Thin Lenses
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Converging
Both sides of _________________ lens curve outwards

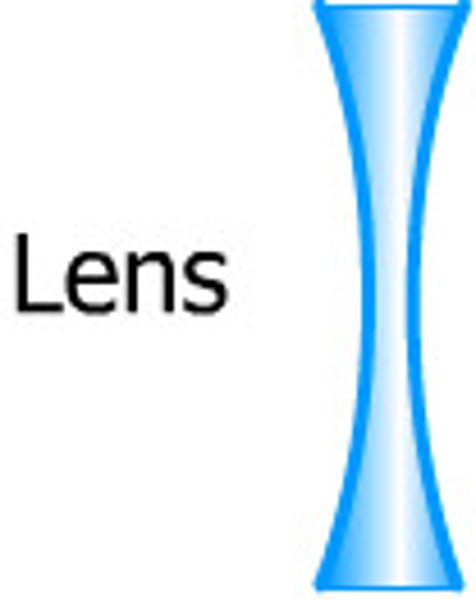
Diverging
Both sides of ________________ lens curve inward
Focal point
Point where light rays meet
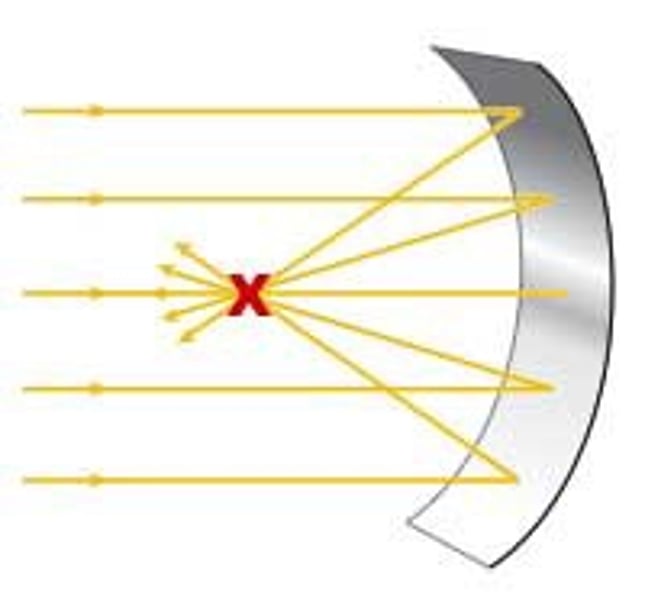
Focal length
Distance from center of lens to focal point
Convex
Other name for converging lense
Concave
Other name for diverging lens
1/f=1/do+1/di
Thin lens equation
Focal length
( 1/f = 1/do + 1/di )
f
Object distance (distance from object to lens)
( 1/f = 1/do + 1/di )
do
Image distance (distance from image to lens)
( 1/f = 1/do + 1/di )
di
do/di
ho/hi =
Object height
( do/di = ho/hi )
ho
Image height
( do/di = ho/hi )
hi
+
Converging lenses have _____ focal lengths
-
Diverging lenses have _____ focal lengths
+
With a single lens, object distance is always _____
+
Image distance is _____ if image and object are on opposite sides of lens
-
Image distance is _____ if image and object are on same sides of lens
