Circadian rythmns
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
Whats a biological rhythm ?
Cyclical changes in way biological systems behave
Due to cyclical changes in environment = evolution
What is a circadian rhythms?
Circadian = 24 hour cycles which regulate processes/behaviour = optimised 2 meet varying demands of night/day cycle =tells body when 2 sleep, wake, eat , when 2 release hormones, body temp at each time for day
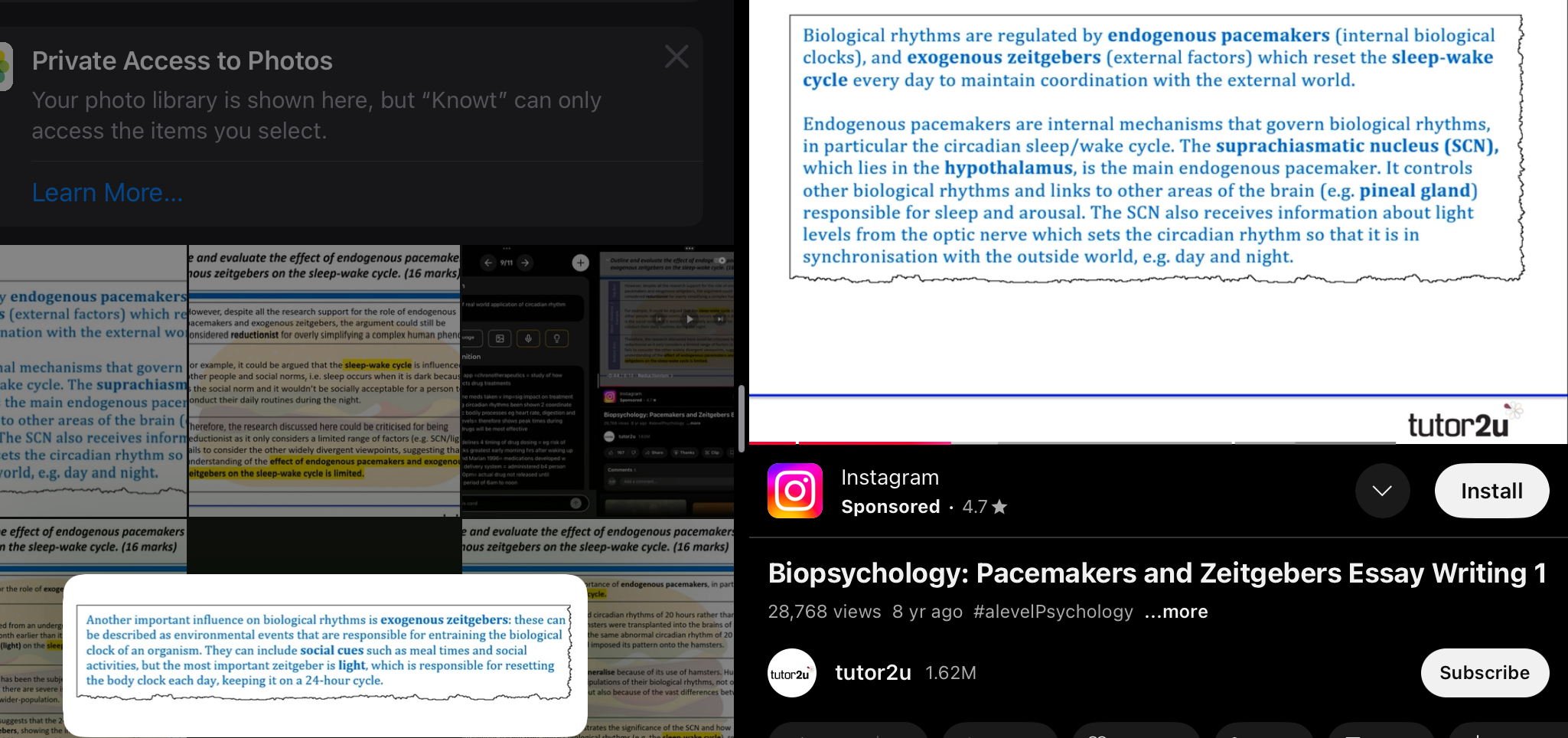
What are endogenous pacemakers and exogenous zeitgebers?
ERPs= internal body clocks that keep biological processes 2 time
Ed’s= external cues that entrainment internal body clocks= altering them 2 match environment
What is the nature of circadian rhythms ?
Driven by internal body clocks (endogenous pacemakers) in all cells of body= synchronised by SCN- suprachiasmatic nucleus (master circadian pacemaker) in the hypothalamus
Must be constantly reset= always in sync w outside world =
What example is there of a circadian rhythm ?
Sleep wake cycle
Light and darkness are exogenous zeitgebers=determine when we should sleep/wake, can reset rhythm by sun =photo entrainment, prompts you to sleep when dark
circadian system= intolerant of major alterations in sleep/wake schedules eg jet lag /shift work =biological body clock 2 be out of balance= conflicts of EZs and EPs= EPs telling us tired but outside still light = EZs take time to entrain EPs
SCN = EP of sleep wake cycle in hypothalamus =light is primary input and reference point, SCN obtains info on light from optic nerve in eye =in the morning =more light vice versa for evening=SCN sends signal 2 pineal gland= lots of light =pineal gland inhibits production of melatonin (sleepy hormone)=Decrease in light detected =pineal gland stimulates production of melatonin =usually at night = SCN uses info and sets body clock ‘correct time’ = photo entrainment = uses info 2 coordinate activity of entire circadian rhythm/sleep wake cycle=
Whats the role of homeostatic control in the sleep wake cycle?
