Stem Cells
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Define haematopoisesis
Where hematopoitic stem cell gives rise to diff blood cell types.
What changes in cell differentiation of a stem cell?
Gene expression, proteome. (SAME DNA).
Define pattern formation
Concept of positional info proposes that cells acquires positional value as in a coordinate system, which they interpret by developing in particular ways to give rise to spatial patterns.
What events can define polarity?
Molecular.
To understand disease what must you understand first?
Normal development.
Define stem cell
Undifferentiated cell of a multicellular organism which is capable of giving rise to indefinitely more cells of the same type, and from which certain other kinds of cells arise by differentiation. Undergo self-renewal.
Define self-renewal
One daughter cell in maintaining SC pop while other daughter cell gives rise to progenitor cell which can generate other cell types. Is needed to maintain SC pops otherwise mitosis would deplete SC pops very fast.
Define asymmetric division
A mitotic cell division that gives rise to progeny with different fate.
Define totipotent
Can form whole new organism. Mammals: can form embryo, extraembryonic membrane + placenta.
Define pluripotent
Can form many cell types but not all. Mammals: can form embryo.
Define multipotent
Can form fewer but still many cell types.
How are embryonic stem cells generated?
Need embryos at the blastocyst stage. Inner cell mass (ICM) (pre-implantation embryo that contains 200 ICM) must be extracted to generate ESCs. A small number of ICM cells will go onto to generate ESCs. Once generated there is potential to maintain these self-renewing ESCs in tissue culture + manipulate them.
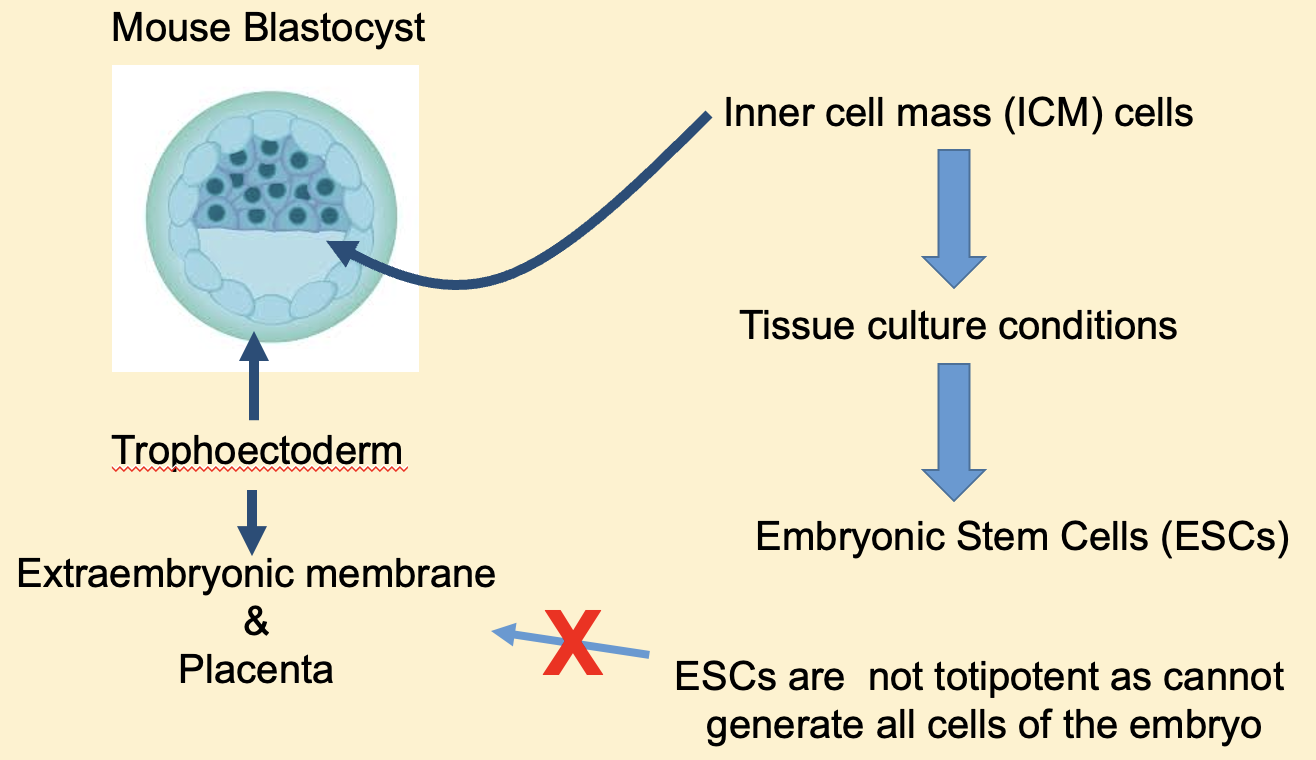
ESCs are pluripotent, why can they not be considered totipotent?
