Corneal Topography 3B
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What are the different types of Topography maps?
Axial or Sagittal
Tangential or Instantaneous
Elevation
Difference
Aberration
Characteristics of Axial or Sagittal map?
Center of Radius of curvature is CENTRAL AXIS
Best to look at central cornea
Better to compare 2 different corneas
Assesses Optical State of Cornea
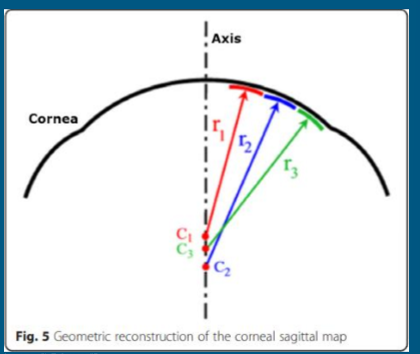
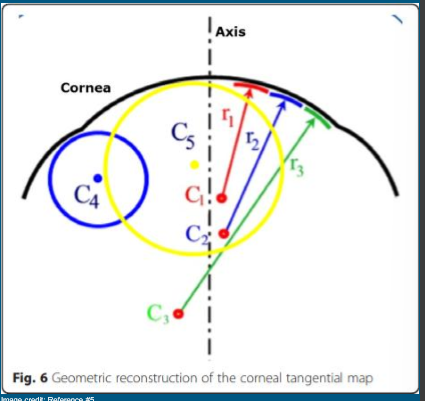
Characteristics of Tangential or Instantaneous Curve?
“True Curve data”
MORE DETAILED AND INDIVIDUALIZED to patient
****Most preferred map in contact lens FITTING along with elevation maps
Characteristics of Elevation Map?
Shows elevation of the eye at different points
Warm colors = more elevated
Cooler color = less elevated
Important for determining peripheral curvature of a lens
Characteristics of Difference Map?
Difference in curvature between EXAMS
Helpful with OrthK
Helpful to Monitor Changes in Cornea
Characteristics of Aberration Map?
Less commonly used
Need wave front aberrometer
Measures optical or refractive state of the eye
Uses Zernike Polynomials
Lower order: regular astigmatism, defocus (Can be corrected with glasses and soft contact lenses)
Higher order: trefoil, coma, spherical aberration (can be corrected with RGPs)
How are Irregularity Indices used?
Help detect corneal irregularity
Different on topographer vs tomographer
More extensive indices available on tomographer
What are common indices for topographers?
I-S or S-I (Inferior-Superior) Value: Superior and Inferior cornea
Values higher than 1.5 D are suspicious for ectasia (thinning)
SAI (Surface Asymmetry Index): One eye to fellow eye
Difference in more than 1 D considered at risk
0.10 to 0.42
SRI (Surface Regularity Index): Power of central 4.5 mm
Normal corneas have low SRI values, usually 0 to 0.56
What are the irregularity indices for Topcon CA 800
AGC (Apical Gradient of Curvature): Curvature changes from center to peripheral
Higher rates of change are more suspicious
AK (Apical Keratometry): Dioptric power at apex of cornea
Steeper values are more suspicious
S-I Value
KPI (Keratoconus Probability Index)
Combines previous values to determine probability of Keratoconus

What are the Irregularity Indices for Tomographers?
BAD (Belin-Ambrosio Display)
Anterior elevation, posterior elevation, pachymetry
PPI (Pachymetric Progression Index)
Change in corneal thickness over entire cornea
Why are Irregularity Indices used?
Help diagnose and monitor corneal disease
Good for general CL fitting and screening
***Different for Tomographer and Topographer
How do you interpret Topography Report?
G-General information
R- Reliability
A- Abnormal/normal
D- Defect
E- Evaluate
S- Subsequent Test
What are some keys to recognize patterns on a Topographer?
Look at color maps
What kind of map are you looking at?
Check Sim-K’s (normal curvature is 40-46.00 D)
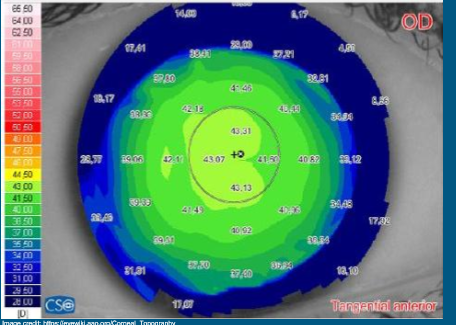
What does this look like?
Spherical cornea
-Even coloring throughout central cornea
-Keratometry readings approximately the same in all quadrants

