resistance exam 2
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
alarm
1
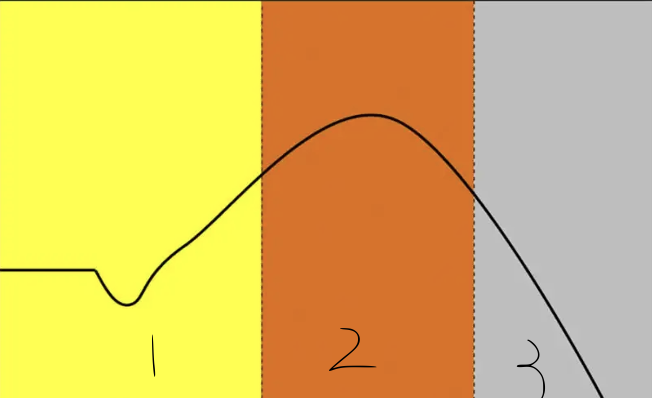
resistance
2
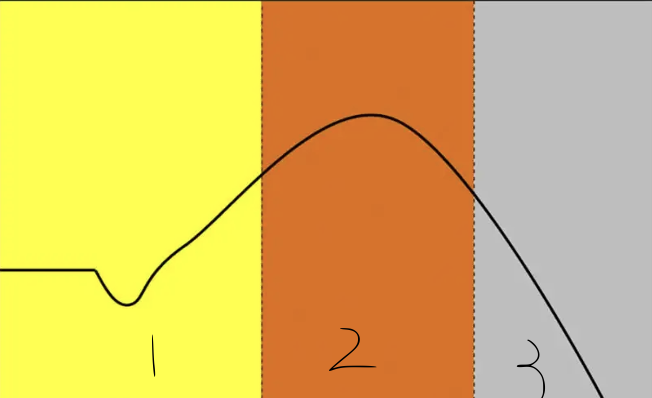
exhaustion
3
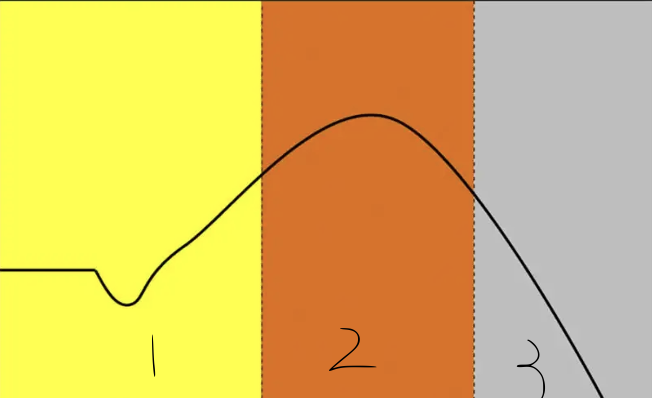
alarm
in general adaptation syndrome - this occurs when there is a new stress or more stress is applied to system
temporary decrease
the alarm phase results in a __ __ in performance
resistance
in general adaptation syndrome - this is the toughening of the system driven initially by neurological adaptation sand later through muscular adaptations
exhaustion
in general adaptation syndrome - this is the reappearance of alarm phase due to extended stress
stimulus
stress to the body classified by magnitude
positive
magnitude to stimulating stimulus
neutral
magnitude of retaining stimulus
negative
magnitude of detraining stimulus
adaptation
response to stress
fatigue
initial negative adaptation due to depletion of energy producing substrates
new level of readiness
over time a positive adaptation should occur due to restoration
supercompensation
after stimulus is applied and adequate restoration the body becomes more prepared for a greater stimulus
restoration periods between sessions should be planned for max recovery
1 factor
super compensation is a __ model
fitness after-effect
blue line
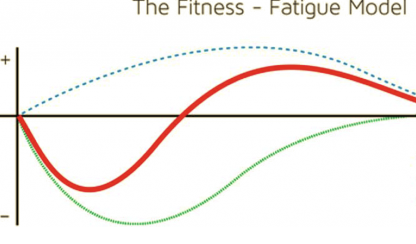
change in performance
red line
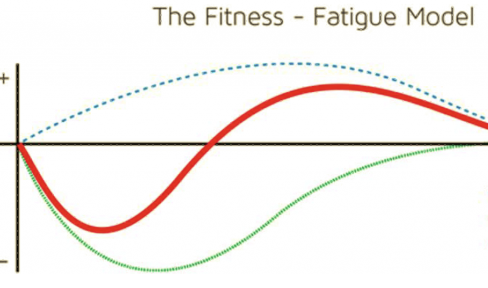
fatigue after-effect
green line
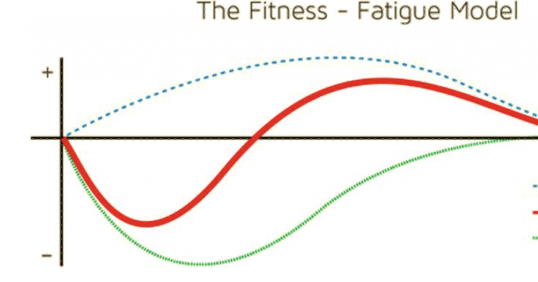
slower, longer
in the fitness fatigue model, increase in fitness is __ and __ lasting
faster, shorter
in the fitness fatigue model, increase in fatigue is __ and __ lasting
law of accommodation
states if an individual is exposed to the same stress over an extended period, positive adaptations experienced early will no longer be present
law of variation
states that to avoid accommodation, training plans should be varied over time including exercise selection, intensity, volume, density and timing
principle of diminishing
as one trains the magnitude of adaptation decreases - potential ceiling
progressive overload
gradual increase in the amount of stress (load demand) placed on the body over time - “ideal training”
undertraining
too little stress or too much recovery over extended periods of time
overtraining
too much stress without adequate recover over extended periods of time
overreaching
suggests that after several sessions of intense stress without adequate recovery, once stress is reduced and recovery is increased the body’s response is even greater
movement specific
best transferability to goal - SAID principle
training age
less experienced athletes will adapt to almost any training program because of their __ __
general physical preparedness (GPP)
multi-lateral training - foundation layer
specific physical preparedness
multi-lateral training - middle layer
skill development
multi-lateral training - top layer
session
single workout
microcycle
involves multiple sessions of training
7-10 days
period of time for a microcycle
mesocycle
block - include multiple microcycles
2-6 microcycles
period of time for a mesocycle
macrocycle
contains multiple mesocycles
depends on sport
period of time for macrocycle
annual plan
1-3 macrocycles
preparatory period
includes both general physical prep and specific physical prep
off season
contains most of preparatory period, all of general physical prep and early specific physical prep
pre season
contain remainder of SPP and 1st transition period
in season
competitive period
post season
contains 2nd transition period - recovery prioritized
training days and goals of each day
short term planning for microcycles includes identifying
wave loading
increases in load from previous week by 3-5% across mesocycle
step loading
loading stays the same for consecutive weeks while volume increases across the mesocycle
overreaching
planned accumulation of fatigue during consecutive microcycles
general preparation
goals are to increase metabolic and anatomical adaptations
hypertrophy, strength, endurance, injury prevention, technique
specific preparation
goals are to develop basic/fundamental and sport-specific strength
precompetition
phase of continuing to strive for maximal strength and conversion of max strength to power
