynx during swallowing
-salpingopharyngeus muscle --> origin = eustachian tube
-palatopharyngeus muscle --> origin = soft palate
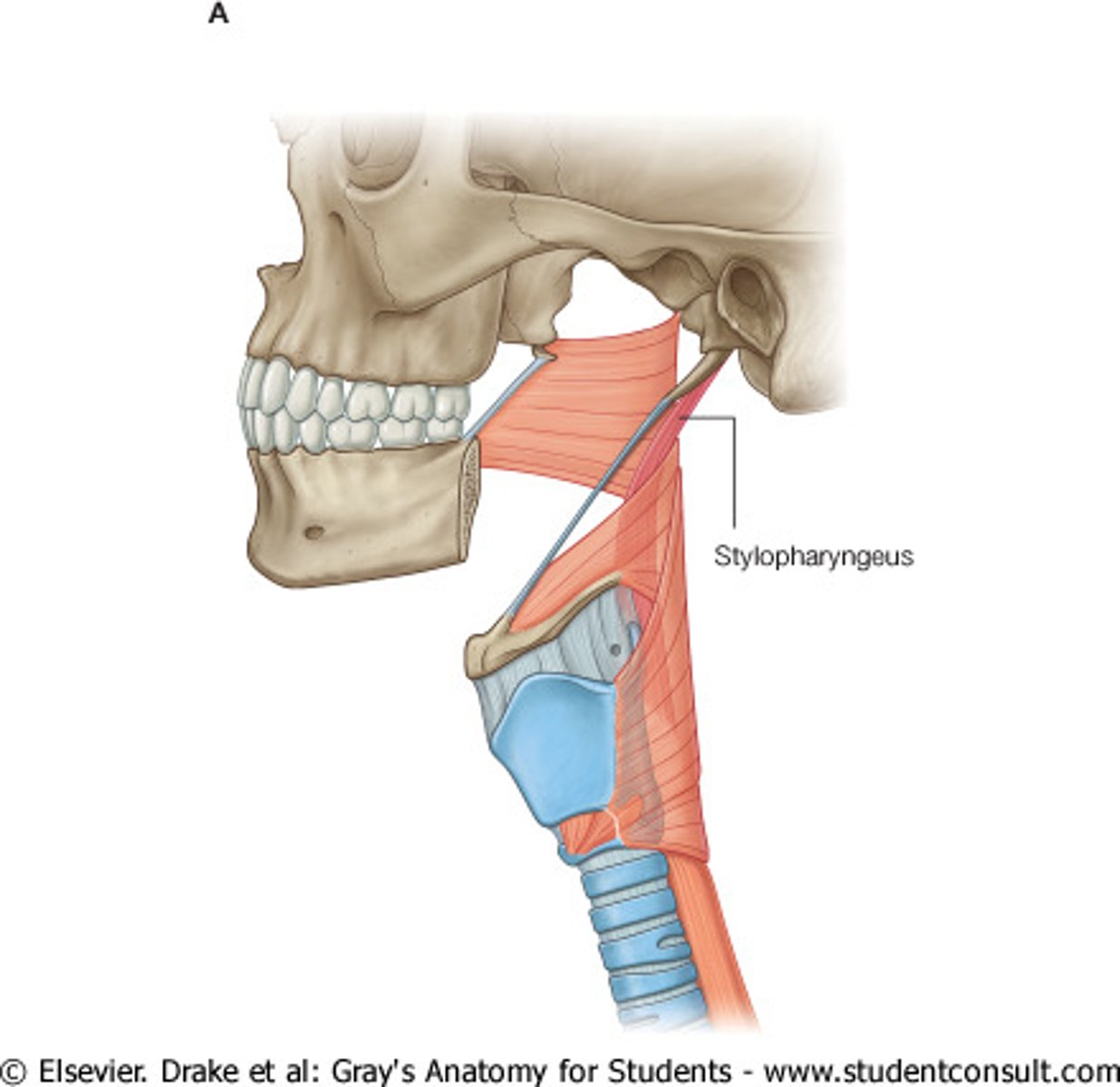
-stylopharyngeus muscle --> origin = styloid process
*All innervated by Vagus Nerve (CNX), except stylopharyngeus (innervated by Glossopharyngeal Nerve CN IX)