Sleep and wakefulness also determine by homeostatic control = due 2 endogenous pacemakers(internal body clocks) = tends to make u sleepier as time goes on throughout wake period regardless of day/night =free running= maintains 24 hr cycles regardless of light/darkness =exogenous zeitgebers
What is the role of social cues in the sleep wake cycle?
light thought 2 be primary EZ in sleep wake cycle= research suggests social cues eg meal times, exercise when others go to bed or env cues eg clocks = also act. As EZs
What evidence was done into the free running nature of the circadian rhythms? + COUNTER of similar research
Case study Siffre = french cave explorer=spends long time underground 2 study own circadian rythms= 2 /6 months at a time
No EZs 2 entrain EPs = no daylight/clocks/radio
Wakes ups eats and sleeps when he feels appropriate= only thing influencing was his free running body clock
Found: almost every time his natural biological circadian rhythm settled around 24/25 hours=supports but external cues /EZs fine tune it
HOWEVER CASE STUDY= CANT GENERALISE plus other studies into sleep wake have small samples or just individuals like siffre= not representative of wider pop = lacks generalisability and ecological validity = Siffres most recent study at age 60in 1999=observed his EP ticke much more slowly when he was young= even when Same person involved=factors vary =prventing general conclusions
Strength of real world application of circadian rhythm research.
Real world app =chronotherapeutics = study of how timing affects drug treatments
specific time meds taken v imp=sig impact on treatment success eg circadian rhythms been shown 2 coordinate many basic bodily processes eg heart rate, digestion and hormone levels= therefore shows peak times during day/night drugs will be most effective
Dev of guidelines 4 timing of drug dosing = eg risk of heart attacks greatest early morning hrs after waking up = Evan’s and Marian 1996= medications developed w novel drug delivery system = administered b4 person sleeps at 10pm= actual drug not released until vulnerable period of 6am to noon
Circadian rhythm research furthered understanding and applications led 2 improved treatments 4 variety of conditions requiring drug therapy eg anti epileptic drugs , respiratory etc..
Whats evaluation info endogenous pacemakers on sleep wake cycle/ circadian rhythms?
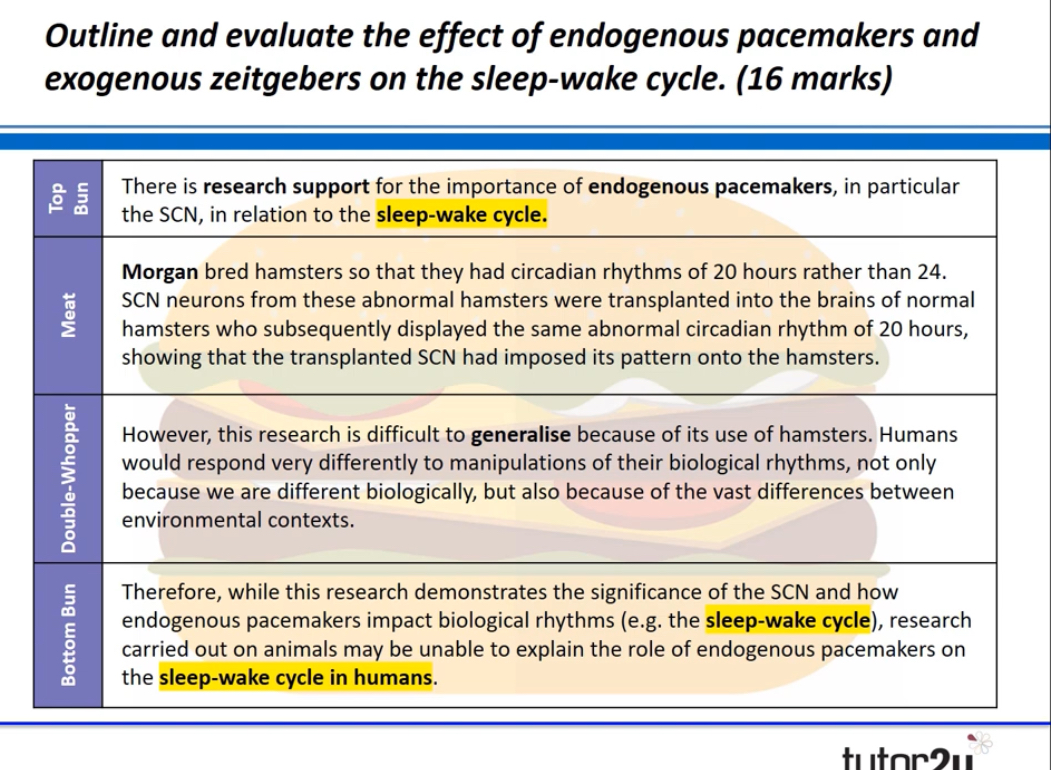
How may endogenous pacemakers and exogenous zeitgebers be reductionist?