What is this look like?
With the Rule Astigmatism
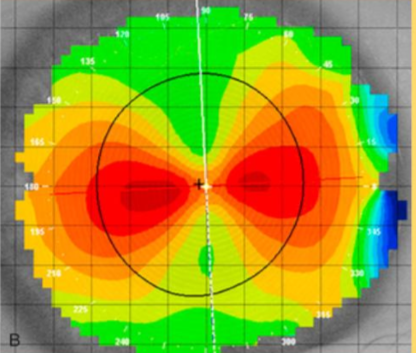
What does this look like?
Against the Rule Astigmatism
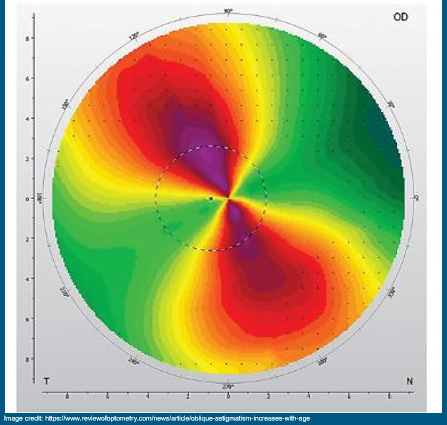
What does this look like?
Oblique Astigmatism
**Angles usually at 120-150 or 30-60 degrees
What are the keys to look for if thinking about Irregular astigmatism?
May have “bowtie” look, but usually ASYMMETRICAL
May not have a particular pattern
Does not necessarily mean disease
Umbrella term

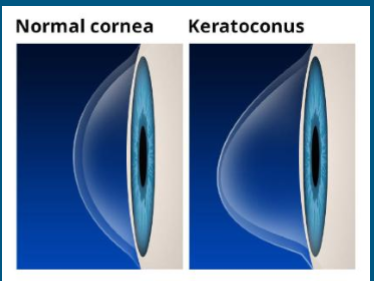
What are characteristics of Keratoconus?
Primary non-inflammatory Ectasia
Cone-like shape INFERIORLY
Progressive
Starts in childhood
Early diagnosis important for best prognosis
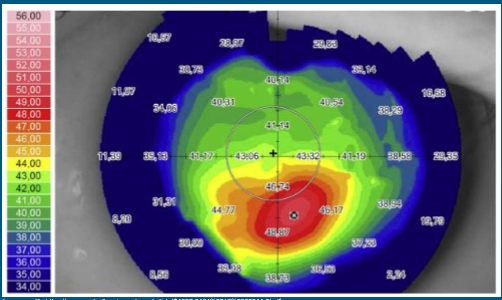
What does this look like?
Keratoconus
**Inferior steepening
Need more than topography findings to diagnose
What is Pellucid Marginal Degeneration?
Idiopathic thinning of peripheral cornea
Rare
Slowly progressive
Usually Inferiorly
Usually OLDER PATIENTS
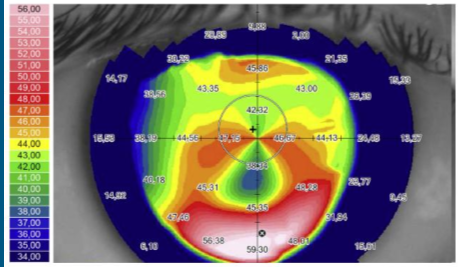
What does this look like?
Pellucid Marginal Degeneration
***Crab Claws or Kissing Doves
Sagging appearance
**Need Pachymetry
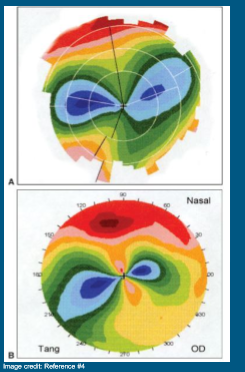
What does this look like?
Corneal Transplant
Variable appearance
Usually irregular astigmatism
Patient dependent
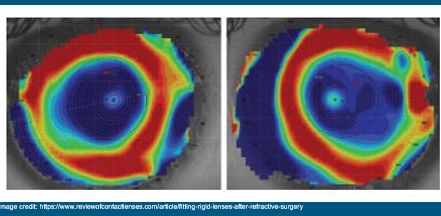
What does this look like?
Post-Refractive Surgery
***Myopic Correction
Flatter in center with relative peripheral steepening
OrthoK can have similar topography

What does this look like?
Post-Refractive Surgery
***Hyperopic correction
Steeper central cornea
Flatter periphery
What is normal corneal shape?
Aspheric
Prolate: steeper in center, flatter in periphery
What measures rate of flattening?
e value
What does it mean if the e value is 0?
Spherical
What if the e value goes up?
Rate of flattening towards periphery increases
What is the average e-value for a cornea?
0.43
How do you apply topography readings clinically?
Standard vs custom fit contact lenses
Custom contacts benefit from corneal topography
Cornea to contact lens relationship is important
Prevents long-term complications
Improves vision and comfort