salpingopharyngeus muscle
longitundinal muscle that helps shorten/widen & elevate pharynx during swallowing
-origin = eustachian tube
*innervated by Vagus Nerve (CN X)
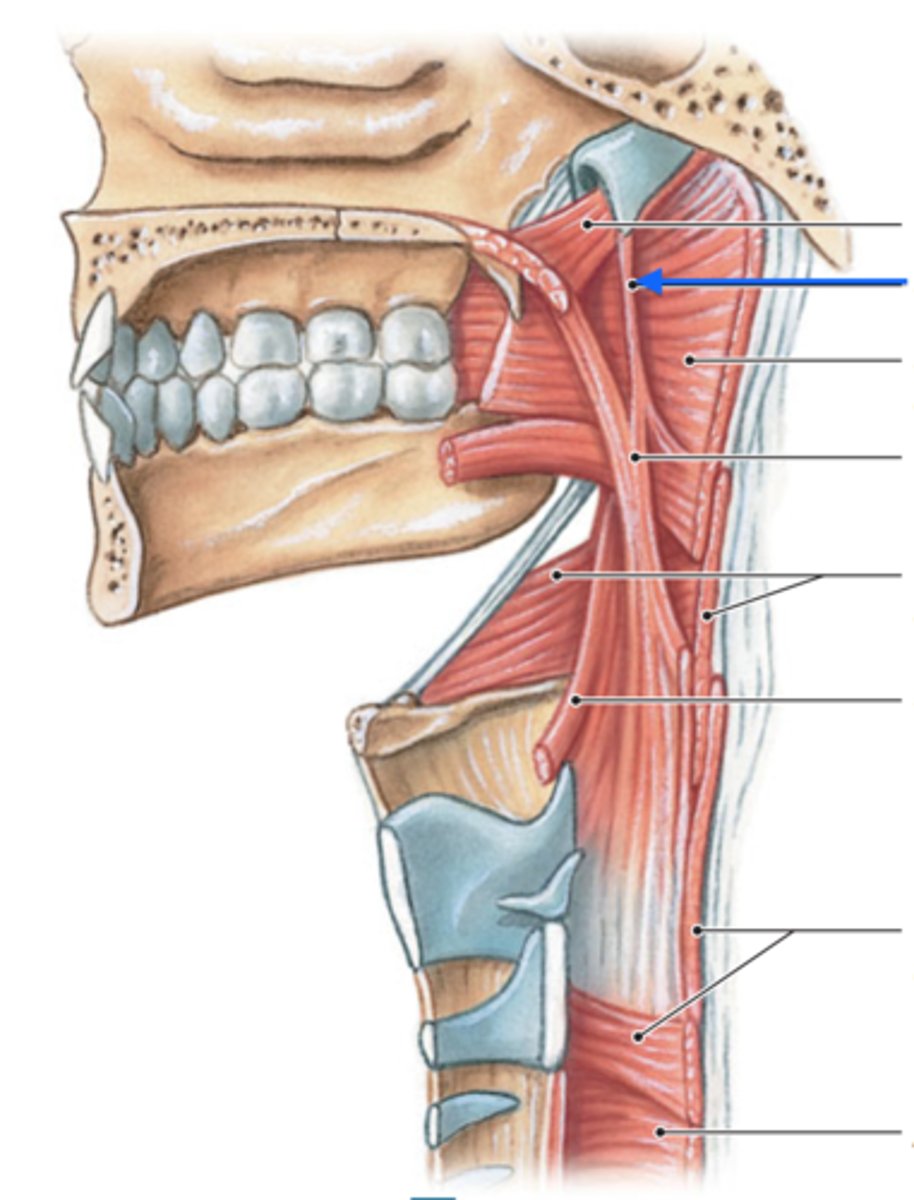
palatopharyngeus muscle
longitundinal muscle that helps shorten/widen & elevate pharynx during swallowing