competition
phase of peaking or maintenance of maximal strength and power
linear
periodization model with the movement of volume to intensity over time
total amount of work reduces over time as intensity goes up
(set x reps)
block
periodization model that uses specific training time dedicated to specific types of training, physical qualities or adaptations
undulating
periodization model that uses more frequent variations, changing training variables on a daily or weekly basis
linear
traditional programming characterized by preparatory and competition periods
entire macrocycle took 1 year
pronated
overhand grip used with barbell presses and squats
supinated
underhand grip used with chin ups and bicep curls
neutral
grip where knuckles point laterally used with DB rows and close-grip pulldowns
mixed
alternating grip used with deadlifts and spotting the barbell in bench press
closed
grip where thumb is wrapped around the bar
bench/incline press
open
grip where thumb does not wrap around the bar
false/suicide grip
back squat
hookgrip
thumb positioned under index and middle fingers
snatch and clean movements
concentric, eccentric
generally it is instructed that athletes exhale through __ movement inhale during __
structural, axial
valsava maneauver is recommended for lifters performing __ exercises that load the __ skeleton
diaphragm breathing
expiring against closed glottis creating rigid compartments of fluid in lower torso/air in upper torso when combined with contracting the abdomen and rib cage musculature
eccentric, concentric
using diaphragm breathing: deep breath, begin __ phase, transition to __ phase, slowly exhale
eyes should be on __ side of the bar from the rack when setting up a bench press
ensure safety
the number one goal of a spotter is to
take it
universal cue for spotting is
load, experience and ability
number of spotters is determined by __, __ and __
face, chest or head
spotting is needed when bar/DB travels over
bench press
most dangerous lift to perform
half distance between top of hip and knee
to promote safety, crossbars in a rack should be placed
85%
belts should not be encouraged with loads less than __% of 1RM
20, 7
mens weightlifting bars are __kg and __ft long and shaft is 28mm
15, 6
womens weightlifting bars are __ kg and __ft long and shaft is 25mm
needle bearing
type of bar used in a power lift where sleeves spin freely with greater whip
strength
type of lift that requires less whip and stiffer bar
rotation isn’t necessary
needs analysis
process of determining the extent to which various qualities/attributes are necessary for a sport or individual athlete/team
primary/secondary, conditioning, injury and evaluation/testing
needs analysis establishes focus on __/__ movements, __ protocols, __ prevention and __ battery
evaluation of sport
in a step 1 needs analysis this component includes: movement/biomechanical and physiological analysis
evaluation of sport
in a needs analysis: analyzes common injury sites/tissues
time of year, length of season, type of season
evaluation of sport in a needs analysis considers
ex. preseason/post season/in season
specificity (exercise selection and order)
movement analysis of the sport, common injury sites, muscle actions
exercise selection and order
force/speed requirements and mobility requirements needed for sport
core lifts
receive priority when selecting applicability to sport
one or more large muscle areas
core lifts recruit
structural lifts
specialized core exercises that emphasize loading the spine
structural
involves muscular stabilization of posture when performing the lift
back squat and deadlift are examples of
power lift
structural exercise performed explosively and requires CNS involvement
assistive lift
uses machines or smaller muscle groups - generally single joint
assistive lift
assist with muscular imbalances and assist in stabilizing joints
may be necessary for rehab purposes
primary lifts
what lifts give the best transferability to training goals and are within athletes abilities
included in testing battery/eval
secondary lifts
what lifts supplement primary lifts
assistance lifts
what lifts aid in injury prevention or address deficiencies
power, structural, other core, assistance lifts
general order of lifts
load
most critical aspect of RT program