Flight Controls System Design Layout
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
The directional control of a fixed-wing aircraft takes place around the ___, ___, and ____ axes by means of flight control surfaces designed to create movement about these axes.
Lateral, longitudinal, vertical
Two major groups of flight control surfaces
Primary or main
Secondary or auxiliary
The primary flight control surfaces include?
Aileron, elevator, rudder
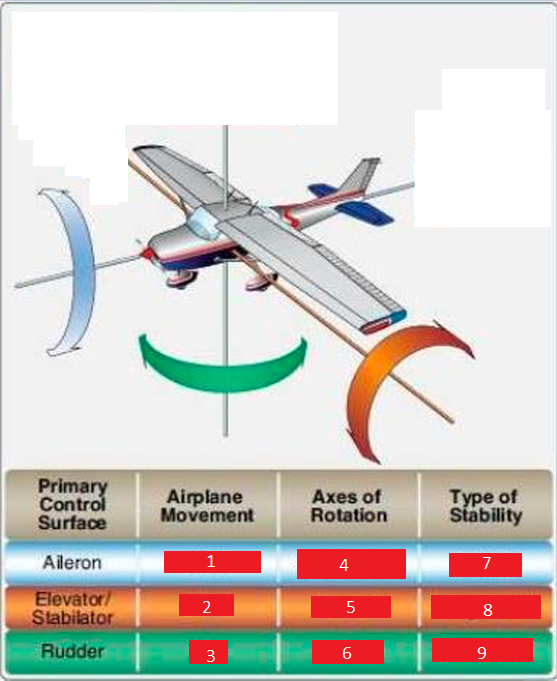
Roll
Pitch
Yaw
Longitudinal
Lateral
Vertical
Lateral
Longitudinal
Directional
Primary flight control surfaces are typically made from?
Alluminum alloy
Primary flight control surfaces are built around a single (1)___ or ____ to which (2) are fitted and a (3) is attached.
Spar member or torque tube
Ribs
Skin
These parts of the rib lighten the assembly.
Holes
In primary flight control surfaces, what is used to attach aluminum skin?
Rivets
Primary control surfaces must be balance so they do not vibrate or flutter in the wind. To balance it, the center of gravity of a particular device is ___ of the hinge point.
At or forward
Performs the combined functions of the ailerons and elevator.
Elevons

Combines the action of both horizontal stabilizer and elevator.
Stabilator

Combines the action of the rudder and elevator
Ruddervator

Extends the camber of the wing for greater lift and slower flight. Allows control at low speeds.
Flaps, Slats, Leading edge flap
Decreases lift. It can augment aileron function.
Spoiler
Directs air over upper surface of wing during high angle of attack. It also lowers stall speed.
Slots
Statically balances the aircraft in flight. Allows “hand off” maintenance of flight condition.
Trim Tabs
Aids pilot in overcoming the force needed to move the control surface.
Balance Tab
Aerodynamically positions control surfaces that require too much force to move manually.
Servo Tabs
Increases the force needed by pilot to change flight control position. De-sensitizes flight controls
Anti-balance or Anti-servo tabs
Enables moving control surface when forces are high. Inactive during slow flight.
Spring Tab
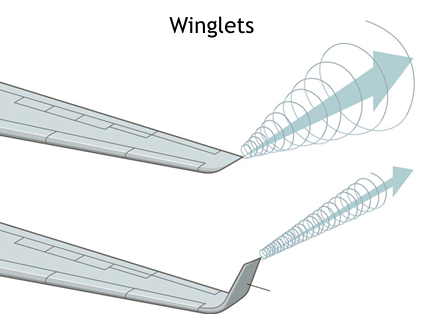
Aerodynamic device designed to reduce the drag created by wing tip vortices. It resembles a vertical stabilizer.
Winglet
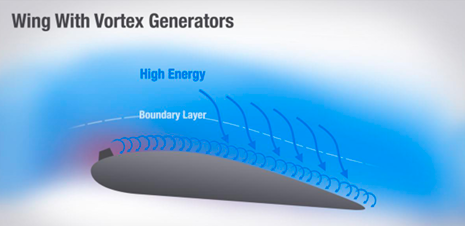
Small airfoil sections usually attached to the upper suface of the wing to promote positive laminar airflow over the wing and control surfaces.
Vortex generator
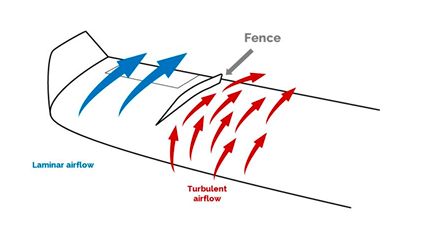
A chordwise barrier on the upper surface of the wing used to halt the spanwise flow of air.
Stall fence
Used to promote smooth airflow in gaps between stationary trailing edge of a wing or stabilizer and the movable control surface.
Gap seals