-origin = soft palate
*innervated by Vagus Nerve (CN X)
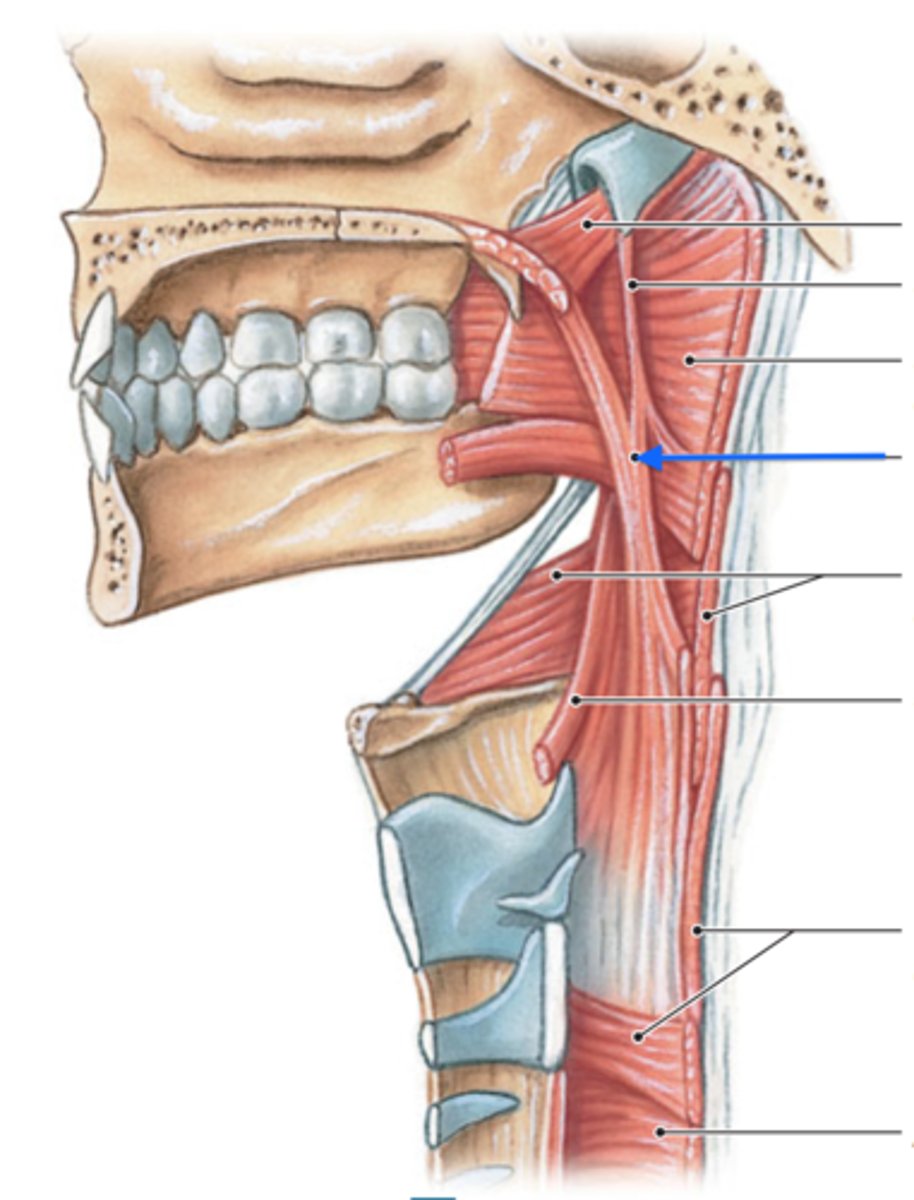
stylopharyngeus muscle
longitundinal muscle that helps shorten/widen & elevate pharynx during swallowing
-origin = styloid process
*innervated by Glossopharyngeal Nerve (CN IX)
What nerves are responsible for the gag reflex?