Cannot generate the extraembyronic membrane + placenta.
State uses of ESCs
Introduce genes, knockout genes, chromosomal rearrangements/deletions, make specific genome edits.
Define chimeria
Has cells from 2 diff cell types + 2 diff genotypes. From ESCs + ICM.
Why will ESCs not generate a mouse in a culture if left to divide + how can this be overcome?
Because the ESCs are not totipotent. Can be overcome by introducing the cultured ESCs containing the specific change into a developing blastocyst. Blastocyst already has ICM so new blastocyst has these + introduced ESCs. This is implanted into a pseudopregnant mouse + develops to give rise to an adult mouse.
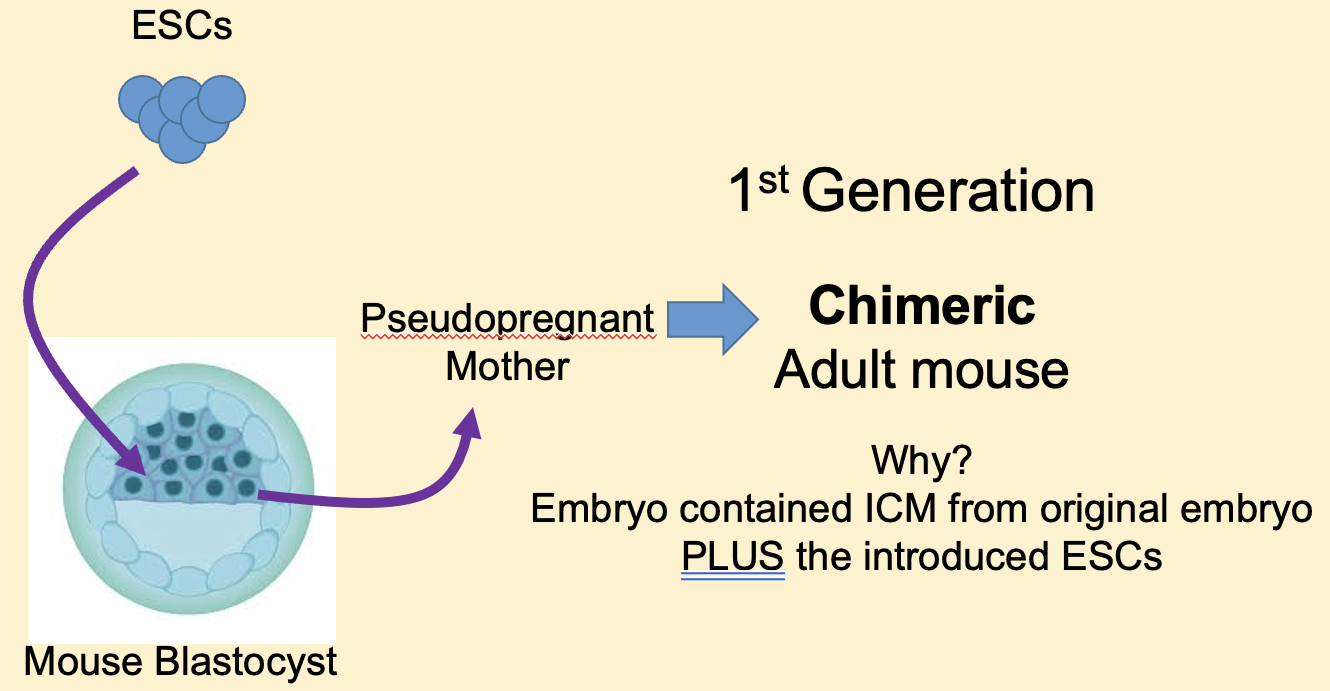
What can be used to keep track of which cells are devised from implanted ESCs + which were already present in the blastocyst of the chimeric adult mouse?
