Mutual Assent: Offer and Acceptance
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Mutual Assent
The parties are in agreement. All parties must be clear as to what is being offered and what will be accepted. Without mutual assent, you cannot have a valid, enforceable contract.
3 Elements of a Valid Offer ( ICE )
INTENT: There must be a serious, objective intention by the offeror
Certain/Clear Terms: The terms of the offer must be reasonably certain or definite, so that the parties and the court can ascertain the terms of the contract.
Expressed to Offeree: The offer must be communicated to the offeree.
Cases Where Intent Would Be Lacking
• 1. Opinions………………………” I believe that you should buy my boat for $ 5,000”
• 2. Future Intent…………………” I hope to sell you my boat for $ 5,000 soon.”
• 3.Preliminary Negotiations……..” Would you consider buying my boat?”
• 4. Invitations to Bid………………….Subcontractor makes bid and contractor accepts
• 5. Ads……………………………….......HP Computer for $ 2,000 vs. Reward for lost dog
• 6. Auctions……………………………..Bidder offeror and auctioneer offeree
• 7. Conditional Offers………………..” If you sell me your boat I will teach you Spanish”
Conditional Offer
A conditional offer is an offer that only becomes binding if a specified condition is met first. Ex: I will do X, if Y happens
What Makes an Offer Definite/Not Vague?
1. The identification of the parties.
2. The identification of the object or subject matter of the contract (also the quantity, when appropriate), including the work to be performed, with specific identification of such items as goods, services, and land.
3. The consideration to be paid.
4. The time of payment, delivery, or performance.
Why is it important that offers must be communicated or authroized?
It is imperative that any offer ( or acceptance for that matter) actually be authorized ( given permission) and communicated ( personally contact intended and relevant party)
Apparent Authority
Someone either has actual authority or due to circumstances appear to have authority. In such cases, if such apparent authority has a reasonable basis, it serves as actual authority.
Example of Apparent Authority
Jill is Rita’s assistant and most people believe Jill has the authority to buy fabrics in Rita’s name. While Rita has never clearly given Jill that authority, she also has never done anything to dispel this view. If Jill buys 1,000 yards of a fabric, this purchase will likely be valid because of Jill’s apparent authority.
Ways a Valid Offer Can Be Terminated (TIRED)
T……time limit ( deadline ) passes………..” Offer will end at 12 noon today”
I…….illness
R……Rejection ( offeree says no) or Revocation ( offeror takes back before accepted)
E……Expiration of a reasonable time…….Ice cream in July vs.stocks
D……Death or Destruction of a key person or item
Counteroffer
Counteroffers occur when offeree either rejects or ignores the initial offer and gives his or her own offer..This terminates the original offer Ex: “I will pay you $ 500 for that laptop” in response to “ I offer my laptop for $ 700”
Mere Inquiries
Mere Inquiries are merely negotiation tactics. This does not end the original offer. Ex: “ Would you consider a 15% reduction in that price?”
Option Contract
•A contract under which the offeror cannot revoke the offer for a stipulated time period (because the offeree has given consideration for the offer).
Example of Option Contract
Real Estate: “I will hold sale of my house for three months if you pay me the amount of $ 5,000 down.”
Acceptance
The act of voluntarily agreeing, through words or conduct, to the terms of an offer, thereby creating a contract.
Mirror Image Rule
Under the Common Law, an acceptance had to exactly mirror the original offer. Any change would be considered a counteroffer terminating that original offer.
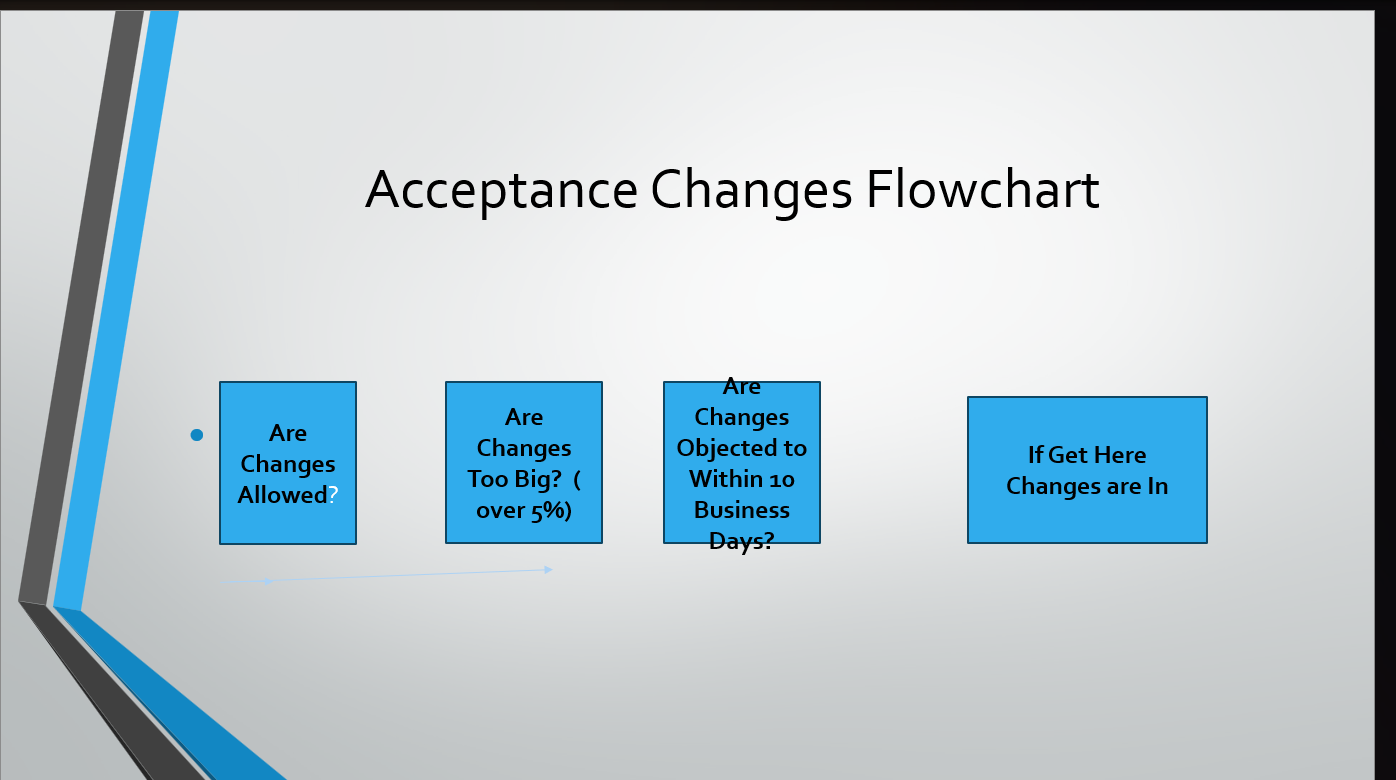
Acceptance Changes Flowchart
Modern Courts allows for changes in an acceptance within certain limits
Mailbox Rule
An acceptance is valid the moment you send it, not when the other person receives it.
Example of Mailbox Rule
Example:
Monday: You mail your acceptance letter
Wednesday: Letter arrives at offeror's office
Contract formed: Monday (when you sent it)
UETA (Uniform Electronic Transactions Act)
Online records and signatures will have the same legal validity as paper records and signatures as long as parties have agreed to conduct their transactions this way.
Objective Theory of Contracts
Intent is determined by objective facts, not by the personal or subjective intent or belief of a party. What most reasonable people would interpret under most circumstances