sensory fibers from both the Glossopharyngeal Nerve (CNIX) & the Vagus Nerve (CNX)
1.) salpingopharyngeus muscle
2.) palatopharyngeus muscle
3.) stylopharyngeus muscle
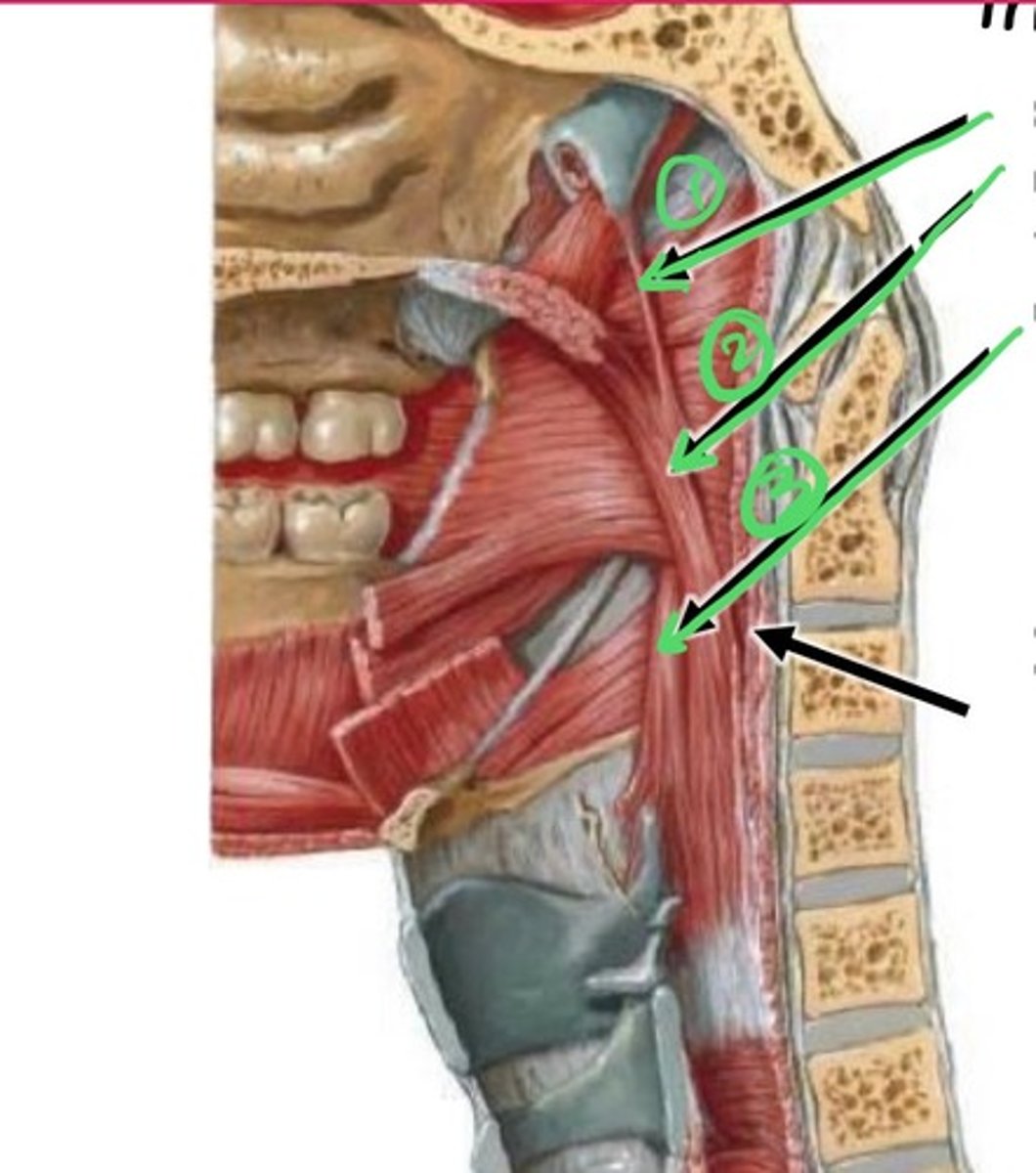
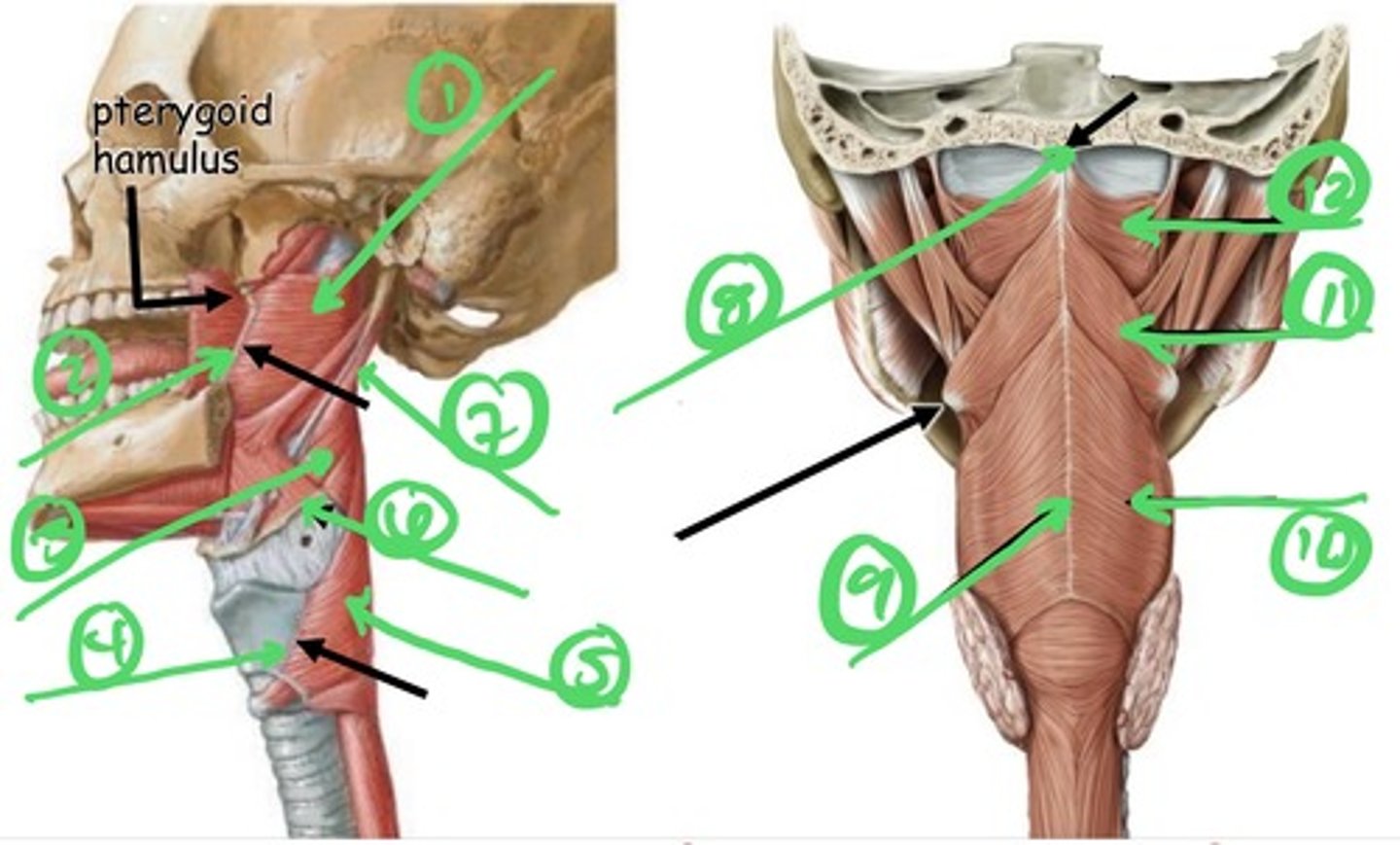
1.) superior constrictor muscle
2.) pterygomandibular raphe
3.) middle constrictor muscle
4.) oblique line of laryngeal cartilage
5.) inferior constrictor muscle
6.) greater horn of hyoid bone
7.) stylopharyngeus muscle
8.) pharyngeal tubercle
9.) pharyngeal raphe
10.) inferior constrictor muscle
11.) middle constrictor muscle
12.) superior constrictor muscle