Genetic markers.
Define genetic mosaic
Derived from a single zygote + 2 diff genotypes arise.
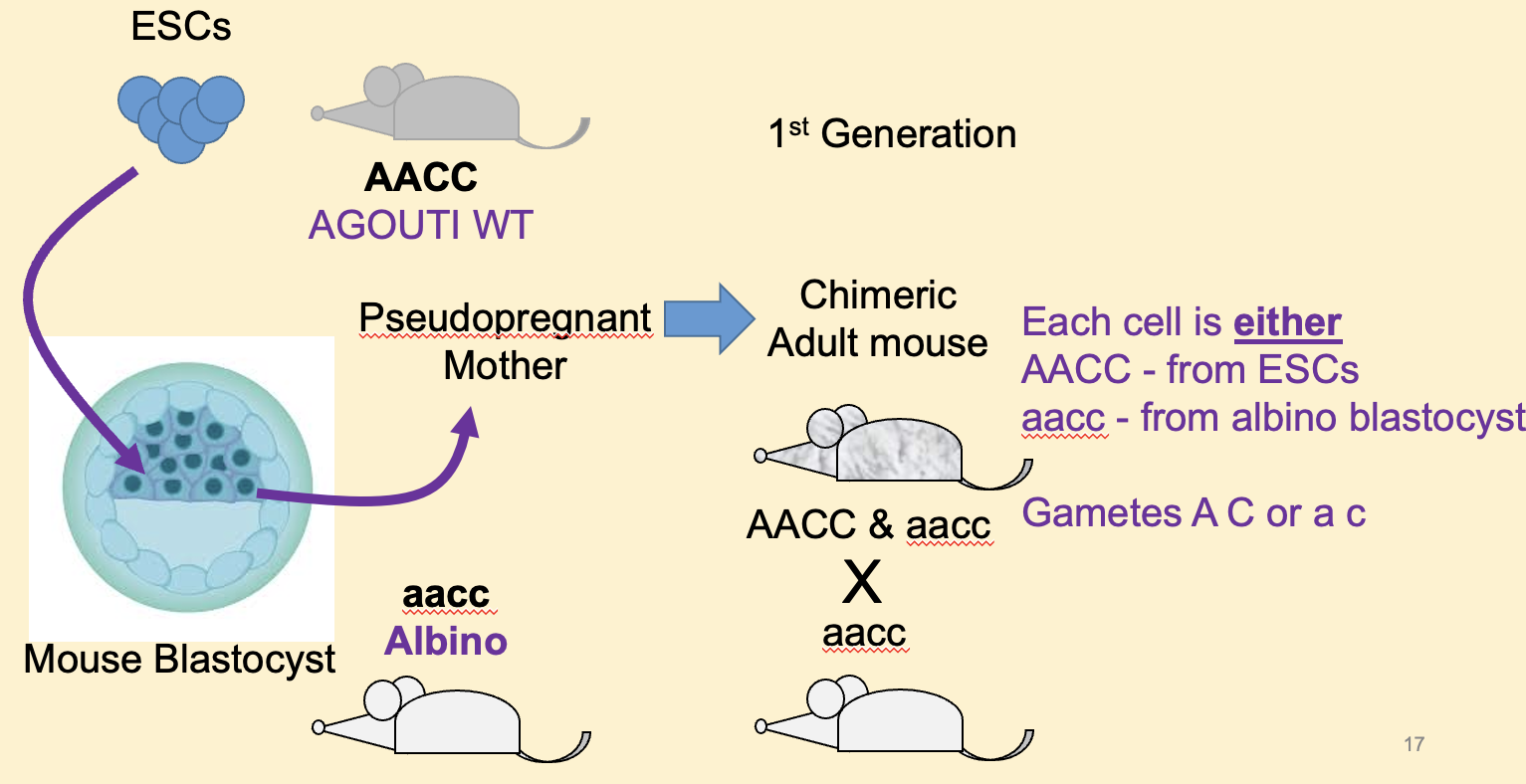
Describe how the genetic marker of coat colour was used on transgenic mice from ESCs
Coat colour determined by banding pattern on bristles + Wt colour needs A + A alleles present giving them greyish colour (agouti) but albino mouse will be homozygous for both a + c allele due to absence of pigmentation.