M=-di/do (M=magnification)
Magnification equation
+
_____ magnification value means image is right side up
-
_____ magnification value means image is up side down
Lens power (p)
1/f =
Diopter
Unit of measurement for lens power (1/m)
Spherical abberation
Light rays do not perfectly intersect at focal point; results in blurred image
Chromatic abberation
Different colors of light are bent to different points
Cornea
Outer lens of eye
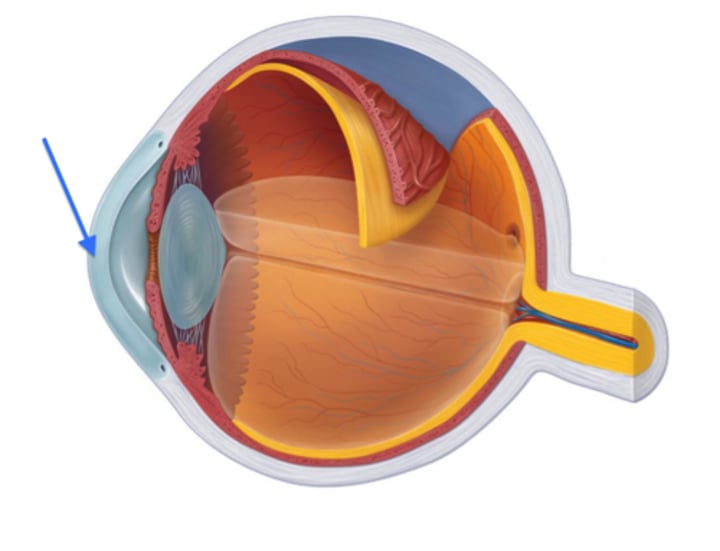
Lens
Inner lens of eye that makes fine adjustments to image
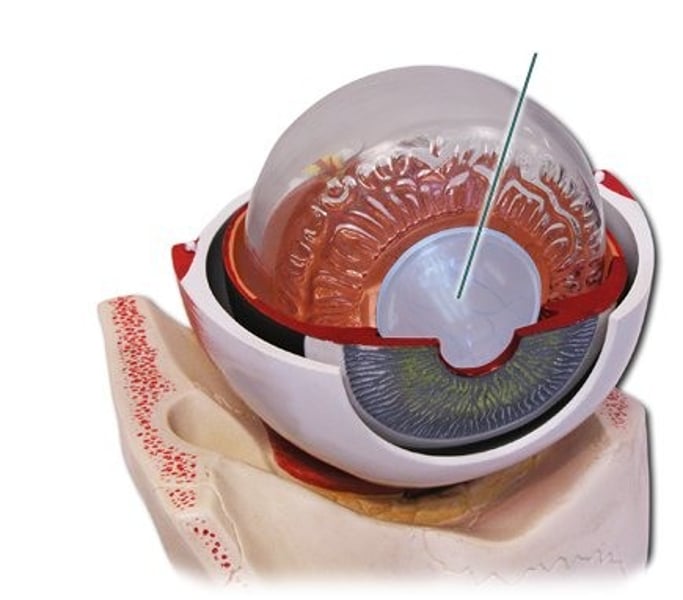
Ciliary muscle
Smooth muscle that alters shape of lens; allowing it to adjust image
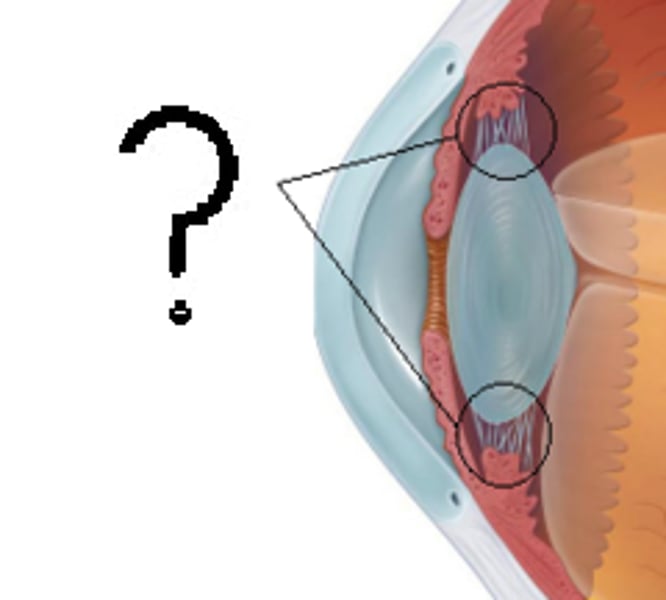
Retina
Light sensitive layer of the eye that image is projected onto
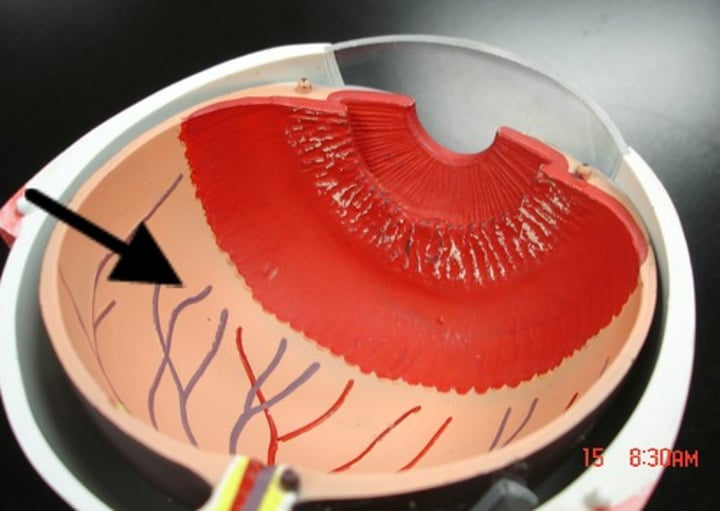
Optic nerve
Nerve that carries neural impulses from the eye to the brain
Nearsighted
________________ vision is corrected with concave lens glasses
Farsighted
_______________ vision is corrected with convex lens glasses