So if ESCs are derived from an AACC (agouti) blastocyst + are transplanted into the blastocyst from an albino (aacc) mouse, the 1st gen of chimeric mouse will have mixed genotype of AACC + aacc = patchy coloured fur. NOT heterozygous as doesn’t have AcCc. Cell will be EITHER AACC or aacc.
Cells in reproductive system will hopefully be chimera + can give rise to gametes that are either: A C (derived from transgenic ESCs) or a c (derived from albino blastocyst cells).
When considering the transgenic mice from embryonic stem cells, the ability of the chimeric 1st generation mouse to pass of genotype derived from the ESCs to the future gens is dependent on what?
If the 1st gen has reproductive organs at least part derived from the implanted ESCs because there needs to be germ line cells derived from the ESCs.
Somatic nuclei can be reprogrammed to be what?
Totipotent.
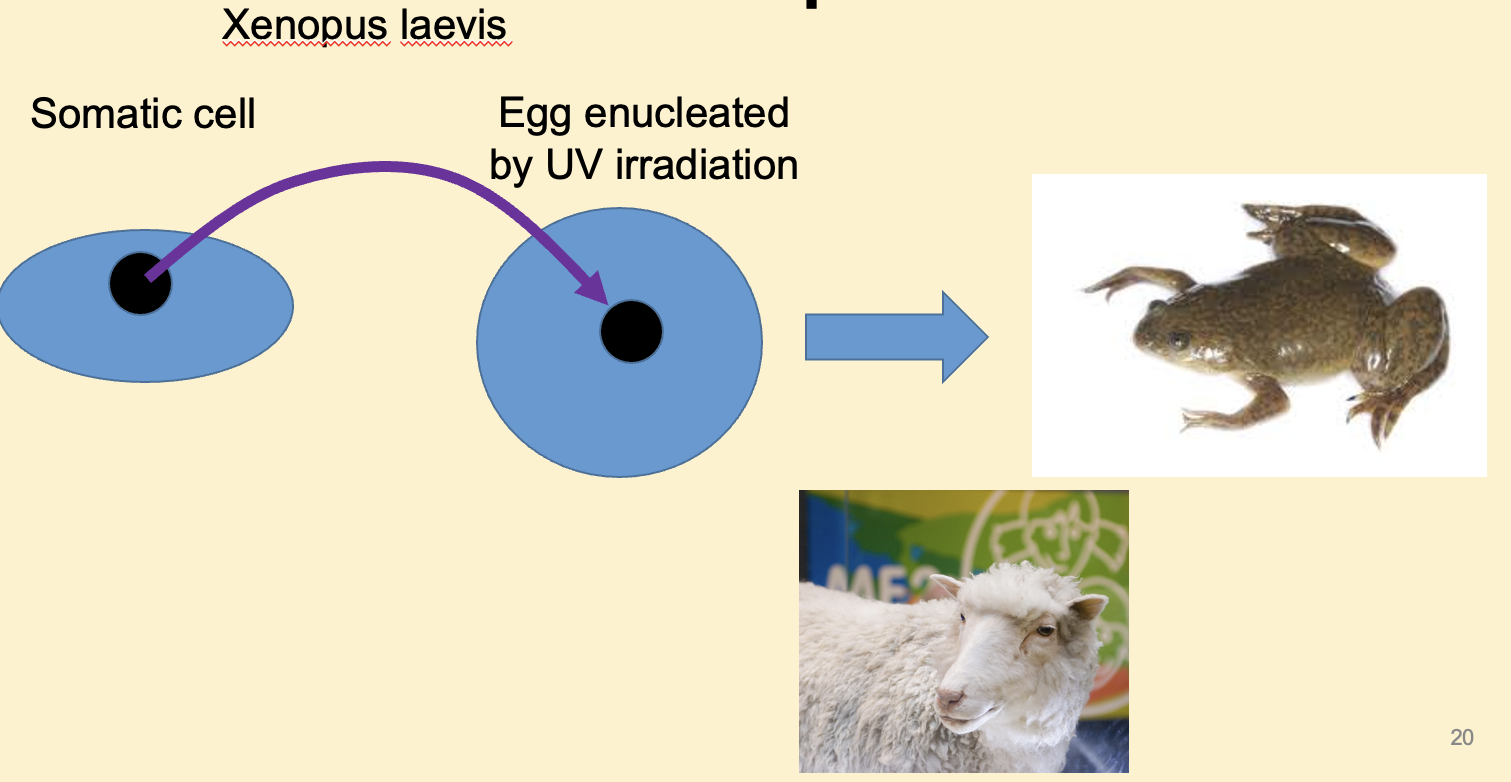
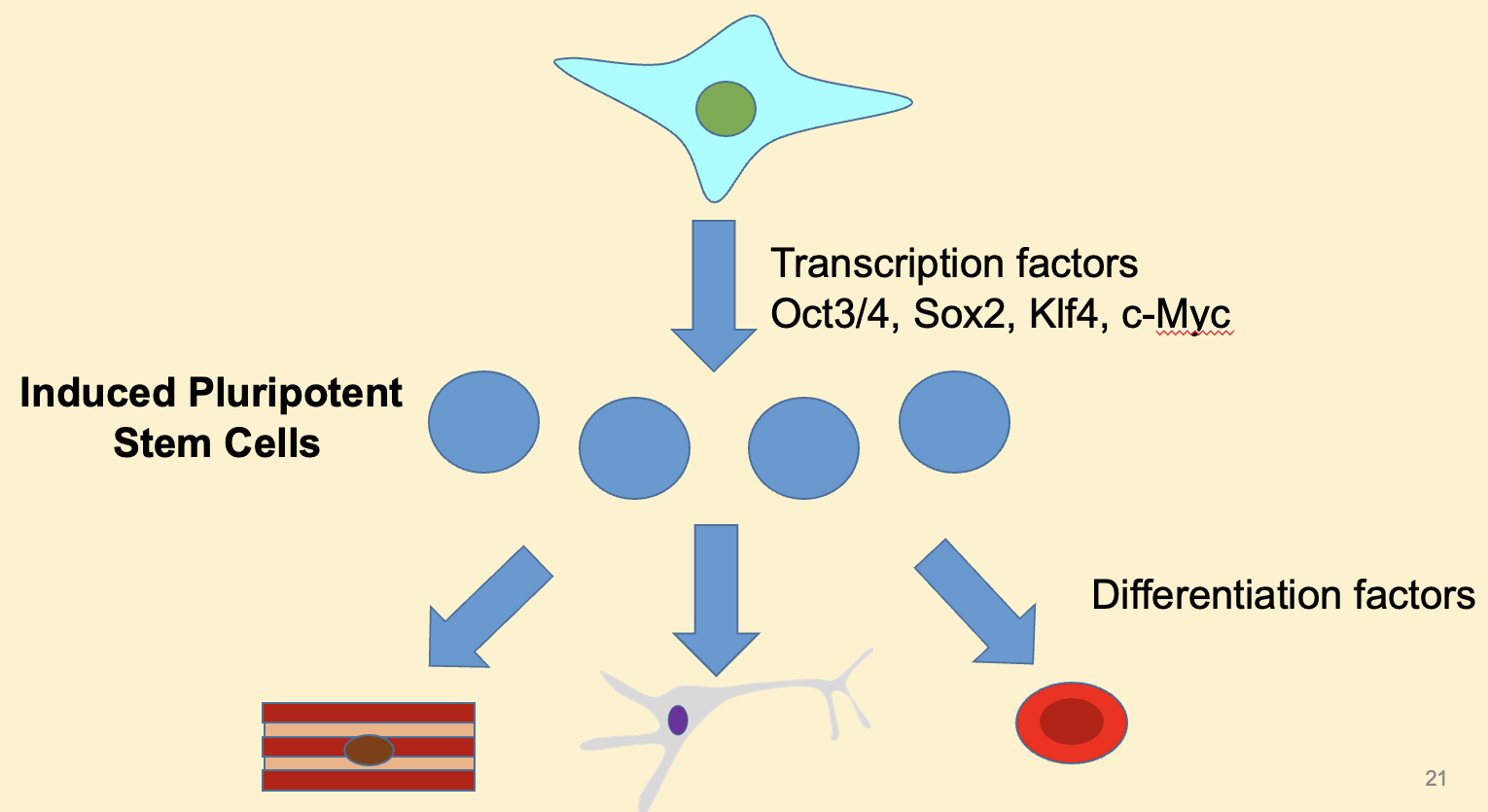
What are induced pluripotent stem cells derived from?
Somatic cells.